Abstract
The development of the domestic pharmaceutical market and the building up its internal potential today is one of the most important socio-economic tasks. One of the key problems of the Russian pharmaceutical market at the present stage is its total import dependence, which has been persisting for many years. The domestic pharmaceutical industry has a low production potential due to the lack of investment in the industry due to its low attractiveness. This circumstance creates conditions under which the country's self-sufficiency in essential drugs in conditions of international isolation is impossible. During the study, the assessment of economic factors in the development of the pharmaceutical market in Russia as one of the largest and most significant in the country's economic system was implemented based on an analysis of trends in changes in the leading indicators of its development physical and value terms. It has been established that a qualitative expansion of the pharmaceutical market in the Russian Federation has not occurred in the last two years, and the nominal growth of its value is associated with a depreciation of the national currency and an increase in average prices for pharmaceutical products. As a key economic factor determining the development of the pharmaceutical market, it is worth highlighting the incomes of the population, which in recent years have tended to decline against the background of an increase in the level of poverty in the country.
Keywords: pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation, sanctions, commercial sector, public sector, economic factors
Introduction
The Russian pharmaceutical market is part of the global pharmaceutical market. In recent years, the Russian pharmaceutical market has been actively growing, dynamically increasing its volume, but remains import dependent. Today, more than 70 % of pharmaceutical products sold on the market are imported, while the share of domestic drugs, respectively, is less than 30 %. This circumstance is because the pharmaceutical industry in Russia is poorly developed and is significantly inferior in the technologies used by the leading pharmaceutical powers. As a result, domestic pharmaceutical products have a low degree of competitiveness compared to imported counterparts due to the lower therapeutic efficacy and quality of the substances used in the production. As a result, Russian medicines are in less demand among the population due to the greatest extent to their incomes since they have a low cost compared to imported ones. The high current dependence on the Russian pharmaceutical market imports determines its integration into the world market. This state of affairs is because the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation is practically unable to exist autonomously. The Russian pharmaceutical market cannot fully satisfy the population's demand for the main pharmacological groups only through domestic production (Mensa Sorato et al., 2020).
Despite the existing contradictions, the development of the domestic pharmaceutical market and the building up of its potential internal today is one of the strategically important socio-economic tasks. This circumstance is due to the significant role of the pharmaceutical industry in maintaining and strengthening the health of the population within the framework of ensuring the country's drug safety as an integral part of national security, the importance of ensuring which has significantly increased in recent years in all countries of the world.
Despite the important role of the pharmaceutical industry for the country, the industry today has systemic and persistent problems. Government spending is one of the catalysts for developing the industry, providing elasticity of investments (Shaikh and Gandjour, 2019). At the state level, measures have been developed, and measures have been taken to support the Russian pharmaceutical industry. These measures aim to implement an import substitution strategy and a transition to export-oriented production by introducing modern technological competencies and increasing the level of material and technical support. However, these measures do not bring the expected results (Zyukin et al., 2020). Over the years of the market functioning under the conditions of sanctions restrictions, there have been no significant shifts. As a result, the coronavirus pandemic, which began in 2020, exposed and actualized the existing problems in the industry. The pandemic also became a kind of driver for the market, defining the vectors of its current development. In this regard, the study of trends in the development of the Russian pharmaceutical market at the current stage and the identification of the economic factors that determined them is an urgent area of analysis.
Problem Statement
One of the key problems of the Russian pharmaceutical market at the present stage is its total import dependence, which has been persisting for many years. Previously, this circumstance did not lead to significant negative consequences. However, today's conditions are the conditions of political contradictions and sanctions of the EU countries against Russia. This was a detailed blow to drug supply since it was the countries of Europe that for many years were the largest importers of drugs in the Russian Federation (Ovod, 2020). As a result, in the period 2015–2016, the availability and level of provision of the country's population with the necessary pharmaceutical products, including essential medicines, significantly decreased, which also inevitably contributed to the increase in prices in the pharmaceutical market (Ovod, 2021).
The decrease in sales volumes on the Russian pharmaceutical market following the sanctions is because the domestic pharmaceutical industry has a low production potential. This state of affairs is due to the industry's lack of investment due to its low attractiveness. Accordingly, it is defined by a significant technological lag behind the level of leading pharmaceutical companies (Lichtenberg, 2018). The current situation is characterized by the use of outdated pharmaceutical technologies at domestic enterprises, a low level of their material and technical equipment, and a shortage of personnel. This situation is also because pharmaceutical production is often located in the regions of the country on the periphery, which hinders the flow of investments and resources to production. As a result, the pharmaceutical industry turns out to be less attractive for young specialists, which is the reason for the shortage of highly qualified personnel for production (Zyukin et al., 2020).
All these circumstances create conditions under which the country's self-sufficiency in essential drugs in conditions of international isolation is not possible (Critchley and Zaric, 2019). Therefore, one of the ways out of this situation was the reorientation of imports towards generics from India, Egypt, and other third-world countries (Chattopadhyay and Bercovitz, 2020). As the researchers' note (Dubois et al., 2015), one of the key trends for the Russian pharmaceutical market at the current stage of its development is the increasing role of generic drugs, which is associated with their price advantage compared to original drugs. As a result, today, more than half of the total sales of pharmaceutical products are accounted for by generics. This volume is steadily growing due to the deteriorating living standards of the population of the Russian Federation, which is the primary consumer in this market.
In the context of import restrictions and protectionist policies, one of the ways for foreign pharmaceutical manufacturers to enter the Russian pharmaceutical market, which is attractive from a business point of view, is the localization of production in the country. For pharmaceutical companies, the localization of their production facilities on the territory of the Russian Federation provides a kind of protection against risks and a guarantee of a global presence in the domestic pharmaceutical market, which becomes relevant in conditions of political instability. At the same time, the localization of foreign industries is actively stimulated by the state.
The use of the "extra third" mechanism, according to which locally produced drugs prioritize imported drugs in the public procurement procedure, to which the latter are not allowed in the presence of locally produced analogs, actually forces pharmaceutical companies to localize their production in the country. As a result, there is an inflow of investments into the industry aimed at organizing local production within the country and replenishing the country's budget through taxes and fees (Lietzan and Acri née Lybecker, 2019). Despite this, there is no qualitative development of the country's pharmaceutical industry, an increase in its internal potential based on research and development, and an increase in the manufacturability of domestic industries.
Consequently, the results were achieved under the conditions of sanctions and the implementation of import substitution over the past 5–7 years. However, developing the Russian pharmaceutical market within the framework of achieving the required level of drug supply for the country remains relevant, which manifested itself in 2020 at the height of the coronavirus pandemic. There was a total shortage of essential drugs with a simultaneous rise in prices for products traded on the market in limited quantities. The sharp deterioration of the epidemiological situation showed that the pharmaceutical industry is not ready for such challenges at the current level of development.
Research Questions
The main issues in this study are:
1) the socio-economic role of the pharmaceutical industry in modern conditions;
2) trends in the development of the Russian pharmaceutical market in the context of economic sanctions and the coronavirus pandemic;
3) economic factors that determined the vector of the current development of the pharmaceutical market and had the most significant impact on it.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the work is to study the economic factors of the development of the pharmaceutical market in Russia at the current stage as one of the largest and most significant in the country's economic system based on an assessment of trends in changes in the leading indicators of its development in physical and value terms.
Research Methods
The research is based on the analysis of data from analytical reports of DSM Group on the development of the Russian pharmaceutical market in 2016–2020. This analysis allowed considering the leading indicators of the market functioning and identify their formation's prevailing trends and factors. The study of economic factors in the development of the Russian pharmaceutical market was carried out based on many methods and approaches, including comparative, logical, and trend analysis. The study identifies trends in the dynamics of the indicators under consideration, which reflects the main trends in the development of the domestic pharmaceutical market and allows identifying the economic reasons for the emerging trends. As the leading indicators for the study, the dynamics of the value of the pharmaceutical market in national and foreign currencies were selected, making it possible to assess the rates of real market growth that are not related to inflationary processes in the economy. The study also assesses the dynamics of growth in the Russian pharmaceutical market in volume and value terms in the context of the main segments. This assessment makes it possible to identify the most promising and dynamically developing areas. The practical significance of evaluating data in physical terms is that it allows assessing the qualitative development, not associated with an increase in drug prices, of specific segments of the pharmaceutical market in the Russian Federation.
Findings
The total value of the Russian pharmaceutical market in the national currency has had a steady upward trend over the past five years. As a result of this process, there is an increase in its volume from 1,523 billion rubles up to 2040 billion rubles, which characterizes an increase of 34 %. At the same time, the trend towards an increase in the growth rates of the pharmaceutical market volumes has been observed over the last three years, when the indicator increased by 21 %, while in the period 2016–2018 – by 10.5 %. The current situation is associated with the deterioration of the foreign policy situation against the background of the events of 2014, which in 2016–2018 had a negative impact on the growth rate of the import-dependent pharmaceutical market. However, in the last two years, the situation has improved. In physical terms, the pharmaceutical market volume has a wavelike character of variation, has increased to 6325 million packs by 2018, which is the highest value in the study period and is 7 % higher than the base year level. Over the past three years, there has been a steady downward trend in sales in the pharmaceutical market, with the result that by 2020 the figure reached 6,018 million packs, which is 5 % below the level of 2018, but almost 2 % above the base year level. As a result, it can be concluded that the growth of the pharmaceutical market in value terms in recent years is due to the increase in prices for medicines and inflation, which is confirmed by the negative dynamics of the volume of sales in the market (Fig. 01).
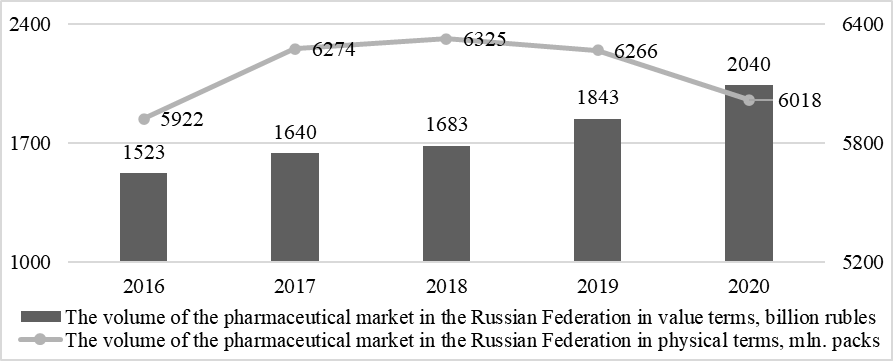
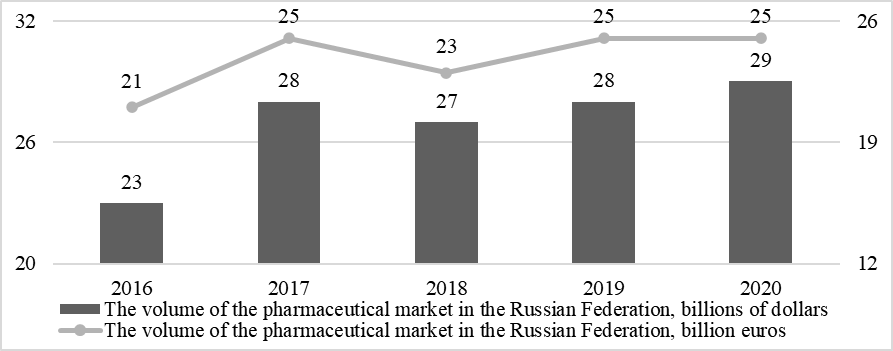
Political contradictions had a negative impact on the Russian economy, contributing to a decrease in the national currency's exchange rate concerning the main world currencies. Therefore, it is crucial to assess the dynamics of the volume of the pharmaceutical market in foreign currency, which makes it possible to identify changes not related to the depreciation of the national currency. As a result, 2016 saw the lowest value of the pharmaceutical market volume in dollars ($ 23 billion) and euros (€ 21 billion) due to the introduction of economic sanctions, which contributed to a decrease in the volume of products on the market. However, in 2017, there is an increase in market volumes up to 28 billion dollars or 25 billion euros, which is the highest value in the period under study. In 2018, negative dynamics began again. As a result, the volume of the Russian pharmaceutical market decreased to $ 27 billion or € 23 billion. In the last two years, there has been another increase in the value of the pharmaceutical market to the level of 2017. Only in dollars, the market volume in 2020 increased compared to the level of previous years, reaching $ 29 billion. As a result, we can say that the actual growth in the volume of the Russian pharmaceutical market in foreign currency is not as significant as in the assessment data in rubles, and the last three years are absent. Thus, the total growth over five years was 26 and 19 %, and over the past three years – 7 and 9 % in dollars and euros, respectively (Fig. 02).
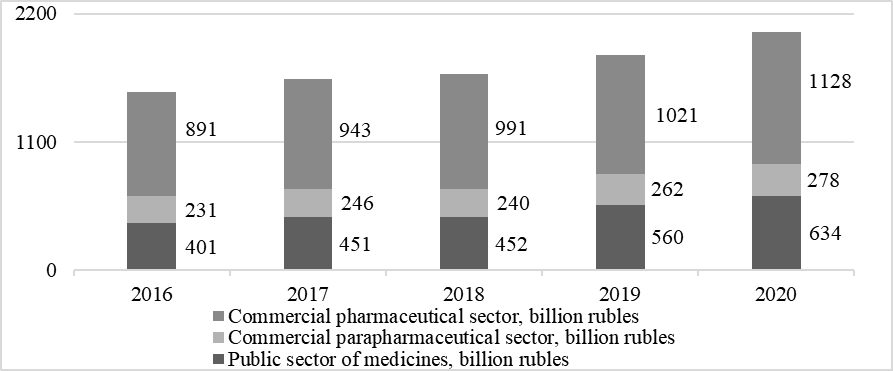
Assessment of the dynamics of the value of the main sectors of the pharmaceutical market showed an upward trend in all segments to one degree or another. Thus, the commercial sector of pharmaceuticals has grown over five years from 891 billion rubles to 1128 billion rubles, which corresponds to a total increase over five years at the level of 26.6 %. The state sector of pharmaceuticals, whose value in 2016 was equal to 401 billion rubles, reached 634 billion rubles in 2020, which is 58 % higher than the base year level. The value of the commercial sector of para pharmaceuticals in the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation in 2016 amounted to 231 billion rubles. During the study period, the commercial sector of para pharmaceuticals increased by 20.3 % and reached 278 billion rubles.
As a result, we can say that the public sector of medicines today is one of the most dynamically developing segments of the pharmaceutical market. Also, it can be noted that in all pharmaceutical market sectors, except the commercial segment of medicines, stagnation was observed in the period 2017–2018. As a result, no growth in their value was observed (Fig. 03).
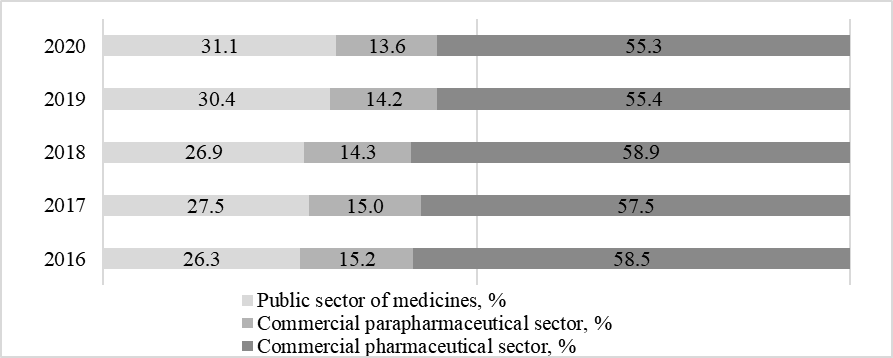
In the pharmaceutical market structure in the entire study period, the overwhelming share belongs to the commercial sector of medicines. The share of the commercial pharmaceuticals sector exceeds 50 % but tends to decline from 58.5 to 55.3 % by 2020. The second largest is the public sector of medicines. On the contrary, the share of the public sector of pharmaceuticals on the market is growing. In 2020, the share of the public sector of medicines was 31.1 %. This indicator in 2020 is higher than the base year level by almost 5 %. The share of the commercial para pharmaceutical sector is the smallest in the overall structure and tends to decline from 15.2 to 13.6 % by 2020. As a result, we can say that at the current stage of development of the pharmaceutical market in the Russian Federation, the state sector of medicines is the most dynamic and actively developing. This circumstance is due to an increase in the volume of public procurement of medicines, including in connection with the onset of the coronavirus pandemic in 2019–2020 (Fig. 04).
Assessment of the dynamics of the physical volume of the pharmaceutical market in the context of the main directions (commercial sector of drugs, hospital purchases, and preferential drug provision) also showed a general upward trend in the study period in all segments, except for hospital purchases. At the same time, it should be noted that the dynamics of the pharmaceutical market volume in physical terms in all sectors have a wavelike character of variation in the study period, increasing in 2017 and 2019 and decreasing in 2018 and 2020. Sales in the commercial segment of pharmaceuticals in physical terms by 2018 increased to 5219 mln packs, which is the highest value in the study period and exceeds the base year level by 6.6 %. By 2020, the physical volume of sales in the commercial segment of pharmaceuticals decreased to 5002 mln packs, which is 2.2 % higher than the level of 2015. The volume of hospital purchases reached its maximum value for the study period in 2017 when the indicator was 1,038 million packs, and by 2020 it decreased to 841 million packs, which is 5 % lower than the base year level. During the study period, the natural sales volume in the sector of preferential drug provision, which is the smallest one, increased from 144 million packs to 175 million packs, which characterizes an increase of 21.5 %. However, this sector's most significant sales volume was recorded in 2019, when the indicator reached 192 million units (Fig. 5).
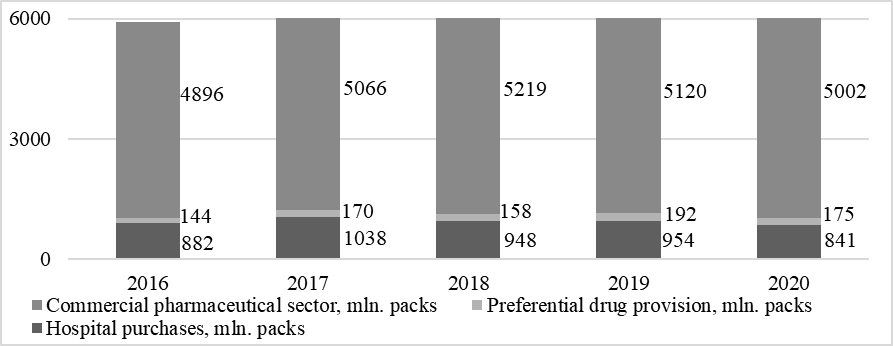
In the pharmaceutical market structure in physical terms, over the entire period under review, the overwhelming share is accounted for by the commercial sector of medicines, the share of which exceeds 80 % and tends to grow from 82.7 to 83.1 % by 2020. The share of hospital purchases at the beginning of the period under review was 14.9 % of the total sales volume. Moreover, by 2020, it decreased to 14 %, although in 2017, it tended to grow to 16.5 %. The share of preferential drug coverage in the total sales on the market at the beginning of the study period was 2.4 %, and by 2019 it increased to 3.1 %, which is the highest value in the study period. By 2020, there is a decrease in the share of preferential drug provision to 2.9 % (Fig. 6).
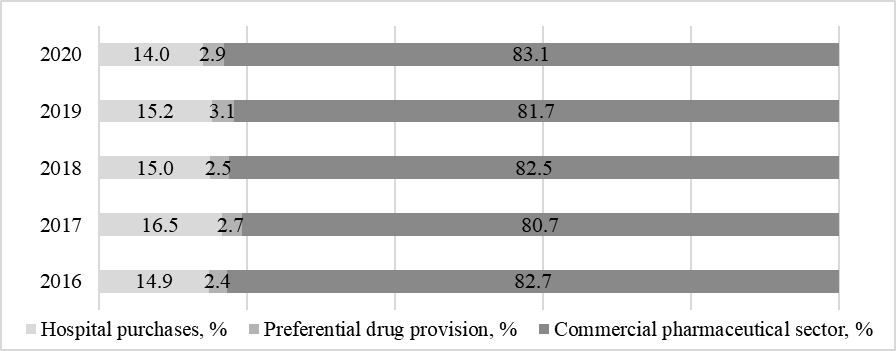
As a result, we can say that the overwhelming share of drug packages sold on the pharmaceutical market goes to the commercial sector, while the share of hospital purchases and preferential drug provision in total accounts for less than 20 %. This process indicates that the state's participation in providing health care institutions and socially unprotected segments of the population with the necessary drugs is minimal and, in fact, nominal, and the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation is focused on commerce and business development.
Conclusion
The value of the Russian pharmaceutical market in the last five years has grown to 2040 billion rubles. However, an assessment of the data revealed that the total number of packs sold varies in waves, reaching its maximum value in 2018 (6325 million packs), and by 2020 it is decreasing. These data indicate that the qualitative expansion of the pharmaceutical market in the Russian Federation has not occurred in the last two years. The nominal growth in the value of the pharmaceutical market is associated with a depreciation of the national currency and an increase in average prices for pharmaceutical products. This fact is also confirmed when considering the value of the Russian pharmaceutical market in foreign currency. At the same time, today, the basis of the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation, both in value and in-kind, is the commercial sector of medicines, which accounts for more than 50 % of the total sales on the market and more than 80 % of the total number of packages sold. The public sector is the second largest (30 %), tending to accelerate growth in the last two years, which is associated with an increase in hospital purchases, including the coronavirus pandemic. At the same time, the volume of preferential drug provision is shallow and does not even exceed 3 %. In turn, the share of the para pharmaceutical sector is the smallest and does not exceed 15 %, which is due to its less significant role in maintaining health.
Economic factors determine the current development of the pharmaceutical market. The population's income should be highlighted as a key economic factor since the commercial sector of drugs on the market is fundamental. Despite the active growth of the public sector in recent years, in our opinion, the commercial segment will continue to be the most significant since the size of public spending on health care and preferential drug provision of the population is relatively small. Therefore, the demand in the commercial sector for medicines and will be saved in the future. At the same time, it should be noted that the current socio-economic situation in the country is unfavorable since there is an increase in poverty and a decrease in the real incomes of the population. In this regard, the upward trend in demand for generics, cheaper analogs of original drugs, will continue. Therefore, a significant increase in drug prices may lead to a drop in demand and a corresponding decrease in sales volumes, so maintaining prices at an optimal level today is becoming one of the most important directions.
References
Chattopadhyay, S., & Bercovitz, J. (2020). When one door closes, another door opens … for some: Evidence from the post-TRIPS Indian pharmaceutical industry. Strategic Management Journal, 41, 988–1022.
Critchley, G. J., & Zaric, G. S. (2019). The impact of pharmaceutical marketing on market access, treatment coverage, pricing, and social welfare. Health Economics, 28, 1035–1051.
Dubois, P., de Mouzon, O., Scott-Morton, F., & Seabright, P. (2015). Market size and pharmaceutical innovation. The RAND Journal of Economics, 46, 844–871.
Lichtenberg, F. R. (2018). The impact of pharmaceutical innovation on cancer mortality in Russia, 2001–2011. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Services Research, 9, 79–89.
Lietzan, E., & Acri née Lybecker, K. M. L. (2019). The innovation paradox: pharmaceutical marketing exclusivity and incentives for drug development. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Services Research, 10, 169–175.
Mensa Sorato, M., Davari, M., Abdollahi Asl, A., Soleymani, F., & Kebriaeezadeh, A. (2020). Why healthcare market needs government intervention to improve access to essential medicines and healthcare efficiency: a scoping review from pharmaceutical price regulation perspective. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Services Research, 11, 321–333.
Ovod, A. I. (2020). The development of the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation in the conditions of sanctions. Azimuth of scientific research: economics and management, 1(30), 252–255.
Ovod, A. I. (2021). Research of growth factors of the Russian pharmaceutical market. Azimuth of scientific research: economics and management, 1(34), 233–236.
Shaikh, M., & Gandjour, A. (2019). Pharmaceutical expenditure and gross domestic product: Evidence of simultaneous effects using a two-step instrumental variables strategy. Health Economics, 28, 101–122.
Zyukin, D. A., Oleinikova, T. A., Evstratov, A. V., Sergeeva, N. M., Reprintseva, E. V., & Ulyanov, V. O. (2020a). Higher Pharmaceutical Education in Russia: Economic Assessment of Accessibility and Regional Specifics. SRP, 11(2), 317–328.
Zyukin, D., Golovin, A., Pshenichnikova, O., & Nadzhafova, M. (2020b). Assessing the functionality of models for predicting pharmaceutical companies. Amazonia Investigation, 9(28), 272–280.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 March 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-124-9
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
125
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1329
Subjects
Freedom, philosophy, civilization, media, communication, information age, globalization
Cite this article as:
Komissinskaya, I. G., Bystritskaya, A. Y., Horlyakova, O. V., & Pasechko, V. V. (2022). Economic Factors Of Russian Pharmaceutical Market Development. In I. Savchenko (Ed.), Freedom and Responsibility in Pivotal Times, vol 125. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 639-648). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.03.77

