Abstract
Currently, rural areas of the country are characterized by socio-economic decline and low investment potential. One of the significant factors hindering the active development of agricultural production in the agricultural territories of Russia is a generally low standard of living and the development of the social sphere. The current situation is characterized by significant differentiation and an overall low degree of accessibility for the population of basic elements of social infrastructures, such as education and health care. During the study, the impact of the infrastructure of the education and health care sectors in rural areas on the prospects for increasing local investment activity and the development of agribusiness was assessed through the analysis of their key characteristics as conditions for attracting human resources that determine the level of investment potential of the territories. It has been established that the current situation in the field of the formation of the social infrastructure of the village is unfavorable and continues to deteriorate, which creates threats that contribute to the leveling of success in the development of agribusiness in Russia, due to the low investment potential of these territories. At this stage, it is important to create all the conditions to attract investment in rural areas, where one of the key roles is played by the state as a regulator and a guarantee of access to social benefits for the population.
Keywords: Investment potential, rural social infrastructure
Introduction
The agricultural sector today plays a large role in the Russian economy, which is associated with the historically established agrarian specialization of the country, as well as the opportunities determined by geographical and climatic factors for the active development of agricultural production and increasing exports. Production of such crops as grain, sugar beet, sunflower, and soybean, which form the basis of the country's food supply, is increasing in the current conditions in the field of crop production. As a result, within the framework of the implementation of the import substitution strategy, the level of self-sufficiency of the country in the main types of agricultural products is increasing, which is important for ensuring economic security within the country and increasing export potential. At the same time, the situation for various types of agricultural products is significantly different (Lipchenko, 2020). Grain and oilseed products occupy a priority place in the structure of Russian agricultural exports and show relatively high efficiency, although several fundamental problems remain, in particular, the existing transport and logistics infrastructure does not correspond to the ambitious tasks of further increasing export potential (Zyukin et al., 2020). For Russian wheat, it is export that is the main incentive for increasing yields. The search for new sales markets and the provision of more efficient transportation are the key directions for the development of grain farming (Generalov, 2018). Russian sugar, unlike wheat, does not have strong competitive advantages and has a higher cost than cane sugar; therefore, the search for ways of its direct export is significantly complicated, while the needs of the domestic market are satisfied (Nadaenko, 2018). In the field of livestock development, the success of Russian agribusiness is significantly less: for dairy products, dependence on imports remains, as well as for several areas of meat production, although Russia has begun to export pork and continues to intensively increase its production (Altukhov et al., 2019).
However, with all the successes and prospects along with the economic development of Russia in recent decades, as a result of the preservation of the raw material model of the economy and the active expansion of the service sector, agriculture has not become more significant in the structure of the economy, which preserves its low investment attractiveness, forming several prerequisites for an increase in influence structural problems. If before, up to the 60s of the 20th centuries, the share of the rural population of Russia was overwhelming, then later, with the beginning of urbanization, the urban population began to actively grow, as a result of which today the rural population accounts for only about 25%. As a consequence, the specifics of the changed socio-economic relations lead to a decrease in both social and economic importance of the agricultural sector, which is aggravated by the lack of investment resources and a decrease in human resources in rural areas, influenced by unfavorable trends in the social development of the village.
Urbanization and the concentration of labor resources in economic centers have led to the fact that the infrastructure of rural areas, which was previously mediocre, began to lag catastrophically, especially due to the lack of the necessary volumes of investment adequate to the needs for its development. Currently, the rural areas of the country are characterized by socio-economic decline and ongoing active labor migration of the population to cities. A negative consequence of these trends is the fact that agricultural production, which in the overwhelming majority is located outside the cities in rural areas, is experiencing a shortage of personnel, which hinders the active development of agriculture. The lack of social infrastructure necessary for a comfortable life and accompanying economic problems determined the limited conditions for the development of agribusiness in rural areas. The actual threat at the current stage is a significant decrease in human resources, due to the reluctance of people to live and work in areas with a low standard of living and the availability of social infrastructure. Personnel problems are of great importance for agricultural production, given its specificity and the large role of qualified labor in ensuring the development of agribusiness, which explains the relevance of the study.
Problem Statement
In the current conditions in the Russian Federation, there is a problem of forming an investment climate in all spheres of the economy, which is caused by a structural crisis, generally unfavorable conditions, as well as a lack of resources and their uneven territorial distribution with a concentration in investment centers. The situation is developing in such a way that business does not invest resources in industries or territories that have several problems that impede the active development of production and economic activity. The prerogative of supporting socially and economically disadvantaged territories belongs to the state; however, due to the limited budgetary funding, adequate to the problems is not carried out, and the financial model of Russia involves the centralization and withdrawal of financial resources from their regions (Zyukin et al., 2020).
One of the significant factors hindering the activation of investment processes in agricultural production in the agricultural territories of Russia is the generally low standard of living and the development of the social sphere. The current situation is characterized by significant differentiation and an overall low degree of accessibility for the population of basic elements of social infrastructures, such as education and health care, as a result of which the rural area has a low degree of attractiveness for living. This is since in modern conditions people strive to provide themselves and their families with a decent standard of living, and children - a good education and quality medical care. Therefore, young and qualified specialists leave rural areas, where people of the older age group, characterized by low labor potential, remain. As a result, businesses in remote agricultural areas suffer from a lack of infrastructure, which intensifies the challenge of investment development and expansion. In such conditions, big business does not strive far into the countryside due to the need to create a comfortable infrastructure for potential employees at the expense of its resources. At the same time, small businesses such as peasant farms and other types, as before, exist in rural areas, including geographically remote, but the scale of its activities is small, which does not have a significant impact on existing problems.
Since the creation of human resources plays an important role in the development of the agro-industrial complex in Russia, the problem of forming a social infrastructure that meets the basic needs of the population comes to the fore, becoming a key one. It should be noted that the solution of this task is entrusted to the state. Since social sectors are traditionally budget-financed, in the face of limited financial resources and a widespread deficit of municipal budgets, it is practically impossible to renovate and modernize the social infrastructure. The creation of a favorable social environment will facilitate the inflow of investments, which, in turn, will have a positive impact on the formation of human resources in rural areas. At the same time, this is a long-term process, which is the foundation for the revitalization of the economy and investment activity. In this regard, the question of creating conditions that would facilitate an active influx of personnel to agricultural areas and create new prerequisites for the development of agricultural production in Russia remains open, constituting one of the most significant current problems.
Research Questions
The main issues addressed in this study are:
- socio-economic relations in the field of investment climate formation in rural areas;
- lack of resources in the education and health care system of rural settlements, which negatively affects the quality and availability of social services for the population;
- difficulties in the formation of human resources adequate to the tasks of investment development in rural areas.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this work is to study the impact of the state of infrastructure in education and health care systems in rural areas through the analysis of their key characteristics as a condition for attracting human resources in the required quantitative and qualitative value, determining the level of investment potential of the territories, on the prospects for increasing local investment activity and business development, primarily turn, agricultural specialization.
Research Methods
During the study, using data from the collection "Russian Statistical Yearbook" for 2020 [6], the main indicators of the development of education and health care in rural areas of Russia in the period 2015-2019 were considered, the main trends and their impact on the development of agro-industrial potential were identified. countries. The study of the state of education and health care in rural areas as a factor in the formation of agro-industrial potential was carried out based on several methods and approaches, including analysis of dynamics, comparative and logical analysis. The study identifies trends in the dynamics of the indicators under consideration, which reflects the situation that is being formed under the influence of socio-economic factors. If the situation develops negatively, according to the methods used, the trend lines will have a downward character. In the absence of pronounced trends in the dynamics of indicators, the assessment can be made through the study of the degree of variation of the time series over the years.
The indicators of the total number of schools, as well as the number and proportion of students, were selected as the key characteristics of the development of the education sector in rural areas. Assessment of the dynamics of the number of rural schools will reveal trends in ensuring the implementation of the educational process in rural areas while assessing the dynamics of the number of students in rural areas - a quantitative change in the needs of the rural population for educational services. As a result of studying the dynamics of the share of students in rural areas, it is possible to establish the degree of significance of the development of the education sector in each territory. In the rural health sector, the main characteristics are considered the dynamics of the number and proportion of medical organizations of the primary (outpatient and polyclinic institutions) and secondary (hospitals) link, which is of great importance in the framework of optimization processes carried out in the industry, as a result of which there was a shift in focus primary link. Despite the optimization, the quantitative value of the hospital network of healthcare institutions in rural areas should remain at a sufficient level to ensure the availability and timeliness of medical care.
Findings
Since the potential of agricultural areas largely depends on the availability and degree of development of social infrastructure, the problem of socio-economic development of rural areas in Russia is significant. Assessing the development of education in rural areas, it can be noted that over the past 5 years in the Russian Federation there has been a steady decline in the total number of rural schools. If in 2015 there were 25.3 thousand rural schools in the country, then by 2017 the indicator dropped to 24.1 thousand schools, and by the end of the study period, it reached 22.9 thousand, which is the lowest value in the study period. As a result, we can say that in the last 6 years alone, the overall decline in the number of schools in rural areas was 9.5%. This indicates that the availability of educational infrastructure in rural areas is declining. Even though the number of rural residents in recent years in Russia has tended to decline against the background of ongoing urbanization, today their share is still significant and amounts to about 25% (Figure 01).
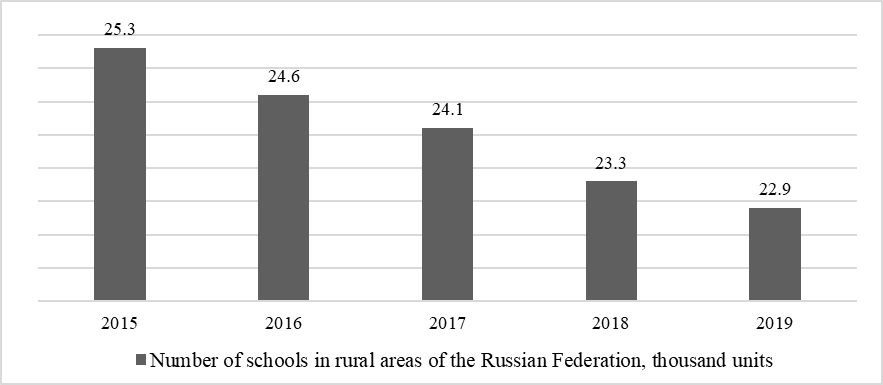
In turn, the number of students in the school area over the past 5 years has varied slightly, with a tendency to increase slightly: in 2015, there were 3.76 thousand students in rural areas, and by 2017 the indicator increased to 3.86 thousand people. In the last 2 years, the number of students in rural areas exceeded 3.9 thousand people and reached 3.94 thousand people by the end of the study period, which is almost 5% higher than the level of the base year (Figure 02).
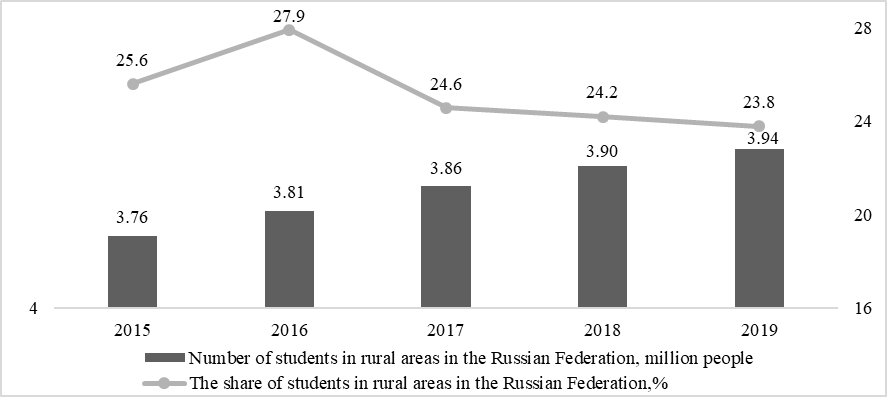
At the same time, the proportion of students in rural areas of the total number of students in the country in 2015-2016. tended to grow to 27.9%, and in the last 3 years began to actively decline, reaching 23.8% by the end of the study period. As a result, we can say that today there is no development of educational infrastructure in rural areas, but a decrease in the number of educational institutions is observed. Because the number of students in rural schools does not decrease and is about ¼ of the total number of students in the country, the current situation indicates a decrease in the availability of educational services for the rural population. As a result, rural areas are less attractive for living in comparison with urban areas, where social infrastructure is more developed, which naturally leads to an outflow of the population to cities and other large settlements.
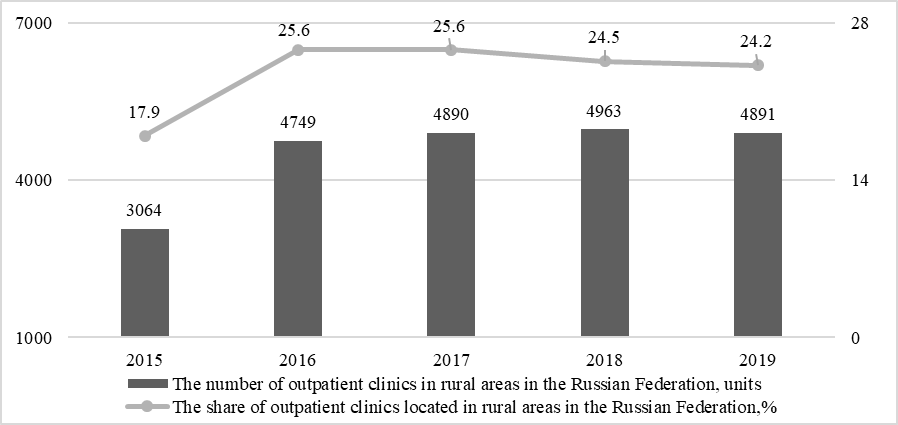
An assessment of the situation in the health sector, which is no less important, showed that capacity is increasing in the primary sector, as evidenced by the increase in the total number of outpatient clinics in rural areas. In the base period, the number of outpatient clinics located in rural settlements was 3064 units, and in the next year, it increased to 4749 units, which indicates an increase of 55% and is associated with the modernization processes in healthcare. In the last 3 years, the indicator has varied insignificantly and is at the level of 4.8-4.9 thousand units. The current situation is due to the optimization of resources in health care, as a result of which the emphasis and the main load on the outpatient-polyclinic link have been shifted, since this approach allows detecting diseases in the early stages and conducting outpatient treatment, thereby reducing the burden from hospitals, which will save limited financial resources. industry.
Along with the growth in the number of outpatient clinics in rural areas, there was an increase in the share of such outpatient clinics from the total number in the country. If in 2015 the share of rural areas accounted for only about 18% of the outpatient clinic in the country, then in subsequent years this figure increased to almost 25%. It is also worth highlighting that the largest number of outpatient clinics during the study period was observed in 2018, and by 2019 there was a tendency for their reduction, while the largest share of rural outpatient clinics was observed in 2016-2017 (Figure 03).
Assessment of the situation in the stationary sector of the industry showed an active decrease in both the number and the share of hospitals in rural areas, which is associated with optimization. Since inpatient medical care is the most expensive type for the healthcare industry, the search for reserves to reduce costs was carried out in this direction. The maintenance and servicing of hospitals and their bed funds are resource-intensive. Therefore, the optimization primarily affected the rural area, due to its small number and low workload of hospital organizations.
As a result, over the past 5 years, the total number of hospitals in rural areas has decreased from 1064 units up to 982 units, which characterizes a decrease of 8%. At the same time, the share of hospitals located in rural areas, despite an increase in 2019 to 19.1%, in the last 3 years tends to decline to 18.7%. Therefore, we can say that the hospital network in rural areas of Russia has undergone reductions over the past 5 years, resulting in a decrease in the number of hospitals (Figure 04).
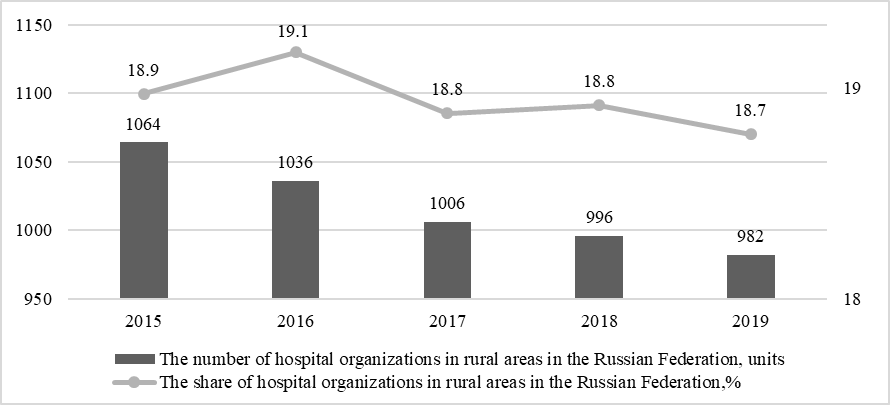
Given the large territorial extent of the country and the remoteness of certain territories from large cities and economic centers, the current situation indicates a decrease in the availability of health care resources for the rural population. Lack of necessary social infrastructure also contributes to a decrease in the attractiveness of rural areas for the population. Despite the strengthening of the primary sector of the industry, the role of hospital organizations in the provision of medical care and health preservation is great, therefore, the availability of medical care and the possibility of its timely provision is one of the key aspects.
Conclusion
The study showed that the main indicators of the development of education and healthcare in rural areas of Russia reflect the existing problems in the development of the social infrastructure of the village. Over the past 5 years, there has been a decrease in the total number of rural schools in the country by almost 10%, as a result of which their number today is 22.9 thousand. Despite this, the number of students in rural areas has a steady upward trend of 5% over the study period, reaching 3.94 thousand people by 2019. The proportion of students in rural areas is decreasing, which is due to the more active growth of the indicator in cities. As a result, it can be concluded that while the trend towards an increase in the number of students in villages continues, a decrease in the total number of educational institutions indicates a decrease in the availability of this type of social services for the corresponding category of the population. Probably, the quantitative reduction of schools was carried out due to the reorganization and enlargement of the network of educational institutions, which made it possible to save on the maintenance and provision of the educational process, but at the same time had a negative impact on the territorial accessibility and proximity of schools for the population, and, ultimately, on the infrastructure attractiveness of the countryside of the country.
The situation is similar when considering the situation in the country's health care sector: as part of the optimization in rural areas, structural changes were carried out, as a result of which there was an increase in the number of outpatient clinics while simultaneously reducing the number of hospitals. In 2019, in Russia as a whole, there are 4891 outpatient clinics and 982 hospitals in rural areas in Russia, which is equal to 24.2% and 18.7% of the total number in the country. At the same time, in our opinion, in rural areas, the provision of the population with hospitals and inpatient medical care is of greater practical importance, since primary medical care often has a long time frame for provision, while inpatient care can be urgent. Therefore, the territorial and physical accessibility of specialized, including high-tech, medical care in a hospital setting is one of the significant criteria for the formation of a favorable social infrastructure and investment potential of rural areas.
Consequently, the current situation in the field of the formation of the social infrastructure of the village is unfavorable and continues to deteriorate, which creates threats that contribute to the leveling of success in the development of agribusiness in Russia, due to the low investment potential of these territories. It is important to create all conditions for attracting investments in rural areas, where one of the key roles is acquired by the state as a regulator and guarantor of ensuring the availability of social benefits for the population. Despite the adoption permanently of various kinds of comprehensive programs for the development of rural areas, the unfavorable economic situation in the country in recent years has a negative impact on their implementation, as a result of which there are no qualitative changes. In addition to a generally low standard of living of the rural population, this negatively affects the possibilities of intensifying the use of rural areas and the development of their personnel potential. In this regard, it is necessary to use a different approach based on increasing the interest of large agribusiness in the development of rural areas from the standpoint of entrepreneurial activity, which is impossible without the creation of a basic list of infrastructure facilities by the state.
References
Altukhov, A. I., Kundius, V. A., & Kovaleva, I. V. (2019). Prospects of development of export of agricultural products and foodstuffs in the countries of the shanghai cooperation organization. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. The proceedings of the conference AgroCON-2019, 012201.
Generalov, I. G. (2018). Factors of economic efficiency of grain production in the region under various agro-climatic conditions. Azimuth of Scientific Research: Economics and Administration, 2(23), 114-116.
Lipchenko, E. A. (2020). Food security in the conditions of structural transformations of the food sector of the economy. Agroindustrial Complex: Economics, Management, 9, 4-10.
Nadaenko, A. Yu. (2018). Problems of import substitution of products of the regional agro-industrial complex. Azimuth of Scientific Research: Economics and Administration, 1(22), 198-200.
Zyukin, D., Svyatova, O., Zolotareva, E., Bystritskaya, A., & Alyokhina, A. (2020). The improvement of the model to develop the infrastructure of the grain product subcomplex as the essential attribute to increase the efficiency and ramp up of Russian grain export. Amazonia Investiga, 9(25), 461-470.
Zyukin, D. A., Bystritskaya, A. Yu., Golovin, A. A., & Vlasova, O. V. (2020). The share of health care spending in the structure of GDP as a criterion for the healthcare system effectiveness. Año 11, 30, 352-363.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 February 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-123-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
124
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-886
Subjects
Land economy, land planning, rural development, resource management, real estates, agricultural policies
Cite this article as:
Pasechko, L. A., Solovyova, T. N., Ovod, A. I., & Grebneva, M. E. (2022). The Social Sphere And Investment Potential In Rural Areas. In D. S. Nardin, O. V. Stepanova, & E. V. Demchuk (Eds.), Land Economy and Rural Studies Essentials, vol 124. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 157-165). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.02.20

