Abstract
The relevance of this research is caused by the fact that the transition to new standards of mathematical education raised a new problem – the development of a methodological system of teaching in “the cultural and historic environment”. This problem is connected with training of pre-service mathematics teachers that would meet the modern requirements. The aim of the research is to point out the basic principles and components of cultural and historical methods of teaching mathematics, as well as to develop the technologies that would provide for the corresponding teaching environment. The leading method of investigation of this problem is the methodology of modeling the process of learning mathematics. It allows considering the problem as a product of a targeted and organized process for the formation of special, cultural and historical, teaching environment. This article represents developed by the authors a model of methodological system of the teaching mathematics cultural-historical environment forming. Its structural-functional model has a target, methodological, informative, productive, subject-culture bridge, technological components. The materials of the article are of practical value to actual teachers of mathematics, before which the problem of learning in cultural-historical environment is appeared. It also targets those professionals who train future mathematics teachers in accordance with the new standards.
Keywords: Cultural and historical environment, cultural and historical technique of teaching mathematics, TeacherProfessional Standard, cultural-historical pedagogy, cultural-historical psychology, mathematics teacher training
Introduction
The term “cultural and historical environment” is widely used in new mathematics curricula (The
Exemplary Curricula, 2011). Teaching mathematics involves developing the views on mathematics as
part of world culture and the one that discovers social, cultural and historic factors of this science
formation (The Federal…, 2010). The whole history of mathematics and mathematical education
proves their multicultural character.
For instance, according to E.A. Yamburg, the psychological and pedagogic principles of “cultural
and historical technique of teaching mathematics” overlap with the principles of cultural and historical
pedagogy (Yamburg, 2000). New educational standards were developed on the basis of the principles
of the cultural and historical psychology designed by L.S. Vygotsky and his school in 20-30-s of XX
century.
Apart from the above it is worth noting the adoption of “The Teacher Professional Standard”, which
is a guideline for all professional activities of school teachers (The Professional Standard, 2013).
Among the labor functions of a school teacher the standard points out the ability “to use psychological
approaches such as cultural, historical and developing” (section 3.1.3).
Currently, all researchers recognize the general cultural nature of mathematics. Students’
mathematical culture is formed in a special environment that includes worldview and spiritual aspects
of education. Under these circumstances special requirements are imposed on the teacher.
Materials and Methods
2.1. Methodological system of teaching mathematics in cultural and historical environment
Methodology of mathematics faces up the task of developing theoretical bases and technologies that
would help to form cultural and historical environment for teaching mathematics.
For this, it is necessary to define the contents and methods of formation of ideas about mathematics
as a part of panhuman culture, universal language of science, allowing describing and studying real
processes and phenomena, to assess the value of mathematics in everyday life.
It is necessary to develop methodologicalsystem of teaching mathematics in cultural and historical
environment in the school, which external environment includes future mathematics teacher training in
the process of continuous historical-mathematical education. This subject of research has both
scientific and practical interest. As an object of study we understand the steps of formation the cultural
and historical environment of learning mathematics, including future teachers of mathematics training.
The complexity of the object suggests the need for a system analysis.
The desired system is constructed in accordance with known principles of methodologicalsystems
(V.P. Bespalko, A.L. Zhokhov, A.M. Piskala, G.I. Sarantsev, etc.). The components of the
methodological system are:
– objectives of learning mathematics in cultural and historical environment;
– the contents of historical-mathematical education of students, future and current teachers;
– regularities, conditions, prerequisites for the functioning of the methodological system;
– the various forms of dialogue of cultures in the collective subject of the educational process
(teacher – learner, trainer – student, etc.);
– the history of mathematics training materials as a collection of various kinds of cultural works –
mathematical, historical, methodological, personal;
– methods, forms, means and technologies of the cultural-historical environment of teaching
mathematics formation;
– the result of teaching mathematics in cultural and historical environment – the aggregate of
individual elements of historic-mathematical culture formed at this time.
The external environment of the system is compiled by common objectives of secondary and higher
education, the subject of mathematics and history of mathematics, the labor functions of teachers etc. A
holistic model of methodological system of teaching mathematics in cultural and historical
environment is represented in Figure 1.
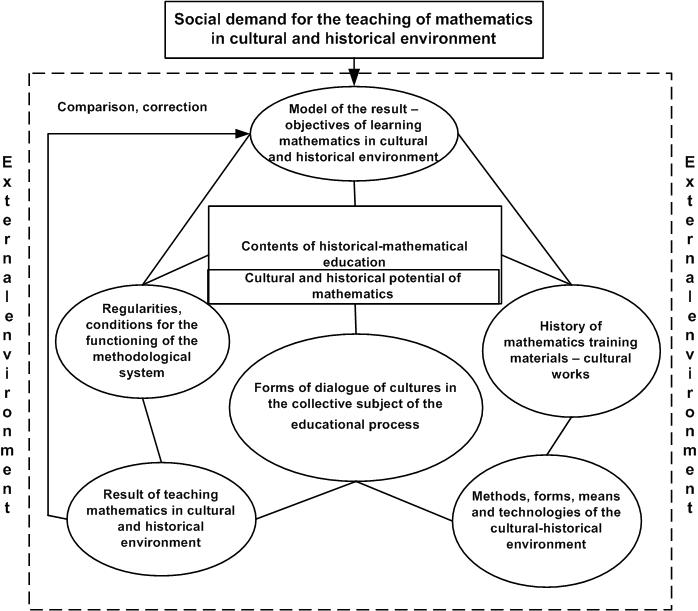
The basic components of methodological system are highlighted by its leading function in the
process of achieving the goal. Appropriateness of the allocation in the structure of methodological
system such components and relations between them bases on the universality of the principles of
ideologically directed learning mathematics to which this system is embedded.
“The cultural and historical environment of mathematical training” is defined as the environment
where students acquire mathematical culture “constants” taking into account their changes and
applications in life and science. Methodological system, which is formed in such an environment, we
call “cultural-historical technique of mathematics teaching” (Gilmullin, 2016, 2009).
2.2.Cultural - historical background of mathematics teaching at school
School mathematics, considered as a reflection of the corresponding face of culture, provides the
students gained in that culture means of orientation in the surrounding world: the ideal objects, the
transformation methods and actions with them, ways of fixing their thoughts and actions, some of the
procedures of mathematical creativity, namely: conversion of operations, relations, tasks; procedure
modeling; new mathematical objects constructing from known; the search for the aesthetic, etc.
For the purposes of general cultural elaboration of students in the content of mathematical education
at school now an additional section “Mathematics in the historical development” is included. The
history of the main mathematical opening, mathematical science creators’ names have to become the
part of mathematical culture of the educated person.
This cultural and historical background is shown also in the educational and methodical sets for the
main school made according to standards. For example, it is possible to estimate this cultural and
historical environment on the methodical device of textbooks for 5-6 classes (Kuznetsova, etc., 2013;
Mordkovich, etc., 2012).
The main assessment procedure of achievement of metasubject results is protection of the final
individual project. Historical and mathematical projects contain many objects of their assessment:
ability to systematic knowledge development, their independent replenishment, transfer and
integration; the ability to address personally and socially relevant problems; the capacity for self-
organization and reflection, and others. For this purpose, for mathematical projects may be proposed
such topics as “Number systems of different nations”, “How to measure the Earth?”, “A comparison of
the old Russian and Tatar measures”, “The contribution of mathematicians from different countries in
the solution of equations” and etc.
The assessment of the formation of almost all kinds of universal educational actions (personal,
regulatory, cognitive, communicative), as well as specially-subject (mathematical) operations can be on
the basis of historical and mathematical material.
2.3. Preparation of the future mathematics teacher to work under the section “Mathematics in the
historical development”
In the list of math teacher competencies laid down in the curriculum of mathematics history, along
with others, there is a willingness to tolerant perception of social and cultural differences, respectful
and careful attitude to the historical heritage and cultural traditions. Let’s consider, for instance, the
creation of cultural and historical background related to the name of the great Leonard Euler. Euler’s
name is mentioned in the “Mathematics in the historical development” several times in connection with
the study of the different sections of school mathematics. He owns significant results in all areas of
mathematics and its applications, which existed in his time.
Scientist made an enormous influence on the development of mathematical education in Russia.
Euler is considered the founder of not only the St. Petersburg school of mathematics, but also Russia’s
first teaching mathematics school. And this cultural and historical background must be displayed
throughout the course of the school mathematics.
The following types of historical and methodological activities in the training of future mathematics
teachers are applied for this:
–creation of chronological dictionary guide of the main achievements of elementary mathematics;
– identification of the characteristics of mathematical objects: sources; personality, the chronotope;
– adaptation of historical and mathematical material;
– identification of mathematical facts with the historical epoch;
– solution of historical-mathematical tests;
– study samples of formulation and solution of practical problems in the history of mathematics;
– analysis of the history of nominal theorems, formulas, figures, algorithms, tasks;
– accumulation of historical examples of selfless service to the mathematical science and education;
– preparation of mathematics development synoptic table.
One of the educational space’s direction vectors, based on the formation of the aggregate quality
mathematical and methodical culture of the future mathematics teachers in teaching the history of
mathematics, is dialogueness, regarded by us as a dominant of cultural approach. In the development of
specialized cultural approach to the history of mathematics, we rely on a general theory of cultural
studies of education, ideologically directed learning math, humanization of mathematics education.
These theories developed in the last twenty years due to new concepts and paradigms of secondary and
higher education (Zhokhov, 2007; Krylova, 2000).
The modern education philosophy aims at new installations which, unlike installations of
technocratic approach, declare a priority of the human person, development of his creative potential,
idea of multiculturalism, development of ability to dialogue of cultures.
When designing the above cited cultural understanding on the process of history of mathematics
learning, we can stand out the following sections (forms) of the cultures dialogue:
– mathematical culture on its individual meaningful lines in different historical periods of its
development;
– mathematics and education, also in different periods and in different geographical locations;
– mathematics and educational texts dialogue, created by the teacher and the pupil, the professor and
the student;
– materialized in the spoken dialogue and research (as to the form and style of communication); its
actors are teacher – student, student – the author of any material (a historical person, the author of a
textbook or some text, and so forth), teacher – student, student – student, trainee and student, etc.
All these kinds of dialogue between cultures have been used by us in teaching the history of
mathematics students in pedagogical high school and at school. The purpose of their use is the
formation of the future mathematics teachers’ professionally oriented qualities.
Results
Structural-functional model of methodical system of teaching mathematics in the cultural and
historical environment developed by us has a target, methodological, informative, productive, subject-
culturebridge, technological components. It should also be taken into account the continuity of the
system of mathematical education. Cultural and historical methods of teaching mathematics cover all
stages of mathematics education, beginning with primary ones and ending with teacher training and
retraining.
Undergraduate teacher training in historical and cultural aspects is included into the curriculum of
the subject “History of Mathematics”, and the optional course “Historical and mathematical
foundations of teachers’ methodological training”. They contribute to the formation of historical
component of the undergraduate teachers’ mathematical and methodical culture, which is attained by
the relevant system of teaching history of mathematics. This system promotes developing teacher’s
labor actions aimed to design cultural and historical training environment.
The formation of cultural and historical environment should begin with primary stages. Federal
Standards of Primary General Education and model curricula involve the use of mathematical
knowledge for the description and explanation of surrounding objects, phenomena, and the assessment
of their quantitative and spatial relations (The Federal …, 2009).
The creation of cultural and historical environment was experimented at “Children's university” in
Elabuga Institute of Kazan Federal University. The authors prepared and conducted a number of
classroom events, which included the following lectures disputes and discussions: “How did people
learn to count?”, “Who is Omar Khayyam – a poet or a mathematician?”, “Are there any child
prodigies in mathematics?”, “Mathematical experiments”, etc.
Such methods, means and forms of historical and mathematical activity of future teacher will help to
detail activities of the mathematics teacher for creation of ideas of social, cultural and historical factors
of mathematical science formation. Similar methodical-mathematical experiences are steps on the way
of development of a cultural and historical technique of training.
The following step where the cultural and historical technique of training formed is professional
development of mathematics teachers. The advanced training courses on a modular and competence-
based basis realized in KFU contain several modules, one of which is “Project work”. At
implementation of the project work according to the chosen section of studying mathematics, or at an
elective course, teachers developed also cultural and historical background of studying of a subject.
Discussions
I.K. Andronov, I.G. Bashmakova, V.V. Bobynin, N.Ya. Vilenkin, G.I. Glazer, B.V. Gnedenko,
Yu.A. Drobyshev, A.L. Zhokhov, F. Klein, A.N. Kolmogorov, D. Polya, T.S. Polyakova, K.A.
Rybnikov, G. Froydental, A.I. Shchetnikov, A.P. Yushkevich etc. dealt with a problem of use of
potential of mathematics history in training. They considered the following aspects:
– formation of mathematical culture by means of mathematics history;
– usage of elements of history of mathematics in training;
– reform of mathematical education in a historical context;
– principle of historicism and historical and genetic method of training in mathematics, etc.
The aspect of the cultural-historical environment formation of training mathematics studied by us
wasn’t considered previously.
Yu.A. Drobyshev investigated a problem of multilevel historical and mathematical training of future
mathematics teacher (Drobyshev, 2011). Need of extension of the contents of historical and methodical
training of mathematics teachers for pedagogical higher education institution in the form of system of
knowledge of history of school mathematical education is proved in the doctoral dissertation of T.S.
Polyakova (Polyakova, 1998).
A number of master’s theses is devoted to various questions of teaching a course of history of
mathematics: to its role and value as one of the most important factors of a humanization and
humanitarization of mathematical education (N.A. Burova), to selection of maintenance of this course
and technique of its realization (A.E. Tomilova), etc.
I.S. Safuanov has developed the theoretical concept of the genetic approach to training in
mathematical disciplines in teacher training university consisting in a support on the natural ways and
methods of knowledge inherent in the science (Safuanov, 2000).
Special attention to a problem of use of historical and mathematical material in foreign methodical-
mathematical researches and practical developments for teachers is paid too (Hands On History, 2007).
Conclusions
It is established that the developed structural-functional model of methodical system of training in
mathematics in the cultural and historical environment can be applied when forming of professionally
focused qualities of future teachers in the course of training of mathematics history and other
disciplines in pedagogical higher education institution. Forms, methods, means of formation of the
cultural and historical environment at various steps of mathematical education are allocated.
Materials of article can be useful on the practical level to the mathematics teachers working
according to new educational standards. Also they have a direct bearing on training of future
mathematics teachers in higher education institution.
Taking into account the received results of this research it is possible to allocate a number of the
scientific problems and the directions demanding further studying: technologization of formation of the
cultural and historical environment for the solution of questions of didactics of mathematics, expansion
and a specification of practical developments for mathematics teachers.
References
Drobyshev, U.A. (2011). Multilevel historical and mathematical training of future mathematics teacher
(Doctoral dissertation). Moscow city pedagogical university, Moscow, Russia.
Gilmullin, M.F. (2015). On the cultural-historical environment. Mathematical bulletin of teacher
training universities and universities of the Volga-Vyatka region, 18. 19-24.
Gilmullin, M.F. (2009). The Historical Component of the Mathematical Methodological Culture of Students Taking the Course of Mathematics History at Teachers’ Training University (Ph.D. Thesis). Ushinsky State Teachers’ Training University, Yaroslavl, Russia.
Hands On History. A Resource for Teaching Mathematics. (2007). / Edited by Amy Shell-Gellasch.
Pacific Lutheran University. MAA Notes. # 72. http://www.maa.org/press/books/hands-on-history-aresource-for-teaching-mathematicsKrylova, N.B. (2000). Initial concepts of a cultural paradigm of education. New values of education, 10. 34-97.
Kuznetsova, L., Minayeva, S., Roslova, L., Suvorova, S. (2013). A role of the textbook of mathematics in achievement of requirements of the standard. Mathematics. 2. 27-33.
Mordkovich, A.G., Zubareva, I.I. (2012). Transformations in education: we work on new FSES. Mathematics at school. 4. 21-26.
Polyakova, T.S. (1998). Historical and methodical training of mathematics teachers at pedagogical university (Doctoral dissertation). Rostov state pedagogical university, Rostov-on-Don, Russia. Safuanov, I.S. (2000). The Genetic Approach to Mathematical Subjects in Teachers’ Training Universities (Ph.D. Thesis). Moscow State Teachers’ Training University, Moscow, Russia.
The Exemplary Curricula. Mathematics. 5-9 Forms. (2011). Moscow: Prosvescheniye.
The Professional Standard. The Teacher (Pedagogical Activity). (2013). Retrieved from http://www.rosmintrud.ru/docs/mintrud/orders/129/ .
The Federal State Educational Standard for Primary General Education. (2009). Retrieved from http://минобрнауки.рф/документы/922/файл/748/ФГОС_НОО.pdf .
The Federal State Educational Standard for Basic General Education. (2010). Retrieved from http://edu.ru/db/mo/Data/d_10/prm1897-1.pdf .
Yamburg, E.A. (2000). School on the Way to Freedom: Cultural-historical Pedagogy. Moscow: PEER SE.
Zhokhov, A.L. (2007). Outlook: formation, development, education through education and culture. Arkhangelsk-Yaroslavl.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 July 2016
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-011-2
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
12
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-451
Subjects
Teacher, teacher training, teaching skills, teaching techniques, organization of education, management of education, FLT, language, language teaching theory, language teaching methods
Cite this article as:
Gilmullin, M. F., & Khaliullina, L. R. (2016). Formation of the Polycultural - Historical Environment of Mathematics Teaching at School. In R. Valeeva (Ed.), Teacher Education - IFTE 2016, vol 12. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 287-294). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2016.07.46

