Model of Professional Activity of a Modern Teacher, Working with Children with Special Educational Needs
Abstract
The relevance of this article is due to the fact that the use of modern technologies (hardware correction methods) in the teaching and psychological practice require specialists not only with a high level of psychological and pedagogical education, but also with other professional competencies for effective work with children with special educational needs. The purpose of the article is to develop a structural-functional model of preparation of specialists of psychological-pedagogical profile to implement multi-level activities in the modern education environment with children with special educational needs. The leading method is a modeling method that allows the consideration of the problem as a purposeful and organized process for improving professional, cultural, educational and special competencies of teachers necessary for the effective implementation of psycho-pedagogical activities. The developed model of training specialists of psychological-pedagogical profile, to be implemented in educational activities in the conditions of modern education includes specific, methodological, substantive, organizational, procedural and effective components. The model aims to integrate professional and psychopedagogical training of teachers, which will improve their professional and inter-professional competencies with children with special educational needs.
Keywords: Children with special educational needs, transformative teacher, multidisciplinary approach in specialist training
Introduction
1.1.Problem statement
The analysis of publications of domestic and foreign authors (Wheeler, 2000; Nazarov, 2001;
Nigmatov, 2004) showed that in most studies the problem of working with children with special
educational needs were studied only from the point of view of orientation towards the children
themselves. The question of training specialists with diverse qualifications remains unattended to. The
need of improvement is due to: firstly, the negative trend of increasing numbers of children with
different levels of readiness for the educational process from preschool to school level, in need of an
organized (quality) education; secondly, the lack of awareness among professionals about the
psychological development of children with disabilities; thirdly, the insufficient training of specialists –
there is no direction in the higher education system, including different levels of the multidisciplinary
training of the teacher (as in the system of tutors and a public education component); fourthly, the
contradiction between communication uncertainty and the sequence of realization of potential elements
of education at the moment and the need for rapid transformation in the context of changing conditions
of the educational environment.
Our available system of teachers' training would prevent these contradictions changing educational
system. The success of modern education is largely determined by the development of modern training
programs, determining the source of theoretical and practical provisions, principles, methods and
techniques that contribute to training effectiveness. In connection with this, we can say that one of the
most important tasks facing the novel system of teachers' training, is qualitative structural changes in
the training programs of specialists. Part of the aim is to increase meaningful, semantic competence of
the teacher (morph depending on the conditions of the educational environment) in the field of working
with children with special educational needs, intensification of the subjective position of specialists, as
direct participants in the integration, which owns multidisciplinary technology.
This study will allow us to determine the content of the didactic process of training a competent
specialist in different educational environments, namely, "the transformative teacher".
Materials and Methods
In the course of the research the following research methods were used: analysis of normative documents
and products of the method of mental experiment, prediction, systematization and generalization of facts and
concepts, modeling, design, method of expert estimations, analysis of the results of the activities of the
trainees, a survey of the state speech and cognitive, emotional sphere of children with special educational
needs (test "Simple instructions"), studying and generalization of experience of training specialists of
psychological-pedagogical profile to the implementation of educational activities, diagnostic methods,
pedagogical experiment.
The experimental work was carried out on the basis of initial classes of secondary and special schools of
Naberezhnye Chelny Republic of Tatarstan. In experiment10.575 students took part, 743 of them – children
with special educational needs (children with disabilities).
The study was conducted in three stages:
- the first stage – the preparatory phase, where we analyzed the modern condition of the studied
problem in the pedagogical theory and practice; developed the methodology program of the study;
- the second stage – here, at the main stage, structural-functional model of preparation of specialists of
psychological-pedagogical profile was devised and implemented for the realization of educational
activity in conditions of modern courses for improvement of qualification and retraining of specialists;
- the third stage – the final stage – the systematization, interpretation and generalization of research
results were carried out; theoretical insights were refined; the results of the study were processed and
entered. In the future we plan to carry out training (retraining) of specialists taking the modern
requirements into consideration.
Results
This study will allow us to determine the content of the didactic process of training a competent
specialist in different educational environments, namely, "the transformative teacher".
Part of the aim is to increase meaningful, semantic competence of the teacher (morph depending on
the conditions of the educational environment) in the field of working with children with special
educational needs, the intensification of the subjective position of specialists, as direct participants in
the integration, which owns multidisciplinary technology.
The main objectives of the study:
1. To determine the most effective ways of transformative teacher preparation, increasing the level
of physical, intellectual, and mental development of children with special educational needs, their
integration in the society, namely to improve the level of competence and flexibility of teachers.
2. To insure the future integration directions.
3. To create educational conditions for a comfortable interaction of all subjects of pedagogical
process in education of individuals with disabilities.
4. The main purpose of this area of novel teacher training is development of an educational process
on the basis of higher education through additional courses and methodological workshops. With it, the
training may be transformative in nature, where one platform of educational process, depending on the
needs of the institutions (both educational and corrective), will promote not only self-development of
experts, but also allow self-development. This process can be carried out not only through courses, but
also through most of the intercollegiate continuation of training based on the region, or the national
component. Functions of the model: educational, communicative, organizational, managerial,
educational and motivating functions. The whole structure of the educational process can be
represented by blocks of levels, built in the form of hierarchical levels.
3.2. The stages of implementation of the model.
The implementation of this model involves the following stages of the experimental work:
- implementation of diagnostics of levels of formation of corporate, communication, research,
psycho-pedagogical competencies of specialists, a survey of cognitive and emotional-volitional sphere
of children of primary school age.
- development of the areas of evaluation of teachers (qualification, training, personal competencies).
The model of professional activity are presented in the form of a pyramid. On each vertex and level,
two components were taken into account: 1, an incoming channel and an outgoing channel of the
relationship, and 2, the interaction of the structural components of the model. After the development of
emotional-volitional and speech activity the teacher moves to a new level. To evaluate the
effectiveness of psycho-pedagogical interventions, it is necessary to assess the effectiveness of a
nearby structural component, and then trace the operation of additional, adjacent structural components
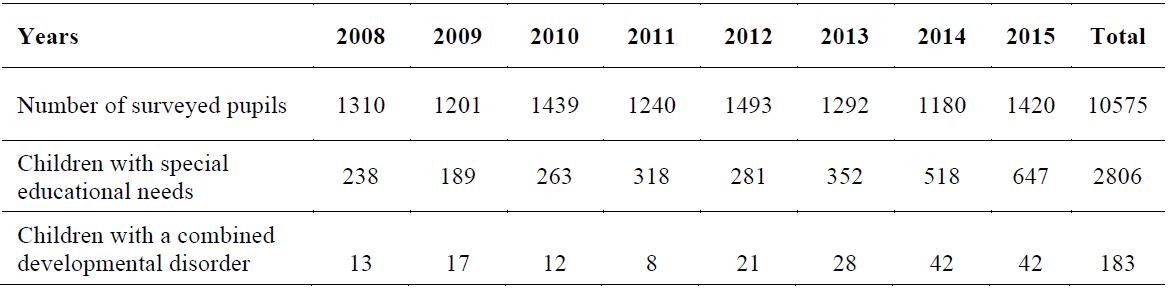
of the model. Studying from the 2008 experience speech development of younger students of
Naberezhnye Chelny Republic Tatarstan, it should be stated that there was a significant increase of
developmental disorders characterized by an increase in the number of combined violations. 1310
Junior schoolchildren were surveyed from ten schools, including children with special educational
needs – 238 (18.2 per cent), and 13 with combined disorders. Already by 2015, number of younger
students with disabilities 647 people (45,6%) and the number of students with combined have
increased - 4
It should be noted that learning was at an appropriate level, and the level of professional training of
teachers was not questioned. However, development of new approaches in the organization of training
is required because there is a need to establish such integrative interactions in the general pedagogical
activities that would allow the creation of conditions for effective and qualitative education process.
The success of modern younger pupils in the conditions of competition is largely determined by the
quality of the elimination and prevention of the difficulties which don't give the individuals at a certain
stage to overcome a problem. One of the problems encountered by younger students is the education of
persons with special needs. As a result, the problem of understanding the significance of the structural
components of the model determined the content of the theoretical part of our study.
At the educational stage of the experiment the major structural components of the model were
designed. The study is currently valid, at least from two points of view: the necessity of development
and improvement of the educational process in accordance with the needs of society, but also from the
perspective of the search for new directions in educational work with children with disabilities.
Summarizing the above mentioned, we can conclude that the model is scientifically based, relatively
autonomous and evolving inside the structure. All psychological and pedagogical work are aimed at
successfully addressing violations developing and maintaining resources of younger students with
special educational needs (including children with creative abilities). A more detailed examination and
different types of feedback in the structure of the model of the teacher of a new type, its advanced
indicators and general parameters are deservedly studied in this problem in details.
The entire structure of the three-dimensional model consists of block – levels, built in the form of
hierarchical levels.
The first technological-didactic block is defined by the following components: a diagnostic survey,
a program of psycho-pedagogical assistance to overcome the disabilities and "didactic aspects" of
action. The entire model is based on data from these components. If we consider diagnostic testing as a
stand-alone option, not as a controlling element, it will act as the pinnacle of psychological and
pedagogical work.
Another structural component of the platform is determined by the interaction between areas of
influence and on the development of individually-typological characteristics of a person with
disabilities. This integration allows the didactic model to solve the problem of development of younger
pupils at all stages without damage in the process of learning the general education curriculum. The
content of these areas is provided by the programs of secondary schools and special psycho-
pedagogical work. Based on the analysis of didactic literature, the experience of teachers and speech
therapists of of Naberezhnye Chelny, the following features in the development of Junior pupils with
special educational needs (including gifted children) were allocated:
- the choice of the optimal rate and the nature of learning for each student;
- the organization of individual selection of material;
- direct work on development of speech, emotional-volitional sphere, as a regional component and
the conditions of the educational environment;
- timely and complex impact on the learner would prevent other somatic and constitutional
violations;
- permanent fixation of the results obtained during the impact;
- the inclusion of additional teaching techniques according to the degree of complexity of program
requirements and their adaptation to the general status of students with disabilities;
- the inclusion of new technologies and the reorganization of a program project to improve its
quality as required;
- tracking the dynamics of the development of a didactic system for an autonomous development.
The second block is the implementation of the technology, characterized by a primary "selection" of
participants for interaction. This selection is done randomly. Tactics development is determined by the
shape and extent of the breach suffered from a junior high school student, as well as competence of the
interaction between members of the educational process. The model involves the purposeful
organization of independent work of younger pupils in accordance with special needs. The central idea
of the organization model is the core, which sends the whole point. When building the second block,
we used generally accepted principles:
1. The principle of consistency: a review of the development process in a holistic view of the
diverse types of relationships with it.
2. The principle of continuity: the solution to the contradiction between the need to ensure the
continuity and integrity of the training and its intermittent nature. The continuity should be reflected in
the content of the training material in the system individually differentiated tasks, forms, methods and
means of learning.
3. The principle problem-solving: the availability of problematic situations and related problems in
training and outside of training, deliberately created with a purpose.
4. The principle of academic-research activities: the acquiring of new knowledge, ways of action,
new techniques and methods application of knowledge to practice by the learner.
5. The principle of motivation: orientation of the teacher on a new type of purposeful formation of
motivation among primary school children with disabilities.
6. The principle of individualization of educational activity: identify individual characteristics of
students, manifested in the process of overcoming disabilities and special needs.
7. The principle of diagnostic and prognostic orientation of psychological-pedagogical influence.
The stages determined the efficiency effects we identified: planning of the validation parameters in
accordance with the criteria; receipt of evidence; the practical experience and contact with other professionals,
parents; documenting the progress of the audit; the generalization of conclusions, formation and expression of
opinion about the status of speech of each primary school pupil. The degree of efficiency in turn is
determined by the results of the inspection. Therefore, the selection of contents of the third block as a separate
element of the model structure allows us to achieve greater consistency in practice. Control parameters were
used in the process, in efforts to overcome the violations that are private compared to general didactic criteria
of control.
If necessary, the teacher can make corrections to every structural component, which is subjected to
analysis at all sub-levels. These components are in interaction. It is valuable that this model can be converted
or redesigned, depending on the conditions of education. A necessary condition for this transformation is the
existence of threshold conditions (as a result of the control), going beyond which will change the organization
of the education system. The proposed model represents a theoretical basis for the analysis of a number of
phenomena and the relationships within the currently observed structure of the model of professional activity
of the modern teacher when working with children with special educational needs.
3. Experimental verification of the effectiveness of the proposed model.
Along with the theoretical quest of creating the didactic model of development of speech of younger
students, experimental work on its implementation was carried out in the school № 46 from 2008 to 2015.
Studies identified opportunities for the functioning model of speech development, its strengths and
weaknesses, and also identified ways to improve the impact of the built hierarchical structure of the model. In
the process of the experiment, all the results obtained by us were analyzed in several aspects.
Discussions
Each concept of creating models of education for persons with disabilities is indicative of the
autonomy. This is especially not so true for the survey and identification of the breach, as the lack of
opportunities to overcome and prevent this violation. In many cases teachers do not have a clear
understanding of the nature, the general orientation and methods of psycho-pedagogical study of the
child with clinical trends for the appearance of violations. At the same time, the doctor overlooked the
possibility of correction of speech disorders without treatment and ignored the psychological and
pedagogical characteristics of children (Akhutina, 2000; Malofeev 1996).
The current stage of development of developmental psychology and the system of correctional-
developmental education is characterized by increased attention to the peculiarities of the mental and
physical development of children. There are growing numbers of children with partial and combined
disabilities, unformed individual cognitive functions and emotional-volitional processes (Akhutina, 2000).
If ten years ago the main task of empirical concept were diagnosis and direction of the student in a
special institution, at this stage, the goals determine the content and methods of correctional influence and
the creation of individualization of the treatment process. It has become obvious that it is necessary to
show concern not only in overcoming of the violations, but in preventing them (Semago, 2000). The
whole procedure of further development of the integrative psycho-pedagogical concept, we believe,
should follow certain principles. One of the important principles – the complexity of impact. Certain
aspects of each conceptual framework are not isolated from each other, and they need to emerge
holistically. In accordance with this provision, the possibility of using one or another diagnostic study that
is required at that stage of overcoming the violations when necessary, is determined. Individual
examination, at the same time, does not mean the autonomy of each specialist in the qualification status of
the child, and provides the most adequate and quality determination of the level of actual development
and forecast training opportunities for child with disabilities, the ability to give adequate advice on the
organization of the appropriate educational route and additional extracurricular work of professionals
(Komarova, 2007).
The allocation of primary and secondary irregularities in the development of younger pupils with
special educational needs allows you to organize the work and enhance its effectiveness. Certain aspects
of verbal, psychological and organizational directions are predetermined by then, in our opinion, the
principle of integrity. The problem of overcoming difficulties in learning at the present stage are due to
the complex interaction of all the conceptual sides. In accordance with this principle, opportunities are
given to be used in a particular direction of maximum informative opportunities for the speedy
surmounting of developmental disorders in children with special educational needs.
Thus, the preparation of children with disabilities is given quite a lot of work, while the problems of
work devoted to the training of specialists are extremely small and debatable.
Conclusions
It is determined that the professional activity of a modern teacher, working with children with
special educational needs, in terms of education allows to organize the process of training specialists in
the education system, aiming at continuous and systematic improvement of their professional, cultural
and educational and special competencies and psycho-pedagogical and organizational-methodical
problems of education of children with disabilities.
Thus, the research urgency was warranted by the aggravation of contradictions between the
objective necessity of the research orientation of training modern teachers, working with children with
special educational needs and the insufficient development of the theory of the problem in its intrinsic,
systemic and conceptual aspect. This contradiction is caused by the discrepancy between:
• requirements of the society applicable to education in general and the lack of research in the field
of development of children with disabilities (including children with different learning abilities and
creative abilities);
• underdeveloped didactic structure of the model for modern teachers (as a set of interrelated
elements of internal operations) and the functional purpose of such a model in the structural content of
a comprehensive training program for children with disabilities;
• need for an algorithmic construction of the process of development from the standpoint of
correction of disturbances in primary school children and the existing development of theoretical and
technological bases of the organization of this process.
The modern concept of creating a model of a new type of teacher when working with children with
special educational needs, in our opinion, ideally, should contribute to the creation of such system of
measures that would promote the potential of each child and give impetus to self-correction of
violations, as well as the creative potential of specialists. This integration of internal and external
influences stimulates the disclosure of potential opportunities. At the same time, the complementary
nature and interdependence of each does not talk about their merger, these systems may exist
separately. The main purpose of this continuity is the provision and maintenance of educational process
with the purpose of rational support for its strategy in overcoming the developmental disorders in
younger children. With this, we believe, that the problems facing the modern concept are:
1. The need to clarify the methods and techniques in all types of surveys, the relationship of
each component of the survey.
2. Create a comprehensive and unified system of overcoming developmental disabilities.
3. The creation of the benefits of innovative technologies to improve the effectiveness of
restorative effects.
4. Identification of preventive effects ways.
5. The development of clear criteria to define adequate forms of modern teacher training.
6. Development directions in the continuity of work on the development of students with
disabilities
7. The creation of a database on contemporary new literature, training courses available for
teachers.
The result of this research points towards the development of model training programs for
transformative teacher, the testing and improvement of training-methodical base of educational process
implementing programs for the integration of children with special educational needs. The
development of criteria for the integration on a theoretical and practical level: the selection of optimal
methods of training of specialists taking into account individual capabilities, the expansion of forms of
self-development and self-education, organization and evaluation of potential opportunities in
transformative teacher preparation, introduction to practice and promotion of the new experience.
References
Akhutina, T. V. (2000) Neuropsychological examination // Under the editorship of M. M. Semago.- M.: Education.- 36-42, 83-86, 118-120 .
Komarova,L.YU, (2007) Didactic model of development of speech of younger school students : dis. ... candidate. PED. Sciences : 13.00.01 N. Novgorod.-230
Malofeev, N. N., (1996) Formation and development of the state system of special education in Russia: Dis. in the form of scientific report.- M.: Russian Academy of education, Institute of comp. - 81 .
Nazarova, L. P. (2001) Integration of children with disabilities in the secondary school // scientific notes.- SPb, 48 .
Nigmatov, Z. G. (2004), Humanistic principles of pedagogy: Textbook. allowance.– M.: Higher. school, 400 .
Zakirova L.M., Burganova N.T., Khamitova L.M. Development of Constructive Features of Intelligence in the Process of Professional Training // Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2015, Unit 191, 773-776
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
20 July 2016
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-011-2
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
12
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-451
Subjects
Teacher, teacher training, teaching skills, teaching techniques, organization of education, management of education, FLT, language, language teaching theory, language teaching methods
Cite this article as:
Zakirova, L. M., Komarova, L. Y., & Burganova, N. T. (2016). Model of Professional Activity of a Modern Teacher, Working with Children with Special Educational Needs. In R. Valeeva (Ed.), Teacher Education - IFTE 2016, vol 12. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 236-244). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2016.07.38

