Abstract
The quality of the products of the financial services market is largely determined by the competition level between its main subjects, which is formed under the influence of many factors of a macroeconomic and global nature. Assessing the competitive environment of participants in the banking services market seem to be quite relevant. The Russian banking system is at the stage of ongoing structural institutional reformation, which is reflected in its quantitative narrowing, statisticization and reduction of financial accessibility at the meso level. This article discusses various aspects of the current state of banking competition in the Russian market of banking services in the main areas of banking activity. The purpose of the study is to identify trends in the development of banking competition. As a methodological basis, indicators of evaluation and analysis of the competitive environment in financial markets in the form of such instruments as the concentration level, as well as the Herfindahl-Hirschman index were used. The authors used the method of dynamic and structural analysis, and the coefficient method. The state of banking competition in the Russian segment of the banking services market is analyzed. The largest players of the banking market in the areas of lending, deposit operations and total banking assets have been identified. The problematic aspects that hinder the formation of a healthy level of competitive environment in the Russian banking system are identified, related to the systematic nationalization, monopolization, and centralization of the banking services market.
Keywords: Banking system, banking competition, banking services market, concentration, total banking assets
Introduction
The development of competition in the commodity and financial markets was one of the highest priorities in various schools of economic thought. Approaches to the development of competition, the expediency and necessity of its regulation, or lack thereof, have caused discussions in recent years between representatives of the classical school, monetarists, and Keynesianism. To date, there is no doubt about the importance and importance of regulating the level of competition in various markets within the national economy. Banking competition is no exception, the state of which has been changing rapidly in recent years in the context of a changing external and internal institutional environment. This task can be called non-trivial, since the banking sector of the national economy is regulated by the state, as well as due to the influence that its condition has on the country's economy.
The relevance of the study is caused by the need to study the trends in the development of banking competition, since both the largest and medium-sized and small banks are interested in its condition because the stable functioning of banks characterizes the effectiveness of the national economy and the banking system of the country. The stability of the banking system is possible if the banking services market is competitive (Salin et al., 2017; Tashtamirov, 2020).
Assessing the impact of competition on financial stability is an important issue for both state economic regulation and antimonopoly authorities. Before the global financial crisis, several studies emphasized the role of competition in the banking industry (Beck et al., 2006). These studies focus on studying the relationship between competition and several different factors, including market structure, market competitiveness, banks' efficiency, their risky behavior, and financial stability. Indeed, one would expect that when banks operate in a more competitive environment, they are more likely to participate in competitive policy, achieving higher levels of productivity and other efficiency (Chortareas et al., 2016; Kazimagomedov, 2017). It is expected that increased competition will simplify access to financial services and external financing for the general population, improve the quality and innovation of financial products and generally lead to an increase in the economic well-being of the country.
On the other hand, competition does not necessarily lead to financial stability (Berger et al., 2009). Competition in the 2000s began to develop in such a way that banks began to take risks more often, especially when they are forced to offer their services at more competitive prices. In the context of the global financial crisis of 2008–2009, the consequences have intensified even more where the danger of a high-risk culture in the banking sector has caused the need to reassess the prudential rules currently in force.
In addition to discussions about the relationship between competition and stability, most of the literature on banking competition focuses on the relationship between banking competition and other factors such as market structure, efficiency, and competitiveness.
In the Russian banking system, the level of competition has significantly decreased in recent years, as evidenced by the data of various researchers. Among the main reasons for this phenomenon in the banking system of Russia are the nationalization (Donetskova, 2020; Ezrokh, 2017), increased concentration of bank capital in the process of general consolidation of banking institutions (Shikhakhmedov & Nechaev, 2019), which as a result leads to the centralization of market power in the hands of a limited group of banks, most often state-owned. Such processes weaken the motivation to increase the efficiency of their activities by credit institutions, whose scale of work in terms of spatial territorial development and the size of capital is negligible. The situation in the banking services market is being formed in such a way that in the conditions of the functioning of several hundred banks, the overwhelming number acts in such a way that their existence is almost imperceptible within the macro-banking level.
Two main conclusions are drawn in the scientific literature regarding the processes of developing a competitive environment in the banking services market: (1) strengthening of the supervisory function by the mega-regulator, which leads to a rapid reduction in the total number of banking institutions and an increase in banking assets in the limited hands of large banks (Ibrahimov et al., 2021); (2) deliberate nationalization of the banking system, monopolization of the banking services market and restriction of foreign participation in Russian banking capital (Ibrahimov & Tashtamirov, 2020).
Problem Statement
An important issue of ensuring the effective development of the banking services market is the achievement of a healthy level of competition between credit institutions. There is a rather difficult situation in the banking services market in Russia, since a group of several banks has secured significant amounts of banking assets and capital in their hands. Accordingly, in such conditions, there is a need for systematic monitoring of the degree of competitive freedom in the banking system.
Research Questions
The study of banking competition in the conditions of increasing statistic of the banking services market is seen as a rather relevant direction for the scientific and economic community and within the framework of this article requires solving the following tasks:
- to determine the level of concentration of banking assets in Russia in recent years;
- to establish the top 10 Russian banks by the main types of banking services provided;
- to assess the level of market power and concentration of the country's largest banks in the market.
Purpose of the Study
In this regard, the purpose of this study is to identify problematic aspects of the current state of banking competition in the Russian segment of the banking services market.
Research Methods
To characterize the Russian banking services market, it is necessary to analyze the state of banking competition in recent years in a relevant way. The solution of this problem requires an analysis of the state of banking competition in a specific period. Let's take a period of time – from January 1, 2015, to January 1, 2022. Using the example of the 5 largest banks (Sberbank, VTB, Gazprombank, Alfa-Bank and Rosselkhozbank), we will identify trends in banking competition over the past 6 years.
The study is based on the use of several coefficient indicators that characterize the qualitative and quantitative state of Russian banking competition in recent years. Firstly, it is the determination of the market share of a credit institution in the banking services market using formula (1):
(1)
where
– the percentage of a particular credit institution in the total volume of sales of banking services in the market;
– the volume of sales of banking services of thecredit institution in the market;
– the total number of credit institutions in the banking services market.
Secondly, the calculation of the market concentration coefficient by the formula (2):
(2)
where
– the percentage share of the i largest credit institution in the banking services market;
– the number of the largest credit institutions in the banking services market under consideration.
Thirdly, the most frequently used indicator for assessing the state of competition in economic research is the Herfindahl–Hirschman index, which is calculated using the formula (3):
(3)
where
– the percentage share of the largest credit institution in the banking services market;
– the total number of credit institutions operating in this market.
Statistical analysis using these coefficients was carried out on such indicators of the banking system as: loan portfolio in the context of borrowers, the size of the bank's own capital, deposits of individuals. The sources of statistical data are the official website of the Bank of Russia, the banking sector statistics section, as well as the Internet resource Банки.ру [Banki.ru].
Findings
According to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, the stable trends of the last five years are represented by monopolization, federalization, and centralization, as well as globalization. Monopolization is the main trend to focus on, whereas federalization/centralization and globalization are concomitant trends that have a directly proportional or inversely proportional effect, respectively, on the trend of monopolization.
Earlier, there was a decrease in the number of banks in the banking system over the designated period. This is a sign of the development of monopolization not only in the banking sector, but also in other commodity markets in general. Another factor is the size of the capital of these banks, namely the fact of its uneven distribution. This factor is also important because banking competition usually boils down to the competition of banks of comparable sizes. That is why one large bank can act as a barrier for many small banks, since in the current realities of the banking system such a bank can compete only with another equally large bank. In addition, the state controls most of the assets of the banking system (the five largest banks are considered state-related) both directly and indirectly, which also indicates the development of monopoly structures in the banking market.
Determining the competition in the banking system, it is possible to observe an increase in the level of concentration of the bank's assets. With this trend, by the beginning of 2021, the TOP 5 largest banks own 60 % of all assets of the banking system, twenty banks own 80 %, and two hundred own 99 % (shown in Table 01).
A significant share of these assets is in the hands of banks with state participation. There has been an increase in total assets and total capital over the last five-year period, where the first indicator increased from 43.9 to 59 %, and the second – from 48.9 to 64.2 %. In general, there is an increase in the banking assets of the five banking leaders, and significant. Banks from the second group are also experiencing growth, but it is difficult to compare it with the growth of banks in the first group. At the same time, the situation has worsened for banks from the last two groups over 5 years: assets are consistently declining, and they are declining very significantly. Interestingly, their reduction is due to the growth of assets of banking leaders.
Banking activity underwent not the best changes during the pandemic. However, in the second half of 2021, the participants of the banking market began to show activity and entered the path of growth. Thus, in the banking system, an increase in assets is visible for 59 % of participants in the top 10 large banks and 37 banks from the top 50. It is important to note that a significant share of assets is in the hands of three "state banks": Sberbank, VTB and Gazprombank. Together, they own 53 % of all banking assets (Table 02).
The quality of the banks' loan portfolio has a huge impact on interbank competition. Considering the impact of the pandemic on the economy, the Bank of Russia believes that for an indefinite period in the banking system there will be an increase in overdue credit debt and poor-quality servicing of credit debt. At the same time, banks can correct the situation by restructuring loans to affected borrowers under programs developed by themselves, as well as by providing credit holidays.
It is for such cases that the Central Bank of the Russian Federation has given the right to temporarily not form additional reserves to credit institutions, believing that loan recipients will return to normal servicing of credit debt soon.
The analysis of the composition and structure of the banking market shows the presence of a leader in the person of Sberbank PJSC, which retains its position during the designated period. In this regard, it is advisable to determine the shares of the 5 largest banks according to various criteria – for example, such as lending to individuals and others (Figure 01).
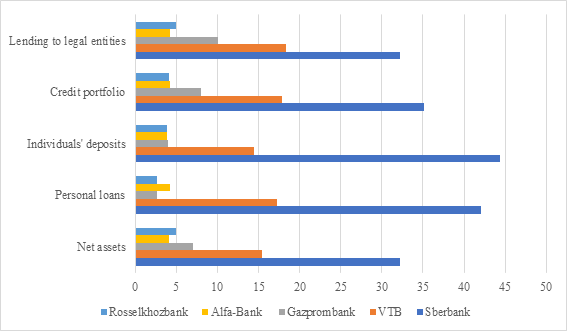
Sberbank is the undisputed leader in each of the 6 criteria. It is followed by VTB, which lags it at least twice in terms of its indicators; in some indicators, the gap between them is even greater, as, for example, in the case of lending and deposits of individuals, where the difference between the market shares of Sberbank and VTB is 24 and 30 %, respectively. Regardless of market shares, according to one level of capitalization of banks, we can talk about the concentration of capital, but to consider the presence of economic concentration as a fact, it is necessary to calculate the Herfindahl-Hirschman index and the concentration index.
The Herfindahl-Hirschman index shows the degree of monopolization of the market. If this indicator is high, it indicates a negative state of banking competition.
HHI = 974.06 (Sberbank) + 239.63 (W) + 50.13 (Gazprombank) + 16.48 (Alfa-Bank) + 14.67 (Rosselkhozbank) = 1294.97.
In terms of total assets, according to calculations, the Russian banking services market can be called moderately concentrated (1000<HHI<1800).
Let us calculate the concentration index, which reflects how much of the market share is accounted for by the largest companies. To do this, it is enough to sum up the shares of these companies:
CR 5 = 31.21 % (Sberbank) + 15.48 % (VTB) + 7.08 % (Gazprombank) + 4.06 % (Alfa-Bank) + 3.83 % (Rosselkhozbank) = 61.66 %.
As you know, the closer the value is to 100, the more monopolized the market is. In this case, this indicator is more than half, and this value falls only on the 5 largest banks (plus 31 % of the 61 % received is the share of Sberbank).
Let us consider the dynamics of the level of concentration of banking assets in the country's largest banks from the top 5 over the past 5 years.
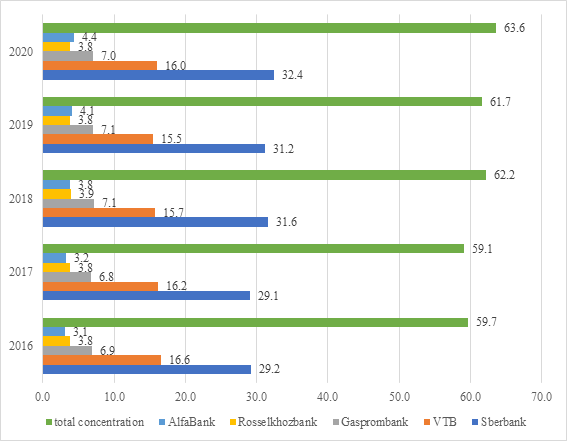
The concentration of banking assets at the disposal of the country's largest bank increases annually, as shown in Figure 2. Almost a third of all total banking assets are held by Sberbank PJSC, while considering the concentration in the hands of the five largest banks, the value increased from 59.7 % in 2016 to 63.6 % in 2020. In accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 26, 2007, No. 409 PJSC Sberbank and PJSC VTB, according to Figure 2, have a dominant position in the banking services market in terms of banking assets, which indicates the presence of risks to ensure a healthy level of competition in the Russian banking system.
There are clear leaders in the banking services market, from which other credit institutions lag, and the gap between them is quite large. Thus, the concentration level can be called high.
Conclusion
The nature of monopolization of the banking services market is influenced by various trends. Thus, the trend of federalization of the domestic banking system is expressed in the systematic continuation of the policy of revoking licenses from small and medium-sized banks, mainly operating in regional socio-economic systems. In turn, larger Russian banks absorb credit organizations and become the only providers of banking services in many regions of Russia through the development of a branch network and operational offices. So, in 2016, the number of regions in which there was no credit institution whose head office was in this subject of the country was 12 units. At the beginning of 2021, there are 24 regions in Russia where there is no credit institution registered in the subject of the country. On the other hand, after the closure of the so-called "regional banks", a branch of a large federal bank does not always take their place, which affects the reduction of financial accessibility.
The trend of centralization is associated with the transfer of the management apparatus to large cities, and it is realized through a decrease in the number of branches and an increase in the dependence of network bank units on the central office. In fact, the trends of federalization and centralization are so closely related that they can be combined into one trend.
Globalization has the opposite effect. In this regard, it is indicative of a decrease in the volume of total assets of foreign banks over 10 years (from 2010 to 2021 – from 10.8 to 6.6 %). Again, there is an increase in state influence in the banking sector of the national economy, as already noted above (it turns out that federalization/centralization and globalization in the Russian banking market are opposite trends to each other, even outside of the influence they have on the development of monopoly structures in this market). In addition, foreign banks are not engaged in lending to individuals, but rather servicing the work of companies from their countries and Russian banks in their countries. In order to compete with Russian banks in lending to individuals, foreign banks could provide loans for a lower fee, which for a combination of reasons is impossible, and if possible, would lead to a significant reduction in the cost of credit resources. In this aspect, the leaders of the banking market act as a barrier for foreign banks.
Thus, in general, in the dynamics of the last five years, there has been an increase in the share of state-controlled banks, which represents the direction of further development of banking competition in the Russian banking services market.
References
Beck, T., Demirgüç-Kunt, A., & Levine, R. (2006). Bank concentration, competition, and crises: First results. Journal of banking & finance, 30(5), 1581–1603. DOI:
Berger, A. N., Klapper, L. F., & Turk-Ariss, R. (2009). Bank competition and financial stability. Journal of Financial Services Research, 35(2), 99–118. DOI:
Chortareas, G., Kapetanios, G., & Ventouri, A. (2016). Credit market freedom and cost efficiency in US state banking. Journal of Empirical Finance, 37, 173–185. DOI:
Donetskova, O. Yu. (2020). Bank management under conditions of interbank competition in the Russian market. Management Sciences, 10(4), 52–66. https://econpapers.repec.org/article/scnmngsci/y_3a2020_3ai_3a4_3ap_3a52-66.htm
Ezrokh, Y. S. (2017). Evolution of monopolism in the Russian banking environment. Society and Economy, 5, 82–99. https://ras.jes.su/oie/s020736760011788-5-1
Ibrahimov, K. K., & Tashtamirov, M. R. (2020). Periodization of the transformation of the banking system in modern Russia. Bulletin of the Chechen State University, 39(3), 62–74. https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=43831594
Ibrahimov, K. K., Tashtamirov, M. R., & Bazaeva, A. R. (2021). Impact of public-political factors on transformational processes in national banking systems. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (EpSBS), (October 22–25, 2020) (pp. 2109–2115). European Publisher.
Kazimagomedov, A. A. (2017). Peculiarities of the competitive environment in the market of banking products. Banking, 4, 80–83. https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=28915302
Salin, V. N., Sevruk, V. T., & Tretiakova, O. G. (2017). Statistical indicators for assessing the level of competition in the banking system. The world of the new economy, 2, 74–81. https://wne.fa.ru/jour/article/view/128/0
Shikhakhmedov, R. G., & Nechaev, A. N. (2019). The impact of banking sector consolidation on its sustainability. Banking, 8, 26–33. https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=39199607
Tashtamirov, M. (2020). The effect of the state of the banking system on national economic resilience. E3S Web of Conferences, 208, 03056. DOI: 10.1051/e3sconf/202020803056
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 November 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-127-0
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
128
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-742
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, translation, interpretation
Cite this article as:
Tashtamirov, M. R., Mazhaeva, M. A., & Betieva, Z. H. (2022). State Of Banking Competition In The Banking Services Market In Russia. In D. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism (SCTCMG 2022), vol 128. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 624-632). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.11.85

