Abstract
Nowadays, the advancement of the internet creates opportunities for product marketing and the introduction of new forms of retail transactions, and it has resulted in a remarkable increase in online shopping activities. Therefore, it is important for the industry to identify the main determining factors in consumer purchase intentions. The aims of this study are to reveal the influence of customer trust on perceived risks and purchase intentions as well as the effect of perceived benefits on purchase intentions. A survey approach was employed to collect data from 268 online shoppers, and quantitative analysis has been used to evaluate the hypotheses. The study discovered that customers' perceived benefit, perceived trust, and perceived risk all had a significant influence on their purchasing intentions. The implications of these findings go far beyond academia, providing useful information to online advertisers. Marketers with a detailed awareness of the elements influencing customers' purchasing intentions can proactively address these determinants, consequently improving the business's overall success and efficacy in fulfilling customer satisfaction. Fundamentally, this study contributes valuable insights to the body of knowledge necessary for managing the complexities of the contemporary digital marketplace.
Keywords: Online shopping website, purchase intention, perceived benefit, perceived trust, perceived risk
Introduction
Currently with the development of information technology, the internet has also grown rapidly and its use has increased over time (Sadiq et al., 2022). The usage of the internet is no longer limited as a networking tools but is now used in the global market place as a transaction medium for customers and has become a popular platform for providing and trading information, services, and products (Rachmawati et al., 2020). The Internet provides many advantages and opportunities for businesses to grow their business around the world without borders and limitations. In fact, the popularity of online shopping is increasing over time due to the rapid development of the internet. According to a statistical report in April 2022, it was found that 5.03 billion active internet users worldwide, this represents 63.1 % of the world’s total population. Of this amount, 59% (4.7 billion), mobile devices are the means used to access the internet (Internet World Stats, 2022).
While there has been a significant increase in online shopping nowadays, the negative effects of online buying are becoming more relevant. Consumer priorities are more concerned with their purchasing decisions and among the fundamental challenges faced by many companies that focus on online businesses is how to gain and maintain customer loyalty (Ariyono et al., 2022; Changchit et al., 2019; Suresh & Biswas, 2020). In many purchase intention studies, researchers frequently identify how the benefits gained while making a transaction can influence purchase intention (Dewi et al., 2020; Peña-García et al., 2020; Rungsrisawat et al., 2019). The user will indirectly think about the risks and the extent to which those risks are unsafe. Since shopping on the internet is done virtually, consumers cannot check the quality of the product and there is no contact with humans, and then that will make consumers feel insecure and unsure of their decision to buy something. They also value the pre-purchase experience because they fear unexpected losses from the purchase and the product (Trivedi & Yadav, 2020).
Previous research also has shown that internet give some impact toward online buying intention which is perceived trust (Bahari et al., 2018) and perceived risk (Ventre & Kolbe, 2020). According to Wu et al. (2020), although buying online will be easier and save user’s time, but it is a risky activity. Consumers are likely to lose money when making online purchases due to unsatisfactory products and not commensurate with the price paid (Kamalul Ariffin et al., 2018). Product specifications may also not be met from what was originally displayed on the website, e.g., its quality, shape, color, and appearance (Qalati et al., 2021). In addition, online buyers are likely to feel the security of delivery, the quality of product information through websites, and transactions over the internet are at high risk (Kasuma et al., 2020; Larasetiati & Ali, 2019; Varma et al., 2020). According to a study by Rahman (2020), the results state that trust is the key factor that can influence a consumer to make an online purchase. Conclusions of a positive relationship between online buying intentions by users and trust is also acknowledged by several other researchers (Alharthey, 2019; Bahari et al., 2020; Sharma & Klein, 2020).
Though many researches has studied the various effect of perceived trust and perceived risk toward purchase intention on online shopping website, however a little study has investigated and focused on the impact of perceived benefit (Bhatti & Rehman, 2019) toward online buying intention to close the gap between the previous study and the present study. Considering the diversity of recent studies in the available literature, therefore this study was conducted to determine the correlation between perceived benefits, perceived trust, and perceived risk in online purchasing intentions.
Literature Review
Purchase Intention
Purchase intent reflects the possibility that customers will intend to buy or are willing to buy a specific good or service in the present (Shang et al., 2020). Previous study has shown that an increase in purchase intention corresponds to an increase in the likelihood of making a purchase. When customers have such a strong purchasing intention, good brand involvement will encourage them to make that purchase. Additionally, purchase intention is the desire to buy a specific goods or service within a specific time frame. According to Le-Hoang (2020), the consumer's desire to purchase from an e-commerce business has an impact on online purchasing intentions. If consumers are aware of and familiar with e-commerce business, they are more interested in visiting an online shopping site with the intention of making a purchase (Dapas et al., 2019; Ghahtarani et al., 2020). The decision to purchase represents whatever customers’ expectations they would buy in the future to meet their needs and desires (Rita et al., 2019). Nevertheless, due to unpredictable circumstances, customers' intentions may change. Thus, it is critical for businesses to take proactive steps to ensure that their goods and services are favourably considered by their customers (Naszariah et al., 2021). Consumer purchase intentions are frequently influenced by marketing approach, attitudes, as well as how much buyers concern about the deals offered by a specific business (Jung et al., 2020). As a result, it is an essential need for online businesses to fulfil customer requirements in terms of enhancing purchase intentions (Dastane, 2020). Purchase intentions is being used to evaluate a potential distribution system, allowing managers in determining if the concept needs further development and deciding which geographical area and customer demographics to seek through all the channel (Akram et al., 2021). Their significance derives from the fact that intentions are regarded as the primary determinant of future actions (Thomas et al., 2019). Hence, their research is critical to the success of any online stores.
Perceived Benefits
The perceived benefits are the consumer's belief and satisfaction with internet and the consumer's perspective that internet shopping is efficient, convenient, more various but also less risky compared to the conventional shopping (Moslehpour et al., 2018). Additionally, perceived benefit is defined as the belief that consumers will receive positive rewards when action is taken (Zhao et al., 2020). However, the perceived benefit felt by the buyer is an extension of the advantages or satisfaction of online shopping that meets customer expectations (Maharsi et al., 2021). In this study, researcher defined perceived benefit as advantages that change the perception of consumers when they buy online. Moreover, Sawitri and Alhasin (2022), stated that perceived benefit is felt when consumers have a subjective perception when making an online purchase and they find that a product is beneficial to them. Lim (2020), found that product variation, convenience, brand, information are the main reasons for customers shopping online. Obviously, if consumers find that the level of benefits earned is higher, it will make their intention to buy online will also increase. In short, the benefits gained will have a strong positive influence on purchase intentions. Therefore, we proposed the following hypothesis:
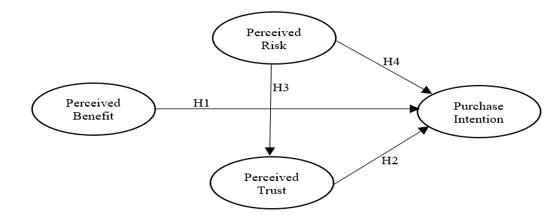
Hypothesis H1: Perceived benefit is positively influence on purchase intention.
Perceived Trust
According to the findings of a previous study, customers are aware that the decision to purchase online is indeed risky, therefore trust is a very important factor to convince consumers that they need to do the transaction (Maia et al., 2019). The results of study by Mosunmola et al. (2019) in business strategy, online trust by consumers is said to be very important and needs to be given attention because it reduces perceived risk and increases customer satisfaction. While, Rehman et al. (2019) state that there is no specific meaning of the belief used in several cases, including management, psychology, social sciences, and many more. Additionally, the consequences of trust are said to be mediated by risk to the customer’s intention to buy (Ashraf et al., 2020). There are several trust researchers who have proven that there is a direct correlation between the trust and ability of consumers to make online purchase (Kaur & Arora, 2021). Moreover, Quang and Thuy (2022) added trust as an important and significant variable in online commerce and consumers will be more confident making purchases on the internet when trust becomes higher (direct effect). Thus, with the increase in trust, consumers tend to feel less risk to buy online (Liew & Falahat, 2019). If consumers have less trust, it will cause them not to shop online (Cheng et al., 2019). Hence, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2: Perceived trust is positively influenced purchase intention.
Hypothesis 3: Perceived risk is positively influenced perceived trust.
Perceived Risk
Perceived risk was interpreted as potential loss in achieving desired results when shopping online; it is a combination of something uncertain and a possible undesirable outcome (Tran, 2020). Users will feel the greater the expected loss, the higher the level of risk. Tham et al. (2020) meanwhile, state risk as an exchange between costs and benefits, for which the consumer makes an overall assessment of the quality of the service or product obtained compared to the value of the payment that has been made. Iriani and Andjarwati (2020), stated perceived risks have negative views and effects on unpredictable and variable outcomes from purchased products. Therefore, consumers' perceptions of risk are very important in determining their purchasing evaluation and behavior (Bangun & Handra, 2021). Compared to buying in a physical store, consumers feel it is riskier when buying in online. Pentz et al. (2020) say consumers are unlikely to purchase a service or product online if they feel it is high risk.
The perception is that in today’s market, risk can be reduced if customers have trust when dealing online because trust is a strong antecedent of perceived risk (Bonnin, 2020; Dogbe et al., 2019; Ha et al., 2021). As suggested by Bhatti et al. (2020), consumers argue that the higher the perceived risk of making online transactions, the less their buying intentions are for online retailers. Hence, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis H4: Perceived risk is negatively influence on online purchase intention.
Research Methods
Sample and Data Collection
Primary data was utilized in this study, which essentially means that all relevant data was obtained directly by the researcher to solve all the study’s aims and issues by adopting a quantitative approach. Quantitative research produces statistics using large-scale survey studies and questionnaire method was applied. Therefore, to avoid any uncertainty, the questions were described as straight forward and simple. As far as the developing of the questionnaire is concerned, six main sections were constructed in response to each of the research objectives as well as research questions. Issues from each section were developed to address the research objective and dimensions of the study framework. A cover letter was drawn up carefully to improve the response rate. Respondents were asked questions related to each variable to obtain the necessary information by using a five-point scale questions starting from one (1) with ‘strongly disagree’ to five (5) with 'strongly agree’. The data collected is a sample of the population that has been identified based on certain criteria, specifically, those who have visited any business website for making online purchases in the last 12 months. A total of 268 respondents were analyzed in this study. Additionally, this research uses an observational research design with cross sectional model approach. Data for the independent variable and the dependent variable were gathered concurrently.
Findings
The results from table 1 indicates that all variables had exceeded the minimum level of the coefficient which is 0.7. Perceived trust variable was measured by 3 items recorded the highest alpha coefficient of 0.846, while perceived risk variable which is measures 4 items and had recorded an alpha coefficient of 0.795. Lastly, it was followed by perceived benefit variable which measures 4 items and recorded an alpha coefficient of 0.735. Therefore, it can be concluded that all variables for this research that measure 22 items have a good strength of association which is the alpha coefficient is 0.832.
Table 2 shows the result of linear regression analysis for the scales of the factors which are of perceived trust, perceived risk and perceived benefit. The finding illustrates that there were 59.7% of the total variation in the variance of perceived trust, perceived risk and perceived benefit were explained by the purchase intention.
Based on table 3, perceived trust (β=0.332, p<0.05), perceived risk (β=0.528, p<0.05) and perceived benefit (β= 1.88, p<0.05) were significantly influenced purchase intention. Therefore, all the hypothesis is verified and the result is fully supporting the results of previous research in which (Ahmed et al., 2021) have successfully realized that perceived benefits, perceived trust and perceived risks tend to influence purchase intentions directly, and trust is also said to influence purchase intentions indirectly by influencing risk perception.
The results in the table 4 displays the correlation of each independent variable which consists of perceived benefit, perceived risk and perceived trust is significant at the 0.01 levels, two-tailed toward purchase intention. All the independent variable that has been highlighted in the research has strong relationship with purchase intention. The value that had been recorded value between perceived benefit between purchase intention is r=0. 730. It shows that perceived benefit has the strongest positive relationship with purchase intention and makes this variable most significant in influencing the purchase intention among consumers. Additionally, this results also fully supported by Ha (2020) statement that the perceived benefit of purchase construction is most often applied to normal shopping behavior and is relevant to an individual's perception of the benefits that will bring advantages by engaging in a purchase behavior. Lastly, the hypothesis which predicts the perceived risk effect on purchase intention is negatively related to purchase intention. This finding supported by the value between perceived risk and purchase intention is r=0.647. Customers are unlikely to buy online because they believe the risk is greater than in traditional methods of buying (Bangkit et al., 2022). When users consider the risk is less, then users tend to have the intention to buy products using the internet.
Conclusion
Basically, the main goal of this study is to identify consumers online purchase intentions and examine the influencing factors. This study found that, in context of online buying, perceived benefits positively influence the customer’s purchase intentions. Moreover, consumers agree that there are several advantages and it is more convenient when shopping online. Perceived benefits are an important factor that motivates online users. Result suggested that to attract and motivate consumers to make online purchases, online stores should expand product selections, provide more benefits and the website should be easy to navigate at any time. In addition, retailers can also use scales to assess the impact of benefits and risk perceptions on online shopping outcomes such as shopping loyalty and satisfaction. For example, online sellers can identify whether online shoppers who are motivated by utility benefits are more likely to be satisfied and repatriating the online retailers than online shoppers who are heavily driven by hedonic benefits.
In e-commerce, perceived risk has become a very important issue. The study shows that perceived risks were influential negatively on online shopping attitudes. Consumers do not trust the ability of online stores to protect their personal information and there are many respondents still perceived that online shopping is risky. In other words, customers' online shopping intentions will indirectly decrease if they consider it risky. Most customers are worried that if they buy goods online and payment is made, their personal information will be leaked to other companies, which could affect their privacy, and the products delivered will not be as expected. Therefore, to reduce perceived risk and in ensuring consumers feel more confident, companies have a responsibility to improve security requirements. Additionally, it is important for online sellers to know what dimensions of risk most of concern to consumers. This aims to reduce consumer perceptions of the risks involved, indirectly increasing the likelihood of purchase.
Besides, the results show that trust has a significant influence on purchase intentions in terms of website visits, increased online orders, sign ups, positive reviews, and marketing for web stores on social apps. Furthermore, trust in online buying reduces the level of perceived risk. This study recommends to online vendors that while it is important for them to focus on increasing trust with customers, they should provide more resources to build their trust strategically according to the level of existing e-commerce institutional mechanisms (e.g., online maturity level of credit card guarantees, services escrow, and privacy protection services). Finally, consumers are concerned with the delivery of their order, they are worried that the product may be damaged during handling and transported or receive the wrong item or item that does not fit its specifications. In ensuring that there is no delay or damage during delivery, online retailers should choose the most reliable and best service provider. In addition, the results of the study confirm the relevance of trust on the internet to increase purchase intentions and actual purchases. Therefore, to develop such trust, managers need to be more focused, for example providing assurances to reduce risk perceptions and provide a secure payment method to make the user switch from intention to action.
Limitation and Future Recommendations
There are some limitations in this study including when simple sampling method are used, the probability of realizing the results is not high. Besides, these studies only pay attention to the effects of perceived benefits, perceived risks and perceived trust on online customer purchases intentions. Other factors that can influence an organization’s or individuals online purchase intentions are fundamentally different in each business model, each specific product line, but are not included in this context. Future research may focus on expanding the scope of the review and sample size, considering the impact of other factors, and recognizing a product line or an e-commerce model. Moreover, this study only covers consumers and online merchants in Malaysia. Thus, it is suggested that the future research can be done in other developing countries, so that the future researcher will have a new insight in term of behavioral characteristic of other countries consumers in online business industry. Additionally, a higher number of respondents will allow for more robust statistical analyses. Although there is a limited sample, the findings from this research can be used to gain a better understanding of the characteristics of internet cyber transaction factors in the industry.
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to express thank you and gratitude to Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Pulau Pinang, the corresponding authors, the respondents for their contribution and support towards completion of this research.
References
Ahmed, S. Y., Ali, B. J., & Top, C. (2021). Understanding the Impact of Trust, Perceived Risk, and Perceived Technology on the Online Shopping Intentions: Case Study in Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business and Government, 27(3). DOI:
Akram, U., Junaid, M., Zafar, A. U., Li, Z., & Fan, M. (2021). Online purchase intention in Chinese social commerce platforms: Being emotional or rational? Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 63(June), 102669. DOI:
Alharthey, B. (2019). The Role of Online Trust in Forming Online Shopping Intentions. International Journal of Online Marketing, 10(1), 32–57. DOI:
Ariyono, K. Y., Irdiana, S., & Darmawan, K. (2022). Effect of Online Buying Experience on Customer Loyalty. International Journal of Social Science, 1(5), 549-552.
Ashraf, M., Ahmad, J., Sharif, W., Raza, A. A., Salman Shabbir, M., Abbas, M., & Thurasamy, R. (2020). The role of continuous trust in usage of online product recommendations. Online Information Review, 44(4), 745–766. DOI:
Bahari, K. A., Abdullah, D., Kamal, S. B. M., Johari, N. R., & Zulkafli, M. S. (2018). The Influence of Hotel Website Design Quality, Perceived Ease of Use and Perceived Usefulness on Loyalty Intention. Turkish Online Journal of Design Art and Communication, 8(SEPT), 701-710. DOI:
Bahari, K. A., Che Azmi, M. N., Mohd Kamal, S. B., Zainol, N., Mahat, F., & Abdullah, D. (2020). The effects of brand image, perceived trust and perceived risk on online booking intention: a conceptual model. ESTEEM Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 4, 203-213. http://ir.uitm.edu.my/id/eprint/29326/
Bangkit, J. L., Tumbuan, W. J., & Tielung, M. V. (2022). Analysis of perceived risk and perceived benefit influencing online shopping behavior in Manado. Jurnal EMBA: Jurnal Riset Ekonomi, Manajemen, Bisnis dan Akuntansi, 10(1), 570-578.
Bangun, C. S., & Handra, T. (2021). How Theory of Planned Behavior And Percieved Risk Affect Online Shopping Behavior. Aptisi Transactions on Management (ATM), 5(2), 169–179. DOI:
Bhatti, A., & Rehman, S. U. R. (2019). Perceived Benefits and Perceived Risks Effect on Online Shopping Behavior With the Mediating Role of Consumer. In International Journal of Management Studies, 26(1), 33–54. DOI:
Bhatti, A., Ur Rehman, S., Kamal, A. Z., & Akram, H. (2020). Factors effecting online shopping behaviour with trust as moderation. Jurnal Pengurusan, 60(October), 1–15. DOI:
Bonnin, G. (2020). The roles of perceived risk, attractiveness of the online store and familiarity with AR in the influence of AR on patronage intention. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 52(August 2019), 101938. DOI:
Changchit, C., Cutshall, R., Lonkani, R., Pholwan, K., & Pongwiritthon, R. (2019). Determinants of Online Shopping Influencing Thai Consumer’s Buying Choices. Journal of Internet Commerce, 18(1), 1–23. DOI:
Cheng, X., Gu, Y., & Shen, J. (2019). An integrated view of particularized trust in social commerce: An empirical investigation. International Journal of Information Management, 45(October 2018), 1–12. DOI:
Dapas, C. C., Sitorus, T., Purwanto, E., & Ihalauw, J. J. O. I. (2019). The effect of service quality and website quality of zalora. Com on purchase decision as mediated by purchase intention. Quality - Access to Success, 20(169), 87–92.
Dastane, O. (2020). Impact of Digital Marketing on Online Purchase Intention: Mediation Effect of Customer Relationship Management. Journal of Asian Business Strategy, 10(1), 142–158. DOI:
Dewi, C. K., Mohaidin, Z., & Murshid, M. A. (2020). Determinants of online purchase intention: a PLS-SEM approach: evidence from Indonesia. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 14(3), 281–306. DOI:
Dogbe, C. S. K., Zakari, M., & Pesse-Kuma, A. G. (2019). Perceived Online Risk, Consumer Trust and M-Shopping Behaviour. e-Journal of Social & Behavioural Research in Business, 10(1), 10-23. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334249266_Perceived_Online_Risk_Consumer_Trust_and_M-Shopping_Behaviour
Ghahtarani, A., Sheikhmohammady, M., & Rostami, M. (2020). The impact of social capital and social interaction on customers’ purchase intention, considering knowledge sharing in social commerce context. Journal of Innovation and Knowledge, 5(3), 191–199. DOI:
Ha, N. T. (2020). The impact of perceived risk on consumers’ online shopping intention: An integration of TAM and TPB. Management Science Letters, 10(9), 2029–2036. DOI:
Ha, N. T., Nguyen, T. L. H., Pham, T. V., & Nguyen, T. H. T. (2021). Factors influencing online shopping intention: An empirical study in Vietnam. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 8(3), 1257-1266. DOI:
Internet World Stats. (2022). Internet Usage Statistics the Internet Big Picture. https://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm
Iriani, S. S., & Andjarwati, A. L. (2020). Analysis of perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and perceived risk toward online shopping in the era of Covid-19 pandemic. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(12), 313–320. DOI:
Jung, H. J., Choi, Y. J., & Oh, K. W. (2020). Influencing factors of chinese consumers’ purchase intention to sustainable apparel products: Exploring consumer “attitude–behavioral intention” gap. Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(5), 1–14. DOI:
Kamalul Ariffin, S., Mohan, T., & Goh, Y. N. (2018). Influence of consumers’ perceived risk on consumers’ online purchase intention. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 12(3), 309–327. DOI:
Kasuma, J., Kanyan, A., Khairol, M., Sa’ait, N., & Panit, G. (2020). Factors Influencing Customers Intention for Online Shopping. International Journal of Modern Trends in Business Research (IJMTBR), 3(11), 31–41.
Kaur, S., & Arora, S. (2021). Role of perceived risk in online banking and its impact on behavioral intention: trust as a moderator. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 15(1), 1–30. DOI:
Larasetiati, M., & Ali, H. (2019). Model of consumer trust: Analyses of perceived usefulness and toward repurchase intention in online travel agent. Journal of Economics and Finance, 3(8), 350–357. DOI:
Le-Hoang, P. V. (2020). Factors affecting online purchase intention: the case of e-commerce on Lazada. Independent Journal of Management & Production, 11(3), 1018.DOI: 10.14807/ijmpv.v1 1i3.10088
Liew, Y. S., & Falahat, M. (2019). Factors influencing consumers' purchase intention towards online group buying in Malaysia. International Journal of Electronic Marketing and Retailing, 10(1), 60. DOI:
Lim, W. M. (2020). An equity theory perspective of online group buying. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 54(May), 101729. DOI:
Maharsi, A. R., Njotoprajitno, R. S., Hadianto, B., & Wiraatmaja, J. (2021). The Effect of Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction on Purchasing Intention: A Case Study in Indonesia. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 8(4), 475–482. DOI:
Maia, C. R., Lunardi, G. L., Dolci, D., & D’Avila, L. C. (2019). Competitive price and trust as determinants of purchase intention in social commerce. BAR - Brazilian Administration Review, 16(4), 1–24. DOI:
Moslehpour, M., Pham, V., Wong, W.-K., & Bilgiçli, İ. (2018). e-Purchase Intention of Taiwanese Consumers: Sustainable Mediation of Perceived Usefulness and Perceived Ease of Use. Sustainability, 10(1), 234. DOI:
Mosunmola, A., Adegbuyi, O., Kehinde, O., Agboola, M., & Olokundun, M. (2019). Percieved value dimensions on online shopping intention: The role of trust and culture. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 18(1), 1–20.
Naszariah, R., Naseri, N., Mohd Esa, M., Abas, N., Zamratul, N., Ahmad, A., Azis, R. A., & Norazmi Bin Nordin, M. (2021). An Overview of Online Purchase Intention of Halal Cosmetic Product: A Perspective from Malaysia. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education, 12(10), 7674–7681.
Peña-García, N., Gil-Saura, I., Rodríguez-Orejuela, A., & Siqueira-Junior, J. R. (2020). Purchase intention and purchase behavior online: A cross-cultural approach. Heliyon, 6(6). DOI:
Pentz, C. D., du Preez, R., & Swiegers, L. (2020). To bu(Y) or not to bu(Y): Perceived risk barriers to online shopping among South African generation Y consumers. Cogent Business and Management, 7(1). DOI:
Qalati, S. A., Vela, E. G., Li, W., Dakhan, S. A., Hong Thuy, T. T., & Merani, S. H. (2021). Effects of perceived service quality, website quality, and reputation on purchase intention: The mediating and moderating roles of trust and perceived risk in online shopping. Cogent Business and Management, 8(1). DOI:
Quang, N. N., & Thuy, D. C. (2022). Influencing Factors on Motorbike Online Buying Intention of Vietnamese People. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 6(5), 5542-5550.
Rachmawati, I. K., Hidayatullah, S., Nuryanti, F., & Wulan, M. (2020). The effect of consumer confidence on the relationship between ease of use and quality of information on online purchasing decisions. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research, 9(4), 774–778.
Rahman, A. (2020). Brand Image, eWOM, Trust and Online Purchase Intention of Digital Products among Malaysian Consumers. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology, XII(III), 4935–4946. DOI:
Rehman, S. U., Bhatti, A., Mohamed, R., & Ayoup, H. (2019). The moderating role of trust and commitment between consumer purchase intention and online shopping behavior in the context of Pakistan. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, 9(1). DOI:
Rita, P., Oliveira, T., & Farisa, A. (2019). The impact of e-service quality and customer satisfaction on customer behavior in online shopping. Heliyon, 5(10), e02690. DOI:
Rungsrisawat, S., Joemsittiprasert, W., & Jermsittiparsert, K. (2019). Factors determining consumer buying behaviour in online shopping. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 8(8), 222–237.
Sadiq, M., Dogra, N., Adil, M., & Bharti, K. (2022). Predicting Online Travel Purchase Behavior: The Role of Trust and Perceived Risk. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality and Tourism, 23(3), 796–822. DOI:
Sawitri, S., & Alhasin, A. (2022). Online music business: The relationship between perceived benefit, perceived sacrifice, perceived value, and purchase intention. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147-4478), 11(5), 111–126. DOI:
Shang, Q., Jin, J., & Qiu, J. (2020). Utilitarian or hedonic: Event-related potential evidence of purchase intention bias during online shopping festivals. Neuroscience Letters, 715, 134665. DOI:
Sharma, V. M., & Klein, A. (2020). Consumer perceived value, involvement, trust, susceptibility to interpersonal influence, and intention to participate in online group buying. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 52(March 2019), 101946. DOI:
Suresh, A. S., & Biswas, A. (2020). A Study of Factors of Internet Addiction and Its Impact on Online Compulsive Buying Behaviour: Indian Millennial Perspective. Global Business Review, 21(6), 1448–1465. DOI:
Tham, K. W., Dastane, O., Johari, Z., & Ismail, N. B. (2020). Perceived Risk Factors Affecting Consumers’ Online Shopping Behaviour. SSRN Electronic Journal, 6(4), 245–256. DOI:
Thomas, M. J., Wirtz, B. W., & Weyerer, J. C. (2019). Determinants of online review credibility and its impact on consumers’ purchase intention. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, 20(1), 1–20.
Tran, V. D. (2020). The relationship among product risk, perceived satisfaction and purchase intentions for online shopping. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(6), 221–231. DOI:
Trivedi, S. K., & Yadav, M. (2020). Repurchase intentions in Y generation: mediation of trust and e-satisfaction. Marketing Intelligence and Planning, 38(4), 401–415. DOI:
Varma, M., Kumar, V., Sangvikar, B., & Pawar, A. (2020). Impact of social media, security risks and reputation of e-retailer on consumer buying intentions through trust in online buying: A structural equation modeling approach. Journal of Critical Reviews, 7(1), 119–127. DOI:
Ventre, I., & Kolbe, D. (2020). The Impact of Perceived Usefulness of Online Reviews, Trust and Perceived Risk on Online Purchase Intention in Emerging Markets: A Mexican Perspective. Journal of International Consumer Marketing, 32(4), 287–299. DOI:
Wu, I. L., Chiu, M. L., & Chen, K. W. (2020). Defining the determinants of online impulse buying through a shopping process of integrating perceived risk, expectation-confirmation model, and flow theory issues. International Journal of Information Management, 52(February), 102099. DOI:
Zhao, S., Fang, Y., Zhang, W., & Jiang, H. (2020). Trust, perceived benefit, and purchase intention in C2C e-commerce: An empirical examination in China. Journal of Global Information Management, 28(1), 121–141. DOI: 10.4018/JGIM.2020010107
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
06 May 2024
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-132-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
133
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1110
Subjects
Marketing, retaining, entrepreneurship, management, digital marketing, social entrepreneurship
Cite this article as:
Bahari, K. A., Abdullah, D., Wahab, J., Kamal, S. B. M., Johari, N. R., & Zulkafli, M. S. (2024). The Factors Influencing A Customer’s Purchase Intention on Online Shopping Website. In A. K. Othman, M. K. B. A. Rahman, S. Noranee, N. A. R. Demong, & A. Mat (Eds.), Industry-Academia Linkages for Business Sustainability, vol 133. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 139-150). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2024.05.12

