Abstract
The paper addresses the issues of managing the sustainable regional development in the context of dynamic socio-economic processes. The authors analyzed the causes and prerequisites for sustainable development and its main directions. Based on the analysis, the paper examines the state management of the economy in modern conditions. The study identifies the main objectives crucial for strategic regional management: 1. Forming competitive advantages. This objective is the basis for further regional development, since it focuses on strengths and improve weaknesses. Based on the identified strengths and weaknesses, new objectives to ensure an effective strategy for the region management are developed; 2. Reducing a negative impact of the external environment. Due to the measures taken, it is possible to eliminate the impact of negative factors and promote the region development. This objecive is closely related to analysis of the external and internal environment of the region, and formation of competitive advantages. According to the authors, practical significance of the study lies in clarifying the theoretical provisions and developing practical recommendations on the main directions for improving the structural policy of local self-government, and determining the strategic priorities for structural transformations of the regional economy using modern innovative developments and contributing to sustainable development and competitiveness of the regional economy and its industries.
Keywords: Management, region, strategy, sustainable development
Introduction
The issues of assessing sustainable development and the practice of strategizing at the level of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have been the subject of numerous studies. The number of municipal strategies for socio-economic development is much fewer. Analysis and generalization of the practice of municipal strategic planning is extremely relevant, since local self-government is an integral part of the system of federative relations.
It should be noted that the permissive regime of municipal strategizing, the unresolved issue of the relationship between strategic and territorial planning, the permanent deficit of municipal budgets, the underestimation of the role of stakeholders in the development and implementation of municipal strategies, and the lack of attention to the institutions of intermunicipal cooperation hamper the potential opportunities inherent in the Institute of Strategy (Dyakov, 2020)
On the one hand, the goals stated in most strategies are extremely abstract, on the other hand, they are objectives, the solution of which, one way or another, is in the local government jurisdiction. Analysis of strategizing in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation revealed that the lack of proper regulatory and methodological support for strategic planning in the regions, varying requirements for the content of strategy sections, and different detailing of approaches to the process of their development result in a similar content and biassed assessment of the competitive advantages of the regional socio-economic complex.
A number of approved, improved and discussed strategies that cover the basic principles of strategic planning (unity and integrity, balance, consistency, delimitation of powers, etc.) are observed fragmentarily, which is largely due to the lack of the most important federal documents, in particular, a strategy for spatial (territorial) development.
Thus, modern approaches to strategic management are based on a set of interrelated measures for strategic development, implementation, and management that correlate with managerial decisions.
A number of authors study the features of strategic planning in the constituent entities of the Southern Federal District, where by the beginning of 2020, 2 out of 8 entities had approved strategic documents for socio-economic development until 2030, and in other regions, projects are being developed and discussed with stakeholders, business, science, and population.
The concept of 'sustainable development' was introduced into wide use by the World Commission on Environment and Development.
The main goal of sustainable development is satisfaction of the needs of society. It is this principle that admonishes a person 'not to dig a hole in which he will be trapped sooner or later', that is, a person needs to limit his needs in order to rationally use resources.
At present, sustainable development pursues the goal of identifying the optimal trajectory of transition from the current state to the 'desired future'. The above definition of sustainable development can be seen through the prism of economic relations. Determination of directions and specific tools for their realization should be the next stage, which is being gradually implemented, including by each country individually. The state plays an equally significant role in the management of modern living conditions of population.
Problem Statement
The complexity of the considered issues lies not only in the absence of a unified methodology for developing a strategic plan, but also in the absence of scientific schools on regional strategic planning and management, similar to the schools created by I. Ansoff and M. Porter (strategic planning at the enterprise level and the boundaries approved by legal documents, which contain the main provisions of the strategy).
Strategic planning is a tool needed for identifying the primary goals of the organization and supported by a set of measures to achieve the chosen goal, either with the help of existing resources and capabilities, or by creating new ones.
At a certain stage of the organization performance, strategic planning serves as an indicator for making the right managerial decisions, depending on the chosen goal (Idigova et al., 2019).
Three provisions should be singled out in the modern paradigm of strategic planning, on the basis of which a strategy is developed and implemented:
1. Strategic managerial decisions aimed at eliminating existing strategic problems in accordance with the strategic course and with regard to the impact of external factors.
2. Changes management focuses on changes through the development of plans, projects and special regional programs.
3. Strategic control needed for assessment of the efficiency of strategic decisions, plans and projects.
Based on the analysis of a number of scientific sources, the following definition of the region is considered to be the most relevant for the study (Strategy, 2021).
Region is an entity of the Russian Federation and the most important element of the national economy with a complex multi-level system, which is characterized by the historically established integrity and unity of socio-economic processes, the commonality of economic structures, and the characteristic direction of the development of production forces based on the conglomerate of a complex of natural resources with the developed and prospective material and technical base (Novikova & Strogonova, 2020)
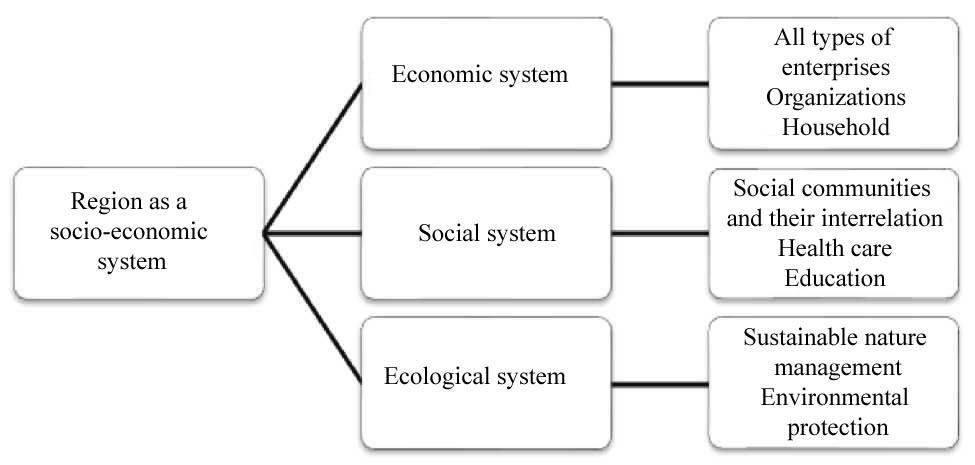
This entity is endowed with certain rights, authorities and management. Figure 01 shows that the economic, social and environmental systems are the most significant and system-forming in the region.
Region as a socio-economic system comprises five subsystems: system-forming base, system-servicing complex, ecology, population, market infrastructure. The combination and interconnection of these subsystems into an integral socio-economic 'organism' is due to human and his activity, which is the basis for each of the subsystems to form a socio-territorial entity.
Research Questions
Considering the region as a complex socio-economic system with an internal environment (economic, social and environmental subsystems), it should be noted that it is a link of a higher hierarchical level, that is, sustainability of the regional socio-economic system depends not only on the stability of its constituent subsystems, but also on the stability of socio-economic systems of a higher level (the state and the world as a whole). The socio-economic environment of a particular region (internal regional product, volume of investments in fixed assets, foreign trade turnover, unemployment rate, etc.) can largely determine the choice of a regional development strategy and the success or failure of a particular strategy (Idigova & Rakhimova, 2021).
In our opinion, the economic and geographical environment of the region is equally important in the process of strategizing, which has serious specifics and thus cannot be ignored. The competitiveness of the region is interconnected with strategic management, which is aimed at maintaining a high level of competitiveness not only at present, but also in the long term perspective, thereby ensuring achievement of the desired goals and regional development in the future, despite volatility in the external environment.
The sustainable regional development is understood as a positive trend in the economic, environmental and economic sphere, which is aimed at preserving and ensuring sustainability, meeting human needs, and improving the living standards now and in future.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is the theoretical and methodological substantiation and development of practical tools for long term strategic management and sustainable development of regions with regard to globalization effects of the modern economy.
Research Methods
The study employed the methods of system and process approaches, the historical and structural-functional method, the method of generalization, and the methods of expert assessments to identify the main theoretical aspects of sustainable development in the regional management system.
Findings
Strategic planning for sustainable socio-economic development of the region implies a strategy for long term regional development aimed at stabilizing the socio-economic situation in the region, which include the enhanced material wellbeing of population, increased quality of life, and efficient use and distribution of resources with regard to the impact of internal and external factors (Serenkov et al., 2018).
To date, most Russian regions do not have strategic development plans, and often the existing plans are just a general direction for development of the territory not supported by measures for their implementation. The state regional policy is aimed at a balanced socio-economic development of the regions of the Russian Federation and reduced inter-regional differentiation in the socio-economic state of the regions and the quality of life. A special aspect can be distinguished in the strategic regional management, namely the effect of integrative and globalization processes.
It is the development of globalization effects that modifies the tools for strategic regional management, which comprises special mechanisms for making strategic managerial decisions, the principles of creating competitive advantages and managing competitiveness, and a strategy as a whole, which can ensure long term sustainable development of the region and the country as a whole (Idigova et al., 2019).
Conclusion
In our opinion, the development goal is the priority for the regional development strategy, since strategic planning implies that the strategic activity should be aimed at achieving the chosen goals.
In turn, goal setting is based on the comprehensive analysis of the socio-economic situation in the region.
Sustainable development aims to improve well-being and protection. The state recognizes that measures to eliminate poverty must be taken together with efforts to increase economic growth and address a range of issues in the field of education, health, social protection and employment, as well as issues on combating climate change and protecting the environment. Public administration in modern conditions is a very complex social phenomenon, which includes management of the economy. The role of the state in the economy is controversial.
The goal of any government is the growth of public welfare and maintenance of socio-economic and political stability. It is equally important to create favorable conditions for economic growth and, in modern conditions, to ensure the innovative development of the economy. The economic policy of the state is aimed to compensate for imperfections of the market. Thus, the market is not able to resist monopolization, and the state is able to protect competition by pursuing an antimonopoly policy. Another goal of the socio-economic policy of the state is associated with the formation of an effective system for public good provision.
The management of the market economy is one of the most important priorities of the state. The market economy, which replaced the command economy, has its specifics; it does not tolerate direct interference from the state. The result could be obtained only by creating certain prerequisites.
All in all, the developed and developing countries with a market and other types of economy must define the objectives of economic and social development with regard to its sustainability.
It can be argued that sustainable development requires a comprehensive solution of economic, social and environmental problems.
Effective management of sustainable development in modern conditions necessitates transformation of conventional methods and approaches to strategic management. The principles of the strategy formation and management, namely the principles of complex adaptability, dynamism, global competitiveness, and strategic marketing management, play a crucial role in the development of goals, objectives, and managerial decisions and ensuring the competitiveness of regions.
References
Dyakov, O. P. (2020). The main components of the formation of corporate culture in the organization. Formation of a market economy. Social and labor relations: theory and practice, 3, 94–100.
Idigova, L. M., & Rakhimova, B. K. (2021). Current issues of digital transformation of the oil and gas industry. Problems of the economy and management of the oil and gas complex, 1(193), 18–21. DOI:
Idigova, L. M., Salgiriyev, A. R., Tasuyeva, T. S., & Chaplayev, H. G. (2019). Use of national economy branches for transition to innovative technological development. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences EpSBS, 2151–2157. DOI:
Idigova, L. M., Tagaev, C. K., Tasueva, T. S., Israilov, M. V., & Magomadov, E. M. (2019). Modernization of regional industry on the threshold of digital economy. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences EpSBS, 2158–2166. DOI:
Novikova, N. V., & Strogonova, E. V. (2020). Regional aspects of studying the digital economy in the system of economic growth drivers. Journal of new economy, 76–93.
Serenkov, P. S., Kuryan, A. G., & Volontey, V. P. (2018). Methods of quality management. Infra-M.
Strategy of digital transformation of manufacturing industries in order to achieve their digital maturity UNTIL 2024 and for the period up to 2030 (2021). Ministry of Industry and Trade of Russia, 3–18.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 November 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-127-0
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
128
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-742
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, translation, interpretation
Cite this article as:
Khagaeva, A. V., Majiev, A. H., & Majiev, K. H. (2022). Principal Directions In Sustainable Development Of The Regional Management System. In D. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism (SCTCMG 2022), vol 128. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 345-350). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.11.48
