Abstract
Malaysia needs 60,000 qualified professional accountants by 2030 to meet the government demand to transform Malaysia into a developed nation. There are around 37,000 registered Malaysian Institute of Accountants (MIA) members, currently. The shortage of professional accountants in Malaysia is due to decrease in number of accounting students in Malaysia to develop their career in accounting profession upon graduation. This study investigates whether intrinsic and extrinsic motivation as well as career exposure influence accounting students in deciding their career path. Data was obtained through questionnaire surveys from penultimate and final year accounting students in a Malaysian private university and 253 usable questionnaires are applicable for data analysis. The results of the study show that intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation and career exposure significantly positively related to the accounting students’ career path. Perhaps, factors motivate the accounting student’s career path are their personal interest, high salary paying offered and adequate knowledge about accounting profession. Additional analysis reveals there is variation in intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, career exposure and career path across the students’ rank of choice of accounting program.
Keywords: Intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, career exposure, career path, accounting students, Malaysia
Introduction
Students commonly in dilemma to choose an appropriate career path upon graduation. A person should carefully consider their career path as it will be a lifelong journey. “A career is a lifelong process which is planned from an early stage” (Yusoff et al., 2011, p. 57). Career path refers to the choice of career by students after his or her graduation (Ng et al., 2017). Malaysian economies develop rapidly through emerging of various industries which required skilled and competent accountants to fulfill demand in the market but Malaysia still lacks a sufficient number of qualified accountants. Malaysia is expected to require 60,000 accountants by 2030, however there is already a significant shortage with only about 37,000 members enrolled with the Malaysian Institute of Accountants (The Star, 2021). The shortage of accounting profession still exists even though accounting course is one of the popular course enrollment in Malaysian education since not every accounting students will pursue accounting areas as their future career path.
Accounting students can receive career guidance from subject instructors and the choice of career path are affected by intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, influences of third parties and career exposure (Ng et al., 2017; Shanthrakumar, 2020). Accounting areas include financial accounting and reporting, management accounting, taxation, and auditing. One of the reasons that lead accounting students for not aspiring to develop their career in accounting is the negative perception towards accounting field that an accountant's job is monotonous (Hung, 2014). Graduates of accounting will choose a career path based on people’s perception and rewards from the chosen career (Samsuri et al., 2016). The declining of accountant profession in Malaysia also contributed by the lack of insufficient knowledge or information about accounting. Professional bodies should provide exposure to students to attract them to relevant professional careers (Giandrea & Sprague, 2017). Though many accounting graduates have a slanted preference towards the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA) compared to other professional bodies (Ng et al., 2017), nonetheless, ACCA must make a significant effort because not all of their trainees will become professional accountants (ACCA, 2018a). This study looks into how accounting students' career path are influenced by intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, and career exposure.
Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
Motivation is an individual attitude towards their action in accomplishing their goal (Acar, 2014). Intrinsic motivation refers to personal satisfaction or personal interest. Intrinsic motivation is defined as a pleasure and enjoyment during task or job performance that exist internally of an individual (Ahmad et al., 2015). Intrinsic motivation includes internal satisfaction, interest, exciting and challenging (2012). A connection was observed between intrinsic motivation and career path (Shanthrakumar, 2020; Thing & Jalaludin, 2018). Intrinsic motivation is the most factor that will influence student's career choice (Ng et al., 2017) and students believe the positive intrinsic outcome will influence them to be an accountant (Porter & Woolley, 2014). The desire of students to enter the accounting profession is significantly influenced by their interest in accounting (Ghani et al., 2019; Liany & Raharja, 2020). Nevertheless, some students have a misguide belief that an accountant's job is boring and too much work to do that would burden their satisfaction in job performance (Hung, 2014), thus, divert from the accounting profession. Meanwhile, Hatane et al. (2021) documented otherwise, whereby intrinsic motivation is not a determinant of accounting students' career choice and supported Acar (2014) who implied that intrinsic motivation not significantly influences Gen X. Therefore, the current study proposes the first hypothesis:
H1. Intrinsic motivation is significantly related to accounting students’ career path in MPU
Returns or outcomes, such as money, incentives, career chances, high salaries, and recognition, constitute extrinsic interest (Ahmad et al., 2015). Extrinsic motivation is when individual doing something with the intention to get a separable outcome, which is to be rewarded when performing the task rather than enjoying the task and it was a major motivation that influenced Gen Y (Acar, 2014). The most common extrinsic motivation in choosing their career path are salary and job opportunities, hence, extrinsic motivation is the second highest factor that influencing student's career choice after intrinsic motivation (Ng et al., 2017). Similarly, Shanthrakumar (2020) documented that extrinsic motivation is linked with accounting students’ career path. Liany and Raharja (2020) implied that job stability and labour demand predicts a decision in pursuing a career. Students believe that accounting offered extrinsic outcome which positively influences their career's decision (Porter & Woolley, 2014). Odia and Ogiedo (2013) revealed that job prospects and higher salary significantly influence career decision of accounting students. Similarly, salary and status was among the determinants of a teaching career in Turkey (Ekin et al., 2021). Therefore, the current study posits the second hypothesis:
H2. Extrinsic motivation is significantly related to accounting students’ career path in MPU
The decision of students to choose an accounting career is influenced by their career exposure (Ghani et al., 2019) whereby students are exposed to career related-information. Educators and subjects may influence students in their perception about accounting (Shanthrakumar, 2020). Mbawuni and Nimako (2015) established that career orientation and trainings by educators give positive impact towards perception of future accounting profession in Sub-Saharan Africa. Besides exposure by academic advisors, professional accounting bodies have a role in providing accounting students with suitable courses, seminars, and campaigns for their career path (Liany & Raharja, 2020; Ng, et al., 2017; Samsuri et al., 2016). Hatane et al. (2021) claimed students that are well knowledgeable about the accounting field may choose to become public accountants as their job. Additionally, Hutaibat (2012) demonstrates that financial accountants are more desirable than management accountants due to the job exposures provided during the students’ university time. However, Yusoff et al. (2011) evidenced that career guidance from educators and adequate knowledge about professional accounting has no significant influence to students in making a decision to choose their career path. Hence, the third hypothesis is formulated as:
H3. Career exposure is significantly related to accounting students’ career path in MPU
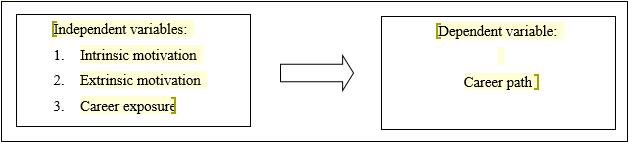
The Social Cognitive Career Theory (SCCT) based on Lent et al. (1994) is employed in the current study which was widely utilised in earlier researches to examine the variables affecting undergraduate students in their career path, as shown in Figure 1. Bandura's Social Cognitive Theory (1986) served as the foundation for Lent et al. (1994)'s SCCT, which was utilised to describe factors influencing profession choice. Using the SCCT framework, one may understand the steps involved in selecting a career. It discusses both internal and exterior elements that could affect someone's decision.
Methods
This study chose penultimate and final year accounting students in a Malaysian Private University (MPU) as the sample. MPU was ranked by the QS World University Ranking as top 20 universities in Malaysia, and the students are chosen because they have taken advanced subjects, more exposure to make decisions about their career path and closer to real working environment compared to their counterparts. After excluding incomplete responses, 253 questionnaires can be used for the analysis, and this is acceptable as it is between 30 to 500. This study used a simple random sampling as everyone has an equal chance of being selected besides it is least biased and most generalizable (Sekaran & Bougie, 2019). When the sample size exceeds 30, the Central Limit Theorem is used, whereby it assumes a normal distribution, hence, this study employed parametric tests for the hypotheses.
Career path, as the dependent variable, is adopted from Yusoff et al. (2011), asking about their plan after graduation. While instruments on intrinsic and extrinsic motivation are measured based on Odia and Ogiedo (2013) and career exposure are adopted from Hutaibat (2012). All the variables consist of five items and a five-point Likert scale is used to elicit the strength of a student’s agreement, ranging from 1 “strongly disagree” to 5 “strongly agree”.
The following is used to test the hypotheses:
it = β0 + β1it + β2it + β3it + it
Where,
it=Career path
β1it=Intrinsic Motivation
β2it=Extrinsic Motivation
=Career exposure
it=Error term
Findings
This study investigates the relationship between intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation and career exposure towards accounting students’ career path in MPU and utilized the Statistical Package of Social Sciences for data analysis.
Reliability of the instruments is determined through a Reliability test. Based on Table 1, all the instruments have Cronbach’s Alpha of higher than 0.7, signifying that the instruments have higher internal reliability as the value approaches 1 (Sekaran & Bougie, 2019).
Table 2 exhibits that out of 253 respondents, almost three quarter are female students (74.3%) and come from third year (60.5%). 72.7% of the respondents obtained a CGPA of 3.00 and above, and only 0.4% with CGPA less than 2.00. More than half of them have no relatives in accounting profession and accounting program is their first choice.
Based on Table 3, in terms of intrisic motivation, the students agree that accounting is a fascinating subject, they would love working as accountants, and they are willing to devote a lot of time to learning it. As for the extrinsic motivation, the students agree that accounting profession provides job security and stability, high paying salary, has a lot of prestige and well respected. They also agree that they have been given career exposure and supports from universities and professional bodies through seminars and workshops about the accounting profession. Besides that, thay are aware about career options in accounting profession that are available to them after graduation.
Through Pearson’s correlation analysis, Table 4 illustrates that the variables do not have coefficients of greater than 0.9, indicating non-existence of multicollinearity problems which satisfies one of assumptions to carry out a regression analysis (Sekaran & Bougie, 2019).
2 = 0.571,-ratio = 110.597,= 0.000
The result in Table 5 proved that intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation and career exposure significantly affect the career path (p<0.05) of accounting students in MPU, therefore, accepting H1, H2 and H3. Based on the b-value, the career path of accounting students rises by 0.334 unit for every unit of intrinsic motivation. In terms of extrinsic motivation, the b-value shows that when the extrinsic motivation increases by 1 unit, accounting students’ career path increase by 0.238 unit. While for career exposure, accounting students’ career path increases by 0.301 unit with the increase of 1 unit of career exposure. The three factors accounts 57.1% of the deviations in accounting students’ career path (F=5.390), implies that the other 42.9% could be affected by other predictors which are not tested in this study. Additional analysis is conducted to examine the difference in motivations, career exposure and career path across the rank of choice of accounting program among accounting students in MPU.
The results from One-Way ANOVA in Table 6 provide evidence that a significant difference exists in intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, career exposure and career path across the rank of choice of accounting program. The mean for students who choose accounting program as their first choice is the highest, followed by second choice and third choice signifying that accounting students’ intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, career exposure and career path affect their rank of choice in accounting program.
Conclusion
This study examines whether intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation and career exposure affect accounting students' career path in a Malaysian private university, through a questionnaire survey. It is observed that students with higher career motivations (intrinsic and extrinsic) as well as greater career exposure have better career path, which is consistent with the SCCT by Lent et al. (1994) whereby the internal and external elements could affect their career decision. The result supports Shanthrakumar (2020) and Ng et al. (2017) who stated that intrinsic motivation is the main factor that influences student’s career choice, and Porter and Woolley (2014) whereby they found a positive intrinsic outcome will lead students to be an accountant. Many students admit that they decided on accounting as their career since it is attractive and they will be happy as an accountant (Ghani et al., 2019; Liany Raharja &, 2020). Perhaps, student’s personal interest, their enjoyment during the task, and student’s perspective towards accounting is exciting and challenging lead them to choose accounting profession as their career path upon graduation. Since accounting professionals work in all types of businesses and industries, students opt to major in accounting in order to fulfil their professional aspirations (ACCA, 2018b). Despite the digital revolution through Industrial Revolution 4.0, “future accountants must be equipped with technological skills, communications and soft skills, critical thinking, strategic and analytical skills, and resilience as well as flexibility” (Mahzan, 2019, p. 12). Nevertheless, the current findings contradict from Hatane et al. (2021) who documented otherwise.
Extrinsic motivation positively influences accounting students’ career choice. This might be due the accounting profession offered job opportunities, rewards, and high paying salary which might influence student’s intention to continue pursuing in accounting as their career path. Furthermore, accounting provides future fast-track job chances compared to other profession (Hatane & Setiono, 2019). The current study is consistent with Shanthrakumar (2020) and Acar (2014) who established extrinsic motivation as one of the predictors, and it is in line with Ekin et al. (2021) who assured that task return such as salary and status predicted a career choice. The result also supports Liany and Raharja (2020) who implied that extrinsic outcomes like job stability, prestige and high market demand significantly affect students decision in choosing their career path.
Students’ career exposure also positively influences their career path which is consistent with Ghani et al. (2019), Liany and Raharja (2020) and Shanthrakumar (2020), implies that career orientation, adequate knowledge about accounting profession and supports from professional bodies during their university time, play important roles in motivating students to make decisions about their career path after graduation. The result supports the assertion made by Samsuri et al. (2016) that academic advisors who actively promote and provide information about the advantages of being a professional accountant have a positive influence on students. As a result, students are more likely to select a job as a public accountant if they have access to more career information (Hatane et al., 2021). This result also consistent with Mbawuni and Nimako (2015) who argued that career orientation and trainings by educators give positive impact toward the perception of the future accounting profession.
Further analysis found differences in students’ intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, career exposure and career path across the rank of choice of accounting program. Accounting students who choose accounting program as their first choice have higher career motivations (intrinsic and extrinsic) as well as greater career exposure and career path, compared to the second choice and third choice.
The outcome of the study provides some insights whereby universities and professional bodies may organise more events that could enhance the accounting students' career path in accounting profession besides implementing innovative teaching and learning environment. Accounting curriculum should be relevant and design to meet the industry requirements in order to nurture students’ interest so that accounting graduates are more prepared to enter the workforce. The current study only covers a private university and three independent variables, hence, future research may use wider samples (more universities and courses), include other determinants and provide a comparison between universities and courses.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to iRMC Universiti Tenaga Nasional for funding the research and publication of this paper in ISEBA 2022.
References
Acar, D. A. (2014). Do intrinsic and extrinsic motivation factors differ for Generation X and Generation Y. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 5(5), 12-20.
ACCA. (2018a). Lifelong learning is essential to remain relevant in an ever-changing world, 2018. https://www.accaglobal.com/gb/en/news/2018/november/ACCAlearning.html.
ACCA. (2018b). The drive to double Malaysia's accountancy profession by 2020. https://www.accaglobal.com/sg/en/member/member/accountingbusiness/2018/03/practice/malaysia- 2020.html
Ahmad, Z., Ismail, H., & Anantharaman, R. N. (2015). To be or not to be : An investigation of accounting students career intentions. Education Training 57(3), 360-376. DOI:
Ekin, S., Yetkin, R., & Öztürk, S. Y. (2021). A Comparative study of career motivations and perceptions of student teachers. Turkish Studies - Education, 16(1), 505-516. DOI:
Ghani, E. K., Mohamad, N. F., Ali, M. M., & Muhammad, K. (2019). University students' intentions to become accountants: Examination using Fishbein and Ajzen's theory. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 6(10), 104-126.
Giandrea, M. D., & Sprague, S. A. (2017). Estimating The US labor Share. Mon. Labor Rev, U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistic. Retrieved from DOI:
Hatane, S. E., Gunawan, F. A., & Pratama, S. W. (2021). Intrinsic motivation, career exposure, and quality of life: How do they influence the accounting students’ career choice? Journal of Education and Learning (EduLearn), 15(3), 335-345. DOI:
Hatane, S. E., & Setiono, F. J. (2019). The intervening effect of current knowledge enhancement on attitude and intention to choose accounting career. Binus Business Review, 10(2), 119-130. DOI:
Hung, D. K. (2014). Perceptions of accounting and accountants. International Conference on Global Economy, Commerce and Service Science (GECSS 2014). DOI:
Hutaibat, K. A. (2012). Interest in the management accounting profession accounting students’ perceptions in Jordanian universities. Asian Social Science, 8(3), 303. DOI:
Lent, R. W., Brown, S. D., & Hackett, G. (1994). Toward a unifying social cognitive theory of career and academic interest, choice, and performance. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 45(1), 79-122. DOI:
Liany, D., & Raharja, S. (2020). Factors affecting accounting students in choosing accounting career path. Jurnal Dinamika Akuntansi, 12(2), 100-113. DOI:
Mahzan, N. (2019). Educating Future Accountants. Keynote address at The Kaplan Forum. Malaysian Institute of Accountants.
Mbawuni, J., & Nimako, S. G. (2015). Modelling job-related and personality predictors of intention to pursue accounting careers among undergraduate students in Ghana. World Journal of Education, 5(1), 65. DOI:
Ng, Y. H., Lai, S. P., Su, Z. P., Yap, J. Y., Teoh, H. Q., & Lee, H. (2017). Factors influencing accounting students’ career paths. Journal of Management Development, 36(3), 319-329. DOI:
Odia, J., & Ogiedo, K. (2013). Factor that affecting the study of accounting in NIgerian Universities. Journal of Educational and Social Research, 3(3), 89-96.
Porter, J., & Woolley, D. (2014). An examination of the factors affecting students' decision to major in accounting. International Journal of Accounting and Taxation, 2(4), 1-22. DOI:
Samsuri, A. S., Tengku Arifin, T. R., & Hussin, S. B. (2016). Perception of Undergraduate Accounting Students towards Professional Accounting Career. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences, 6(3), 78-88.
Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2019). Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach. John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Shanthrakumar, K. (2020). Factors influencing accounting students’ career paths in Trincomalee Campus, Eastern University, Sri Lanka. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications (IJSRP) 10(10), 189-194. DOI:
The Star. (2021). Accounting a recession proof profession. https://www.thestar.com.my/starpicks /2021/07/18/accounting-a-recession-proof-profession#:~:text=%E2%80%9CWe%20currently%20 have%20around%20only,by%202030%2C%E2%80%9D%20she%20said
Thing, O. G., & Jalaludin, D. (2018). Career path in Accounting: What are the drivers? International Academic Journal of Accounting and Financial Management, 5, 66-82.
Yusoff, Y., Omar, Z. A., Awang, Y., Yusoff, R., & Jusoff, K. (2011). Does knowledge on professional accounting influence career choice. World Applied Sciences Journal (Special Issue on Bolstering Economic Sustainability), 12, 57-60.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
18 August 2023
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-963-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
1
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1050
Subjects
Multi-disciplinary, Accounting, Finance, Economics, Business Management, Marketing, Entrepreneurship, Social Studies
Cite this article as:
Abdul Rauf, F. H., Mohd Khalid, F., Ariffin, A., Aminuddin, N., & Shamsul Bahri, N. N. (2023). Motivations, Exposure on Accounting Students’ Career Path of a Malaysian Private University. In A. H. Jaaffar, S. Buniamin, N. R. A. Rahman, N. S. Othman, N. Mohammad, S. Kasavan, N. E. A. B. Mohamad, Z. M. Saad, F. A. Ghani, & N. I. N. Redzuan (Eds.), Accelerating Transformation towards Sustainable and Resilient Business: Lessons Learned from the COVID-19 Crisis, vol 1. European Proceedings of Finance and Economics (pp. 1019-1027). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epfe.23081.94

