Abstract
The problem of successful socialization of students with disabilities is relevant when setting priorities for the development of the educational system of Russia. In recent years, the number of students with disabilities has been steadily increasing. The aim of the study was to develop a model and a program of psychological and pedagogical support of students in the system of secondary vocational education, ensuring their personal and professional development, successful socialization in modern society. The methods of the scientific search were used. The problem field in the organization of psychological and pedagogical support of the studied category of students has been established, due to persistent health disorders that contribute to the formation of specific personality characteristics. The article presents a program of vector psychological and pedagogical support for students with disabilities and disabilities in the system of secondary vocational education, which allows to purposefully influence the development of the student's personality, and contributes to his successful socialization. The content of the program was implemented in several directions, including socio-psychological diagnostics, information and educational work and correctional and formative activities. The result of the work carried out was the formation of adequate self-esteem among students, an increase in the level of socialization. Vector psychological and pedagogical support of students with disabilities provides a comprehensive solution to problems, provided that all participants in the educational process are involved in this process. The presence of a clear program and the possibility of its implementation allows you to achieve your goals (diagnostic, adaptive, rehabilitation-forming).
Keywords: Health restriction, model, psychological and pedagogical support, program
Introduction
One of the priority and significant directions of the progressive movement of the education system of the Russian Federation is the solution to the health problem of the younger generation. From this point of view, the creation of favourable conditions conducive to the successful entry of students into the social environment, and the guarantee of equal starting opportunities for them, including for children with disabilities, and the disabled, becomes an important task facing the system of SVE (secondary vocational education). The unfavourable trend of a systematic increase in the number of disabled children noted in many studies requires the search for solutions to work with this category.
The materials published on the website of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation for 2020 indicate that 13626 people with disabilities due to various health conditions are studying in the secondary vocational education system, and accordingly they need special psychological and pedagogical support that meets their needs. At the same time, the educational organization is entrusted with the mission of creating guaranteed conditions for the full and free development of students, obtaining high-quality secondary vocational education without compromising their health. Purposeful psychological and pedagogical support provides substantial assistance and support to a future mid-level specialist and provides conditions for professional and personal development. The materials published on the website of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation for 2020 indicate that 13626 people with disabilities due to various health conditions are studying in the secondary vocational education system, and accordingly they need special psychological and pedagogical support that meets their needs. At the same time, the educational organization is entrusted with the mission of creating guaranteed conditions for the full and free development of students, obtaining high-quality secondary vocational education without compromising their health. Purposeful psychological and pedagogical support provides substantial assistance and support to a future mid-level specialist and provides conditions for professional and personal development.
The basic principles of children with deviations in their development are set out in the work of Vygotsky (1983). The modern scientific paradigm of psychological and pedagogical support as a subject of scientific research was considered in various directions: school education (Bokova & Tarakhov, 2019), including those with disabilities (Bayramov et al., 2018; Bikbulatova et al., 2018); higher education students (Aismontas & Odintsova, 2017; Panov & Kaptsov, 2021; Sobkin et al., 2020). Separate studies present domestic and foreign experiences of universities in providing and supporting students with disabilities (Melnik et al., 2017). It should be noted that several studies raise the issue of building a model of interaction between the subjects of the educational process in the psychological and pedagogical support of healthy students (Subbotina, 2007) and the problem of training and individual socio-psychological support of persons with disabilities in the health of certain nosological groups (Stanevsky & Khrapylina, 2017).
However, there are not enough studies on the implementation of this process in the system of secondary vocational education. The organization of training for students with disabilities in obtaining secondary specialized education has its characteristics. Vector support provides the creation of conditions for the subject of development to make optimal decisions in various situations of life choice.
Any educational process, including the vocational education of students with disabilities, is closely related to the process of upbringing and, as a result, the socialization of the individual (Mudrik, 1997; Ospuk, 2018). In an educational institution, a system of pedagogical support should be created, moreover, managed, coming not only from the demands of society but also from the very personality of the child (Gazman, 1995).
Social education is connected, first of all, with the creation of pedagogical conditions for students with disabilities for full and versatile development, obtaining professional education for further inclusion in everyday life. The purpose of social education in a vocational education institution should be the prevention of social insufficiency and the formation of the ability and readiness for a relatively independent life in modern society (Fedorova, 2006).
In the system of secondary vocational education, psychological and pedagogical support is aimed primarily at the development of the personality of the student as a whole, and in particular at the development of professionally significant qualities that contribute to adaptation to the conditions of life in the society of students with disabilities.
Problem Statement
Our research was carried out with students who had health limitations, including disabled students studying at the Faculty of Secondary Vocational Education in the number of 12 people of the Amur State University of Blagoveshchensk. The study group included students of 1-2 courses who had a category of "disabled child" for a general disease with a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus - four people, two oncological pathologies, 4 people with musculoskeletal disorders and two students with disabilities had problems with the organ of vision. The students participating in the experiment (7 people) entered the faculty of vocational education based on basic general education and the rest based on secondary education.
The presence of restrictions in the student's state of health due to somatic pathologies often leads to restrictions in communication with fellow students, adults, the outside world. This kind of narrowness of contacts leads to the formation of egocentric attitudes. At the same time, in the conditions of family upbringing, as a rule, such children are subjects to overprotection, unconditional acceptance of him as special, experiencing various kinds of difficulties. Such an approach can lead to the inability of a developing personality to predict his future, to socialize in society. The task of psychological and pedagogical support in this situation is the removal of such complexes from students and the formation of the ability to make their own decisions and feel comfortable in society. From these positions, it is also important to create a healthy living environment for students with disabilities.
Research Questions
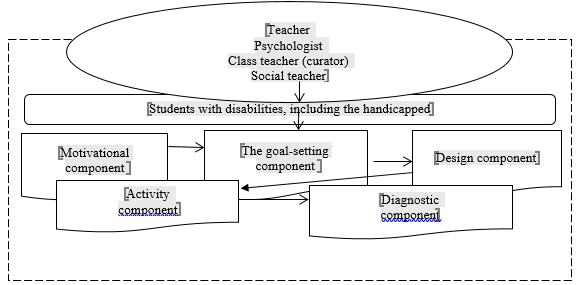
Based on the results of preliminary studies, the process of psychological and pedagogical support is considered by us from the standpoint of implementing a model that includes the following components (Fig. 1):
- motivational - aimed at establishing emotional contact between the subjects who find themselves in the process of these relationships (the student and the psychologist, teachers). This interaction involves working together and discussing the results and the process based on mutual cooperation;
- goal-setting consists in setting near and far goals, outlining prospects to determine the content of the work, finding options for interaction and joint activities to solve the tasks;
- design (development of PPPS based on primary diagnostic data, creation of pedagogical conditions for the implementation of the program and its information and analytical support);
- activity - practical implementation of the developed program taking into account the existing shifts, based on the results of current diagnostics, analysis and interpretation of data, and correction of interactions in case of unforeseen situations;
- diagnostic, aimed at a reflexive analysis of the results of the implementation of the program, making possible adjustments with the prospect of further work in this direction.
At the beginning of the experiment, we studied the characteristics of students with disabilities to create their social portrait. The psychometric test of K. E. Sishora, G. N. Kazantseva (diagnosis of the level of self-esteem of the individual), the method of Rozhkov (2004) to assess the socialization of students with disabilities.
As a result of the diagnostic methods, the characteristics of students with health problems (including the disabled) were identified. Analysing the results of the psychometric test by K.E. Sishore (as cited in Rozhkov, 2004), it can be noted that for students with disabilities, inclusion in a group is a problem.
"How would you assess your belonging to the group?" Answering the question, the majority (10 people) of the respondents do not feel like full-fledged members of the group, as a rule, their life activity proceeds separately from the collective. At the same time, 8 people would like to stay in their group, which follows from the answers to the question about the possibility of transferring to another educational team. Asking the question about the relationship between the members of the group, we pursued the goal of determining the comfort of being in this environment for students with disabilities. However, the respondents had difficulty describing their relationships among classmates ("I don't know how to say it"; "it's hard for me to assess", etc.). Thus, the level of group cohesion in groups where students with health disabilities study are low according to the results of the survey from the position of the respondents.
The results of the study show that the relationship with the management (class teacher, social teacher, subject teachers) of students with disabilities is quite stable, eleven respondents recognized them as such. This indicator shows that, in general, students trust their leadership, and, accordingly, the program of psychological and pedagogical support is perceived by them positively.
Analysing the results of the study at the preliminary stage of work according to the method of Kazantseva (as cited in Rozhkov, 2004), aimed at diagnosing the level of self-esteem of the individual, it was found that the majority of respondents (10 people) had low self-esteem and only two students had it adequate. Students with disabilities hardly count on success in their affairs (75% of answers), they lack confidence in their abilities. In some students' answers, there were pessimistic notes related to their future, it seems to them that they will not achieve anything in the future (58.3% of answers). Some students (33.3% of responses) noted that at times they feel they are not needed by anyone. This situation requires making adjustments to the process of psychological and pedagogical support.
Having studied the data of the factual material obtained based on the method of Rozhkov (2004), used to identify the level of socialization, it was found that it is 1.9 ± 0.23 points for the studied category of students, which corresponds to a low level. According to individual indicators, social adaptability - 1.8 ± 0.21 points (low level), autonomy - 1.4 ± 0.17 points (low level), social activity 1.9 ± 0.22 (low level), morality 2 .7 ±0.18 (medium level).
The level of socialization of the individual depends on endogenous and exogenous factors. The family has the most significant influence on the process of socialization of the child. External factors include the influence of the environment of the educational institution where the teenager is studying, therefore, the creation of the necessary conditions for the psychological and pedagogical support of students with disabilities will allow them to determine their life trajectory in the future and successfully socialize in society.
Purpose of the Study
One of the objectives of the program was to increase the level of socialization of students with disabilities, including the handicapped people, involvement in collective activities, raising self-esteem. The developed program was implemented vector-wise in several directions. At the initial stage, a psychologist conducted a socio-pedagogical diagnosis, the results of which are described above in our work. This ensured timely identification of the contingent with disabilities, conducting a comprehensive examination of them and preparing recommendations for providing them with psychological, medical and pedagogical assistance in an educational institution. Together with a psychologist, a class teacher and a social pedagogue, individual maps were compiled for each student with health problems based on identifying the characteristics of the personal sphere, physical condition, level of adaptability, studying various aspects and conditions of family education. At the pedagogical consultation, on the based onta obtained, the model of individual and group consultations was determined. In addition, the expediency and scope of necessary assistance and support to the family were indicated.
An important component of the program was informative and educational work aimed at explanatory activities on issues related to the peculiarities of the educational process for this category of children, with all its participants - students (both with and without developmental disabilities), their parents (legal representatives), teaching staff. The content of the outreach work included a discussion by the Deputy Dean for Academic Affairs on the proper organization of the school day to ensure efficiency and relieve fatigue in the learning process. A social teacher and class teacher play an important role in adapting to the conditions of education in the SVE institution, who, together with the entire teaching staff, ensured the conditions for the successful inclusion of wards in educational and extracurricular activities. In parallel, correctional and formative activities were carried out. In this direction, targeted assistance was provided in the successful development of an educational program in the field of training (mastering the chosen speciality) and creating an atmosphere conducive to the rehabilitation of this category of students both in physical and mental aspects, which contributed to the formation of the necessary competencies among students. Diverse conversations, training, practical classes were held, in which not only students with disabilities participated, but also their healthy classmates.
The main organizational forms for the implementation of psychological and pedagogical support were consultations (individual and less often group consultations), group training.
The developed program of psychological and pedagogical support for students with disabilities in the state of health had a vector content (Table 1). It was consistently implemented in the natural conditions of the educational process, where at each stage-specific goals were pursued, embodied in activities of various directions.
Research Methods
In the course of the study, the method of analysis and generalization of scientific and methodological literature, psychological and pedagogical testing using the psychometric test of K.E. Sishora, G. N. Kazantseva (diagnosis of the level of self-esteem of the individual), methods of M. I. Rozhkov to assess the socialization of students with disabilities (as cited in Rozhkov, 2004) and methods of mathematical and statistical processing of research materials.
Findings
At the end of the formative experiment, we carried out the diagnostics of students with disabilities, including the handicapped, using the same methods with the same number of students. At the end of the formative experiment, we conducted diagnostics of students with disabilities, using the same methods with the same composition of students. During repeated analysis according to the method of K.E. Sishor (as cited in Rozhkov, 2004), there is a higher involvement of students with disabilities in joint collective activity. Of the respondents, all 100% would like to remain in their group, since they consider their existing relationship to be better than in most courses. The results obtained indicate that the implementation of the psychological and pedagogical support program had a positive impact on the group cohesion of the team, and the acceptance of students with disabilities in a particular educational team. If at the ascertaining stage of the experiment the assessment of belonging to the group was 1.2 points, then at the forming stage it was already 2.3 points. When it was possible to transfer to another group, most of the students, almost as at the initial stage of the experiment, persistently did not express such wishes, but after the end of the experiment, they confirmed their position. Answering the question "What is the relationship between the members of your group?" the respondents were able to characterize them quite clearly. In the groups where there were students with disabilities, friendly relationships were established (1.8 points at the beginning of the experiment and 2.4 points after its completion). As for the relations with the management, they have become more trusted and stable. When analysing the data, it should be noted a positive trend in such aspects as the attitude to study, public assignments from 2.1 points to 3.1 points, respectively. The overall level of group cohesion has increased from 10.8 points to 14.0 points, which indicates a positive impact of the implemented program. After the end of the formative experiment, the group cohesion index increased by 29.6%, students with disabilities became more actively involved in extracurricular activities, their attitude and status in the team changed. They began to be perceived as more equal, and able to make a positive contribution to the common cause.
Analysing the data according to the method of G. N. Kazantseva (as cited in Rozhkov, 2004), one can note an increase in the level of self-esteem among students with disabilities, including the handicapped. Of the children who participated in the experiment, only one student had low self-esteem. In the general group, in two students, the level of self-esteem increased to a high level, and in 9 people it became adequate. After the work on the vector psychological and pedagogical support of students with disabilities, most of them (7 people) gained confidence in their abilities, promising plans for graduation were revived, and five students wanted to continue their studies at the university. At the same time, 50% narrowly define their future professional activities. The process of psychological and pedagogical support affects the personality in various directions, both morally and ethically, broadens the horizon, forms a versatile and determines the future life trajectory, increases social and motor activity, which is fundamentally important for students with disabilities, including the disabled.
Having studied the research data on the level of socialization of students, we can note the dynamics in terms of their social activity by 57.8%, the increase in the level of social adaptation of students with disabilities by 38.8%, which affected the integral result of socialization, where it improved by 31,5%.
In the course of working with the wards, one can note their desire to make more independent decisions, which was reflected in such a criterion as autonomy (by 15%). The data characterizing such an aspect as morality have not undergone significant changes. The results obtained suggest that students have become more attentive to themselves as individuals, have seen opportunities and prospects for self-development and self-improvement, gained self-confidence and the ability to resist external adverse circumstances.
Conclusion
Thus, the results obtained indicate the importance of vector psychological and pedagogical support for students with disabilities and the evidence of the positive impact of the program being implemented on their socialization. This approach enables students to feel confident in their abilities, move forward progressively and adapt to modern conditions of life. Psychological and pedagogical support of students in an institution of secondary vocational education provides a solution to the problems of professional and personal formation and development of students in the context of the interaction of all participants in the educational process, achieving diagnostic, adaptive, rehabilitation and formative goals.
References
Aismontas, B. B., & Odintsova, M. A. (2017). [Sotsial'no-psikhologicheskoye soprovozhdeniye studentov s invalidnost'yu i ogranichennymi vozmozhnostyami zdorov'ya] Socio-psychological support of students with disabilities and disabilities. Psychological Science and Education, (1), 71–80.
Bayramov, V. D., Bonkalo, T. I., Raidugin, D. S., & Voevodina, E. V. (2018). Metodologicheskiye podkhody k aktualizatsii professional'nogo samoopredeleniya obuchayushchikhsya s invalidnost'yu i OVZ v usloviyakh stanovleniya sistemy inklyuzivnogo obrazovaniya [Methodological approaches to the actualization of professional self-determination of students with disabilities and disabilities in the context of the formation of an inclusive education system]. Psychological Science and Education, (2), 19–28. https://doi.org/pse.2018230203
Bikbulatova, A. A., Karplyuk, A. V., Parshin, G. N., Jafar-Zade, D. A., & Serebryakov, A. G. (2018). Method of identifying career guidance interests and inclinations among high school students with disabilities. Psychological Science and Education, (2), 50–58.
Bokova, O. A., & Tarakhov, S. I. (2019). Psikhologo-pedagogicheskoye soprovozhdeniye obuchayushchikhsya v obrazovatel'noy srede: sovremennyye teoreticheskiye predposylki issledovaniya [Psychological and pedagogical support of students in the educational environment: modern theoretical prerequisites for research]. World of Science, Culture, Education, (5), 243-247.
Fedorova, S. S. (2006). Psikhologo-pedagogicheskoye soprovozhdeniye detey s OVZ [Psychological and pedagogical support of children with limited opportunities]. SGU.
Gazman, O. S. (1995). Pedagogicheskaya podderzhka detey v obrazovanii kak innovatsionnaya problema [Pedagogical support of children in education as an innovative problem]. New Values of Education: Ten Concepts and Essays, (3), 58-54.
Melnik, Yu. V., Panyukova, S. V., Saitgalieva, G. G., & Serebryannikova, O. A. (2017). Otechestvennyy i zarubezhnyy opyt vuzov po obucheniyu i soprovozhdeniyu studentov s invalidnost'yu [Domestic and foreign experience of universities in training and accompanying students with disabilities]. Psychological science and education, (1), 88–97.
Mudrik, A. V. (1997). Sotsializatsia i obrazovanie [Socialization and education]. Publishing firm "September".
Ospuk, L. A. (2018). Samorealizatsiya studentov s invalidnost'yu kak bazovyy mekhanizm sotsial'noy inklyuzii [Self-realization of students with disabilities as a basic mechanism of social inclusion]. Psychological Science and Education, (2), 59–67.
Panov, V. I., & Kaptsov, A. V. (2021). Struktura stadiy stanovleniya sub"yektnosti obuchayushchikhsya: svyaznost', tselostnost', formalizatsiya [The structure of the stages of formation of the subjectivity of students: coherence, integrity, formalization]. Psychological Science and Education, (4), 91–103.
Rozhkov, M. I. (2004). Strategia i taktika vospitania [Strategy and tactics of education]. Leaders in Education, (4), 21-25.
Sobkin, V. S., Lykova, T. A., & Sobkina, A. V. (2020). Psikhicheskoye blagopoluchiye studentov pri realizatsii inklyuzivnogo vysshego obrazovaniya v sfere iskusstva: opyt strukturnogo analiza [Mental well-being of students in the implementation of inclusive higher education in the field of art: the experience of structural analysis]. Psychological Science and Education, (6), 19–30.
Stanevsky, A. G., & Khrapylina, L. P. (2017). Teoreticheskiye osnovy formirovaniya modeli obucheniya i individual'nogo sotsial'no-psikhologicheskogo soprovozhdeniya lits s narusheniyem slukha (na primere napravleniya «Inzhenernoye delo, tekhnologii i tekhnicheskiye nauki» [Theoretical foundations of the formation of a model of training and individual socio-psychological support of persons with hearing impairment (on the example of the direction "Engineering, Technology and Technical Sciences"]. Psychological Science and Education, (1), 50–59. https://doi.org/10.17759/pse.2017220107
Subbotina, L. G. (2007). Model' vzaimodeystviya sub"yektov vospitatel'no-obrazovatel'nogo protsessa v psikhologo-pedagogicheskom soprovozhdenii uchashchikhsya [Model of interaction of subjects of educational process in psychological and pedagogical support of students]. Siberian Psychological Journal, (25), 120-125.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1983). Printsipy vospitaniya fizicheski defektivnykh detey [Principles of education of physically defective children]. Pedagogy.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
03 June 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-125-6
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
126
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1145
Subjects
Social sciences, education and psychology, technology and education, economics and law, interdisciplinary sciences
Cite this article as:
Yurechko, O. V. (2022). Vector Psychological And Pedagogical Support Of Students With Health Disorders. In N. G. Bogachenko (Ed.), AmurCon 2021: International Scientific Conference, vol 126. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1097-1106). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.06.121

