Abstract
This article discusses such a phenomenon as electronic commerce. Basic concepts with the study of their history are given. The prerequisites for the emergence of e-commerce in two types are considered: economic and technical support. Each type of background is described separately, for technical background a table was made about the functions of the Internet at various stages of the business cycle. We learned a detailed history of the development of e-commerce. It was studied that e-commerce was divided into more than 14 stages, and described the main ones, such as B2B, B2C, C2C, C2B, B2A, C2A. It was also studied what is included in these stages. An important part of the article is the analysis of trends in the development of e-commerce in the world and in Russia separately. In the world from 2014 to 2020, in Russia from 2011 to 2019. Conclusions are drawn about the future of e-commerce, mainly influencing it at this point in time.
Keywords: Electronic commerce, electronic commerce history, electronic commerce development trends
Introduction
The rise of the Internet is widely regarded as one of the greatest technological breakthroughs of the twentieth century. With the advent of the global network, people's lives have changed dramatically: it is gradually becoming difficult to imagine more and more areas of a person's life without the Internet. Progress does not stand still, the bandwidth of various networks is constantly increasing, the capacity of computer and mobile components is increasing, and it is obvious that the current degree of integration of the Internet into the life of mankind is not the limit.
It is not surprising that the Internet has not bypassed the sphere of commerce either. The first online stores began to appear in the 90s of the last century, and then few could imagine that after a couple of decades, anything could be purchased without leaving home: food, household appliances, a ticket to rest, concert ticket and much more. Now we can say with confidence that for everyday life, you don't need to visit simple shops at all. This state of affairs can be explained quite simply: Internet commerce has a number of undeniable advantages. For customers, this is round-the-clock access, the ability to place an order from any store around the world, a convenient search, and more recently, a system for analyzing the interests and needs of each user, which contributes to accurate and useful recommendations. In turn, the same features of e-commerce are useful for entrepreneurs as well, providing increased sales, an increase in the client base, and the automation of various trade processes.
Problem Statement
The Internet gave companies the opportunity to enter the global market, significantly expand the list of potential customers and create a single system that unites suppliers and buyers. Not surprisingly, most companies have long been involved in e-business and e-commerce. The exchange of data within private networks began even before the advent of the Internet in the usual form, representing the electronic transfer of documents in large companies that could afford such complex and expensive systems at that time. With the development of the Internet, electronic business (Alvin, 2019) and electronic commerce entered the life of not only large corporations, but also small firms and even individual entrepreneurs (Zhang et al., 2020).
Therefore, analysis of the development trend of electronic commerce is an important point of investigation.
Research Questions
According to N. T. Sorokin, to achieve the level of the developed countries in Russia, it is necessary to ensure advanced (in relation to other industries in general) innovative development of mechanical engineering (its growth must be at least 8-10% per year) (as cited in Fedorova et al., 2020).
These days, the terms "e-business" and "e-commerce" are often used interchangeably, although they are related, they have different meanings. Let's understand these concepts in more detail (Zhanys & Tursinbaeva, 2018).
In general, e-business is any form of business process that uses the potential of information networks. Most experts divide e-business into two main components:
- Creation and application of information systems that automate and optimize the internal business processes of the company, such as work with personnel, workflow and much more.
- External coordination with suppliers, partners and customers.
That is, e-business contains all forms of e-business activities between various entities. When giving examples of e-business, three main categories should be distinguished (Babenko et al., 2019):
- Business on the Internet (internet service and hosting).
- Business around the Internet (website development, supply of hardware, software).
- Internet business (advertising, online auctions, trade).
Based on the foregoing, we can assume that the concept of electronic business combines any activity of organizations through information and telecommunication technologies (Zhang et al., 2020).
In turn, e-commerce is only part of e-business, limited to transactions through information networks, such as the sale of goods or the provision of services. It is customary to refer to the main types of e-commerce (Boyko et al., 2019):
- E-commerce.
- Email marketing.
- Electronic money.
- Electronic banking.
- Electronic insurance.
Purpose of the Study
E-commerce can be considered one of the most important components of e-business, which is a new way of organizing, managing and executing transactions using information networks, that is, this is any type of transaction where the parties interact using information technology. So, the purpose of the study is to analyze the development trend of electronic commerce.
Research Methods
The share of machinery and equipment production in the total volume of industrial production is about 20%. In developed countries, this share ranges from 35 to 50%, which allows updating technological equipment in most industries every 7–10 years, providing these countries with another leap in technological development (Boyko et al., 2019).
The prerequisites for the emergence of e-commerce can be divided into economic and technical.
Economic preconditions.
The development of production in the last century took place in different ways. First, it was the introduction of mass production, then - the expansion of mechanization, automation of production and management of design and production of products.
As a result, over the past century, labor productivity has grown significantly (Demiroglu, 2021), thereby reducing labor costs and the cost of production. Despite such positive dynamics, the end consumer had little feeling of all the changes in view of the fact that the concentration of production, which directly depends on its automation, led to an even greater separation of production from consumption markets both geographically and structurally. This division revealed the need for some structures that would promote products from manufacturer to consumer. This promotion is commonly referred to as the commercial production cycle. ABOUT:
- Analysis of the market for goods and services.
- Managing the parameters of goods and services.
- Market notification.
- Preparing the market for the use of the given parameters.
- Receiving, processing and fulfilling orders for goods and services.
- Optimization of commodity flows and stocks.
- Settlements with consumers and suppliers.
- After-sales service.
Thus, by the end of the last century, the situation was such that the level of automation of commercial cycles did not match the level of automation of production. It turns out that the economic prerequisite for the emergence of e-commerce can be called the need to automate commercial production cycles lagging behind in development from production cycles, in particular, the need to reduce financial and time costs.
Technical prerequisites.
Obviously, the main technical prerequisite for the emergence of e-commerce can be considered the emergence of the Internet, with the help of which the necessary modernization of commercial production cycles became possible. The Internet has become an indispensable tool for meeting the long-standing needs of business cycle automation.
The Internet performs three main functions (Fedorova et al., 2020): information, communication and management, which were exactly what e-commerce needed. The commercial production cycle has clearly defined stages that can be compared with the Internet functions used in them (Table 1).
Thus, the emergence of the Internet can be considered a technical prerequisite for the emergence of e-commerce, in view of the fact that the functions of the Internet are well suited for the task of automating the processes of commercial production cycles (Kukartsev, 2019).
Speaking about the first examples of the use of information technology in commerce (Fedorova et al., 2019), let us turn to 1960. At that time, two American companies American Airlines and IBM jointly began developing a system for the automatic procedure for booking seats for flights to aircraft - SABER (Semi-Automatic Business Research Environment - semi-automatic equipment for commercial research). The system has had tremendous success: By automating the fare calculation process for seat reservations, helping customers better navigate increasingly complex tickets and flights, the system has increased the availability of air travel and increased revenues for the company.
In the early 60s, active, when the world was recovering from the Second World War and there was an active growth in production and trade, the successful application of mathematical algorithms for accounting and inventory management begins, which ultimately leads to significant cost savings. By the middle of the decade, credit cards appear that automate the process of financial and settlement operations, and the first projects to create a global distributed network appear. In 1967, a plan was published to create the ARPANET, the prototype of the modern Internet.
On October 20, 1969, a group of Californian scientists succeeded in making a new breakthrough: they connected their computer with another computer at the Stanford Research Institute. Despite the failure of the first communication attempt, by the evening of the same day, the researchers were expected to succeed.
In the late 60s and 70s, there was a rapid development of credit cards. Banks are moving from their own local card systems to global ones, the world's first centralized electronic network for accounting for bank checks is being created, work is underway on state accounting of electronic money circulation, and security protocols are being developed. In the mid-70s, the use of electronic data interchange (EDI - ElectronicDataInterchange) and electronic money transfer (EFT - ElectronicFundsTransfer) tools began for the first time.
On May 9, 1977, the now world famous interbank financial messaging network - SWIFT (Society for World-wide Interbank Financial Telecommunication - Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) appears. In the late 70s, early 80s, the first card programs changed their name, orienting it towards the international market. This is how VISA and MASTERCARD appeared, which to this day are the leaders in the field of electronic payments.
On August 12, 1981, IBM unveils its first personal computer. At that time, IBM did not rely on personal computers, but now we can clearly observe the results of the revolution that has taken place, not only in technical, but also in socio-cultural terms. Today people can no longer imagine their life without smart machines (Makoto Yokoo, 2008).
On January 1, 1983, the ARPANET completely switched to a new network model of data transmission, developed under the leadership of WintonSurf in 1972 - TCP / IP, defining this date as the birthday of the Internet. By the middle of the decade, the international standard EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Trade and Transport), adopted by ISO (ISO 9735), was developed, which greatly simplified the processes of doing business using information technology. Around the same time, Toshiba created the first laptop, pioneering the history of the laptop industry and paving the way for the emergence of mobile commerce.
By the end of the 80s, the WWW standard is being developed - WorldWideWeb, a global hypertext system. Work in this direction also led to the emergence of the http protocol, which has become the main transport protocol of the Internet.
In the 90s, the Internet takes on a more recognizable form today. Browsers, search engines, websites appear. In 1994 JeffBizos created the Amazon company and in 1995 he opened the first online store, which is currently the largest online store in the world. In the same year, the first online trading systems appeared on the FOREX market, whose round-the-clock operation and convenient access ensure a significant increase in investment from individuals.
In the late 90s, the rapid growth of e-commerce continues: payment systems, Internet banks are created, Google appears - one of the largest corporations today.
The above events show the incredible trends in the development of e-commerce, its scale and impact on the global economy.
E-commerce is conventionally divided into more than 14 types. Let's highlight and consider the main ones:
B2B - “business to business”.
B2C - “business for the consumer”.
C2C - “relationship between consumers”.
C2B - “relationship between consumers and trade organizations”.
B2A - "business administration".
C2A - Consumer Administration.
Business to Business (B2B) is a type of e-commerce in which both participants are commercial enterprises. This sector covers the relationship between companies, established in electronic form: organizing supplies and purchases, coordinating plans and contracts, receiving and paying invoices (Yurasov, 2008).
Business to Consumer (B2C) is a type of e-commerce that involves working directly with the consumer. The main task of this type of trading is to ensure the reduction of the influence of the geographical separation of organizations and clients, providing the opportunity to trade from anywhere in the world to any. B2C allows direct sales, dramatically reducing the number of intermediaries and providing competitive pricing. B2C systems include:
- Web-showcases of trading companies, which make it possible to get acquainted with the goods in order to attract potential buyers.
- Online stores that sell goods directly and provide an opportunity to immediately place an order.
- Online trading companies, in which the electronic sales system is fully integrated with all trading business processes.
Comparing shopping online and shopping in a classic store - online shopping has a number of advantages. One of these benefits is access to much more information (Gek et al., 2019). Due to the fact that online stores cannot provide the buyer with the opportunity to examine the product personally, touch, examine in detail, etc., they compensate for this by providing more complete information, providing access to full characteristics, reviews, introducing new technologies for visualizing the product.
Consumer e-commerce (C2C) is a form of e-commerce aimed at organizing the sale and purchase of goods and services between non-business consumers. In this case, transactions between consumers take place with the help of an intermediary - a kind of platform, which is an analogue of a bulletin board. The transaction takes place either entirely on the Internet, subject to the availability of electronic payment systems to each individual in the transaction, or with the help of cash, with the coordination of all other issues through electronic communications.
Consumer Business (C2B) is a form of e-commerce that allows individuals to sell their goods and services to companies. Examples of this practice are the markets for photography, music and other multimedia, freelance exchanges, websites of lawyers, consultants and other professionals who can provide their services to companies.
Business Administration (B2A) is a section of e-commerce covering all kinds of online transactions between organizations and a government agency. This form is typical for areas such as fiscal, social security, employment, legal documents, registers, and more.
Consumer Administration (C2A) is the part of e-commerce that encompasses all transactions between individuals and government. The main areas in which this form of trading can be applied are as follows:
- Education - online lectures, training videos, distance learning, etc.
- Social security - disseminating information, making payments, and so on.
- Taxes - payments, filing tax returns, etc.
- Healthcare - making an appointment, online consultations and payment for medical services.
Findings
Speaking about the trends in the development of e-commerce, let us refer to the data of the research and consulting department of IPG. Estate (Gorbachevskaya et al., 2019). According to their research, the global e-commerce market grew 17.9% in 2019 to $ 3.46 trillion. The market leaders were China and the United States, which accounted for about 40% of the market. The dynamics of the global e-commerce market is shown in Figure 1.
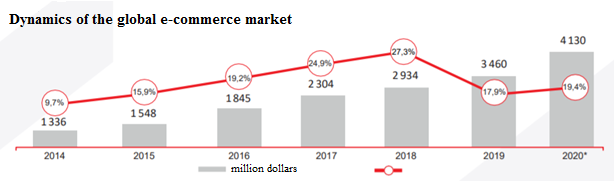
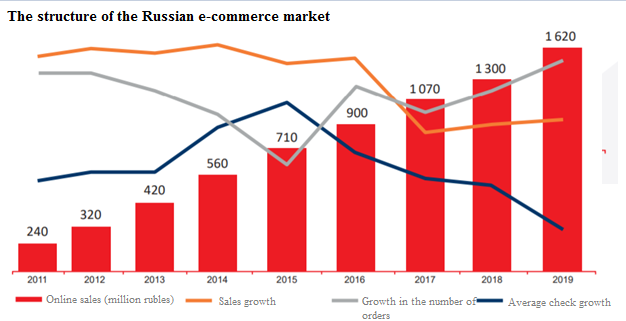
In Russia, e-commerce is also one of the most dynamic sectors of the economy. Moreover, the growth is not due to an increase in the average check, but due to an increase in the number of orders associated with both an increase in online buyers and an increase in the frequency of orders (Figure 2) (Kukartsev et al., 2019).
Conclusion
In general, the future of e-commerce largely depends on the decisions of market participants in certain tasks. Problems such as low Internet bandwidth in some countries, the lack of a developed standard for ensuring the security of the buyer's personal data and a standard for returning goods / money for goods.
One of the most significant factors affecting the development of e-commerce today is the COVID-19 pandemic. Many entrepreneurs faced the problem of inability to conduct business offline as before and were simply forced to adapt to new realities, adapting their business to online (Zambalaeva & Yang, 2020).
References
Alvin, A., & Kurniawan, B. (2019). Electronic Commerce Use of Agriculture for Creating a New Business Opportunity. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 662(3).
Babenko, V., Kulczyk, Z., Perevosova, I., Syniavska, O., & Davydova, O. (2019). Factors of the development of international e-commerce under the conditions of globalization. SHS Web of Conferences, 65.
Boyko, A. A., Kukartsev, V. V., Tynchenko, V. S., Eremeev, D. V., Kukartsev, A. V., & Tynchenko, S. V. (2019). Simulation-dynamic model of long-term economic growth using Solow model. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1353(1), 012138.
Demiroglu, N. (2021). E-commerce as a tool for the development of small business. SHS Web of Conferences, 106.
Fedorova, N. V., Kukartsev, V. V., Tynchenko, V. S., Atluhanov, S. M., Gek, D. K., & Zagudaylova, E. A. (2019). Problems of the digital economy development in the transport industry. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 315(3), 032047.
Fedorova, N. V., Kukartsev, V. V., Tynchenko, V. S., Danilchenko, Y. V., Ezhemanskaya, S. N., & Sokolovskiy, N. V. (2020). Methodology for the formation of indicators balanced system for marketing activities of an industrial enterprise. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 734(1), 012084.
Gek, D., Kukartsev, V., Tynchenko, V., Bondarev, A., Pokushko, M., & Dalisova, N. (2019). The problem of SEO promotion for the organization’s web representation. SHS Web of Conferences, 69, 00122.
Gorbachevskaya, E. Y., Nikityuk, L., & Timchuk, O. G. (2019). Features of e-business development in the construction industry. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 667(1).
Kukartsev, A. V., Boyko, A. A., Kukartsev, V. V., Tynchenko, V. S., Bukhtoyarov, V. V., & Tynchenko, S. V. (2019). Methods of business processes competitiveness increasing of the rocket and space industry enterprise. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 537(4), 042009.
Makoto Yokoo (2008). Electronic Commerce: Theory and Practice (Studies in Computational Intelligence). Springer.
Yurasov, A. V. (2008). Basics of e-commerce. Hotline-Telecom.
Zambalaeva, T. B., & Yang, C. (2020). The impact of digital currency on the activities of digital platforms. SHS Web of Conferences, 80.
Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., & Song, X. (2020). Research on the Influence of New Generation of Information Technology on Contemporary Enterprise Logistics Management Information System. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1648(4).
Zhanys, A. B., & Tursinbaeva, A. F. (2018). Internet Technology in Electronic Commerce. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1015(3).
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 February 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-123-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
124
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-886
Subjects
Land economy, land planning, rural development, resource management, real estates, agricultural policies
Cite this article as:
Kasianova, T., Kukartsev, V., Shalaeva, D., Strokan, A., Stashkevich, A., & Ivanenko, V. (2022). Analysis Of The Development Trend Of Electronic Commerce. In D. S. Nardin, O. V. Stepanova, & E. V. Demchuk (Eds.), Land Economy and Rural Studies Essentials, vol 124. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 217-225). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.02.27

