Abstract
In modern times, the problems of rural administration are at the centre of scientific, official and community leaders' attention. The efforts of the Russian authorities focus on forming and efficiently operating a system of strategically sustainable, integrated rural development. The most important element in this system is the institution of municipal service. It is the professionalism of these servants that determines the competent, clear and efficient implementation of government programmes at the level of rural settlements. Municipal administration is becoming more complex, its qualitative nature and content are changing and, thus, requires a higher level of qualification, knowledge and motivation from servants. Using human capital in the human resources management of rural municipalities is expressed through the development of the competencies that are essential in solving management tasks. The purpose of this study is to examine the formation and development of human capital of municipal servants in rural areas and to substantiate the mechanisms of its development based on the competency-based approach. The issues raised in the article include an examination of the education, length of service and competencies requirements for rural municipal servants established both by specialized municipal service legislation and by educational standards and administration training programmes. The paper analyses modern trends in additional education of municipal servants, characterizes the current state of the human capital of municipal servants in rural settlements of the Tambov region and substantiates the main directions of its development.
Keywords: Competency-based approach, human capital, municipal servants, rural areas
Introduction
The formation of human capital for servants at the municipal level involves tackling more than just the territory's human resources policy. The development of human capital is an indicator of the overall performance of administration, further determining the level of trust in government. Strategic development of the territory implies accumulating and improving the human capital of administration human resources (Ivanova & Nikitin, 2018; Popova, 2015).
Municipal personnel policy, unlike public policy, primarily addresses the immediate life of the people in a particular territory, the allocation of personnel services to areas of activity and does not touch on ideology, politics or the sphere of power relations. There is a strong emphasis on the implementation of municipal social policy, where people with their needs, interests and creativity are paramount. Municipalities are also in the process of forming human capital, as part of the organization's human resources policy (Brozgunova, 2020; Popova, 2015). Rural areas have personnel problems in the structure of municipal administration. This manifests in both the qualitative composition of servants, their professional and educational compliance with the position, and other factors of imbalance in the staffing of territorial administration (Krutikova, 2014; Kulikov & Minakov, 2018).
Problem Statement
Rural settlement as a type of municipality is the most common in the Russian Federation. The main efforts of the federal and regional authorities in recent decades have focused on the formation and effective functioning of a system of strategically sustainable, integrated rural development. The most important element in this system is the institution of municipal service. It is the professionalism of these servants that determines the competent, clear and efficient implementation of government programmes at the level of rural settlements. In this regard, the study of problems of human capital development of municipal servants in rural areas based on the competency-based approach seems particularly relevant in the regions with an agrarian orientation.
Research Questions
The issues addressed in this paper cover the problems of forming and developing the human capital of municipal servants in rural areas and include the study of the following aspects:
-the legal and regulatory framework for municipal service, which sets out requirements for the education, length of service and competencies of municipal servants in rural areas;
-the requirements of the federal state educational standards and programmes of educational institutions in the areas of administration training to the level of mastery of universal, professional and general professional competencies;
-the current trends in the organization and improvement of supplementary education for municipal servants, including in pandemic contexts;
- the current state of the human capital of municipal servants in rural settlements in the Tambov region and the main directions of its development.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to examine the formation and development of human capital of municipal servants in rural areas and to substantiate the mechanisms of its development based on the competency-based approach.
Research Methods
The research employed the methods of logical and comparative analysis, using information review and statistical data as general scientific methods.
Findings
The Tambov region is part of the Central Federal District and rightfully belongs to the agrarian region. Rural settlements account for 84% of all municipalities in the region. The total area of the rural areas is 3002177 km. As of 2020, the rural population is 388731, which is 39% of the total population of the region.
In our study, we will refer to citizens of the Russian Federation who perform professional and service activities in positions of municipal service in local self-administration bodies of rural settlements and receive remuneration from the local budget (Lindsay et al., 2021).
The legislation establishes requirements for municipal service positions in terms of education, length of service and competencies. Figure 01 shows current data for the year 2020 on the qualitative composition of municipal servants in rural settlements of the Tambov region regarding the level of education. 56% of servants have higher education, 41% have secondary vocational education and 2% have no vocational education at all. We should note that the lack of professional education since 2018 is not a barrier to entry into junior positions of municipal service in the Tambov region, so the above fact is legitimate (Al-Daihani et al., 2015; Nikitin et al., 2019).
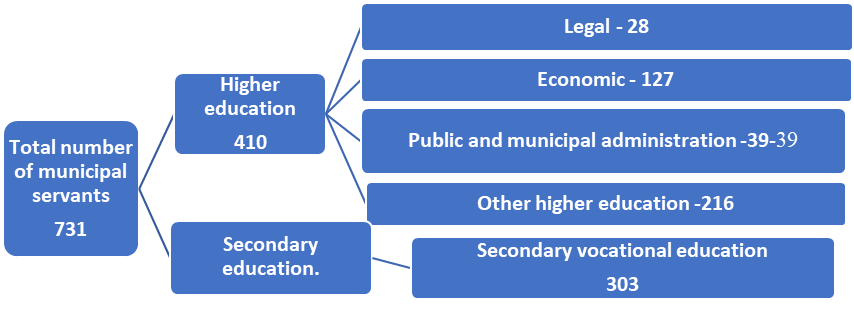
Figure 1 shows that only 5% of municipal servants have a university degree in Public and Municipal Administration. The relevant education for municipal servants is necessary but not mandatory for taking up a position. At the same time, further training courses, internships, etc. contribute to deepening professional self-identification. Labour resources and potential human capital will find application in the employee's activities at their initial recruitment. His future career will depend on how well he realizes his potential.
Length of municipal service is one important characteristic of human resources, which stems from the following provisions:
- first, it is a statutory requirement for the highest, principal and leading groups of positions;
- second, practical experience makes it possible to prioritize work more effectively and solve management problems more quickly, and advise younger colleagues;
- third, the longer the length of service, the greater the number of supplementary vocational programmes the servant has mastered and, as a consequence, the more advanced competencies in the organization and functioning of local self-administration the servant has acquired;
- fourth, as the length of service increases, so does the monthly salary increment for the municipal servant, which is certainly an incentive to continue and improve the professional activity in the chosen field.
Municipal servants of rural settlements in the Tambov region have the following length of service in municipal services: 8% have less than one year of experience, 19% have 1 to 5 years of experience, 18% have 5 to 10 years of experience, and more than half of all municipal servants have more than 10 years of special experience.
The third statutory qualification requirement for the position of a municipal servant is the condition of mastery of professional competencies. As a rule, these are requirements for knowledge of the legal and regulatory framework of the organization of state and municipal administration, specialized legislation in professional and service activity, the skills required for a particular type of activity and the presence of professionally relevant qualities.
The professional competence of a municipal servant will depend on the set of knowledge, skills and abilities (Figure 02) developed at the time of assuming the position.

In terms of developing the qualities required of a municipal servant, human capital focuses more on the socially necessary orientation. The priority is to have the following characteristics mandatory for any servant: social responsibility, honesty, psychological stability, tolerance. The principles of promotion, as in the civil service, include professionalism, length of service and competitiveness.
Higher vocational education and training is one of the opportunities for promotion in municipal service. However, higher education institutions implementing the FSES in the programme of Public and Municipal Administration according to the latest requirements face a number of problems:
- lack of a professional standard in this area;
- linking the Bachelor's and Master's degrees to the general profile of the higher education institution;
- lack of expert consultants in public and municipal administration willing to cooperate with educational institutions in the profile of the educational institution in terms of general methodological assistance.
Since 2019, the Tambov region has been implementing the subprogram "Administration Human Resources" of the Tambov regional state programme "Economic Development and Innovative Economy", which has the following objectives:
- developing a highly qualified team for the municipal service in the Tambov region;
- ensuring the effectiveness of municipal administration;
- training administration human resources for the innovation economy of rural settlements;
- increasing the attractiveness, prestige and performance of municipal service;
- increasing the human resources capacity of local authorities in rural areas of the Tambov region
- raising the level of trust of the inhabitants of the municipality in the authorities.
- modernizing and improving the system of further vocational education for municipal servants in rural areas.
Municipal service legislation enshrines the principle of "Longlife Learning", which implies lifelong learning for administration human resources by acquiring new knowledge and developing skills both through continuing vocational education programmes at least once every three years and through individual educational events - master classes, webinars, trainings, conferences, etc.
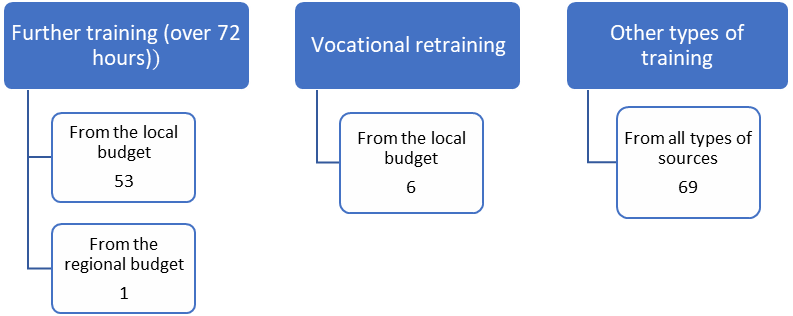
Supplementary vocational programmes for municipal servants in rural areas of the Tambov region are funded as follows:
- from the budget of the rural settlement;
- from the regional budget;
- from the local budget and subsidies received from the budget of the federation.
In 2020, 129 municipal servants from rural settlements in the Tambov region received training. Municipal servants from rural settlements in Bondarsky, Kirsanovsky, Nikiforovsky, Pichaevsky, Sampursky, Sosnovsky and Tambovsky municipal districts were the most active participants in the supplementary vocational education programmes. Figure 03 provides information on the types of programmes and sources of funding.
Conclusion
Vocational education and further training of civil servants contribute to the acquisition of special administration competencies necessary for the management of a particular socio-economic area and the development of a broader perspective on the professional problems of administrating rural areas.
New educational technologies require modernized approaches to learning. The system of certification and licensing of educational activities does not guarantee high-quality education. Higher education should not be mandatory for municipal servants, but further training should be a source of new knowledge and skills. This is particularly relevant in the current context of the introduction of distance learning technologies.
Distance learning for rural municipal servants has become the only option in the current COVID-19 pandemic. This training format involves online lectures, seminars, individual consultations and self-study group work by video conferencing. The organization of distance learning is associated with a number of problems, including insufficient equipment for the learning process, congestion and low speed of the Internet, and the inability to use printed publications and methodological recommendations in the process. Both students and teachers are confronted with these problems. A positive aspect of the learning process in distance format is the accessibility and convenience of learning time, the visibility of the materials for students (electronic format of textbooks), and the possibility of distance forms of feedback to teachers.
For municipal servants in rural areas, the issue of increasing their own human capital involves interaction with public institutions. This includes not only educational institutions, but also health care, cultural and sports institutions and non-profit organizations that perform various functions in the creation of public goods. For example, participation in voluntary and other voluntary organizations creates a positive image of the municipal servant and also contributes to the accumulation of his or her individual human capital.
The socially necessary human capital of a municipal servant in a rural settlement is 'embedded' in the staffing structure and functions more effectively than is the case with a spontaneous recruitment policy from outside. We can conclude that a good human resources policy at the municipal level does not cancel a servant's desire to increase their individual human capital. The amount of human capital and its "range" will also depend on successful interaction between educational institutions and municipal territories, fulfilling the social order for training and retraining of managers.
References
Al-Daihani, E. H., Pamesko, G., Matar, M., Raza, S. M., & Nandi, A. K. (2015). Talent management, opportunities and challenges. SPE Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference, MEOS, Proceedings 2015-January, 1381-1387.
Brozgunova, N. P. (2020). Application of information technologies in local self-administration bodies in rural areas. In Engineering support of innovative technologies in agriculture: Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference (pp. 121-127). Publishing house of Michurinsk SAU.
Ivanova, E. V., & Nikitin, A. V. (2018). Сluster-cooperative project of innovative development of agriculture. Quality - Access to Success, 19(S2), 8-14.
Krutikova, V. V. (2014). Human Capital Administration at the Municipal Level. Socio-economic Phenomena and Processes, 9(11), 92-95.
Kulikov, I. M., & Minakov, I. A. (2018). Socio-economic Study of the Food Sector: The Supply Side. European Research Studies Journal, XXI(4), 175-184.
Lindsay, A. R., Sanchirico, J. N., Gilliland, T. E., Ambo-Rappe, R., Taylor, E., Krueck, N. C., & Mumby, P. J. (2021). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(52), 33170-33176.
Nikitin, A. V., Trunova, S. N., & Voropaeva, V. A. (2019). The assessment of the effectiveness of the implementation of scenarios for the sustainable development of agriculture. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 8(10), 3002-3005.
Popova, V. B. (2015). Statistical analysis of economic data. Bulletin of the University of the Russian Academy of Education, 4, 13-20.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 February 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-123-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
124
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-886
Subjects
Land economy, land planning, rural development, resource management, real estates, agricultural policies
Cite this article as:
Guseva, M. N., Krutikova, V. V., Brozgunova, N. P., Erin, P. V., & Sinepupova, O. S. (2022). A Competency-Based Approach To Developing The Human Capital Of Rural Municipal Servants. In D. S. Nardin, O. V. Stepanova, & E. V. Demchuk (Eds.), Land Economy and Rural Studies Essentials, vol 124. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 255-261). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.02.31

