Abstract
The purpose of the article is to analyze the factors that determine the integrity of human existence in the new conditions. The problem of developing personal potential is relevant at all times. The modern emphasis on this problem is due to the fact that in the conditions of new social conditions, within which the main characteristics of social coexistence are erased, the younger generation finds themselves in a precarious state of choosing the path of their existence. Digital culture and the formation of virtual reality result in a world of new opportunities. The coexistence of two realities, both physical and virtual, produces a conflict of possibilities in the mind of the subject. The modernized part of humanity, which is an information society, a consumer society, a society of postmodern quasi-values is experiencing an anthropological crisis. Both now and always, they have been searching for the meaning of life and found it in certain values that were relevant to the era. The modern Russian school, being part of globalization trends, should think about preserving the traditional cultural values of education and upbringing, and, at the same time, contribute to the flexible entry of the younger generation into the new digital reality. The development of personal potential implies the use of the younger generation resources in an adaptive manner to new social conditions.
Keywords: Communication, personality/personal potential, personality development, post-social conditions, thinking
Introduction
It is to be supposed that at all times the development of mankind has been uneven, i.e. some peoples were more developed than others in terms of civilization, who used to live in the conditions defined as primitive. In accordance with their traditions and customs, a specific mental and cognitive culture of representatives of various social communities was formed. The development of the world of culture had a local and value-based feature, which made it possible to talk about the unique cultures of Ancient India or Ancient China, Ancient Egypt or Ancient Greece. The listed civilizations were not just cultural centers, but a consequence of the triumph of progressive human thought. The existence of these cultures was characterized by a duration in time, when centuries and millennia contained a certain mental community. In the modern conditions of a globalizing world, which is represented by an ambiguous desire, on the one hand, for unity, and, on the other hand, for the search for one’s unique identity, such phenomena as technologization and digitalization determined the situation of total changes in all fields of human existence. In this context, we are not talking about millennia or centuries of historical change, but about the modern world, which is constantly being updated, changing social, mental and cognitive styles. In terms of events, time has become capacious, but fast. The set of events creates the fullness of life, and at the same time, we understand that life is not an event as an act of a certain action, but is co-existence as an act of experiencing one’s own presence in one or another status.
Under the conditions of modern social metamorphoses, a subject-centered society is being transformed into an object-centered space. The target of the ongoing transformations is the younger generation.
In the oversaturation of information flows, the impression of the fullness of life is created. In the Brownian motion of spatial displacements, social interaction is seen. Communication as a form of subject-subject interaction in the context of object-centered communications acquires a new feature of mediated interaction. The observed metamorphoses are not the product of one day. The technological order has accelerated the pace of time and the modernized part of humanity is experiencing an anthropological and personal crisis, from which it is necessary to find a way out.
Problem Statement
The situation as a whole is ambiguous. And in this ambiguity, totally imposed digital reality, digital school, digital university, from which there is no escape, the traditional question of the development of personal potential has been updated. Digitalization is given a human face. The ultimate goal of all the observed processes in the educational space is not to digitize a person, but to contribute to the development of his personality, the disclosure of his potential. The reason for the irony lies in the depreciation on a global scale of human traits in a man. The axiological crisis of human existence is the subject of reflection in the social sciences and humanities.
Research Questions
The author’s hypothesis is that the development of personality and personal potential should contribute to the integrity of human existence, and vice versa, the integrity of human existence guarantees the development of his or her personal potential. To substantiate the proposed hypothesis, the following research objectives are identified:
To consider the content of personal potential concept.
- To offer analysis of the essential features and characteristics of public relations in post-social conditions.
- To conduct a survey for schoolchildren in the regions of the Russian Federation, to find out their personal position in social activity at school and in the family.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to discover the factors that determine the integrity of human existence as a subject of a new digital reality.
Research Methods
In the process of writing the article, the authors used general logical methods of analysis and synthesis of the considered literature. The work with the article was organized within the framework of setting and clarifying research objectives that should help achieve the above goal, formulating a hypothesis, and searching for authors who study related issues.
The work with the article was carried out on the basis of the research analysis by Russian scientists: in the field of personal potential development (Asmolov, 2007; Leontiev, 2019a; Leontiev, 2019b; Yasvin, 2020a; Yasvin, 2020b, etc.); problems of communicative behavior of an individual (Muskhanova, 2019), communicative nature of thinking (Betilmerzaeva, 2020), communication and social conditions (Knorr, 2002).
Findings
The development of personality of younger generation is the subject of research in various humanitarian disciplines, and, among other things, is considered in the context of a philosophical understanding of the cultural characteristics of the process of formation and development of a modern young person. The integrity of human existence implies the formation of a person who is aware of his or her individuality and sociality. Only within the framework of comprehending one’s social nature can one educate a person. A person is a product of society. As for the cultural studies, there is a phenomenon of Mowgli kids. It’s only in R. Kipling’s fairy tale that for a child with the fate of Mowgli everything has “a happy ending”, in real life, the longer the child stays in a different (non-human) environment, the less chance that the child will be able to restore or develop physiological and social adaptation skills in the context of human society.
A detailed review of the role of the environment in personality development was proposed by the Russian scientist Vitold Yasvin (2020b), who identified six stages of environmental studies of personal development: “pedological – 1920s – early 1930s; cultural and activity – 1930–1960s; spatial – 1970s; personal and environmental – since the mid-1990s; ecological and psychological – from the beginning of the 21st century; ecological and pedagogical is being formed at the present time” (Yasvin, 2020b, p. 300). The concept of “environment” has long played an important role in research on the issue of personality development. From the point of view of Yasvin, the process of personality development is determined by the logic of positioning the environment and the individual relative to each other. Two sides are distinguished in the structure of social and environmental communication: the agent of social reality is the personality of the growing individual and a specially organized space with its own resource potential. An individual initially has a certain personal potential, which is provoked to be realized in conditions of active interaction with social environment.
The concept of personal potential, as noted by Leontiev (2019a), was introduced to denote the basic dimension – the actual personal in the personality, which, from his point of view, ‘does not directly correlate with intellectual development, with the depth and content of the inner world and with creative potential’ (p. 410). Personal potential appears as an integral, self-determining value, reflecting the measure of overcoming by a person of given circumstances, ultimately, overcoming by a person of himself (Leontiev, 2019a). According to Leontiev, personal potential reveals the idea of Asmolov (2007) a changing personality in a changing world.
In connection with the predicament of personal potential development by the environment, the question of a new sociality or post-sociality of digital culture is becoming topical. The problem of the transformation of social relations has become the subject of active analysis by modern researchers (Knorr, 2002; Grechko, 2009, etc.). The phenomenon of postsociality or postsocial conditions refers to the coming situation of transformation of social reality, which is characterized by the formation of an object-centered environment (Knorr, 2002). The digital revolution in the educational space inevitably leads us to a new format of interaction between a
teacher and a student, when artificial intelligence occupies an authoritative position in their interaction as the main object of observation, acquiring “subjective” autonomy Knorr Cetina (2002) is right when she states that objects replace people as partners in interaction and increasingly mediate human relationships, making the latter dependent on them. At the same time, we find ourselves in greater global threat, when the modern world with its new trends in social interaction in the context of digitalization and intellectualization of all fields, including educational field, causes threats to the human in a person through the degradation of the individual as an individual and the transformation into an object (Zyazyun, 2008). If in the logic of the value-cognitive definition of the relationship between subject and object, the subject, acting from time to time as an object, retained the features of subjectivity, then in the conditions of modern object-centered sociality, the subject is identified with the device he uses.
Digitalization as the basis for the development of modern communications entails the evolution of thinking. As the author notes, communications play a sense-organizing and formative role in the process of thinking (Betilmerzaeva, 2020). Understanding and accepting the inevitability of digital revolution, objectively assessing all its advantages and disadvantages, we see that personal potential development is becoming popular.
At the next stage of our research, we conducted a large-scale sociological survey among students in general education schools (see Figure 1). Two questions from this questionnaire, which show personal attitude of students to their classmates, are proposed in this study. The survey involved 2,975 schoolchildren from primary to senior grade. 55.09 % out of this number are girls and 44.91 % are boys. The survey covered the following regions of the Russian Federation:
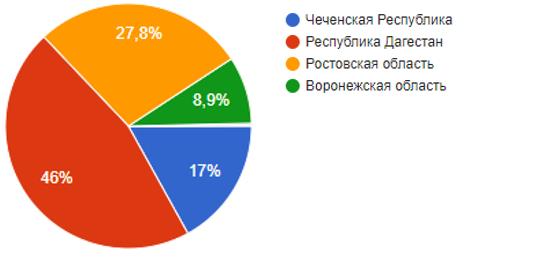
The following open-ended question was stated: What things in the class are you not interested in? Why? The result of the survey showed that the majority of schoolchildren at this stage of socialization are set up for active interaction within the framework of student activities. For example, the following positive answers were given: I am the class representative and the president of the school... I am interested in all the matters of my class; I am interested in all the cases related to my class; I am one of the active guys in the class and I can participate everywhere if I am asked; Everything what takes place in the class is interesting and exciting, because I like to take part in school life; I am interested in everything what relates to my class, since I am part of this society; I am interested in all the activities that we carry out together with my class, i.e. participation in competitions; It is interesting and I take it as an opportunity for self-development; At the moment, I want to run for class president, etc.
The answers of schoolchildren who stayed away from school activities provided the following answers: The events are not interesting to me, since they do not affect me; I hate contests, they are distracting. I need to get knowledge at school; I’m not interested in being a class representative. There a lot of activities following this position; Participation in the life of the class takes extra time; Cleaning because you clean, and then again, a mess; Cleaning class… I’m lazy, etc.
The following answers were received to an open question about what could be changed in the life of the class: I want to have such a class teacher who could support us and take us somewhere. We had another class teacher, and when he was gone for a long time, everyone quarreled and began to behave badly. In the 7th grade we behaved well and we were set as an example, but since that time everything has changed. I hope a new class teacher would resolve this conflict, but it will be very difficult for her. I understand that our class is very difficult and I think everything will calm down once we graduate from school. I wish children in our class were quieter. Some students are constantly talking, which prevents teachers from teaching a lesson, and students from ingesting the information received during the training. Some students do not listen to teachers’ remarks and argue with them about their bad behavior. I would like the number of students in our class to be reduced, because there are 39 students in my class, which is at least not entirely safe in our time, and I don’t even want to write about the noise they make. In my understanding, there should be up to 30 people in the class. I don’t know if this will pass as an example, but I would like the class teacher to warn about various events that are going to be held at school so that there is an opportunity to sign up for them. Organize more events (trip to museums, cinemas, excursions), celebrate holidays with our class (parties, holidays), have field trips, joint research work and projects. Something interesting in addition to standard training. Teaching financial literacy, for example, so that children from an early childhood know how to save or invest money properly. I would like my class to become more active, they do not want to participate in various events and as I am a responsible person, I have to prepare everything by myself. I would like to improve our relationships, I mean the relationship between the students, and so far it leaves much to be desired. Every man is for himself. Cohesion. Understanding. Mercy. For a moment, I want our class to have these qualities. Add more extracurricular activities. For example, joint trips, as they bring people closer together.
Conclusion
The conducted research shows that, firstly, the process of developing personal potential is relevant within the boundaries of modern object-centered sociality. Secondly, childhood is preserving its traditional feature of expecting the best, striving for knowledge, communication, and social interaction. Despite the fact that some of the students have a desire to distance themselves from social activity, but this fact is not total and not ubiquitous. Goal-directed activity of the representatives from the educational field, theorists and practitioners should contribute to the preservation and multiplication of those fundamentally valuable features of traditional education and upbringing in order to develop the personal potential of students and create a guaranteed subject-subject interaction of participants in social reality.
References
Asmolov, A. G. (2007). Psychology of Personality: Cultural and Historical Understanding of Human Development. Sense.
Betilmerzaeva, M. M. (2020). On the question of the communicative nature of thinking. Society: Philosophy, History, Culture, 6(74), 18–22.
Grechko, P. K. (2009). New sociality: experience of interpretation. Questions of social theory, 3, 302–317.
Knorr, C. K. (2002). Object Sociality: Social Relations in Post-Social Knowledge Societies. Journal of Sociology and Social Anthropology, 1. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/obektnaya-sotsialnost-obschestvennye-otnosheniya-v-postsotsialnyh-obschestvah-znaniya
Leontiev, D. A. (2019а). Psychology of meaning: nature, structure and dynamics of meaning reality. Sense.
Leontiev, D. A. (2019b). Three targets: personal potential – why, what and how? Educational policy, 3(79), 10–16.
Muskhanova, I. V. (2019). Problems of the formation of a person’s communicative behavior in ethno-cultural environment. Pedagogical Bulletin, 11, 52–54.
Yasvin, V. A. (2020a). Technology of environmental design in education. Social and political studies, 1(6), 74–93.
Yasvin, V. A. (2020b). Formation of the theory of personality development environment in domestic pedagogical psychology. Psychology. Journal of the Higher School of Economics, 17(2), 295–314.
Zyazyun, I. A. (2008). Philosophy of pedagogical activity. Cherkasy National University named after B. Khmelnytsky.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
23 December 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-128-7
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
129
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1335
Subjects
Science, philosophy, academic community, scientific progress, education, methodology of science, academic communication
Cite this article as:
Betilmerzaeva, M., Musaeva, M., & Sugaipova, E. (2022). Personal Potential Development In Post-Social Conditions. In D. K. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Knowledge, Man and Civilization- ISCKMC 2022, vol 129. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 228-234). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.12.29

