Abstract
Empowering microentrepreneurs is essential for the sustainability of the microfinance ecosystem. As a result of their lack of financial skills, many microentrepreneurs have sought assistance from microfinance institutions. In order to achieve their two-fold goals, microfinance institutions must ensure both financial and social sustainability. This study draws attention to the unique and significant resources accessible in Malaysian Islamic social finance, specifically zakat. The institutions provide nonrepayable micro funds and are responsible to stakeholders for managing zakat funds. A systematic literature review technique was used to analyse and evaluate the existing information and knowledge gaps regarding the key factors that contribute to the empowerment of zakat microentrepreneurs for social sustainability. The analysis reveals five themes: entrepreneur values and interpersonal skills, sound and prudent financial management, corporate governance practices, strong customer service and support, and technology and infrastructure. The study suggests implementing measures to strengthen good governance and effective financial management, interpersonal and customer service competency, and technological adoption to attain financial sustainability.
Keywords: Empowerment, financial sustainability, microentrepreneurs, Zakat institutions
Introduction
The empowerment ofmicroentrepreneur is a key element towards a financial sustainability in microfinance sector. However, studies within the context of Islamic social finance are still lacking. Islamic social finance uses practices, conducts, and offerings that provide good value and sustained benefit to the economy, community, and environment as a means of orienting its attention beyond shariah compliance and towards accomplishing the desired outcomes of. The shift toward comprehensive value creation and value-based activities is in line with the initiative of the Financial Sector Blueprint 2022–2026, Bank Negara Malaysia (2022) which aims for greater adoption of sustainable financing, also known in Malaysia as value-based intermediation (VBI) financing.
Beyond the health and human tragedy, the Covid-19 pandemic triggered the most serious economic crisis since World War II (The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, 2020). Many governments at all levels have reacted quickly, applying a ‘place-based’ or territorial approach to policy responses to the Covid-19 crisis, on the socio-economic to protect small businesses, households and vulnerable populations. Financial incompetence has led many small businesses, especially microentrepreneurs, to seek financial support from microfinance institutions. Microfinancing has been shown to be a crucial factor in helping to enhance the living conditions of the microentrepreneurs, in addition to making it possible for them to gain access to various forms of financial capital. It does this by giving significant amounts of financial aid to microentrepreneurs who are unable to afford to supply physical collateral in exchange for finance; instead, the financing requires social collateral. The dual role of achieving social and financial objectives requires the microfinancing programmes to aim for long-term social and financial sustainability.
The microfinance programmes are broadly divided into two categories: repayable and non-repayable. In Malaysia, Amanah Ikhtiar Malaysia, TEKUN Nasional, and Yayasan Usaha Maju, Sabah are among the major microfinance institutions that provide repayable micro funds. Non-repayable micro funds are provided to micro entrepreneurs by zakat institutions (e.g., Selangor, Penang, Negeri Sembilan, and Kuala Lumpur) and non-governmental organisations (NGOs) such as Yayasan Basmi Kemiskinan. Zakat institutions have been working for years to achieve financial sustainability and ethical practices. The institutions are in the front line of providing support for microfinance by providing non-payable micro funds to microentrepreneurs. While there have been many studies on the economic success of microentrepreneurs, knowledge on the elements that help zakat micro-entrepreneurs achieve social sustainability remains scant. It is essential that microfinance providers, such as zakat institutions, are able to empower the beneficiaries (mustahiq), including microentrepreneurs in order to maximize the potential social and economic impact. The efficient and effective delivery of microfinance initiatives requires their initiatives that give impact and promote socioeconomic well-being of communities. This can have positive social effects at various levels of society, ranging from the individual to the community to the regional level.
In order to accomplish this, it is crucial to establish long-lasting, sustainable relationships between institutions and microentrepreneurs. Simultaneously, microfinance services must be inclusive and have a positive impact to mustahiq. Therefore, to facilitate efficient and effective management of microfinance programmes, it is essential to identify key success factors in empowerment of microentrepreneurs towards financial sustainability. Thus, microfinance programmes should be financially and socially sustainable to achieve their dual goals as Islamic social finance focuses on shariah's desired outcomes rather than solely on financial benefit. This study draws attention to the unique and substantial resources available in Islamic social finance in Malaysia, i.e zakat that managed by zakat institutions. The institutions offer non-repayable micro funds and require discharging accountability of the zakat funds to the stakeholders. This study aims to identify key success factors in empowering zakat microentrepreneurs towards financial sustainability using systematic literature review approach. This study makes use of systematic literature review (SLR) approach to maps and assesses the existing knowledge and gaps on key success factors in empowering zakat microentrepreneurs. The remaining sections of this work are structured as follows. Section 2 provides a review structure. In section 3, present analysis of results of this study. Next, section 4 describes the study's commentary and discussion of findings. Finally, section 5 concludes.
Research Methodology
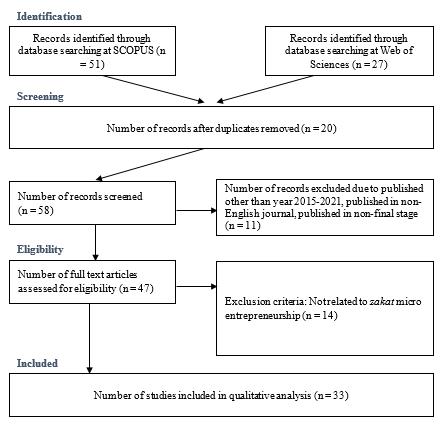
The SLR approach helps to gather all relevant papers and materials that meet inclusion requirements to answer research query (Mengist et al., 2020). It uses clear and methodical techniques to eliminate bias in finding, identifying, evaluating, synthesizing, analysing, and summarizing studies. The procedure begins with the creation and validation of the protocol for review. The protocol's purpose is to ensure that the evaluation is methodical, transparent, and reproducible (Xiao & Watson, 2019). The SLR used in this study is governed by Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), which was developed by Moher et al. (2009). PRISMA, on the other hand, exclusively employs systematic reviews because this meta-analysis is quantitative rather than qualitative. According to Page et al. (2021), PRISMA procedure in SLR has four benefits, which are as follows: to demonstrate the quality of the review; to enable researchers to evaluate the strengths and limitations of a study; to permit replications; and to permit future advancements of the protocol. As shown in Figure 1, the PRISMA protocol in this study includes four procedures: identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion. These four procedures will be discussed in detail in a subsequent section.
Review Structure
There were two phases to the literature search: random and systematic. The purpose of the articles search is to delve into zakat and micro-entrepreneur. This first phase covers the groundwork for a deeper dive into the topic of micro-entrepreneurs and zakat. An exhaustive search of papers on zakat and micro-entrepreneurship is the first step in this study, with the goal of gaining an understanding of the context of identifying success characteristics to empower zakat microentrepreneurs. In the second phase, this study systematically looked for the characteristics that helped in empowering zakat micro-entrepreneurs. A well-defined research question should guide the SLR process. During the identification phase, the term "zakat micro-entrepreneur" emerged as the most relevant to the study.
Elsevier's Scopus, according to Baas et al. (2020), has the highest quality data that are indexed through careful content selection and re-assessment. Meanwhile, Li et al. (2018) discovered that the Web of Science (WoS) has become an increasingly important scientific tool in almost every country and knowledge area. As a result, these scholarly databases were used to collect relevant articles. Several relevant articles related to micro-entrepreneurship were collected and reviewed using the funneling and filtering method. In the article search, the following keywords were used: " Microentrepreneur", "Micro business", "" and " Microentrepreneur".
Formulation of Research Question
The study builds an inquiry using the PICo strategy. When formulating the research questions that would guide this review, PICo was utilised as one of the research question tools. There are three crucial elements of PICo that must be incorporated into a research question: the population (P), the research interest (I), and the context (Co). In designing a research question, therefore, the researchers have incorporated three major components: microfinance institutions (Population), key success factors in empowering microentrepreneurs (Interest), and faith-based (Context). By merging these three components, the research question is phrased as follows: What are the institutions’ key success factors identified in empowering micro-entrepreneurship in faith based?”. This study developed a comprehensive search string employing the Boolean Operator, phrase searching, truncation, wildcard, and field code operations for two databases: Scopus and Web of Sciences, after upgrading the keywords. Multiple databases must be searched to minimise publication bias, compensate for the limits of a single database, and encourage transparency in this process (Kraus et al., 2020; Page et al., 2021; Xiao & Watson, 2019).
Table 1 displays how search terms were formulated for Scopus and Web Sciences. The field code search is based on the title, abstract, and keywords. Scopus therefore identified 51 publications, while Web of Sciences identified 27. The subsequent procedure is screening.
Screening
In this study, the second step of the PRISMA protocol is screening. This screening procedure necessitates that the study decides whether to include or exclude articles from review. The database automates this procedure by using a filtering system. According to Kraus et al. (2020) and Meline (2006), the screening procedure has the advantage of ensuring that the selection criteria from the database are adequate, not too narrow or too broad. The duplicate article was removed from the Scopus and Web of Sciences databases as part of the study (Shamseer et al., 2015). This procedure is critical to avoiding double review, which would result in the detection of 20 instances of duplication. The articles were then excluded based on the study's timeframe (2015-2021), article language (English), document type (journal or article), and publication stage (final). As a result, 11 items must be eliminated because they do not meet the specific criteria.
To obtain the most appropriate articles, several steps were taken in the screening process. This study assesses prior research onmicro-entrepreneurship from 2015 to 2020. This time period is considered relevant because the number of published articles in this domain is greater than several years ago and offer more comprehension in the current context. Following the evaluation of abstracts, 58 articles were successfully collected. Following that, the articles were filtered based on a set of mandatory inclusion criteria, including it must be written in English. Furthermore, these articles must be complete and easily accessible. Previous systematic reviews were rejected because this study only considered articles that used primary data and should fall within the domain of social science. There were 78 articles found. Finally, 20 articles were eliminated due to duplication, not being strongly related to the study's area, or being a student's thesis/dissertation. At the final review, 47 articles were successfully retrieved and evaluated.
Eligibility
The third step of the PRISMA process is the determination of eligibility. In addition to identification and screening, manual labour makes this procedure challenging (Mohamed Shaffril et al., 2021). Consequently, the inquiry adopts a comprehensive methodology. There are 47 qualifying articles. The study adhered to the recommendation of Kraus et al. (2020), which advocates commencing the reading of articles with their titles and abstracts. The study can then determine if the publication is accepted and relevant to its research question. Therefore, 14 publications are disqualified since they do not answer the required research question. After assessing eligibility, the inclusion approach can be implemented.
Inclusion and Data Extraction
Following the completion of the eligibility process, the study reviewed 33 articles as illustrated in Figure 1. The data was extracted in the study by first creating an extraction sheet. As a result, data extraction helps to answer the research question. Furthermore, the matrix table is an effective tool for increasing transparency and shedding light on the current synthesis process (Kraus et al., 2020; Mohamed Shaffril et al., 2021).
Data analysis
The data for this investigation were analysed using data synthesis. The synthesis is necessary for conducting analysis since it disperses the information from the matrix table across 33 articles to be evaluated. Consequently, the result of the synthesis will be analysed and presented in line with the qualitative technique of thematic analysis. The purpose of thematic analysis is to recognise, examine, and interpret meanings (themes) within qualitative data (Clarke & Braun, 2014). Various topics have been found in this study based on the significant findings of the selected article, which will be discussed in the next part.
Analysis of Result
Geography and Research Design
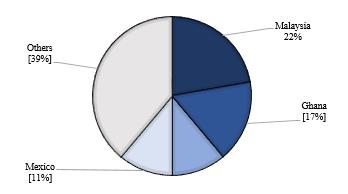
Based on the analysis, many studies have been conducted on micro entrepreneurship across the world including Muslim minority countries such as Israel, USA, and United Kingdom. Meanwhile, Muslim countries such as Malaysia, Turkey or Pakistan have more tendency to research on micro-entrepreneurship in terms of zakat or asnaf. Figure 2 below demonstrates the sources of qualitative-based studies by countries. Most of the qualitative studies on micro entrepreneurship discovered in Malaysia which comprise 4 out of 16 reviewed articles. These articles show that Malaysia-originated papers commonly have focus on zakat micro entrepreneurship and asnaf. Malaysia appeared the most originated articles discussed on this context. These papers were focusing on micro entrepreneurship except two articles by (Neise et al., 2021) and (Izzati et al., 2020) from Indonesia, one paper by (Wolmarans & Meintjes, 2015) from South Africa and one article by (Şahin, 2018) from Turkey that have concern on both micro entrepreneurship and small or medium enterprises.
In terms of quantitative-based studies, 21 outcomes were successfully obtained from 15 countries namely Malaysia, Pakistan, India, Peru, Israel, Democratic Republic of Congo, United Kingdom, Mexico, South Africa, Bangladesh, Uganda, Ghana, Chile, Yemen, and Poland. Apparently, Malaysia-originated articles also have emerged as the majority among the quantitative-based articles which comprise of 5 out of 21 reviewed papers. The nature of research design that employed by previous researchers were disseminating questionnaires to different types of respondents. In addition, among these quantitative articles, there were several studies that have moderating or mediating effect in order to gain more comprehension in micro entrepreneurship. For instance, Monnickendam-Givon et al. (2018) who employed strong ties and weak ties as their mediating variable or study by Bin-Nashwan et al. (2021) who used perceived behavioural control as their moderating variable. Figure 3 shows the sources of qualitative- studies by countries.

The themes
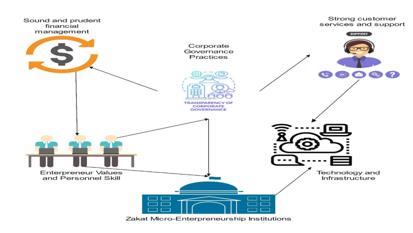
The study identified and selected 33 articles for review. Six articles were published in 2015, three in 2016, four in 2017, eight in 2018, four in 2019, five in 2020, and three in 2021. In terms of geographical distribution, Malaysia produced the most contributions (6 articles), followed by Ghana (3) and Indonesia (3). The study's methodology is numerically diverse, including 18 quantitative publications, 12 qualitative articles, and 3 mixed-method articles. There are five themes can be attributed to five overarching principles of empowering microfinance. Table 2 shows the matrix summary of the selected articles to discuss in more depth.
Entrepreneur Values and Personnel Skill
One of the most important success factors in microfinance is having good values and entrepreneurship skills (Alhassan & Goedegebuure, 2015). Good values in this theme refer to the guiding principles of the attributes. Four positive values have been identified as contributing to the success of microfinance. First, religious values must be instilled in the personnel (Quagrainie, 2018). This is due to the fact that different religions have different goals for microfinance. In Islam, for example, sharia allows microfinance to fund permissible business activities but forbids usury (riba). Second, the community should have good values by implementing an entrepreneurship equality system for men and women. There should be no gender discrimination or patrilineal system (S. Boateng & Poku, 2019). Third, education is required to increase a community's value. It is because education raises community awareness of the importance of microfinance, which helps to improve people's quality of life (Asencios-Gonzalez et al., 2018; Goswami et al., 2017). Fourth, entrepreneurs must instil positive attitudes and subjective norms in order to effectively use microfinance funding and practise good entrepreneurship (Mensah et al., 2018; Thaker et al., 2016). Microfinance, on the other hand, can be a major success if microentrepreneurs have relevant skills. Personnel must have experience managing microfinance and know-how (Hanif & Zafar, 2020; Ssekiziyivu et al., 2018). The expertise possesses not only the microfinance mechanism, but also internal personnel skills to reconcile the goal of assisting entrepreneurs when they require assistance (Allet, 2017). Yusoff et al. (2018) identified technical skills, communication skills, market orientation, and networking skills as required skills for microfinance personnel. Thus, without skills, microfinance cannot be implemented smoothly and efficiently.
Institutional Sound and Prudent Financial Management
To ensure their success and efficiency, microfinance providers must have sound and prudent financial management (Ramírez-Urquidy et al., 2018; Yusoff et al., 2018). Three strategies are available to ensure sound and prudent financial management in microfinance. First, the providers or lenders must have easy access to credit (Goswami et al., 2017; S. Boateng & Poku, 2019). It is because a lack of credit leads to lenders viewing loans as risky. Lenders must take an active role in mobilising deposits and commercial transactions. As a result, the funding pool expands and credit for microfinance activities becomes available (Okoye et al., 2019). Second, providers or lenders must be proficient in the use of management accounting tools that incorporate microfinance financial management. To properly monitor microfinance performance, management accounting tools are required to control revenue and cost (Najera Ruiz & Collazzo, 2021) and cash flow movement (De Amorim Braga et al., 2018). To attract microfinance entrepreneurs, they must first reduce borrowing costs (Gill et al., 2016) and efficiently manage working capital (Wolmarans & Meintjes, 2015). Mental budgeting, on the other hand, can be used as a management accounting tool to refer to financing amounts that do not exceed the cap (Hoque, 2017). Third, they can pursue good limited financial rationality, which refers to the decision whether to approve or reject the financing application (Ahmed & Malik, 2015; Palacios-Duarte et al., 2019). It ensures that lenders use an appropriate credit appraisal method to provide funding to the right entrepreneur.
Practices of Corporate Governance
Governance is also essential to ensure that administration and management are carried out effectively, hence delivering great success in microfinance (Okoye et al., 2019). There are four ways in which effective governance practises contribute to the success of microfinance. First is the reliability of greater administration and management through fortitude (Hanif & Zafar, 2020; Lekaj & Qirezi, 2020). It indicates that administration and management procedures are consistent during economic expansion and recovery. Second, microfinance must implement a prudent and effective collecting policy (Ahmed & Malik, 2015). It is to ensure that the borrowers or entrepreneurs do not feel pressured or uncomfortable when it comes to repayment if their business position is not favourable. Thirdly, the microfinance organisation must have an effective board of directors and shareholders to ensure that it is well-governed (Ssekiziyivu et al., 2018). If anything, unfavourable happens to microfinance organisations, the board of directors and shareholders can be held liable. Fourth, the microfinance institution must place a high value on entrepreneurs via corporate entrepreneurship disclosures (Albu & Mateescu, 2015) and guarantee the viability of their businesses (Allet, 2017; Abdullah & Ismail, 2017). In four ways, microfinance institutions can not only function efficiently and be conservative, but also make sound judgements regarding the path of the institution.
Exceptional Customer Service and Support
Microfinance institutions are essential to the success of entrepreneurs, who require both financial aid and dependable support and services (Abdul Razak et al., 2017). As a result, there are four ways in which services and assistance can help microfinance flourish and benefit business owners. First, microfinance organisations may help company owners succeed by giving them the skills they need to keep going (Goswami et al., 2017). It's meant to address the issue of microfinance institution support employees lacking the same level of expertise as the entrepreneurs they assist (Abbas & Shirazi, 2015). Second, if the entrepreneur is having trouble, the microfinance institution can offer monitoring and consulting services (Adnan et al., 2021; Ahamad et al., 2020; Monnickendam-Givon et al., 2018; Şahin, 2018). Therefore, it is important to pay attention to issues associated with entrepreneurship, as doing so will foster a mutually beneficial partnership between established organisations and pioneering start-ups. Third, microfinance organisations might introduce plans for societal progress (Mensah et al., 2018). This initiative will provide young people with opportunities to participate in entrepreneurial endeavours that have the potential to provide substantial financial gains. Forth, microfinance organisations should invest more resources into improving their collection and repayment division services. To this end, it is possible to provide appropriate reimbursable programmes for severely low-income business owners (Nadzri et al., 2018) and to give training for efficiently managing borrowers (Tabot Enow & Kamala, 2016). The aforementioned quartet of services and support significantly raises the bar for how effective microfinance can be.
Technology and Infrastructure
Technology and infrastructure contribute significantly to the speed and effectiveness of microfinance processes. Due to the demand for microfinance from SMEs, the institution must expedite the application procedure (Allet, 2017; Palacios-Duarte et al., 2019). It is possible with the application of information management and process methodologies. In addition, microfinance needs the support of information technology systems and tools to improve operational efficiency, cut marketing expenses, and raise profits (Izzati et al., 2020; Malanga & Banda, 2021). Additionally, the advanced information technology can accelerate the institution's account receivable collection, thereby increasing its productivity (Tabot Enow & Kamala, 2016). Historically, one of the most important financial management instruments is management accounting. Therefore, improved information technology and infrastructure can facilitate access to a company's financial data and facilitate the efficient management of total revenues and total assets (Perez-Estebanez et al., 2018). As a result, these information technologies and infrastructure will boost the productivity of microfinance, which is one of its primary success criteria.
Discussion
This study's primary research question is "What are the institutions' important success criteria found for supporting faith-based zakat micro entrepreneurship". Consequently, the analysis identifies five major themes as illustrated in Figure 4: entrepreneur values and interpersonal skills, sound and prudent financial management, corporate governance practices, strong customer services and support, and technology and infrastructure. Based on these topics, the study provides the following three important arguments:
First, the administrative staff centralises the microfinance institution's operations in accordance with corporate governance principles and solid and responsible financial management. Even though the institutions were effective at offering microfinance services, this was one of the obstacles they faced. Still, the objective of improving entrepreneurs' standard of living has not been widely attained (Milana & Ashta, 2020). A number of institutions exhibited poor corporate governance (Amha, 2008). It was due to board members abusing their authority to seek facilities well beyond the microfinance regulation limit (Acha, 2012; A. A. Boateng, 2015). In terms of solid financial management, the institutions confront obstacles such as excessive transaction costs, inappropriate collection procedures, and loan mismanagement (Dey, 2015; Nasir, 2013). Due to this, a number of institutions struggled to function profitably, particularly in terms of loan recovery and revenue margins, owing to rising management costs and low lending margins (Govindasamy & Viswanathan, 2020; Prathap et al., 2018). Consequently, there are three important factors to strengthen corporate governance in institutions: the board setting the correct goals, improved decision-making by senior management, and collaboration with external governance to assure compliance with standards, rules, and procedures (Hussain & Ahmed, 2020).
Second, the institutions faced difficulties in terms of personnel competence. The availability of a labour force with microfinance expertise is restricted. In addition, these personnel lacked sufficient product expertise and microfinance mechanism training (A. A. Boateng, 2015; Ussif, 2020). Therefore, it weakens the functioning of the institutions, which borrowers might exploit to delay loan repayment. Furthermore, the low degree of customer service expertise prevents personnel from servicing microfinance and following up with customers regarding loan repayment (Abu Hassan et al., 2022). The low competency level of personnel poses a substantial threat to the institutions, putting borrower confidentiality and openness in question (Jaiswal & Ambrish, 2022).
The third important point raised by the study is that certain microfinance institutions still suffer technological and infrastructure challenges. Due to data flow, security difficulties, and a lack of credit access, the institutions failed to embrace the technology and infrastructure (Rozzani & Rahman, 2013). Furthermore, some universities have inadequate infrastructure facilities. Consequently, borrowers and businesses, particularly those from rural areas, are unable to visit the institutions. Their residences are distant from the site (Abubakar, 2020; Gadekar, 2021). Therefore, technology enters the playing field to accelerate the microfinance process in rural areas. With these essential issues solved, there is no doubt that institutions will improve and expand.
Conclusion
The main objective of this study is to examine the key factors that contribute to the effectiveness of microfinance in facilitating zakat micro entrepreneurship within a religious framework. To address the main issue of this study, a systematic literature review and theme analysis are employed. The primary research question is: "What are the key factors identified by institutions that contribute to the success of faith-based zakat micro entrepreneurship?". Based on the study results, there are five key factors that contribute to the success of microfinance in empowering zakat micro entrepreneurship. These factors include the values and skills of entrepreneurs, effective financial management, good corporate governance practices, excellent customer services and support, and advanced technology and infrastructure. Furthermore, the study identified three significant issues: inadequate governance and effective financial management; insufficient interpersonal and customer service competency; and limited adoption of technology and infrastructure by microfinance institutions. The primary conclusion from the analysis provides three suggestions for future institutional enhancement in strengthening zakat micro entrepreneurship. First, institutions should enhance their adoption of technology. To improve the effectiveness of zakat micro entrepreneurship utilising blockchain technology, including the implementation of smart contracts and rural repaying loans. Consequently, it is recommended that the authorities engage in a collaborative effort to establish a zakat micro-entrepreneurial training programme with the aim of enhancing the skills and capabilities of employees. Hence, this training programme will enhance their comprehension and proficiency in debt recovery and loan management. Furthermore, the preservation of trust between stakeholders is important. The study identified three limitations in the current study. First, the number of papers on zakat microentrepreneurs is limited compared to those on microfinance and microentrepreneurs. Hence, this study suggests for further investigation into microentrepreneurs who integrate elements of zakat as inventive microfinance. Furthermore, the study proposes examining the policies and practices of zakat microentrepreneurs in diverse Islamic countries in order to assess their advantages and disadvantages. Given that this study is carried out using a systematic literature review spanning from 2015 to 2021, it is feasible to expand it up to 2022 considering the growing trend in this research domain.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) awarded by the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia [FRGS/1/2021/SSO1/UiTM/02/1].
References
Abbas, K., & Shirazi, N. (2015). The key players' perception on the role of Islamic microfinance in poverty alleviation: The case of Pakistan. Journal of Islamic Accounting and Business Research, 6(2), 244-267. DOI:
Abdul Razak, A., Muhammad, F., Mohd Hussin, M. Y., Zainol, Z., & Abd. Hadi, F. S. (2017). The Role of Ar-Rahn in Enhancing Financial Inclusion: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Jurnal Pengurusan, 50, 97-109. DOI:
Abdullah, R., & Ismail, A. G. (2017). Taking stock of the waqf-based Islamic microfinance model. International Journal of Social Economics, 44(8), 1018-1031. DOI:
Abu Hassan, M. H., Shari, W., & Wahab, M. Z. H. (2022). Repayment behaviour in microfinance: The role of accountability as mediator and customer service as moderator: A conceptual paper. International Journal of Accounting, Finance, and Business, 7(44), 1–15.
Abubakar, B. (2020). Problem and prospects of microfinance banks in Adamawa. International Journal of Humanities & Social Science, 11(6), 204–214.
Acha, I. A. (2012). Microfinance banking in Nigeria: Problems and prospects. International Journal of Finance and Accounting, 1(5), 106–111.
Adnan, N. I. M., Roselam, M. A. C., Hamat, Z., & Furqani, H. (2021). The Distribution of Zakat Fund to the Poor Entrepreneurs Using Micro Finance. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 11(2). DOI:
Ahamad, S., Al-jaifi, H. A., & Mostafiz, M. I. (2020). Conceptualizing recourses as antecedents to the economic performance of family-based microenterprise - the moderating role of competencies. Journal of Family Business Management. DOI:
Ahmed, S. F., & Malik, Q. A. (2015). Credit risk management and loan performance: Empirical investigation of micro finance banks of Pakistan. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 5(2), 574–579.
Albu, N., & Mateescu, R. A. (2015). The relationship between entrepreneurship and corporate governance. The case of Romanian listed companies. Amfiteatru Economic, 17(38), 44–59.
Alhassan, A.-N. I., & Goedegebuure, R. (2015). The value of skills training in the improvement of the socio-economic status of microfinance beneficiaries a case study at Grameen Ghana. Savings and Development, 1–38. https://www.jstor.org/stable/savideve.2015.1
Allet, M. (2017). Mitigating environmental risks in microenterprises: A case study from El Salvador. Business & Society, 56(1), 57-91. DOI:
Amha, W. (2008). Corporate Governance of the Deposit Taking Microfinance Institutions ( MFIs ) in Ethiopia. Association of Ethiopian Microfinance Institutions.
Asencios-Gonzalez, Z., Vara-Horna, A., McBride, J. B., Santi-Huaranca, I., Chafloque-Céspedes, R., & Díaz Rosillo, A. (2018). Factors associated with intimate partner economic violence against female micro-entrepreneurs in Peru. International Journal of Emerging Markets, 13(6), 1597-1614. DOI:
Baas, J., Schotten, M., Plume, A., Côté, G., & Karimi, R. (2020). Scopus as a curated, high-quality bibliometric data source for academic research in quantitative science studies. Quantitative Science Studies, 1(1), 377-386. DOI:
Bank Negara Malaysia. (2022). Financial sector blueprint 2022-2026. Bank Negara Malaysia. https://www.bnm.gov.my/documents/20124/5915429/fsb3_en_book.pdf
Bin-Nashwan, S. A., Abdul-Jabbar, H., Dziegielewski, S. F., & Aziz, S. A. (2021). Moderating Effect of Perceived Behavioral Control on Islamic Tax (Zakah) Compliance Behavior among Businessmen in Yemen. Journal of Social Service Research, 47(2), 292-302. DOI:
Boateng, A. A. (2015). An examination of challenges and prospects of microfinance institutions in Ghana. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development, 6(4), 2222–2855.
Boateng, S., & Poku, K. O. (2019). Accessing finance among women-owned small businesses: Evidence from lower Manya Krobo municipality, Ghana. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, 9(1). DOI:
Clarke, V., & Braun, V. (2014). Thematic Analysis. In Encyclopaedia of Critical Psychology. Springer.
De Amorim Braga, F. J., De Souza Silvestre, F., & Oliveira, U. R. (2018). Analysis of individual micro-entrepreneur vision from the perspective of financial management. Brazilian Journal of Operations & Production Management, 15(2), 182-192. DOI:
Dey, S. K. (2015). Challenges & issues of microfinance in India. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development, 6(7), 195–198.
Gadekar, U. (2021). A comparative study of entrepreneurship development in slums of Kolhapur city through of self-help groups and private microfinance institutions. Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research, 8(7), 209–218.
Gill, A., Maung, M. T., & Chowdhury, R. H. (2016). Social capital of non-resident family members and small business financing: Evidence from an Indian state. International Journal of Managerial Finance, 12(5), 558-582. DOI:
Goswami, K., Hazarika, B., & Handique, K. (2017). Determinants of financial risk attitude among the handloom micro-entrepreneurs in North East India. Asia Pacific Management Review, 22(4), 168-175. DOI:
Govindasamy, P., & Viswanathan, E. (2020). Exhilarating challenges of rural credit and microfinance modelling. Mukt Shabd Journal, 9(4), 211–218.
Hanif, M., & Zafar, K. (2020). Developments in Islamic finance literature: Evidence from specialised journals. Journal of King Abdulaziz University, Islamic Economics, 33(2), 3–23.
Hoque, M. Z. (2017). Mental budgeting and the financial management of small and medium entrepreneurs. Cogent Economics & Finance, 5(1), 1291474. DOI:
Hussain, M. D., & Ahmed, I. (2020). Corporate governance in microfinance organizations: review and agenda. Albukhary Social Business Journal, 1(1), 33-45. DOI:
Izzati, B. M., Nur Fajrillah, A. A., Saputri, R. A. A., Oktavian, I. T., & Widyastri, L. A. (2020). Perancangan IT blueprint menggunakan TOGAF ADM untuk mendukung transformasi digital pada UMKM. Jurnal RESTI (Rekayasa Sistem Dan Teknologi Informasi), 4(3), 404–417.
Jaiswal, A., & Ambrish. (2022). An empirical study on microfinance institutions of sustainability. International Journal of Advanced Research in Commerce, Management & Social Sciences2, 5(3), 187–192.
Kraus, S., Breier, M., & Dasí-Rodríguez, S. (2020). The art of crafting a systematic literature review in entrepreneurship research. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 16(3), 1023–1042. DOI:
Lekaj, D., & Qirezi, B. (2020). Strategic change process in practice: Four case studies in Kosovo. Management Issues, 18(1), 54–80. DOI:
Li, K., Rollins, J., & Yan, E. (2018). Web of Science use in published research and review papers 1997-2017: a selective, dynamic, cross-domain, content-based analysis. Scientometrics, 115(1), 1-20. DOI:
Malanga, D. F., & Banda, M. J. (2021). The use of mobile phones by women microenterprises in Malawi: a sustainable livelihoods perspective. Global Knowledge, Memory and Communication, 70(8/9), 777-800. DOI:
Meline, T. (2006). Selecting studies for systemic review: Inclusion and exclusion criteria. Contemporary Issues in Communication Science and Disorders, 33(Spring), 21-27. DOI:
Mengist, W., Soromessa, T., & Legese, G. (2020). Method for conducting systematic literature review and meta-analysis for environmental science research. MethodsX, 7, 100777. DOI:
Mensah, J. V., Yaw, W., & Kodwiw, A. (2018). interactive effects of socioeconomic conditions and personal attributes of individuals on microenterprise establishment decisions in the Mfantsiman municipality of Ghana. International Journal of Management Studies, 8(4), 303–314.
Milana, C., & Ashta, A. (2020). Microfinance and financial inclusion: Challenges and opportunities. Strategic Change, 29(3), 257-266. DOI:
Mohamed Shaffril, H. A., Samsuddin, S. F., & Abu Samah, A. (2021). The ABC of systematic literature review: the basic methodological guidance for beginners. Quality & Quantity, 55(4), 1319-1346. DOI:
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., & Altman, D. G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6(7), e1000097. DOI:
Monnickendam-Givon, Y., Schwartz, D., & Gidron, B. (2018). The surprising lack of connection between social networks and the enterprise success of ultra-religious female micro-entrepreneurs. Journal of Enterprising Communities: People and Places in the Global Economy, 12(3), 395-415. DOI:
Nadzri, F. A. A., Omar, N., & Rahman, R. A. (2018). Enterprise governance of micro entrepreneurs in Malaysia: Comparison between the Amanah Ikhtiar Malaysia and Asnaf’s economic development program. Global Journal Al-Thaqafah, Special Issue (January), 25–40.
Najera Ruiz, T., & Collazzo, P. (2021). Management accounting use in micro and small enterprises. Qualitative Research in Accounting & Management, 18(1), 84-101. DOI: 10.1108/qram-02-2020-0014
Nasir, S. (2013). Microfinance in India: Contemporary issues and challenges. Middle East Journal of Scientific Research, 15(2), 191–199.
Neise, T., Sambodo, M. T., & Revilla Diez, J. (2021). Are Micro-, Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises Willing to Contribute to Collective Flood Risk Reduction? Scenario-Based Field Experiments from Jakarta and Semarang, Indonesia. Organization & Environment, 34(2), 219-242. DOI:
Okoye, L. U., Omankhanlen, A. E., Ahmed, A., & Ojo, A. (2019). Driving inclusive growth through rural financial intermediation: A study of the microfinance model in Nigeria. Proceedings of Intcess 2019- 6Th International Conference on Education and Social Sciences, February, 1126–1134.
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., … Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Systematic Reviews, 10(1). DOI:
Palacios-Duarte, P. D., Pérez-Paredes, A., & Torralba-Flores, A. (2019). Bounded financial rationality by owners or administrators of mexican micro-enterprises. Cuadernos de Administración, 35(64), 78-95. DOI:
Perez-Estebanez, R., Urquía-Grande, E., & Rautiainen, A. (2018). Technological and economic factors determining ICT level: Evidence from rural micro-businesses in Democratic Republic of Congo. Journal of International Development, 30(1), 118-133. DOI:
Prathap, B. N., Subrahmanya, K. C., & Harisha, B. S. (2018). Microfinance delivery - challenges and remedies. International Journal of Management Studies, 3(9), 138. DOI:
Quagrainie, F. A. (2018). Relationship between religious and entrepreneurial values: views from Ghanaian women entrepreneurs. International Journal of Business and Globalisation, 21(3), 367. DOI:
Ramírez-Urquidy, M., Aguilar-Barceló, J. G., & Portal-Boza, M. (2018). The impact of economic and financial management practices on the performance of mexican micro-enterprises: A multivariate analysis. Review of Business Management, 20(3), 319-337. DOI:
Rozzani, N., & Rahman, R. A. (2013). Applying technology: Issues in microfinance operations. Middle East Journal of Scientific Research, 17(3), 374–381.
Şahin, Ö. (2018). Happiness management in micro, small and medium sized food and beverage enterprises: Menteşe/Muğla case. Journal of Business Research - Turk, 10(4), 843-867. DOI:
Shamseer, L., Moher, D., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., Shekelle, P., Stewart, L. A., Altman, D. G., Booth, A., Chan, A. W., Chang, S., Clifford, T., Dickersin, K., Egger, M., Gøtzsche, P. C., Grimshaw, J. M., Groves, T., Helfand, M., … Whitlock, E. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ (Online), 349, 1–25. DOI:
Ssekiziyivu, B., Mwesigwa, R., Bananuka, J., & Namusobya, Z. (2018). Corporate governance practices in microfinance institutions: Evidence from Uganda. Cogent Business & Management, 5(1), 1488508. DOI:
Tabot Enow, S., & Kamala, P. (2016). The accounts payable management practices of small, medium and micro enterprises in the Cape Metropolis, South Africa. Investment Management and Financial Innovations, 13(1), 77-83. DOI:
Thaker, M. A. B. M. T., Mohammed, M. O., Duasa, J., & Abdullah, M. A. (2016). The Behavioral Intention of Micro Enterprises to Use the Integrated Cash Waqf Micro Enterprise Investment (ICWME-I) Model as a Source of Financing. Gadjah Mada International Journal of Business, 18(2), 111. DOI:
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. (2020). OECD Policy Responses to Coronavirus (COVID-19: The territorial impact of COVID-19: Managing the crisis across levels of government. https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/the-territorial-impact-of-covid-19-managing-the-crisis-across-levels-of-government-d3e314e1/
Ussif, R. (2020). Microfinance institutions challenges in poverty and unemployment reduction in Ghana. International Journal of Engineering and Information Systems, 4(7), 114–123.
Wolmarans, H. P., & Meintjes, Q. (2015). Financial management practices in successful Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). The Southern African Journal of Entrepreneurship and Small Business Management, 7(1), 88. DOI:
Xiao, Y., & Watson, M. (2019). Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. Journal of Planning Education and Research, 39(1), 93-112. DOI:
Yusoff, M. N. H. B., Al Mamun, A., Ibrahim, M. D., & Hassan, H. (2018). Measuring and Comparing Functional Business Skills and Knowledge among Asnaf Community in Malaysia. Economics & Sociology, 11(2), 229-247. DOI:
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
06 May 2024
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-132-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
133
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1110
Subjects
Marketing, retaining, entrepreneurship, management, digital marketing, social entrepreneurship
Cite this article as:
Zaini, N., Mustaffa, A. H., Muda, R., & Osman, I. (2024). The Key Success Factors in Empowering Zakat Microentrepreneurs Towards Financial Sustainability. In A. K. Othman, M. K. B. A. Rahman, S. Noranee, N. A. R. Demong, & A. Mat (Eds.), Industry-Academia Linkages for Business Sustainability, vol 133. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 395-411). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2024.05.33

