Abstract
In the era of information technology, Big Data analytics enable us to get the updated information and have an in-time overview of certain situations. With the help of Baidu Index, a kind of Big Data, we can figure out the top 5 popular tourism sites in China, and how bad they have been influenced in pandemic, as well as what degree they have rebounded in the post-pandemic era. By analyzing the data of Baidu Index, comparing this data in the beginning of pandemic and in post-pandemic era with that in the normal situation, we find that, while there is no record for search query keyword: COVID-19 or Coronavirus updated news, tourism in china's top three hot cities, as well as in Wuhan had high demand, while The search index record of COVID-19 remained a high value, The search index record of Travel Guides reached its minimum value correspondingly. From the breakdown of searcher image, it shows Xian is the most popular tourism destination in East, North and Northwest China. At last, we proposed suggestions to promote the further development of tourism industry in China.
Introduction
In today’s travel industry, effective integration of GPS, smartphones and 5G allows people to experience new travel patterns through mobile phones. The concept of smart tourism has been proposed for many years, and tourism industry also gained an unprecedented growth due to smartphone affordability, faster Internet access at cheaper rates, and the influence of social media. Using big data analytics enabled mobile travel space to grow rapidly. Many companies who have engaged big data analytics in their customized tourism products have seen a growing market share (Sunagar, et al., 2020) However, The outbreak COVID-19 pandemic has crippled this progress, China’s tourism industry faces mounting negative economic impacts. Meanwhile, we should also see that this disaster bring not only brings challenges but also produces opportunities to fasten the transformation of smart tourism. Therefore, it is important and meaningful to explore these issues in China’s tourism industry in the period of before, within and after post-COVID-19 (Smart et al., 2021).
Problem Statement
Nowadays, researchers have studied tourist behaviour and predicted tourism demand with the help of search engine data. Bangwayo-Skeete and Skeete (2015) took advantage of Google search index to forecast Caribbean's tourist volume and found Google search data can improve the forecasting performance. In China, Baidu is the wide used search engine, and the Baidu Search Index (BSI) is easily to access for the public. Many scholars have applied Baidu search queries to conduct research on different subjects, such as Li et al. (2018) proposed a model named PCA-ADE-BPNN to forecast tourist volume based on Baidu index with case studies of Beijing City and Hainan Province in China, the results indicate the proposed PCA-ADE-BPNN is a potential candidate for the effective forecasting of tourist volume. Wang et al. (2020) analyzed the impact of haze weather on tourist arrivals and examine whether haze weather affects tourists’ destination preference for scenic spots by using the Baidu Index, they got conclusions that, from a regional perspective, haze weather and its severity have a significant and negative impact on tourist arrivals, and they also estimated that Beijing lost 5.22 million tourists and 8.95 billion yuan in tourism revenue due to haze from 2016 to 2018.
Literature reviews have proved big data is an efficient research method can be used to analyse different subject including tourism industry, and improve prediction accuracy. However, few scholars adopted this method to study China's tourism situation in national-level, especially during the pandemic era. Therefore, this paper aims to:
- Explore changes in Chinese tourism industry in the period of before, within and post-COVID-19.
- Forecasting tourist volume based on Baidu index.
Research Questions
Baidu, as a major search engine in China, has become the main tool for Chinese netizens to search any information they are interested in and concerned about, because Baidu offers a Big-data-based tool, Baidu Index. In the era of Information and Communication Technology (ICT), when people search for information through Internet, the search engines, such as Baidu Index and Google Index, will record the keywords they enter such as what Baidu Index and Google Index do, and with the help of these tools, people’s concerns, needs, and preferences in a particular period can be studied objectively. In recent year, Baidu Index has become a very good data source for scholars in China due to its excellent performances (Li et al., 2018).
Purpose of the Study
The reason we use Baidu Index as a convenient approach to study selected hot tourist destinations before, within and after COVID 19 pandemic is based on two aspects of considerations. First, as we still in the post-COVID 19 era, we need timely updated data to trace how this pandemic affected tourism industry in China by comparing the relative data before pandemic with within and after COVID 19. However, data released by most official website or statistic resources have a lag time, Baidu Index can access the timely data and get the timely response compared with probability sampling methods. Second, the wide use of Baidu engine and Baidu Index in tourist industry in China has indicated that information-rich data or information communication technologies (ICTs) has played more and more important role in people’s daily life and cloud services in the network also enables people in China to better search for all kinds of information needed. In this paper, we use the Baidu Index to trace five famous tourist attractions in China to see how people’s attention to these scenic spots has changed before and after the COVID 19 pandemic, the data shown by Baidu Index will give us a visual insight.
Research Methods
Referring to the Top ten scenic spots in China, the selection launched and organized by China Travel Daily in 2019 and duo to the limitation of article length, we picked up three cities where the top three scenic spots located and traced the changes of their Baidu Index, that’s Terra-Cotta Warriors in Xian, the Forbidden City in Beijing, and West Lake in Hangzhou. In order to emphasize the impact of pandemic, we put Wuhan, Hubei province into consideration particularly. Since most travellers will use a search engine to find information and then make an appropriate travel decision before travelling, such as the destinations, restaurants, transportations, and attractions and so on (Li et al., 2018). After we quickly checked these probably search queries in Baidu Index, we eventually choose the highest frequency search query, Travel Guides, and we studied this search query of above selected four tourist destinations respectively in the big data of Baidu Index during the period of Jan.1st, 2018- Apr.20th, 2021. In addition, the relevant searcher images in the same period can also be provided us some useful information and hints to contribute to the development of smart tourist in China (Li et al., 2018).
Findings
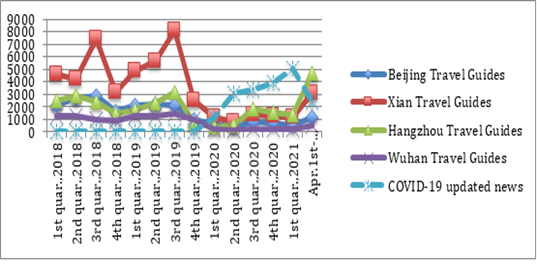
Quarterly daily average for search queries of keywords: Travel Guides VS. keywords: COVID-19 updated news
We record the quarterly daily average for search queries of keywords: Beijing Travel Guides, Xian Travel Guides, Hangzhou Travel Guides and Wuhan Travel Guides in Baidu Index from Jan.1st, 2018 to Apr. 20th, 2021, As seen in Figure 1 below, and we find that from the first quarter, 2018 to the fourth quarter, 2019, while there was no record for search query keyword: COVID-19 or Coronavirus updated news. The Internet users in China remain a high search index record for the keywords: Beijing Travel Guides, Xian Travel Guides, Hangzhou Travel Guides and Wuhan Travel Guides while the daily average indexes are 2101, 5063, 2152 and 1187 respectively, indicating that during this period, tourism in these top three hot cities and Wuhan had high demand, especially during the public and national holidays, as well as winter and summer holidays, we can see the search index record for the keywords: Travel Guides in these four cities peaked in the third quarter in both 2018 and 2019 due to the summer holidays, when there was always a boom of student and family trips. The turning point was remarked in the first quarter, 2020, the search index records of keywords: Beijing Travel Guides, Xian Travel Guides, Hangzhou Travel Guides and Wuhan Travel Guides dropped by 70%, 75%, 77% and 78% year over year, and there was a sharp decline on Jan.20th and 23rd, 2020 after the news releasing in the People’s Daily that Coronavirus cases broke out in Wuhan, and later spotted in Beijing and Guangdong city, and followed by the lockdown of Wuhan. The search index record of COVID-19 remained a high value from the second quarter, 2020 to the first quarter, 2021, which is from 3000-5000, specifically, it reached its peak value of 5000 in the first quarter, 2021 as there were signs for outbreak rebound and Chinese government called on a stay-put policy during Chinese tradition spring festival, and meanwhile, in the same period, the search index record of Travel Guides reached its minimum value of below 1000 in the second quarter, 2020. (See in Figure 1).
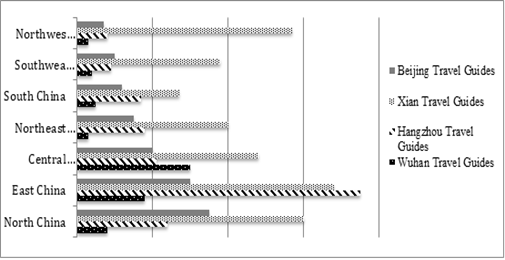
Breakdown of searcher image based on location in China
Up the keywords search box shows the searcher image. According to the breakdown of searcher image based on location in China from Jan.1st, 2018- Apr. 21th, 2021 (Figure 2), we can get the following information, firstly, Xian, the capital of several ruling dynasties in ancient China and a market and trade center in modern China attracts successfully most Chinese people from different part of China and especially becomes the most popular tourism destination in East, North and Northwest China. Secondly, Hangzhou, the subtropical monsoon climate makes it one of China's most popular travel destinations. It especially attracts by people from east China and has a high popularity in north China, central China, as well as northeast China.
Conclusion
Since scholars have proved there is a positive correlation between the increasing Baidu keyword search index and the increasing observed tourist flow (Huang et al., 2017), we have good reason here to believe that:
- Low Baidu search index in our observed four cities indicated that low tourist flow is necessary to these four cities correspondingly, bringing challenges to Chinese tourism during pandemic.
- Similarly, the arising Baidu search index in the post-pandemic since Apr.1st, 2021 also indicated an increasing tourist flow to these four cities, showing signs of revival of Chinese tourism.
Considering that the important various indicators of service innovation of smart tourism system are Scientific development view, tourism market competitiveness and Pre-tour information service (Hong, 2020), we believe that the following measure may contribute to China’s tourism industry, for example, it is a must to make timely response to people's travel, shopping, search and other activities through big data, and timely push relevant scenic spot information, especially when people browse self-service tour information through intelligent devices. We also should provide real-time on-the-spot information precisely to targeted customers with certain age group and gender, such as traffic conditions, route Settings, accommodation arrangements, tourist reviews, shopping prices, consultation phone numbers and so on. Only in this way can tourism consumption be stimulated to the maximum extent, and the experience satisfaction of passengers can be improved.
Future Direction
This paper used Baidu Index to give a big data analysis on the Challenge and Opportunities of China’s tourism industry during the Pandemic, gave methods to trace timely changes in people’s interests or concern in tourism industry during this special period. However, due to time limit, we failed to study more sample tourism cities, neither examined more data for the observed tourism destination and COVID-19 report cases. These limitations open avenues for future research. Future research may set up a linear regression model, choose more sample tourism cities, use more keyword search queries and more COVID-19 report cases to find out their correlation coefficient which can lead to more scientifically accurate predictions.
Acknowledgments
Tianjin (China) Philosophy and Social Science Planning Research Project, Research on Service Innovation Models in the Smart Tourism System of Tianjin in the New Era, Project Number: TJGL19-033.
References
Bangwayo-Skeete, P. F., & Skeete, R. W. (2015). Can Google data improve the forecasting performance of tourist arrivals? Mixed-data sampling approach. Tourism Management, 46, 454-464.
Hong, L. (2020). Study on intelligent tourism service innovation of Tianjin classic scenic spots based on grey correlation method. Tourism Overview, 2020(5), 40.
Huang, X., Zhang, L., & Ding, Y. (2017). The Baidu Index: Uses in predicting tourism flows–A case study of the Forbidden City. Tourism Management, 58, 301-306.
Li, S., Chen, T., Wang, L., & Ming, C. (2018). Effective tourist volume forecasting supported by PCA and improved BPNN using Baidu index. Tourism Management, 68, 116-126.
Smart, K., Ma, E., Qu, H., & Ding, L. (2021). COVID-19 impacts, coping strategies, and management reflection: A lodging industry case. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 94, 102859.
Sunagar, P., Hanumantharaju, R., Siddesh, G. M., Kanavalli, A., & Srinivasa, K. G. (2020). Influence of big data in smart tourism. In Hybrid Computational Intelligence (pp. 25-47). Academic Press.
Wang, L., Zhou, X., Lu, M., & Cui, Z. (2020). Impacts of haze weather on tourist arrivals and destination preference: Analysis based on Baidu Index of 73 scenic spots in Beijing, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 273, 122887.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 January 2022
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-122-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
123
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-494
Subjects
Communication, Media, Disruptive Era, Digital Era, Media Technology
Cite this article as:
Hong, L., Qimin, Q., Xianhang, X., Binti Ismail, N. A., & Chunshu, Z. (2022). Covid-19 and Its Impact on Tourist Attractions in China: A Baidu Index Analysis. In J. A. Wahab, H. Mustafa, & N. Ismail (Eds.), Rethinking Communication and Media Studies in the Disruptive Era, vol 123. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 346-351). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.01.02.29

