Abstract
Many models for assessing the level of financial security are based on a study of a small number of public industrial enterprises in a particular industry, while the vast majority of financial risks are generated by small and medium-sized enterprises, for which these models are inapplicable. This study aims to present a new model for assessing the level of financial security, differentiated by industry and applicable not only for large companies but also for assessing small and medium-sized businesses. To improve the efficiency of the model, an array of accounting data was collected from 13,324 companies belonging to sectors of the economy that generate most of the added value: construction, manufacturing, mining, trade. The main research methods include cluster analysis method, discriminant analysis method, correlation and regression analysis method, factor analysis, economic modelling. The result of the study is the creation of a new six-factor model for assessing the level of financial security of companies, differentiated by industry. To improve the performance of the model, the most relevant coefficients were selected to explain the nature of the company's financial condition problems. Also, for diagnosing financial health, recommended values of the main financial indicators were developed, taking into account the scope of companies.
Keywords: Assessment of the financial security of an enterprise, determinants of financial security, financial security
Introduction
The financial security of enterprises and organizations is an important indicator of the development of any company (Kovalenko et al., 2019). A high degree of company insurance against internal and external threats is the key to achieving the goals planned by the company (Sergeev, 2019). Financial analysis as the most important component of financial science has received the most powerful development in recent decades. Research scientists around the world have made a huge contribution to the formation of this branch of science. Algorithms and methods for its implementation were created, methods for assessing the probability of bankruptcy, rating models, as well as criteria for evaluating such a complex and multidimensional concept as the financial security of a company were developed.
The importance of finding new financial analysis tools, as well as improving existing ones, lies in the range of tasks that such an analysis helps to solve. First of all, the financial security analysis is necessary when checking the counterparty of a legal entity to reduce credit risks (Safargaliev et al., 2019). Also, the analysis of financial security expands the possibilities for assessing the probability of bankruptcy of an enterprise. Finally, the financial security analysis is used when choosing long-term investment objects, since the priority in such a strategy is the stability and reliability of companies.
Modern methods of data processing, as well as the creation of information and analytical systems, create the necessary conditions for the development of science and the improvement of methods for assessing the financial security of a company.
Problem Statement
The relevance of this study is due to the following reasons:
1. The concept of financial security and the analysis of the financial security of an enterprise have been widely developed in Russian science since the beginning of the 21st century. Having analyzed the main methods of Russian authors, such as Papekhin (2007), Blazhevich (2011), Zaporozhtseva and Ryabykh (2013), Kavyrshina and Sharykina (2016), Sapozhnikova and Tkacheva (2019), it can be concluded that they are not suitable for the study of small and medium-sized businesses, as they are based on an array of accounting data of a limited number of public manufacturing enterprises. This feature is due to the simplicity of collecting information, since the presence of errors or inaccuracies in the audited financial statements of large industrial companies is unlikely, while in openly published reports of small and medium-sized businesses, such inaccuracies occur in every fifth company, creating statistical outliers in the data array, for the search and exclusion of which specialized methods are also needed. Applying the recommended values of financial coefficients of large companies to small and medium-sized businesses, we can make unreasonable conclusions about their financial condition, since these values for them will be overestimated (Kovalev, 2010). One of the objectives of the study is to create a financial security model suitable for companies of any scale of activity.
2. Earlier studies are limited to the study of industrial companies, without providing an opportunity to assess the financial condition of companies in other industries. Undoubtedly, the added value created by industrial enterprises is a significant share of GDP. But, speaking of the generated financial and credit risks, it is worth pointing out that in terms of the absolute number of bankrupt companies from year to year, such industries as trade and construction are leading. The objectives of this study include the differentiation of the financial security assessment model by industry. At the same time, the work explores such industries as trade, construction, manufacturing and mining. Industries were selected based on two criteria: systemic importance and frequency of bankruptcies.
3. Modern models are also not suitable for analyzing large amounts of data and generating ratings, since they partially use qualitative coefficients or non-public information, which limits the use of the author's models to assess the financial security of a small number of companies.
Research Questions
Various methods are currently used to determine the level of financial security of an enterprise. The most common is the indicator approach, which consists in choosing certain indicators that characterize financial security, comparing actual values with threshold ones.
Among the indicators should be indicators that take into account industry specifics, the most typical for a given enterprise and of great strategic importance for the latter. The system of indicators should correspond to the composition and importance of the main threats to the financial security of the enterprise. That is, when determining the threshold values, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the enterprise, the specifics and conditions of the market where the products are sold, and other factors.
The existing assessment models, on the one hand, are a vivid reflection of the scientific progress of Russian scientists in the field of studying the financial security of companies. However, not all of them are suitable for checking counterparties, forming credit ratings (Volna et al., 2020).
A significant contribution of researchers lies in the development of recommended ranges of values of the main financial indicators. The existing models define criteria for assessing the level of financial security for specific values of financial coefficients.
According to the authors, the main disadvantage of the existing methods is that they can all be used for a small group of industrial companies. Another negative aspect of the basic techniques is the presence of linearly dependent variables in them that create autocorrelation in the models. The most difficult task in determining the determinants of financial security that any researcher faces is the absence of a target value (guideline) since financial security is an abstract concept that has no material expression (Kočišováa & Mišankováa, 2014).
After analyzing the methods of Russian authors, the resulting score according to the Kavyrshina method (Kavyrshina & Sharykina, 2016) was adopted as a guideline for this study. At this stage, this author's methodology is the most appropriate for analyzing large amounts of data.
Purpose of the Studу
The main purpose of the study is to improve the methodology for assessing the financial security of companies by presenting the author's model for assessing financial security. Also, to achieve the goal of the study, the authors formed the recommended values of the most relevant indicators that reflect information about the financial condition of the company.
The proposed financial security assessment model is based on the financial statements of 13,324 companies for the period 2015-2020. The model evaluates financial security through 4 aspects of the company's activity: financial stability, liquidity and solvency, performance efficiency and business activity. These aspects of activity are assessed through the 6 most relevant indicators. The model is also suitable for assessing small and medium-sized businesses, as it is based on reporting data from companies of various sizes. The proposed model is differentiated by industry, which makes it suitable for valuing companies in industries such as construction, trade, mining and manufacturing. Another advantage of the model is the possibility of its use in the formation of ratings of companies by the level of financial security since all the data used in it are quantitative and are in the public domain.
Research Methods
The most important research methods include economic modelling and correlation and regression analysis (Lei et al., 2021). The most important indicator of the relevance of indicators is the degree of closeness of their connection with the resulting account (Fang, 2021). During the initial data selection, the optimal search method was used (Xian et al., 2020), which consists in creating an algorithm for checking reports and excluding objects from the array that do not meet the specified rules. The indicator evaluation method was used to create classification rules. The author's model is focused on the simplicity of interpreting the results depending on whether the resulting account belongs to a certain interval. A financial security class is being formed that allows making specific conclusions about the financial condition of the company. Also, in the course of the study, such methods as the method of cluster analysis (when analyzing clusters of companies of different dimensions), the method of discriminant analysis (when adapting the model to bankruptcy forecasting), the method of factor analysis (when determining the most relevant indicators) and others were used.
Findings
[It is reasonable to divide the presentation of the research results into five stages:
1. Formation of an array of accounting data of the studied group of companies.
2. Determination of the most relevant indicators affecting the level of financial security, assessment of the closeness of their connection with the resulting account.
3. Determination of recommended values for the specified parameters of financial security.
4. Formation of the model.
5. Evaluation of the model's performance.
Formation of input data for model construction
The collection of accounting data was carried out using the information and analytical systems SPARK and Rusprofile. The main criterion for choosing companies was the revenue indicator in 2019. For mining, manufacturing and construction, the minimum figure is 500 million rubles in 2019. For trading companies, the threshold value of annual revenue was taken at 2 billion rubles. The second selection criterion was the availability of financial statements (balance sheet and income statement) for the period 2015-2019. The processing of such a large amount of data takes a long time, while the financial statements for the reporting year become publicly available in April-May of the next calendar year. This is the reason why the study is limited to 2019.
The main characteristics of the studied companies by industry are presented in Table 1.
As a result of the selection, the final array amounted to 13,324 companies from four sectors of the economy.
Definition of financial security determinants
In the course of determining the most relevant indicators reflecting the level of financial security, the authors tested 35 parameters used in previous studies. An integral part of the selection is the method of correlation-regression analysis, which evaluates the relationship of parameters with the resulting score. Because in some cases the correlation does not reflect a causal relationship (Shorokhova et al., 2015), the method of expert assessments was additionally applied.
The highest correlation naturally showed such coefficients as the financial independence ratio (0.698), financial stability ratio (0.615), return on assets (0.449), current liquidity ratio (0.310). The analysis also found that none of the business activity ratios showed a significant relationship with the resulting score.
Figure 1 shows the relationship between the indicator of financial autonomy of manufacturing enterprises and the resulting account.
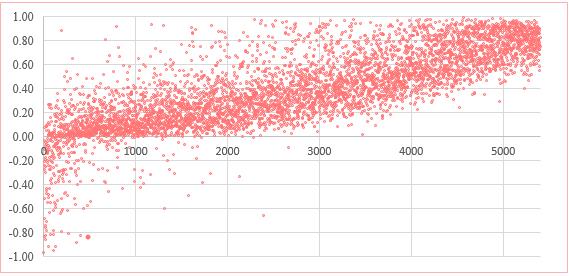
As a result of selecting parameters and checking the absence of autocorrelation, the following indicators were selected: financial autonomy ratio, financial stability ratio, current liquidity ratio, absolute liquidity ratio, return on assets ratio. These parameters are the most relevant and significant in assessing financial security. In addition to the five coefficients, the authors also propose to introduce a new parameter that most accurately reflects the financial stability of the company - the stability of asset turnover.
Asset turnover stability (ATS) is a measure of assessing the variation in asset turnover and proceeds from the hypothesis that, depending on the company's industry, asset turnover may vary, but in a steadily developing company, this indicator is in a certain range, and its value fluctuates slightly.
The parameters are calculated according to the formulas (1 - 4):
(1)
where ATS – asset turnover stability;
ATV - asset turnover variation.
(2)
Where ATV - asset turnover variation coefficient;
– standard deviation of asset turnover;
–the average value of asset turnover in the period.
The standard deviation of asset turnover is calculated by the formula:
(3)
where – asset turnover in the i-th period;
N is the number of observation periods.
The average value of asset turnover in a period is found using the arithmetic mean formula:
(4)
The recommended value of the ATS parameter is more than 5, which corresponds to a volatility level of less than 0.2.
Formation of recommended values of financial security parameters
To form a model, the authors have formed the recommended values of the main parameters characterizing financial security. The values are shown in Table 2.
The recommended values in the framework of this work are the average values of the ratios of financially stable companies. The recommended values are close to the values of the third quartile, that is, they divide the population of companies in the ratio of 75:25, while a quarter of the companies achieve the recommended values, reflecting a high level of financial security.
Formation of the author's model for assessing the level of financial security
The author's model for assessing the level of financial security is based on the achievement by the company of the standard values of the parameters indicated in Table 3. The achievement of the standard is the ratio of the actual value of the coefficient to the standard value according to the formula:
(5)
Where - is the degree of achievement of the i-th parameter;
Пф - is the actual value of the parameter;
Пр - the recommended value of the parameter.
The resulting score is the sum of such achievements and is calculated using the formula:
(6)
where – financial security parameter (resulting account).
The criteria for determining the levels of financial security are presented in Table 3.
Thus, according to Table 3, the level of financial security is proposed to be determined on the CLASE scale (Critical, Low, Average, Secure, Excellent).
Model performance evaluation
The final stage of the study is to determine the levels of financial security for 13,324 companies understudy and assess the classification performance of the model. The results of the distribution of companies by levels of financial security are presented in Table 4.
The model provides for a proportional distribution of companies by levels of financial security, while the annual adjustment of the standard values of indicators will preserve the nature of the distribution. Table 5 shows the distribution of bankrupt companies.
The distribution shows that, on average, the level of financial security of bankrupt companies is classified as “low” in 85-95% of cases, which allows the model to be used when checking counterparties and assessing credit risks.
Conclusion
We have developed a conceptually new six-factor model for assessing the financial security of companies. The model is based on accounting data of 13,324 legal entities and applies to the analysis of large amounts of data. It is possible to use the model in evaluating trading, construction, mining and processing companies of various sizes to verify the counterparty, assess credit risks, identify potential bankrupts and form credit ratings. To improve the classification performance of the model, recommended values were developed for the main parameters that reflect the financial security of the company. Adjustment of the recommended values and sub sectoral diversification of the normative ranges are the tasks of further research.
References
Blazhevich, O. G. (2011). Finansovaya bezopasnost' predpriyatiy: opredeleniye minimal'no neobkhodimogo urovnya [Financial security of enterprises: determination of the minimum required level]. Nauchnyye trudy NAPKS.
Fang, Z. (2021). The Methods and Tools for Clustering Analysis. Systems Medicine, 1, 9-13.
Kavyrshina, O. A., & Sharykina, A. L. (2016), Finansovaya diagnostika v sisteme ekonomicheskoy b ezopasnosti predpriyatiya [Financial diagnostics in the system of economic security of an enterprise]. FES: Finansy. Ekonomika, (1), 8-12.
Kočišováa, K., & Mišankováa, M. (2014). Discriminant Analysis as a Tool for Forecasting Company's Financial Health. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 110, 1148-1157.
Kovalenko, O. A., Malyutina, T. D., & Tkachenko, D. D. (2019). Ekonomicheskaya bezopasnost' predpriyatiya. Modelirovaniye i otsenka [Economic security of the enterprise. Modelling and evaluation]. Infra-M.
Kovalev, V. (2010). Finansovyy menedzhment: teoriya i praktika [Financial Management: Theory and Practice]. Prospekt.
Lei, Z., Menghao, L., & Metawa, N. (2021). Financial Risk Evaluation Z-Score Model for Intelligent IoT-based Enterprises. Information Processing & Management, 58(6), 24-31.
Papekhin, R. S. (2007). Faktory finansovoy ustoychivosti i bezopasnosti predpriyatiy [Factors of financial stability and security of enterprises]. Volgogradskiy gosudarstvennyy universitet.
Safargaliev, E., Aetdinova, R., & Karimova, А. (2019). Indicators of financial security of small and medium enterprises. Revista San Gregorio, 34, 81-88.
Sapozhnikova, N. G., & Tkacheva, M. V. (2019). Ekonomicheskaya bezopasnost': praktikum [Economic security: workshop]. Izdatel'skiy dom VGU.
Sergeev, A. (2019). Ekonomicheskaya bezopasnost' predpriyatiya [Economic security of the enterprise]. URIGHT.
Shorokhova, I. S. Kislyak, N. V, & Mariyev, O. S. (2015), Statisticheskiye metody analiza [Statistical Methods of Analysis]. Izdatel'stvo Ural'skogo universiteta.
Volna, Y. S., Savchenko, N. L., & Mishina, Ye. B. (2020). Analiz finansovoy bezopasnosti predpriyatiy na primere rossiyskogo metallurgicheskogo kompleksa [Analysis of the financial security of enterprises on the example of the Russian metallurgical complex]. Regional'nyye problemy preobrazovaniya ekonomiki, 4, 132-141.
Xian, L., He, K., Wang, C., & Lai, K. K. (2020). Factor analysis of financial time series using EEMD-ICA based approach. Sustainable Futures, 2, 47-55.
Zaporozhtseva, L. A., & Ryabykh, M. A. (2013). Razrabotka strategii obespecheniya finansovoy bezopasnosti predpriyatiya [Development of a strategy for ensuring the financial security of the enterprise]. Fundamental'nyye issledovaniya, 11(8),1637-1642.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
03 June 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-125-6
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
126
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1145
Subjects
Social sciences, education and psychology, technology and education, economics and law, interdisciplinary sciences
Cite this article as:
Volna, Y. S., & Savchenko, N. L. (2022). Improving The Assessment Of Enterprises Financial Security In Basic Sectors Of Economy. In N. G. Bogachenko (Ed.), AmurCon 2021: International Scientific Conference, vol 126. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1041-1049). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.06.115

