Abstract
This paper presents a preliminary study on corporate financial distress and performance in emerging countries, utilizing a bibliometric analysis approach. The aim of this study is to identify key research themes, influential authors, and prominent journals in the field, while providing an overview of the existing literature on corporate financial distress and performance in emerging economies. A comprehensive bibliographic database which is SCOPUS was applied to identify relevant articles, extract data, and analyse the bibliometric indicators. The study's findings, based on 925 papers, have revealed several noteworthy insights. Firstly, the analysis highlights the increasing interest in research related to corporate financial distress and performance in emerging countries, indicating its growing significance in the field of finance. Secondly, it identifies key research themes, such as the financial crisis, which have received significant attention in literature. Moreover, the study uncovers influential authors that have contributed substantially to the research in this domain. Overall, this preliminary study serves as a valuable resource for researchers, practitioners, and policymakers interested in understanding the dynamics of corporate financial distress and performance in emerging economies. The identified research themes and influential authors provide a foundation for further investigations and help guide future research directions in this area. By shedding light on the existing literature and research trends, this study contributes to the advancement of knowledge and facilitates evidence-based decision-making in the context of corporate financial distress and performance in emerging countries.
Keywords: Bibliometric Analysis, Co-Authorship, Emerging Countries, Financial Distress, Performance
Introduction
Corporate financial distress and performance are critical issues that have significant implications for both individual firms and the overall economy. In emerging countries, where economic conditions, regulatory environments, and market structures often differ from those of developed nations, understanding the dynamics of corporate financial distress and performance becomes even more crucial (Khanna et al., 2015). The unique challenges and opportunities faced by businesses in these economies necessitate a comprehensive examination of the factors influencing their financial health and the subsequent impact on their performance.
Corporate financial distress refers to a situation where a company is facing significant financial difficulties or is at risk of bankruptcy or insolvency (Dirman, 2020). Financial distress can be caused by a variety of factors, such as declining revenues, increasing costs, high debt levels, or poor management decisions. Financial distress can have serious consequences for a company, including loss of market share, decreased profitability, and potential bankruptcy. In some cases, financial distress may also impact the broader economy, especially if the distressed company is a significant player in a particular industry or sector.
There are several warning signs that a company may be in financial distress, including declining revenues, rising debt levels, decreasing profitability, and missed loan or debt payments (Lins et al., 2017). Companies may take various measures to address financial distress, such as cost-cutting measures, asset sales, or seeking financial assistance from investors or lenders. However, these measures may not always be sufficient, and in some cases, the company may be forced to file for bankruptcy or insolvency.
Corporate performance in accounting research refers to the evaluation of how well a company is doing financially based on various accounting and financial measures (Ghazali et al., 2018; Taticchi et al., 2010). Corporate performance is usually measured using financial ratios, which are calculated based on a company's financial statements, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Emerging countries, characterized by rapid economic growth, expanding markets, and evolving financial systems, offer fertile ground for studying corporate financial distress and performance. These economies are often characterized by higher levels of uncertainty, increased exposure to macroeconomic fluctuations, weaker institutional frameworks, and limited access to capital markets. Consequently, businesses operating in these contexts face a distinct set of risks and vulnerabilities that can significantly affect their financial stability and operational efficiency.
Given the importance of understanding and managing corporate financial distress and performance in emerging countries, extensive research has been conducted in this field. Scholars have investigated various aspects related to financial distress, including its causes, prediction models, impact on firm performance, and potential mitigation strategies (Altman, 2013; Verma & Gustafsson, 2020). However, due to the breadth and diversity of research conducted in this domain, a systematic analysis of the existing literature is necessary to identify key research themes, influential authors, and prominent journals. Such a comprehensive overview can guide future research efforts, highlight gaps in knowledge, and inform policymakers and practitioners about effective strategies to mitigate financial distress and enhance corporate performance in emerging economies.
In light of these considerations, this paper presents a preliminary study on corporate financial distress and performance in emerging countries using a bibliometric analysis approach. By examining the existing literature, we aim to provide insights into the key research themes, influential authors, and prominent journals in this field. This study serves as a foundation for further investigations, facilitates evidence-based decision-making, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the context of corporate financial distress and performance in emerging economies.
Financial Distress in Emerging Market
Financial distress is a common and pervasive phenomenon in emerging markets, characterized by a multitude of challenges arising from volatile economic conditions, political instability, limited access to financing, and weak regulatory environments (Marquis & Raynard, 2015). The underdeveloped financial sector in many of these markets further exacerbates the difficulties faced by companies, as securing financing or managing financial risks becomes an uphill task. The ramifications of financial distress in emerging markets can be severe, impacting companies on multiple levels. Decreased profitability, loss of market share, and the looming threat of potential bankruptcy are among the immediate consequences that companies may confront (ElBannan, 2021). However, it doesn't stop there; the effects of financial distress extend beyond individual companies and reverberate throughout the broader economy. Distressed companies may find themselves unable to repay their debts or invest in new projects, ultimately impeding economic growth and diminishing job opportunities, affecting both stakeholders and society as a whole.
Despite these significant challenges, companies in emerging markets do have avenues to navigate through financial distress and enhance their financial performance. One promising approach lies in accessing alternative sources of financing. For instance, venturing into international capital markets or exploring Islamic finance can present opportunities to secure funding at lower costs compared to traditional sources of financing (Alam et al., 2019; Ghazali et al., 2018). Embracing these diverse funding mechanisms can bolster liquidity and provide companies with the necessary resources to weather financial hardships. Furthermore, companies can adopt more robust and effective financial management practices to address financial distress. Implementing comprehensive risk management strategies can help mitigate potential threats and safeguard against future uncertainties. Additionally, exploring and implementing cost-cutting measures can lead to more streamlined operations, heightened efficiency, and improved profitability. Debt restructuring also remains a viable option, allowing companies to renegotiate debt terms and ease repayment burdens (Suffian et al., 2022). Such measures, when executed strategically, can set the stage for financial recovery and sustainable growth.
While financial distress indeed poses significant challenges for companies in emerging markets, it also presents opportunities for resilience and growth (Leal Filho et al., 2020). By capitalizing on diverse financing sources, embracing efficient financial management practices, and undertaking necessary restructuring measures, companies can navigate through adversity and emerge stronger on the other side. Additionally, policymakers and regulators play a pivotal role in supporting these companies by fostering a conducive business environment, reinforcing financial infrastructure, and creating an atmosphere that encourages growth and innovation in these vibrant markets. Ultimately, overcoming financial distress demands a combination of astute decision-making, adaptability, and a proactive approach to seize the opportunities that lie within the challenges.
Mechanisms in Overcoming Financial Distress in Emerging Countries
There are several mechanisms that companies in emerging countries can use to overcome financial distress. In times of financial distress or when faced with the need to strengthen their financial position, companies have several options to explore. Debt restructuring is a common approach wherein companies engage in negotiations with their lenders to modify the terms of their debt. This could involve reducing the principal amount, extending the maturity period, or lowering the interest rate on their loans (Acker et al., 2020). By doing so, the company can achieve more manageable debt payments and decrease the risk of default, which can ultimately ease the burden on their financial health.
In addition to debt restructuring, companies can also implement cost-cutting measures to improve their profitability. These measures may include reducing headcount, consolidating operations, or renegotiating contracts with suppliers, all aimed at reducing expenses and enhancing overall efficiency (Nayal et al., 2022; Suffian et al., 2015). Streamlining operations and optimizing resource utilization can help companies navigate challenging financial situations and bolster their financial stability. Another viable option for companies seeking to bolster their financial position is asset sales. By selling non-core or underperforming assets, companies can generate cash inflow, which can be used to address immediate financial challenges or invest in more promising opportunities (Chan & Abdul-Aziz, 2017; Idris et al., 2015). Shedding assets that no longer align with the core business strategy can allow companies to focus on their strengths and allocate resources more effectively.
To infuse additional capital into the business, companies may opt for equity infusion. This entails issuing new shares to investors, thereby raising equity capital that can be used to fund operations or repay existing debts (Gilson, 2012). Equity infusion can strengthen the company's financial foundation, improve liquidity, and enhance the potential for growth and expansion. Furthermore, forging strategic partnerships with other companies can be a valuable approach for enhancing financial stability. By pooling resources, expertise, and market reach, companies can collaborate to reduce costs and improve overall efficiency (Zamir et al., 2014). Strategic partnerships can also open up new avenues for revenue generation and innovation, offering a win-win scenario for all involved parties.
In conclusion, when confronted with financial challenges, companies have an array of options to consider. Debt restructuring, cost-cutting measures, asset sales, equity infusion, and strategic partnerships all present opportunities for improving financial health and positioning the company for long-term success. The choice of the most appropriate approach will depend on the specific circumstances and objectives of the company in question. Overall, the mechanisms for overcoming financial distress in emerging countries can vary depending on the specific circumstances of the company and the country. Companies should evaluate their options carefully and seek expert advice to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Research Methodology
The bibliometric methodology encapsulates the application of quantitative techniques (i.e., bibliometric analysis – e.g., year, subject, source, country, author, and affiliation. Data was collected from the SCOPUS database. It represents the highest available quality of journals and articles in the field of social sciences and is widely used in conducting studies such as bibliometric analysis (Donthu et al., 2021). The idea of this method is based on the analysis of database research to decipher how to target the highest quality articles and reviews on the impact of financial distress on performance (Liu et al., 2017). It has been a focus of the past researcher to make use of the ‘bibliographic’ web versions of the database (Archambault et al., 2009). It is critical to the success of our data collection, as the accuracy in picking the right keyword highly affects the results number.
To ensure selecting all or most of the related papers from SCOPUS database, this study adopted this query which was chosen after careful consideration: TITLE-ABS-KEY (*financial and distress) AND (performance) and (LIMIT-TO) (EXACTKEYWORD, "Financial Distress”) or LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, "Financial Crisis"). The rationale behind using this query is the various use of terminologies like financial distress and financial crisis…etc. by researchers to express this topic. Hence, this query is more likely to bring most of the papers related to this topic, especially when searching in the topic area. Initially, the articles and reviews on the related field was 2,946. However, this study has conducted several ways to exclude and include irrelevant papers. To ensure that the collected data is of direct relation to the designated aim rather than discussing the topic in a non-marginal and non-flimsy way, this study has undergone a careful and cursory examination of the title and abstract of each article to include or exclude irrelevant papers (Suffian et al., 2023). Thus, the final sample of the data in this study is 925 articles and reviews that remain. The final data covers the period for 52 years from 1971 until 2022.
Findings and Discussion
Co-authorship based on Author
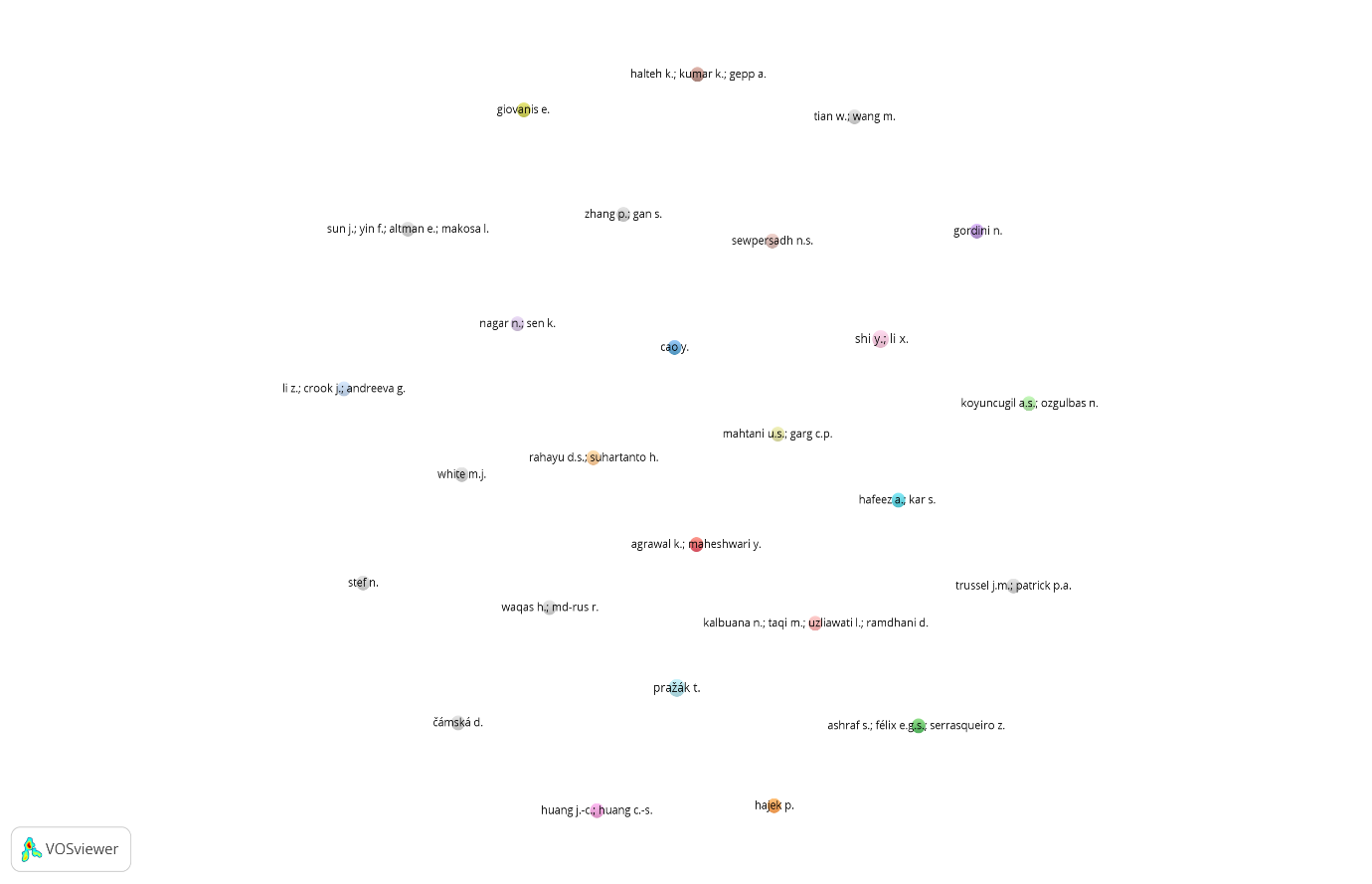
In Figure 1, a network of 26 authors out of a total of 896 authors is depicted. These 26 authors have all met the specified thresholds, indicating that each of them has at least two publications published in SCOPUS journals between 1971 and 2022. The network visualization represents countries as nodes, and co-authorship ties between authors are illustrated as edges, offering a graphical representation of the co-authorship landscape among the selected countries (and their respective authors). One noteworthy aspect of the graph is that each of the 26 authors has an equal contribution to the dataset. This suggests that all these authors are highly influential and prolific in their respective fields, actively engaging in research collaborations. The absence of variation in author contributions implies that they are all on equal footing in terms of their research output and collaborative endeavors.
Surprisingly, there seem to be no distinct clusters or subgroups of authors that commonly collaborate with each other within the network. This observation highlights a scarcity of explicit research networks or theme areas for collaboration among the chosen authors. The lack of evident collaboration clusters may indicate either unique research interests among the authors or the presence of more diverse and interdisciplinary collaborations. Despite the absence of apparent clusters, the network analysis can still offer valuable insights into the co-authorship trends among the selected authors based on the minimal document criterion. It allows researchers to identify and recognize prolific authors who actively participate in collaborative research efforts. These influential authors play a vital role in shaping the scientific landscape and contributing to the advancement of knowledge.
Additionally, the network analysis can reveal the existence of interdisciplinary collaborations that might not be immediately apparent from traditional research analyses. Such interdisciplinary partnerships can foster innovative ideas and breakthroughs at the intersection of different fields, leading to new avenues of research. By investigating the dynamics of author partnerships within the co-authorship network, researchers can better understand research relationships and uncover potential opportunities for further collaboration. These findings can inspire writers to explore prospective collaborative prospects and initiate partnerships with other authors in complementary areas of expertise.
Overall, the study's insights into co-authorship trends among the selected authors provide a comprehensive picture of research collaborations within the chosen dataset. It sheds light on the prolific authors, uncovers potential interdisciplinary collaborations, and highlights the collaborative dynamics among researchers. These findings can serve as a foundation for further research and exploration of collaborative opportunities, fostering a culture of knowledge sharing and advancement within the academic community.
Co-authorship based on Countries.
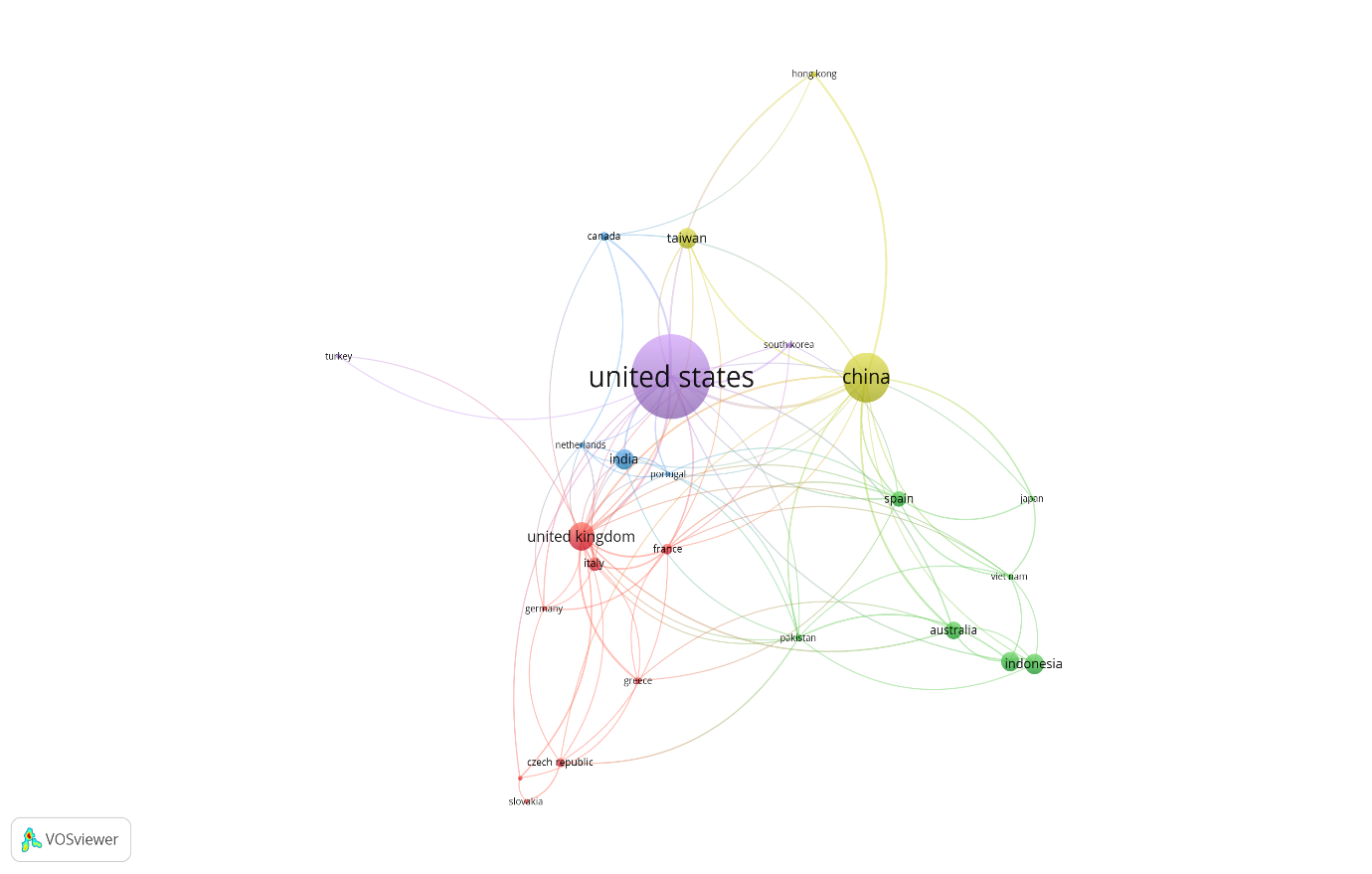
Figure 2 illustrates a network of 25 interconnected countries that have established co-authorship ties in their research endeavors. The initial dataset comprised 91 countries, but the analysis focused on those countries that had a minimum of 10 documents, resulting in the selection of the 25 countries that met this threshold. In the network visualization, each country is represented as a node, and the co-authorship connections between them are depicted as edges, highlighting the collaborative relationships between these nations (Robertson et al., 2020).
Upon examining the figure, it becomes evident that the United States stands out as the country with the highest number of collaborations within the dataset. Following closely behind are China and the United Kingdom, showcasing their strong presence in building robust research networks and collaborative alliances. This observation underscores the prominent role played by these three global powers in fostering international research cooperation and knowledge exchange. By analyzing the co-authorship patterns among these selected countries, researchers can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of international research collaborations. The visual representation of the network facilitates a clear understanding of the overall co-authorship landscape, shedding light on the relationships and connections between nations in the context of their scholarly pursuits.
This analysis not only presents the current state of research collaboration but also opens up avenues for further exploration and investigation. By studying the patterns and interactions within the co-authorship network, researchers can identify countries that actively participate in research cooperation, both regionally and thematically. Such information can be pivotal for policymakers and funding agencies to encourage and support collaborative research initiatives among nations.
Moreover, the findings from this study can pave the way for more targeted and strategic research collaborations. Identifying areas of mutual interest and strength within the network can guide researchers and institutions in forging partnerships that capitalize on shared expertise and resources. This can foster innovative research projects and enhance the collective knowledge base across borders. Ultimately, the analysis of the co-authorship patterns provides a comprehensive understanding of the dynamics of research collaboration among countries. By highlighting the leading players in international research networks and exploring themes and regional trends, this research can contribute to the advancement of global scientific cooperation. The insights gained from this analysis can inform future strategies for promoting research collaboration, strengthening international partnerships, and fostering a culture of knowledge sharing and innovation worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this preliminary study on corporate financial distress and performance in emerging countries, based on bibliometric analysis, provides valuable insights into the research landscape and collaboration patterns in this field. The analysis considered both co-authorship on authors and co-authorship on countries, revealing important findings and trends. Regarding co-authorship on authors, the study identified 26 authors who met the minimum document threshold. By examining their collaboration patterns, it became evident that certain authors played a prominent role in fostering research partnerships. These influential authors not only contributed significantly to literature but also actively collaborated with other researchers, indicating the existence of robust research networks within the field.
The findings highlight the importance of these authors in shaping the research landscape and suggest potential avenues for future collaborations and knowledge exchange. In terms of co-authorship on countries, the analysis encompassed 25 countries that surpassed the minimum document threshold. By examining their collaboration patterns, the study shed light on the international research networks in corporate financial distress and performance in emerging countries. It identified countries that actively engaged in research collaborations, suggesting the existence of cross-national partnerships and knowledge sharing initiatives.
The findings also revealed potential regional clusters or thematic groups that displayed higher levels of collaboration, indicating the importance of regional dynamics in research activities. Overall, the findings of the co-authorship analysis on authors and countries underscore the global relevance and collaborative nature of research on corporate financial distress and performance in emerging countries. The identified influential authors and countries provide valuable insights into key contributors to the field and potential hubs of research activity. These insights can guide future research efforts, facilitate cross-disciplinary and cross-national collaborations, and inform policymakers and practitioners on effective strategies to address corporate financial distress and enhance performance in emerging economies.
Future research could look into the relationship of co-authorship based on the organisational unit of analysis. This can contribute to the existing body of literature by identifying which institutions have made the most contributions to the study field. Aside from that, future research can analyse the number of citations and co-citations depending on documents, sources, or authors, as well as the cited references, cited sources, and cited authors. This will provide accurate information on the most prolific authors with the most citations.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals in providing support for this research under a research grant of Covid-19 Pandemic, Financial Distress, Earnings Quality and Performance: Evidence from Emerging Markets (Grant No: INFRE2201) and the anonymous reviewers of the International Conference in Technology. Humanities and Management (ICTHMS2023) for their valuable insights and comments.
References
Acker, K., Bräutigam, D., & Huang, Y. (2020). Debt relief with Chinese characteristics. Acker, Kevin, Deborah Brautigam, and Yufan Huang.
Alam, N., Gupta, L., & Zameni, A. (2019). Fintech and Islamic finance: Springer.
Altman, E. I. (2013). Predicting financial distress of companies: revisiting the Z-score and ZETA® models. In Handbook of research methods and applications in empirical finance (pp. 428-456). Edward Elgar Publishing.
Archambault, É., Campbell, D., Gingras, Y., & Larivière, V. (2009). Comparing bibliometric statistics obtained from the Web of Science and Scopus. Journal of the American society for information science and technology, 60(7), 1320-1326. DOI:
Chan, T. K., & Abdul-Aziz, A.-R. (2017). Financial performance and operating strategies of Malaysian property development companies during the global financial crisis. Journal of Financial Management of Property and Construction, 22(2), 174-191. DOI: 10.1108/jfmpc-02-2016-0009
Dirman, A. (2020). Financial distress: the impacts of profitability, liquidity, leverage, firm size, and free cash flow. International Journal of Business, Economics and Law, 22(1), 17-25.
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285-296. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
ElBannan, M. A. (2021). On the prediction of financial distress in emerging markets: What matters more? Empirical evidence from Arab spring countries. Emerging Markets Review, 47, 100806. DOI: 10.1016/j.ememar.2021.100806
Ghazali, A. W., Suffian, M. T. M., Sanusi, Z. M., & Alsudairi, F. S. (2018). Managerial Opportunism: Monitoring Financial Risk of Malaysian Shariah-compliant Companies. GLOBAL JOURNAL AL-THAQAFAH, 99-115.
Gilson, S. (2012). Coming Through in a Crisis: How Chapter 11 and the Debt Restructuring Industry Are Helping to Revive the U.S. Economy. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 24(4), 23-35. DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-6622.2012.00398.x
Idris, A., Mohd Sanusi, Z., & Mohd Suffian, M. T. (2015). The Influence of Monitoring Mechanisms and Opportunistic Behaviors Toward Earnings Management. Paper presented at the A New Paradigm for International Business: Proceedings of the Conference on Free Trade Agreements and Regional Integration in East Asia.
Khanna, T., Palepu, K. G., & Sinha, J. (2015). Strategies that fit emerging markets. In International Business Strategy (pp. 615-631). Routledge.
Leal Filho, W., Brandli, L. L., Lange Salvia, A., Rayman-Bacchus, L., & Platje, J. (2020). COVID-19 and the UN Sustainable Development Goals: Threat to Solidarity or an Opportunity? Sustainability, 12(13), 5343. DOI: 10.3390/su12135343
Lins, K. V., Servaes, H., & Tamayo, A. (2017). Social capital, trust, and firm performance: The value of corporate social responsibility during the financial crisis. The Journal of Finance, 72(4), 1785-1824. DOI:
Liu, M.-Y., Li, N., Li, W. A., & Khan, H. (2017). Association between psychosocial stress and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurological research, 39(6), 573-580. DOI:
Marquis, C., & Raynard, M. (2015). Institutional strategies in emerging markets. Academy of Management Annals, 9(1), 291-335. DOI:
Nayal, P., Pandey, N., & Paul, J. (2022). Covid-19 pandemic and consumer-employee-organization wellbeing: A dynamic capability theory approach. Journal of Consumer Affairs, 56(1), 359-390. DOI: 10.1111/joca.12399
Robertson, J., Pitt, L., & Ferreira, C. (2020). Entrepreneurial ecosystems and the public sector: A bibliographic analysis. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 72, 100862. DOI: 10.1016/j.seps.2020.100862
Suffian, M. T. M., Mohd-Sanusi, Z., Rashid, M. Z. A., Puteh, M. S., & Ghazali, Z. M. (2022). The effects of related party transactions on firm performance: empirical evidence from Malaysia. International Journal of Business and Systems Research, 16(4), 469-483. DOI:
Suffian, M. T. M., Rahman, R. A., Tarmizi, M. A., Omar, N., Naomi, P., Akbar, I., & Mayasari, I. (2023). Earnings Management: A Study from Bibliometric Analysis. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences, 13(1). DOI: 10.6007/ijarafms/v13-i1/16141
Suffian, M. T. M., Sanusi, Z. M., Osman, A. H., & Azhari, M. I. M. (2015). Manipulation of Earnings: The Pressure of Opportunistic Behavior and Monitoring Mechanisms in Malaysian Shariah-compliant Companies. Procedia Economics and Finance, 31, 213-227. DOI: 10.1016/s2212-5671(15)01223-x
Taticchi, P., Tonelli, F., & Cagnazzo, L. (2010). Performance measurement and management: a literature review and a research agenda. Measuring Business Excellence, 14(1), 4-18. DOI: 10.1108/13683041011027418
Verma, S., & Gustafsson, A. (2020). Investigating the emerging COVID-19 research trends in the field of business and management: A bibliometric analysis approach. Journal of Business Research, 118, 253-261. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.06.057
Zamir, Z., Sahar, A., & Zafar, F. (2014). Strategic alliances; a comparative analysis of successful alliances in large and medium scale enterprises around the world. Educational Research International, 3(1), 25-39.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
15 November 2023
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-130-0
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
131
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1281
Subjects
Technology advancement, humanities, management, sustainability, business
Cite this article as:
Suffian, M. T. M., Bakather, A. A., Ariff, A. M., & Hermawan, A. A. (2023). Corporate Financial Distress and Performance in Emerging Countries via Bibliometric Analysis. In J. Said, D. Daud, N. Erum, N. B. Zakaria, S. Zolkaflil, & N. Yahya (Eds.), Building a Sustainable Future: Fostering Synergy Between Technology, Business and Humanity, vol 131. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 698-708). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2023.11.59

