Abstract
In essence, the blockchain is a digital ledger with centralized, public, and decentralized records of executed transactions. One of the many features of blockchain technology is the interoperability capability that permit data to be exchanged between multiple systems and be considered simultaneously by multiple systems. Interoperability features in blockchain have the potential to significantly enhance outcomes in healthcare. In healthcare, blockchain researchers continue to explore how to bring innovation to this technology and how to make it interoperable. The purpose of this study is to present a systematic literature review (SLR) of research on healthcare blockchain interoperability. The researcher used the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews guidelines, along with a systematic mapping study process, in which search protocols were used to identify, extract, and analyses all relevant publications across two scientific databases. The study highlights recent advances in the development of healthcare blockchain based on interoperability, their limitations, and the areas that require further research. Consequently, further research is needed to characterize and evaluate Blockchain interoperability in the healthcare sector.
Keywords: Blockchain interoperability, blockchain interoperability in healthcare, healthcare, interoperability
Introduction
The blockchain, as the basis of digital currency, is a decentralized, public, and digital ledger that contains all committed transactions. It is a technology-based on the peer-to-peer ledger and has been gaining a lot of attention from various industries, such as finance, healthcare, supply chain, etc. It uses consensus algorithms to synchronize data distributed across several users, unlike centralized digital ledgers. Initially introduced with Bitcoin, the blockchain allowed users to avoid the double-spending problem without relying on a trusted authority or central server, which revolutionized the field of digital currency. The blockchain system lets users record and look at data, but they cannot edit or remove any information that has previously been recorded (Zhou et al., 2020).
Interoperability is defined as the capability of different systems to communicate with each other without limitations (Kwon & Yoo, 2021). By exchanging data between multiple systems and allowing access to it simultaneously, blockchain technology can improve interoperability. In many proposed systems, data is shared within institutions or user-centric, in which user maintain full control over their data. It is possible for interoperability to improve system outcomes (Prasad, 2021).
The medical field defines interoperability as a means of optimizing the health of individuals and society through the compatibility of different medical information systems, medical equipment, and applications (Kwon & Yoo, 2021).
Traditional healthcare interoperability has been focused on the exchange of data between business entities, such as between different hospital systems. Interoperability centered around the patient is an important trend that has the potential to lay the groundwork for more efficient data sharing in healthcare. To achieve scale in patient-centered interoperability, however, new challenges and requirements are needed for security and privacy, technology, incentives, and governance, and the challenges remain unresolved in traditional interoperability models (Gordon & Catalini, 2018).
Problem Statement
Everybody deserves to get a healthcare program whether provided by the government or the private healthcare provider. Sometimes it is necessary for a patient to be treated by more than one healthcare provider. This requires the exchange of information across the different healthcare providers. In information communication technology (ICT) it involves data being able to be transmitted across different platforms and infostructure. Apart from that, data integrity is also critical to ensure data transferred from one provider to another are genuine, accurate, and trustworthy. Thus, the interoperability characteristics of blockchain play an important role in the information exchange to happen. However, not much has been revealed on this. Thus, it is important to uncover the healthcare blockchain interoperability in a systematic manner (SLR). The review will analyze and discuss the implications related to the current use of blockchains in healthcare based on the articles classified by years.
Research Questions
The questions determined by the study included the following:
What is blockchain interoperability in healthcare?
How blockchain interoperability components can be used to develop a healthcare system?
What is blockchain interoperability application has been developed in the healthcare domain?
In the healthcare domain, what research limitations need to be addressed?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to present a systematic literature review (SLR) of research on healthcare blockchain interoperability. Search parameters were used and results from the search parameters were then filtered by four research questions that were devised to conclude. The review presented the current implications and gaps referring to the use of blockchain interoperability in healthcare sectors.
Research Methods
Data Sources:
This study presents a systematic literature review on blockchain-based interoperability in healthcare using the PRISMA statement. The researcher searched the Google Scholar, PubMed, and Microsoft Academic search engines for articles discussing blockchain interoperability, components of blockchain interoperability, applications of blockchain interoperability in healthcare, as well as limitations. Researchers searched only for articles mentioning the term "blockchain interoperability in healthcare". Researchers examined article titles and abstracts between 1st June 2016 and 30th August 2021, systematically searching the reference lists of articles included in the search.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:
The study focused mainly on blockchain interoperability in healthcare. Accordingly, the inclusion criteria for the articles were blockchain interoperability components, blockchain interoperability applications, and limitation-based healthcare.
As the search terms focused only on terms synonymous with the term "blockchain interoperability in healthcare", the search results included many articles that didn't mention blockchain interoperability in healthcare but used it for other purposes, such as education, finance, or logistics. These articles were not included in this study. Articles that were not published in English were also excluded.
Study Selection and Data Extraction
Based on the selection criteria described in the previous section, the titles and abstracts of the identified citations were read to screen the articles. Once the titles and abstracts of the articles had been read, the full texts were read to extract valuable information. Information extracted from these sources is presented in tables 1,2, and 3 that include Popular Blockchain Interoperability Definitions, Blockchain Interoperability Applications in Healthcare, and Research Healthcare Issues.
Result
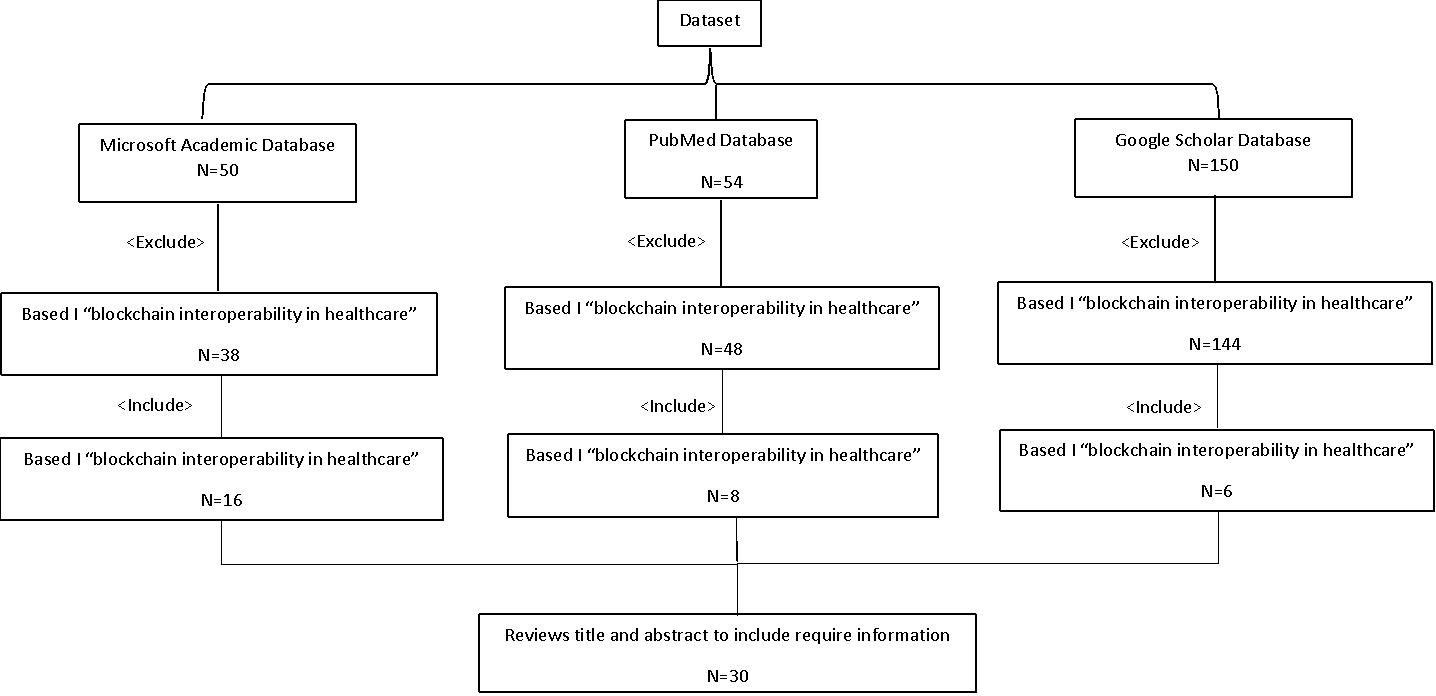
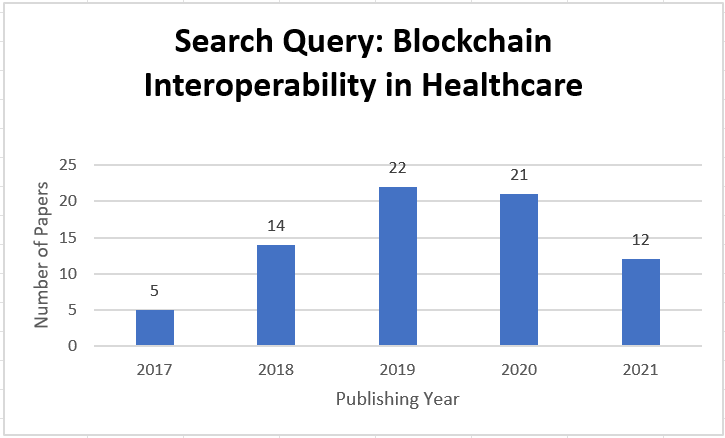
Figure 1 illustrates the flow diagram of identifying articles eligible for this study. After conducting literature searches in three databases, 254 articles were obtained, which were then initially screened based on titles and abstracts. 230 articles were excluded from the review based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria described previously. The full text of 30 articles was then reviewed. In the end, 30 articles met the criteria, discussing blockchain interoperability in healthcare, blockchain interoperability in healthcare applications, and future research areas in that field. According to figure 2, the earliest eligible articles were published between 1st June 2017 and 30th August 2021.
Findings
Based on the research questions provided above, this part presents the outcomes of the SLR.
First question
In the various areas of application, interoperability encompasses several different perspectives and approaches from various communities. Based on the results of the search for "blockchain interoperability in healthcare", the following table 1 displays the most popular definition used by the researcher:
According to table1, research conducted by (Centobelli et al., 2021; Dimitrov & Gigov, 2020; Jabbar et al., 2020; Monika & Bhatia, 2020; Nehra et al., 2020; Pillai et al., 2020), had described blockchain interoperability in healthcare as the ability of various systems to work together and in harmony across healthcare business boundaries in order to provide more effective and advanced healthcare services. Whether a blockchain network, unit, or force can provide or receive services from other blockchain networks, units, or forces and be able to utilize such exchanged services effectively has not been proven by some researchers, such as Besancon et al. (2019) and Kiechl et al. (2021). Others, like Gordon and Catalini (2008), defined blockchain interoperability as the process of exchanging electronic information securely and seamlessly between authorized users, preventing unauthorized access or use of this information.
Based on its findings, this study defined blockchain interoperability as the combination of multiple blockchain platforms which are connected to a single network.
Based on its findings, this study determined that blockchain interoperability is the combination of multiple blockchain platforms which are connected to a single network.
Second question
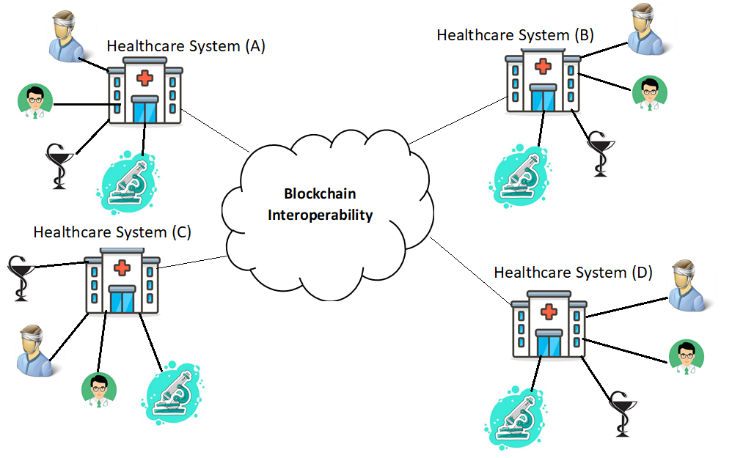
There are various blockchain interoperability components in healthcare, including software, systems, and applications. Moreover, it can be combined blockchains from different networks into one. Figure3 shows how different healthcare systems are interconnected through blockchain interoperability, allowing for a seamless exchange of information between them.
In the healthcare sector, Pillai (2020) emphasized the importance of blockchain interoperability, which allows a seamless transfer of data between blockchain systems that are compatible with one another.
Third question
Several applications of blockchain interoperability have been identified for healthcare because of the growing popularity of blockchain and its adoption in different organizations and industries. There is also a lot of hype about blockchain technology in the context of articles, commentaries, blog posts, interviews, and opinion pieces that are primarily in the press and grey publications, which results in some inaccurate information, speculations, and uncertainties concerning blockchain's potential utility in healthcare.
As shown in the following table 2, some applications have been developed based on blockchain interoperability in healthcare domain.
Blockchain interoperability frameworks and applications enable the sharing of information among various healthcare systems electronically. Consequently, users can share data and discuss it with others with ease. However, it still has some limitations, including that it does not cover all stakeholders (hospital, patient, doctor, pharmacy, drug supply chain, insurance companies). As well, some of the applications lack the "decentralize" function, which is crucial for increasing security and privacy.
Fourth question
As the healthcare industry adapts to new technologies, there are several priorities to address. Considering the recent research which took place between July 2021 and 2020. Table 3 below shows some healthcare-related issues that can be improved and addressed by technology.
As a result, ensuring security, data sharing, interoperability, and data integrity are the most urgent priorities. Researchers identified the lack of progress in integrity and security since most hospitals can still send records to community-based physicians. Also, the researcher has shown that blockchain can be used to create and manage a distributed database to handle transactions involving multiple nodes of a network. However, its implementation of it in healthcare hasn't met interoperability standards. Furthermore, they identified user authentication, blockchains, and IoT in the drug supply chain, data exchange structure, performance, cost, efficiency, and big data of medical records, projects that are not integrated, privacy and scalability as issues that need to be addressed.
Conclusion
Blockchain interoperability in healthcare allows for medical data exchanges and interactions between various blockchain healthcare systems, boosting the energy efficiency and efficiency of each. This study reviews the research on healthcare blockchain interoperability in a systematic manner (SLR). The review analyzed and discussed the implications related to the current use of blockchains in healthcare based on the articles classified by years. As the result, this technology is not perfect due to its shortcomings, which include the fact that not all stakeholders (hospital, patient, doctor, pharmacist, drug supply chain, insurance companies) are provided with access to it. In addition, some of the applications do not provide "decentralization", an essential step in securing data. In addition, research studies highlighted the security and interoperability challenge and acknowledged a lack of progress. Blockchain researchers are still investigating how this technology can be interoperable in healthcare and how to bring innovation to it. The report contains valuable information to help researchers evaluate the value of blockchain and interoperability in the healthcare domain.
Acknowledgments
My sincere appreciation and deep gratitude go to my research supervisors for providing me with the opportunity and guidance in doing this research paper.
References
Belchior, R., Vasconcelos, A., Correia, M., & Hardjono, T. (2021). HERMES: Fault-Tolerant Middleware for Blockchain Interoperability. TechrXiv 14120291/1.
Belchior, R., Vasconcelos, A., Guerreiro, S., & Correia, M. (2020). A Survey on Blockchain Interoperability: Past, Present, and Future Trends.
Besancon, L., Silva, C. F. Da, & Ghodous, P. (2019). Towards blockchain interoperability: Improving video games data exchange. ICBC 2019 - IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency, 81–85.
Capece, G., & Lorenzi, F. (2020). Blockchain and healthcare: Opportunities and prospects for the ehr. Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(22), 1–17.
Centobelli, P., Cerchione, R., & Riccio, E. (2021). A novel architecture for enhancing Electronic Health Record interoperability: A Blockchain-based approach, 1–6.
Chukwu, E., & Garg, L. (2020). A systematic review of blockchain in healthcare: Frameworks, prototypes, and implementations. IEEE Access, 8, 21196–21214.
De Aguiar, E. J., Faiçal, B. S., Krishnamachari, B., & Ueyama, J. (2020). A Survey of Blockchain-Based Strategies for Healthcare. ACM Computing Surveys, 53(2).
Dimitrov, I., & Gigov, R. (2020, October). Exploring Interoperability of Blockchain Technology and the Possibility of Collaboration with the Existing Information Systems of the Enterprises. In 2020 III International Conference on High Technology for Sustainable Development (HiTech) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
Ding, D. (2018). InterChain: A Framework to Support Blockchain Interoperability. https://conferences.sigcomm.org/events/apnet2018
Durneva, P., Cousins, K., & Chen, M. (2020). The current state of research, challenges, and future research directions of blockchain technology in patient care: Systematic review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 22(7), 1–16.
Ellouze, F., Fersi, G., & Jmaiel, M. (2020). Blockchain for Internet of Medical Things: A Technical Review. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics): Vol. 12157 LNCS. Springer International Publishing.
Ghaemi, S., Rouhani, S., Belchior, R., Cruz, R. S., Khazaei, H., & Musilek, P. (2021). A Pub-Sub Architecture to Promote Blockchain Interoperability. http://arxiv.org/abs/2101.12331
Gordon, W. J., & Catalini, C. (2018). Blockchain Technology for Healthcare: Facilitating the Transition to Patient-Driven Interoperability. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 16, 224–230.
Gürdür, D., & Asplund, F. (2018). A systematic review to merge discourses: Interoperability, integration and cyber-physical systems. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 9(October), 14–23.
Hasselgren, A., Kralevska, K., Gligoroski, D., Pedersen, S. A., & Faxvaag, A. (2020). Blockchain in healthcare and health sciences—A scoping review. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 134(November 2019), 104040.
Jabbar, R., Fetais, N., Krichen, M., & Barkaoui, K. (2020). Blockchain technology for healthcare: Enhancing shared electronic health record interoperability and integrity. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Informatics, IoT, and Enabling Technologies, ICIoT 2020, 310–317.
Kamau, G., Boore, C., Maina, E., & Njenga, S. (2018). Blockchain technology: Is this the solution to EMR interoperability and security issues in developing countries? 2018 IST-Africa Week Conference, IST-Africa 2018, 1–8.
Kiechl, P., Scheid, E., & Date, C. K. (2021). Extension and Standardization of a Blockchain Interoperability API. http://www.csg.uzh.ch/
Kothari, P., Nuce, M., Vasiliu-Feltes, I., Hurley, D., Fox, M., Sneha, S., Charles, W., Nasr, J., & Iyengar, R. (2021). Blockchain predictions for health care in 2021. Blockchain in Healthcare Today, 1, 1–4.
Kwon, O., & Yoo, S. K. (2021). Interoperability reference models for applications of artificial intelligence in medical imaging. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 11(6).
Lipton, A., & Hardjono, T. (n.d.). Blockchain Intra- and Interoperability, 1–29. https://www.numerairefinancial.com/s/32-2021-Lipton-Hardjono-Blockchain-Intra-and-Interoperability-ptrz.pdf
Madine, M., Salah, K., Jayaraman, R., Al-Hammadi, Y., Arshad, J., & Yaqoob, I. (2021). appXchain: Application-Level Interoperability for Blockchain Networks. IEEE Access, 9, 87777–87791.
Mazlan, A. A., Daud, S. M., Sam, S. M., Abas, H., Rasid, S. Z. A., & Yusof, M. F. (2020). Scalability Challenges in Healthcare Blockchain System-A Systematic Review. IEEE Access, 8(4), 23663–23673.
Monika, & Bhatia, R. (2020). Interoperability Solutions for Blockchain. 2020 International Conference on Smart Technologies in Computing, Electrical and Electronics (ICSTCEE), 381-385.
Nehra, V., Sharma, A. K., & Tripathi, R. K. (2020). Blockchain Implementation for Internet of Things Applications. In Handbook of Research on Blockchain Technology (Issue March 2021).
Pang, Y. (2020). A New Consensus Protocol for Blockchain Interoperability Architecture. IEEE Access, 8, 153719–153730.
Pascal, L., & Lombard-Platet, M. (2020). about blockchain interoperability. ScienceDirect, 1-5, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipl.2020.105976
Perrons, R. K., & Cosby, T. (2020). Applying blockchain in the geoenergy domain: The road to interoperability and standards. ScienceDirect, 1-6.
Pillai, B., Biswas, K., & Muthukkumarasamy, V. (2020). Cross-chain interoperability among blockchain-based systems using transactions. Knowledge Engineering Review (Vol. 35). Cambridge University Press, April 2021.
Poon, J., & Dryja, T. (2016). The bitcoin lightning network: Scalable off-chain instant payments. Technical Report, 2016.
Prasad, P. J. (2021). Electronic Health Record Using Blockchain and Off Chain Storage: a Systematic Review. Information Technology in Industry, 9(1), 247–253.
Reegu, F., Mohd Dau, S., & Ala, S. (2021). Interoperability Challenges in Healthcare Blockchain System A Systematic Review. Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 25, 15487–15499. https://www.annalsofrscb.ro/index.php/journal/article/view/5177Firdaus
Scheid, E. J., Hegnauer, T., Rodrigues, B., & Stiller, B. (2019). Bifröst: a Modular Blockchain Interoperability API. Proceedings - Conference on Local Computer Networks, LCN, 2019-Octob, 332–339.
Sharma, Y., & Balamurugan, B. (2020). Preserving the Privacy of Electronic Health Records using Blockchain. Procedia Computer Science, 173(2019), 171–180.
Tandon, A., Dhir, A., Islam, N., & Mäntymäki, M. (2020). Blockchain in healthcare: A systematic literature review, synthesizing framework and future research agenda. Computers in Industry, 122.
Tariq, N., Qamar, A., Asim, M., & Khan, F. A. (2020). Blockchain and smart healthcare security: A survey. Procedia Computer Science, 175(2020), 615–620.
Usman, M., Kallhoff, V., & Khurshid, A. (2021). The Case for Establishing a Blockchain Research and Development Program at an Academic Medical Center. Blockchain in Healthcare Today, 1, 1–9.
Vervoort, D., Guetter, C. R., & Peters, A. W. (2020). Blockchain, health disparities and global health. BMJ Innovations, 7(2), 1–9.
Yaqoob, I., Salah, K., Jayaraman, R., & Al-Hammadi, Y. (2021). Blockchain for healthcare data management: opportunities, challenges, and future recommendations. Neural Computing and Applications, 34, 11475–11490.
Zhao, Q., & Thompson, R. (2020). Blockchain-Based Access Control Framework in Patient-Centered Interoperability. International Journal of Scientific Research & Engineering Trends, 6(5), 2780–2784. https://ijsret.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/IJSRET_V6_issue5_632.pdf
Zhou, Q., Huang, H., Zheng, Z., & Bian, J. (2020). Solutions to Scalability of Blockchain: a Survey. IEEE Access, 8, 16440–16455.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 October 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-958-0
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
3
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-802
Subjects
Multidisciplinary sciences, sustainable development goals (SDG), urbanisation
Cite this article as:
Aljabri, M. G., Ahmad Shukor, N. S., Ahmad Nawi, H. S., & Almmamari, M. (2022). Blockchain Interoperability On Healthcare: A Systematic Review. In H. H. Kamaruddin, T. D. N. M. Kamaruddin, T. D. N. S. Yaacob, M. A. M. Kamal, & K. F. Ne'matullah (Eds.), Reimagining Resilient Sustainability: An Integrated Effort in Research, Practices & Education, vol 3. European Proceedings of Multidisciplinary Sciences (pp. 619-628). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epms.2022.10.58

