Abstract
This article presents a comprehensive analysis of the current problems faced by the City Council in the context of facility management. By conducting a questionnaire survey exclusively within the Department of Integrity and Internal Audit's staff, this study identifies key challenges and assesses their level of risk. The research findings highlight critical issues including inadequate technology, deficient management planning, fund shortages, lack of training, and incompatible parking space. Notably, poor equipment emerges as the root cause of several organizational problems. While acknowledging that this study represents an initial exploration, the research emphasizes the need for further investigation into the relationships among identified factors. The data gathered, though limited, reveal significant gaps in knowledge regarding the underlying causes of the challenges faced by the council. Consequently, this paper serves as an essential starting point, shedding light on the subject and laying the groundwork for future studies. The outcomes of this research provide valuable insights into the current issues confronting the City Council, offering a prioritization based on their impact on the facility management department and the overall environment. These findings contribute to bridging the knowledge gap and enable the formulation of relevant strategies to address critical constraints. By taking practical steps to mitigate the identified challenges, the council can strive towards achieving optimal outcomes in their operations.
Keywords: Equipment, facility management, knowledge gap, organizational challenges, parking space, training
Introduction
Effective management is universally recognized as a cornerstone of success for businesses, whether in the government or private sector. Within this context, facility management emerges as a key service sector that significantly contributes to day-to-day operational objectives (Amos et al., 2019). Maintenance and facilities are widely acknowledged as vital components by management in organizations (Raghavaiah & HariPrasad, 2019). In the realm of local government, the third level of institutions assumes the responsibility of administration, planning, and enforcement at the local level (Mohd et al., 2018).
The efficiency and effectiveness of facility management exert a profound influence on various elements of a company, encompassing management practices, equipment utilization, workforce productivity, and the overall work environment (Ali et al., 2020). These interconnected factors collectively ensure that the workplace operates at its full potential, with facilities playing a central role. However, persisting facility-related issues often plague workplaces, persisting over time and hindering progress due to a lack of improvement efforts. Even within the seemingly complete facility infrastructure of the City Council, there are specific areas that require further refinement, despite their seemingly minor nature.
This study endeavors to explore strategies for enhancing facility management practices to achieve optimal organizational performance, utilizing the City Council as a case study. By examining existing challenges and proposing practical solutions, this research sheds light on critical areas that demand attention and improvement (Selvaraju et al., 2017; Zulfakar et al., 2019). The outcomes contribute to the existing body of knowledge in facility management and offer valuable insights for local government organizations seeking to optimize their operational outcomes.
The City Council, encompasses several departments such as tax payment, business licensing, traffic summonses, complaints, and more. The focus of this report is specifically on the organization's facilities, encompassing management, staff, equipment, and financial aspects. Despite the facility problems faced by the organization, it is worth noting their noteworthy achievement of winning the Best of Cities award for Sustainable Destination at Palais am Funkturm, ITB Berlin. With the aim of detecting and addressing facility-related issues, the objectives of this report are as follows:
- Identify the inefficiencies and ineffectiveness in the City Council's facilities: This objective involves a comprehensive assessment to identify specific problem areas where inefficiencies and ineffectiveness exist within the facilities. By pinpointing these issues, the report aims to shed light on areas that require improvement.
- Provide recommendations for improving the service facility: Once the problems have been identified, this objective focuses on offering practical recommendations to enhance the service facility. These recommendations should address the identified issues and propose viable solutions that can improve efficiency and effectiveness in the City Council's operations.
- Analyze the overall improvement in the council's operations: The final objective centers around evaluating the potential impact of implementing the recommended improvements on the overall functioning of the City Council. This analysis will consider the expected outcomes, such as increased productivity, cost savings, improved service delivery, and the establishment of a conducive working environment.
It is crucial to address the persistent facility problems faced by the City Council, as recurring repairs without substantial changes can be costly and inefficient. By achieving these objectives, the report aims to provide a clear pathway for the City Council to enhance its facilities, transforming it into a better government authority with a positive and conducive environment.
Problem Statement
Government institutions nowadays face increasing complexity in delivering complete services (Alshammari et al., 2015). The provision of adequate infrastructure, including physical facilities such as roads, communication systems, and utilities, is crucial (Akhtar et al., 2018). However, the City Council examined in this study lacks in various aspects of its facilities, leading to deficiencies in several factors. From the staff perspective, the lack of skills or training in handling facility-related matters becomes an issue, causing delays in resolving facility problems. This deficiency in skills and knowledge among the workforce can have a detrimental impact on overall management (Halawi & Haydar, 2018). If these issues persist, they can disrupt daily operations, making it a serious concern for the future.
Furthermore, inadequate technology is evident in the City Council's equipment, with outdated versions causing frequent breakdowns. The reliance on outdated technology, such as malfunctioning computers or printers, indicates a failure to adapt to better and more efficient technology used by other organizations (Juárez et al., 2018). This reliance on old technology results in recurring problems that hinder employees from effectively performing their duties. Management's late action in addressing facility-related issues or resolving complaints further compounds the problem. Effective management is crucial in creating a satisfactory work environment (Chong et al., 2019; Nurul Syakirah et al., 2020). Delays in acting can lead to prolonged disruptions and dissatisfaction among employees.
Additionally, insufficient funding poses a challenge in purchasing or upgrading facilities (Samson et al., 2015; Sivan et al., 2023). Funding is a major issue for government institutions striving to create a comfortable workplace and ensure a conducive environment (Nzewi et al., 2018). While some departments may have adequate facilities, others are still lacking, leading to interruptions in workflow. According to employees, the government does not allocate sufficient funds, relying solely on tax revenues and business-related income. This financial constraint hampers the ability to upgrade or make necessary changes. In conclusion, this study aims to investigate and identify facility-related problems that affect the workplace, aiming to improve effectiveness and efficiency. A well-balanced workplace with adequate equipment and a comfortable environment contributes to better performance. Thus, this study aims to provide evidence of the facility problems discussed above and propose potential solutions.
Literature Review
Most government authorities face limitations due to their funding, which is typically allocated by the Finance Ministry of Malaysia. If a particular authority lacks sufficient funds, they may need to organize events to generate additional revenue and ensure the environment is well-maintained. The issue of staff lacking skills or training is directly linked to facility-related problems (Abdurraheem, 2016). Training programs are crucial for organizations to enhance the quality of new employees and equip them with the necessary skills to address facility issues. This lack of skilled staff creates difficulties for management in resolving problems within the required timeframe.
Moreover, while most organizations adopt common and up-to-date technology to facilitate their operations (Aubert-Tarby et al., 2018), the City Council relies on outdated equipment, particularly computers. These outdated technologies often malfunction, such as being unable to turn on or experiencing issues with peripherals. This persistent problem hampers employees' daily work, and the interconnection between facility and technology exacerbates the challenges faced by the council. Effective management is crucial for any organization, and issues such as late instructions or unfair decisions can arise if management fails to fulfil its responsibilities. It is important for management to be proactive in preventing such issues from recurring.
Furthermore, the persistent facility problems can be attributed to a shortage of funds, which delays improvements in the affected areas (Che-Ani & Ali, 2019; Rajagopal et al., 2016; V. P. Sundram & Jaafar, 2021). It is essential for government authorities to assess the specific needs of the council, even in seemingly small aspects. For example, upgrading computers or expanding employee parking may require budget allocations. Budgeting becomes a challenge as it involves operating costs, investment costs, and potential benefits associated with implementing changes (Princewill Lekara, 2019; V. P. K. Sundram et al., 2022). In conclusion, conducting a literature review allows researchers to gather information and insights to avoid repeating past mistakes or issues. Based on the findings of this article, steps can be taken to address the identified problems and develop suitable recommendations for the City Council.
Research Methods
The research methodology used for this study involved a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches to collect and analyze data (Mkumbo et al., 2019; Selvaraju et al., 2019). The researcher employed the following steps:
- Literature review: The researcher reviewed relevant literature to gain insights into facility management, organizational efficiency, and related concepts.
- Data collection: Data was collected through various methods, including interviews with employees and management, observation of facility operations, and document analysis of past facility-related incidents and resolutions.
- Flowchart development: A flowchart was developed to visualize the process flow of facility-related problems, incorporating the identified steps and potential decision points.
- Fishbone Analysis: The Fishbone Analysis technique (also known as the Ishikawa diagram) was used to identify and categorize the main factors contributing to facility inefficiency and ineffectiveness.
- Data analysis: The collected data, including interviews, observations, and documented incidents, were analyzed to identify patterns, recurring issues, and potential root causes.
- Recommendations: Based on the analysis, recommendations were formulated to address the identified facility-related problems, improve efficiency, and enhance overall operations.
- Reporting: The findings, analysis, and recommendations were documented in a research report, presenting a comprehensive overview of the facility issues and proposing appropriate solutions.
By following this methodology, the researcher aimed to gain a deeper understanding of the facility’s problems, identify their root causes, and propose effective recommendations for improvement (Vatumalae et al., 2022, 2023).
Findings
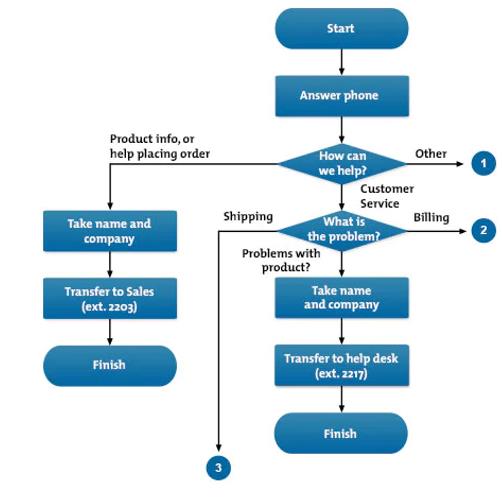
Step 1: Study of information using a flowchart
The flowchart allowed the researcher to systematically analyze the problem by following a step-by-step approach. It helped in understanding the process of identifying and resolving facility-related issues. Figure 1 illustrates how the problems in the workplace, specifically related to facilities, are identified and addressed. If problems persist, it becomes crucial to determine the reasons for the unresolved issues and question the department responsible for the matter. Additionally, the flowchart guides the researcher in providing recommendations to address these issues effectively.
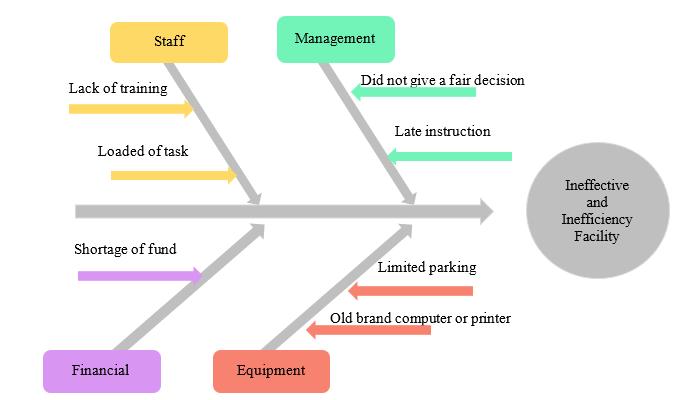
Step 2 Finding the cause of the problem by using fishbone
To further analyze the problem, the researcher utilized a Fishbone Analysis (Figure 2). This analysis highlighted the major issues affecting the City Council, particularly the inefficiency and ineffectiveness of its facility management, staff, equipment, and financial resources. These four main areas were identified as significant factors interconnected with facility-related problems. For instance, the equipment aspect revealed issues such as limited parking space and the use of outdated computers. The crowded parking area, utilized by both employees and customers, creates difficulties for the workforce. Moreover, the continued use of old computers contributes to functionality problems within the City Council.
Step 3 Conduct a questionnaire survey
When conducting a survey on facility usage satisfaction, this study uses clear and concise close-ended questions to gather specific feedback. The followings are the measure item for the survey:
- On a scale of 1-10, how satisfied are you with the overall condition and maintenance of the facilities provided by the City Council?
- How would you rate the availability and accessibility of necessary equipment and resources in your department/work area? (Scale: Very Satisfied - Satisfied - Neutral - Dissatisfied - Very Dissatisfied)
- Are you satisfied with the cleanliness and hygiene of the restroom facilities in the workplace? (Yes/No)
- On a scale of 1-5, how would you rate the parking availability and convenience for employees? (1: Very Poor - 5: Excellent)
- Have you received adequate training and support to effectively utilize the facilities provided? (Yes/No)
- How satisfied are you with the functionality and reliability of the computer systems and other technological equipment available to you? (Scale: Very Satisfied - Satisfied - Neutral - Dissatisfied - Very Dissatisfied)
- Are there any specific facility-related issues or concerns you would like to bring to the attention of the management? (Open-ended response)
- Do you feel that the City Council allocates sufficient funds for facility maintenance and improvements? (Yes/No)
- On a scale of 1-5, how well do you think the management addresses and resolves facility-related issues? (1: Very Poorly - 5: Excellent)
- Are you satisfied with the efforts made by the City Council to enhance facility quality and create a comfortable working environment? (Yes/No)
These questions helped to gather quantitative data and measurable feedback regarding facility usage satisfaction. Additionally, incorporating an open-ended question allows respondents to provide specific details or suggestions for improvement. The study kept the survey concise and easy to understand to encourage higher participation and accurate responses (Zarina et al., 2020).
Discussion
Figures 1 and 2 provide valuable insights into the root problems that contribute to poor services and operations in the facilities of the City Council. To further understand these issues, an Ishikawa diagram, as depicted in Figure 2, was created to highlight and categorize the major problems identified. One major problem identified through interviews and analysis is the issue of limited parking. Several staff members agreed that this is a significant problem stemming from equipment-related issues. The available parking space is insufficient, causing congestion and inconvenience for both employees and visitors. Additionally, the workplace still relies on outdated computer systems, which frequently encounter technical difficulties. These recurring issues disrupt daily work processes and hamper productivity.
Another major problem relates to the inadequate condition of the toilet facilities. The toilets have several areas that show signs of wear and tear, including cracks and malfunctioning fixtures. This not only compromises the comfort and hygiene of the employees but also poses potential safety risks. It is crucial to address these facility deficiencies to provide a satisfactory and secure working environment. The shortage of funds emerges as a significant financial problem affecting the improvement of facilities. Resources are often allocated to address more critical financial obligations, leaving limited funds for facility upgrades and maintenance. This scarcity hinders the Council's ability to provide necessary improvements, resulting in an ineffective and inefficient work environment.
The staff also face challenges, primarily due to a lack of training and a heavy workload. Training deficiencies, especially in facility management, contribute to difficulties in addressing issues promptly and effectively. Furthermore, employees are burdened with excessive work responsibilities, making it challenging to allocate adequate time and attention to facility-related matters. Lastly, management's decision-making processes and communication practices contribute to the overall facility problems. Unfair decisions regarding facility management and delayed instructions exacerbate the issues faced by various departments. A lack of timely and clear communication leads to confusion and inefficiency in addressing facility-related concerns.
By understanding and addressing these major problems, the City Council can work towards improving facility conditions and operations. For example, allocating more resources to expand parking capacity, upgrading computer systems, renovating and maintaining toilet facilities, providing comprehensive training programs, and ensuring fair and timely decision-making can all contribute to a more efficient and satisfactory work environment. In conclusion, the Ishikawa diagram helps to illustrate the interconnectedness of the major problems impacting facility services and operations. By identifying these root causes, the City Council can implement targeted solutions to enhance facility usage satisfaction and promote overall organizational effectiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study revealed that the City Council faced significant challenges due to ineffective and inefficient facility management. The Fishbone Analysis highlighted several key factors contributing to these issues, including unfair decision-making, lack of training, shortage of funds, and inadequate technology. To address these problems and improve the organization's quality, the following recommendations are proposed:
- Empower Management: Management should actively participate in addressing facility issues across all departments. By being involved and informed, problems can be resolved more efficiently, and information can be updated promptly to prevent misunderstandings.
- Enhance Training Programs: Implement regular training programs for both new and existing employees. This will equip them with the necessary skills to handle facility-related problems effectively. Motivating employees through training and development activities will contribute to achieving short-term and long-term organizational goals.
- Upgrade Equipment: Conduct a thorough assessment of equipment in all departments, such as computers, air conditioning, and printers. Replace outdated equipment with new, reliable alternatives to improve efficiency and productivity. Investing in modern technology will ensure smoother operations and fewer disruptions.
- Optimize Car Parking Space: Dedicate parking spaces exclusively for staff members by collaborating with other offices or implementing parking permits. This will alleviate congestion and provide convenience for employees, enabling them to focus on their work without parking-related inconveniences.
- Upgrade Sanitary Facilities: Renovate and upgrade the restroom facilities to enhance sanitation and hygiene. Providing adequate safety measures and protective gear will mitigate potential hazards and ensure a safe environment for employees.
- Generate Additional Income: Develop programs or initiatives that generate additional sources of income for the City Council. This will help fund facility renovations and improvements, ensuring a timely and effective response to facility-related issues.
Implementing these recommendations will not only improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the City Council's facility management but also create a better working environment for employees. By addressing the identified challenges and embracing positive changes, the City Council can thrive and provide better services to the public. Let's build a future where facilities are well-managed, employees are empowered, and the community benefits from a well-functioning City Council!
References
Abdurraheem, M. R. (2016). The Impact of Training and Development on Employees Performance and Productivity. International Journal of Management Sciences and Business Research, 5(7), 36-70.
Akhtar, A., Naheed, K., Akhtar, S., & Farooq, U. (2018). Impact of Job Stress on Employees’ Job Satisfaction: An Empirical Study of Private Banks of Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Social Sciences, 38(1), 137-151.
Ali, S. N. R., Rajagopal, P., Sundram, V. P. K., Saihani, S. B., & Noranee, S. (2020). ERP System Implementation in a Leading LED Manufacturing in Malaysia: A Supply Chain Perspective. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 9(2), 104.
Alshammari, A., N. Almutairi, N., & Fahad Thuwaini, S. (2015). Ethical Leadership: The Effect on Employees. International Journal of Business and Management, 10(3). DOI:
Amos, D., Musa, Z. N., & Au-Yong, C. P. (2019). A review of facilities management performance measurement. Property Management, 37(4), 490-511. DOI:
Aubert-Tarby, C., Escobar, O. R., & Rayna, T. (2018). The impact of technological change on employment: The case of press digitisation. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 128, 36-45. DOI:
Che-Ani, A. I., & Ali, R. (2019). Facility management demand theory: Impact of proactive maintenance on corrective maintenance. Journal of Facilities Management, 17(4), 344-355. DOI:
Chong, A. K. W., Mohammed, A. H., Abdullah, M. N., & Rahman, M. S. A. (2019). Maintenance prioritization - a review on factors and methods. Journal of Facilities Management, 17(1), 18-39. DOI:
Halawi, A., & Haydar, N. (2018). Effects of Training on Employee Performance: A Case Study of Bonjus and Khatib And Alami Companies. International Humanities Studies, 5(2), 24-45.
Juárez, M. R., González, V. M., & Favela, J. (2018). Effect of technology on aging perception. Health Informatics Journal, 24(2), 171-181. DOI:
Mkumbo, F. A. E., Ibrahim, A. R., Salleh, A. L., Sundram, V. P. K., & Atikah, S. B. (2019). The influence of supply chain practices and performance measurement practices towards firm performance. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 8(3), 809-819.
Mohd, E., Ayub, Z. A., & Anuar, H. M. (2018). The Challenges of Local Authority in Malaysia. International Journal of Law, Government and Communication, 3(13), 34-43.
Nurul Syakirah, M. Z., Rajagopal, P., Sundram, V. P. K., Raja Zuraidah, R., Nor Ratna, M., & Zamry, G. (2020). Achieving Supply Chain Excellence through Effective Supplier Management: A Case Study of a Marine Organisation. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 9(4), 11-23.
Nzewi, H. N., Augustine, A., Mohammed, I., & Godson, O. (2018). Physical Work Environment And Employee Performance In Selected Brewing Firms In Anambra State, Nigeria. Journal of Good Governance and Sustainable Development in Africa, 4(2), 131-145.
Princewill Lekara, B. (2019). Technological Challenges in Management of Organizations. International Journal of Business & Law Research, 7(2), 99-111.
Raghavaiah, N. V., & HariPrasad, I. (2019). Maintenance and Reliability Strategy of Mechanical Equipment In Industry. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 6(6), 3430-3432.
Rajagopal, P., Azar, N. A. Z., Bahrin, A. S., Appasamy, G., & Sundram, V. P. K. (2016). Determinants of supply chain responsiveness among firms in the manufacturing industry in Malaysia. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 5(3), 18-24.
Samson, G. N., Waiganjo, D. M., & Koima, D. J. (2015). Effect of Workplace Environment on the Performance of Commercial Banks Employees in Nakuru Town. International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research, 3(12), 76-89.
Selvaraju, M., Beleya, P., & Sundram, V. P. K. (2017). Supply chain cost reduction using mitigation & resilient strategies in the hypermarket retail business. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 6(2), 116-121.
Selvaraju, M., Bhatti, M. A., Sundram, V. P. K., & Azmir, S. (2019). The influence of critical success factors of Lean Six Sigma towards supply chain performance in telecommunication industry, Malaysia. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 8(6), 1062-1068.
Sivan, S., Lian, C. L., Ghapar, F., Sundram, V. P. K., & Munir, Z. A. (2023). The relationship between information technology and logistics integration: A case study of the logistics and distribution industry in Malaysia. SMART Journal of Business Management Studies, 19(2), 1-11. DOI:
Sundram, V. P. K., & Jaafar, P. (2021). Logispreneurship: Promising Prospects. New Straits Times.
Sundram, V. P., Ali, N. M., Ya, S., Harun, S., Muhamed, A. A., Bahrin, A. S., & Rashid, A. H. (2022). Supply Chain Logistics Management. Selangor, MLSCA Asian Academy.
Vatumalae, V., Rajagopal, P., Sundram, V. P. K., & Hua, Z. (2022). A study of retail hyper market warehouse inventory management in Malaysia. SMART Journal of Business Management Studies, 18(1), 71-79. DOI: 10.5958/2321-2012.2022.00009.4
Vatumalae, V., Rajagopal, P., Sundram, V. P. K., Munir, Z. A., & Ghapar, F. (2023). Linking Factors Leading to Retail Hypermarket Warehouse Operations Performance in Malaysia. SMART Journal of Business Management Studies, 19(1), 1-9. DOI: 10.5958/2321-2012.2023.00001.5
Zarina, D., Zarina, A. M., Rahayu, A. R., Kardina, K., & Sundram, V. P. K. (2020). Adoption of technology on E-learning effectiveness. Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, 9(3), 1121-1126
Zulfakar, M. H., Chan, C., Jie, F., & Sundram, V. P. K. (2019). Halal accreditation and certification in a non-muslim country setting: Insights from Australia halal meat supply chain. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 8(1), 10-17.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
06 May 2024
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-132-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
133
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1110
Subjects
Marketing, retaining, entrepreneurship, management, digital marketing, social entrepreneurship
Cite this article as:
Munusamy, K., Lasi, M. A., Chew, L. L., Othman, A. K., & Sundram, V. P. K. (2024). Examining Critical Challenges for Effective Management: A Case Study of City Council. In A. K. Othman, M. K. B. A. Rahman, S. Noranee, N. A. R. Demong, & A. Mat (Eds.), Industry-Academia Linkages for Business Sustainability, vol 133. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 653-662). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2024.05.54

