Abstract
Nowadays many families face problems caused by differences in their view of parental and educational style of upbringing. Progress of the child at school is one of important criteria of its assessment. The relationship in the family where emotionally atmosphere is warm, the family where parents are respectful to the identity of the child is defined, recognizing his rights, accepting it as the personality – give to the child the chance successfully to develop and be successful in study. We used certain methods: Varga, Stolin Questionnaire of the parental attitude towards children, Schubert Test "Definition of school motivation", «School test of IQ development" (ShTUR), Phillips Test level of school anxiety. We divided participants (48 students) on two groups (Control and Experimental). According to results of research EG showed low level of school motivation of 33,3%, these children attended school reluctantly, preferred to skip classes. At lessons students often were engaged in foreign activity. We found significant differences in results of IQ test between EG and CG. The problem of influence of the dominating type of the parental relation on the child gained special relevance today. From strategy of behavior which parents choose depends emotional, motivational children development.
Keywords: IQMotivationStudentsParental styleEducation
Introduction
The family is the most important source of social and economic development of society; it makes the most important public wealth - the person. The most important function of a family is education of children. The family represents basic model for socialization of the child, and parents are the first teachers. They are obliged to lay the foundation of physical, moral and intellectual development of the child at children's age.
Education in a family is emotional, individual, and specific. Family nurture is focused, constant and includes objective opportunities in various fields of activity (household, economic, leisure, public). The wide range of different subsystems (age, gender, professional occupation) is presented in a family; it allows the child step by step join a social life, and also show and realize the emotional and intellectual opportunities. In the numerous researches (Eydemiller &Yustitskis, 2001) directed on studying of family influence on mental development of the child were shown that crucial importance had type of the relations between parents and the child. The position taken by parents, the attitude towards the child in a family in many aspects defines all course of its mental development, abilities which are formed at the child and a trait of personality. The variety of family relationship depends on their traditions, values, culture and education of parents etc.
Problem Statement
Nowadays the institute of a family endures crisis, but, despite it, the family remains the stable, effective and economic system bringing up and promoting disclosure of potential opportunities of children. According to Andreyeva, Gulyga (1991) the crisis phenomena in a family are shown, first of all, in its instability. Instability of a family leads to growth of incomplete families, reduces parental authority, is reflected in opportunities of formation of families, on health of adults and children. Parenting is both a biological and a social process (Lerner, Castellino, Terry, Villarruel &McKinney, 1995). Parenting is the term summarizing the set of behaviors involved across life in the relations among organisms who are usually nonspecific, and typically members of different generations. Thus, parenting is a complex process, involving much more than a mother or father providing food, safety, and succor to an infant or child. Parenting involves bidirectional relationships between members of two (or more) generations (Ford & Lerner, 1992). Scoblik (1996) in her research found connection between parent’s emotional attitudes and cognitive skills.
Research Questions
The role of the father, mother and child is established according to public requirements and ideas of values prevailing in society. If the main attention of ideology goes only to the husband and the father, mother retreats into the shadow, and her status is equated to the child status. On the contrary, if society is interested in preservation of health and education of the child, attention goes to mother who becomes the main character.
According to historical analysis paternity isn't an obligatory component of a family; it expresses belonging to a certain type of culture, but not biological function rather. Kohn (2006) divides human cultures on "fatherly", (in which the father plays main role), and "fatherless" (in which the man mostly acts as a male, not as the father). "Fatherless" of culture are characterized by bigger male aggression, sharp antagonism between men and women, less cordial relations between all family members (Kohn, 2006).
From centuries main duty for male is getting food for females and children (hunting). In all known human societies everywhere in the world future man acquires that when he will grow up to as full member of society, he will have to provide food to woman and her descendants. However degree of social responsibility of the man for life support of his family depends on various social conditions, but usually decisive the aspiration of the man will provide wellbeing of own children though there are exceptions.
According to report of Agency of Statistic (The KazakstanTruth, 2015) the quantity of divorces in last 5 years is rapidly growing. The following list of disturbing symptoms shows that not everything is safe in a condition of the Kazakhstan family:
every fifth couple living together isn't married;
every seventh family – incomplete;
in every twelfth family there are stepsons or stepdaughters;
the woman is at the head in 90 percent of incomplete families;
30 percent of the Russian families are incomplete, for comparison: 20 percent of the Kazakh and 5 percent of families of other ethnic groups are incomplete.
Purpose of the Study
The influence of parental style of education is purpose of our study. We assume that condition of upbringing affects on cognitive abilities of students which estimated by
Research Methods
Research of influence of style of family education on progress of seniors was conducted on the basis of school No. 13. The total number of participants is 48 pupils of 9 courses.
In research part during the work with children we used the following methods:
"Test questionnaire of the parental relation of Varga, Stolin".
"Determination of level of school motivation". Schubert.
School Test of Intellectual Development (ShTIQ).
Diagnostics of level of school anxiety of Phillips.
Findings
During experimental research we divided participants on two groups Experimental Group (EG) and Control Group (CG). Participants from Control Group have full families (both parent), in Experimental Group one of parents is exist (incomplete families).
As a result of the statistical analysis in the SPSS 15 program we revealed reliable correlation between EG and data of the ShTUR test.
From ninth-graders it was required to show abilities in finding the most essential general sign, to bring concepts under a certain category. The most often found mistakes were: substitution of a general word synonymic, relative concept or, on the contrary, very sweeping categorical generalization. Sometimes, these mistakes are caused by the same reasons which were described above: not identification of concepts as logical category, and still initially – the weak level of awareness, a conceptual stock as it is impossible neither to analyze nor to classify, to generalize concepts which sense isn't clear.
From the obtained data it is visible that in Experimental Group participants showed low level of school motivation of 33,3%, these children attend school reluctantly, prefer to skip classes. At lessons often are engaged in foreign affairs, games.
16,6% of examinees showed the high level of school motivation. They are interesting in education. Examinees of this group have an informative motive, aspiration most successfully to fulfill all requirements imposed by school. Pupils accurately follow all instructions of the teacher, are conscientious and responsible, strongly worry if receive unsatisfactory estimates.
8,4% participants showed good school motivation. Examinees successfully coped with educational activity.
25% of examinees rather safely feel at school, however go to school more often to communicate with friends, with the teacher.
33,3% participants have a low school motivation. Such children experience serious difficulties in educational activity.
Some of participants (16.6) showed negative attitude to school. Examinees test serious difficulties in training: they don't cope with educational activity, have problems in communication with schoolmates, in relationship with the teacher. The school is quite often perceived by them as the hostile environment stay in which for them is intolerable.
Participants of CG showed the following results:
The formation at the child of the motivational sphere plays an important role for his success in educational activity. Existence at the child of motive is good to fulfill all requirements imposed by school, to prove to be from the best party forces it to show activity in selection and storing of necessary information.
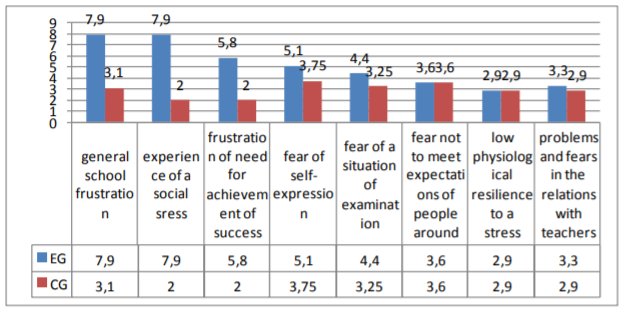
According to results of the test 80% of the examinees from EG demonstrated an increased level of school anxiety. In CG 56% of examinees showed the average level of anxiety. Thus, we revealed the fears prevailing at all examinees. These are such fears as: fear not to meet expectations of people around, problems and fears in the relations with teachers, fear of a situation of examination. Also at children low physiological resilience to a stress is revealed.
It is possible to draw a conclusion that children have fears, connected with various forms of life in school. Also existence of fears rather emotional a condition of the child against which his social contacts (first of all develop is observed - with contemporaries), there are negative emotional experiences of the situations interfaced to need of self-disclosure, presentation of to another, demonstrations of the opportunities; negative attitude and experience of alarm in situations of check (especially public) knowledge, achievements, opportunities; the general negative emotional background of the relations with adults at school reducing success of training of the child; the features of the psycho physiological organization reducing adaptability of the child to situations of stress character.
So, we will consider the received results of " test of the parental relation of Varga, Stolin”.
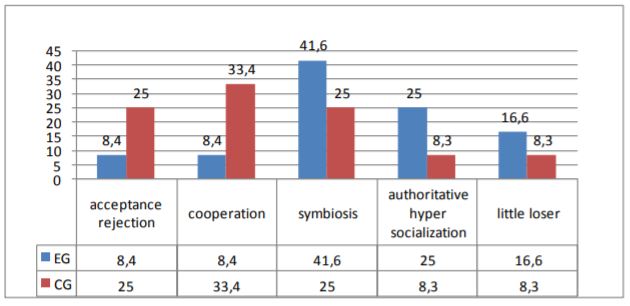
According to conducted research and compared results among two groups it is possible to tell that most common style of parental relation is “symbiosis” (41.6% in EG and 25% in CG), which means the parental tendency to come into close intense emotional contact with the child, to participate in all trifles of his life.
16.6% of participants in EG demonstrated a type of “bad” family relationship known as parental style “little looser”. It’s rejecting with elements of an infantilization and a social invalidization - emotional rejection of the child, low value of his individual and personal needs and values. Growing up in “incomplete family” is a key factor of difficulties in adolescent socialization.
25% of participants showed that their parents tend to hyper patronage and control children’ behavior. Parents in these families are blocking of implementation of children's need for psychosocial identification.
Conclusions
The conducted research allowed us to draw the following conclusions: 1. Family socialization is understood as such development of the child in a family during which he acquires ethno cultural and social experience, family traditions, customs, the gender and age roles, optimum style of communication with family members.
2. Absence of necessary pedagogical culture of parents and other tutors belittles efficiency of socialization of children in a family and therefore a necessary condition of successful family socialization is pedagogical competence of parents, their psychological readiness for activities for education, development to formation, specialization of children in the conditions of a family and interaction with teachers, especially with social teachers and psychologists of child care educational institutions and schools.
3. Children from “incomplete families” faced more difficulties in school activity and performance.
References
- Andreyeva, I. S.Gulyga, A. V. (1991). Marriage and family today. Family.. Moscow, M: Publishing house of political literature
- Eydemiller, E. G.Yustitskis, V. (2001). Psychology and psychotherapy of a family. St.. Petersburg, SPb.: Piter
- Ford, D. L.Lerner, R. M. (1992). Developmental systems theory: An integrative approach.. Newbury Park, CA: Sage
- Kohn, I. (2006). Why do we need fathers? Journal Star (12), 124-145
- Lerner, R. M.Castellino, D. R.Terry, P. A.Villarruel, F. A.McKinney, M. H.Bornstein, M. H. (1995). A developmental contextual perspective on parenting. , Handbook of parenting: Biology and ecology of parenting (Vol. pp. 285-309).. Hillsdale, NJ, 2
- Skoblik, O. N. (1996). Influence of the emotional attitude towards parents on development of the general abilities of the child.. Moscow, M: Sense
- Soloviyeva, G. (2015, January). Happy family, happy society. The Kazakhstan Truth.. Retrieved from, http://www.kazpravda.kz/articles/view/schastlivaya-semya--schastlivoe-obshchestvo/
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
03 August 2015
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-005-1
Publisher
Future Academy
Volume
6
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-220
Subjects
Child psychology, psychology, developmental psychology, psychological testing, psychological measurement, family psychology
Cite this article as:
Naurzalina, D., Shumeiko, T., Almurzayeva, B., Tolegenova, A., & Kubiyeva, V. (2015). The impact of family style education on high school student’s grades. In Z. Bekirogullari, & M. Y. Minas (Eds.), Cognitive - Social, and Behavioural Sciences - icCSBs 2015, August, vol 6. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 214-220). Future Academy. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2015.08.21
