Abstract
The ability of regional authorities to build a competent territory brand is becoming increasingly significant in today’s fast-growing world. Having a strong and highly-demanded brand is a key condition for success. Product trademarks, countries, cities and regions need a brand in modern realities. The economic and social state of the region depends on how competently branding is carried out. Many experts point out that branding of places is required for territories that do not have significant natural resources. However, branding is necessary for all territories, since it is impossible to be competitive without a well-built brand in modern market conditions. The concept of territorial positioning of brands is gaining more and more importance, namely, the direct dependence of the brand on the place of development and production. The choice of a product depending on the place of the goods origin is becoming more and more relevant; the number of consumers who prefer to choose a product according to the relevant criteria is increasing. Thus, we can draw a conclusion about the direct dependence of the country brand and the product brands produced in the territory of this country or region. The branding of countries and regions is gaining in importance. Regions that do not have significant natural resource conditions need to build an origin of financial inflow to the region by creating a favorable investment climate. To create a successful territory brand, it is necessary to attract a team of specialists in the field of brand management and regional marketing.
Keywords: Branding methods, place marketing, territory brand, territory image
Introduction
Territorial branding is a young direction in marketing that has established itself as a scientific discipline at the beginning of the 21st century. If earlier goods, services and people were considered brands, then with the advent of Anholt’s works, territories began to be attributed to brands. The main task of specialists in the field of brand management is to create a positive image in the minds of consumers, increase the importance of a branded product or service among products of an identical or similar category, and create brand value. Countries, cities and regions are actively competing with each other, as well as product brands, for attracting investments, tourists and, as a result, improving the economic and social indicators of the territory (Eskiev, 2019).
In order to understand why a particular territory is a brand, we should consider the concept of “brand” and its meaning. In modern realities, brands include: companies, universities, social networks, sports clubs, movie stars, regions, countries, and etc.
A brand is a response to the wishes of people, it is an opportunity to become a part of a certain image, and it is compliance with expectations, life principles and status. The main feature that distinguishes a brand from an ordinary product is that the brand is formed in the minds of people; the brand is a set of certain emotions, feelings, opinions and expectations of the consumer.
Brand management is a complex system for creating and developing brands. The success of the company depends on how competently the branding is built. There are many types of branding which, depending on a large number of factors, are designed to ensure the effectiveness of a given company. It is necessary to consider the basic concepts and definitions of brand management, the history of its origin in order to understand its significance as a science of brand development and management. The main goal of brand managers is to make the product most attractive for consumers, it is essential to create a positive image. Brand management is a complex system for creating and developing brands. There are many definitions of the brand concept; various characteristics of the definition are given depending on the direction. There are many concepts and interpretations of the “brand” definition. Marketing guru Philip Kotler identifies about 80 definitions of the brand concept of in his works (Ankholt, 2004).
Thus, one of the most commonly used definitions for a brand is the following: Brand management is a brand controlling system. It is a set of marketing technologies applied to a specific brand, product or service in order to increase the value in the perception of final consumers and target audience. The brand definition of the American Marketing Association is often used (Eng. American Marketing Association): “Brand is a name, term, sign, symbol or design, or their combinations that are intended to identify the goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to distinguish them from the competitors” (Eskiev, 2020, p. 221). The main goal of any branding is to increase the product significance in the perception of consumers, and to enhance brand value. Based on the main goals of branding development, the following main tasks of brand management can be distinguished: creation of conditions for brand formation; building brand benefits; formation of brand value and personality (brand DNA); positioning of brand; management of brand hierarchy; development of brand sustainability and integrity; brand evolution, and etc.
In 2002, the term “place branding” was first used by Simon Anholt, an expert in the field of brand management and image-making of countries, regions, and cities. He is the founder of the national brand theory the main essence of which is that a territory can be presented as a kind of product that has its own brand. Marketing specialists Philip Kotler, Seppo Rainisto (How to Build Brands of States, Cities and Resorts: A Plan for Territory Brand), and others, have also used the concept of place marketing. Anholt considers “national branding” in his work “Branding of places and public diplomacy” as “an area of knowledge and practice aimed at measuring, building, and managing the reputation of countries.” He developed his own system for assessing the effectiveness of the state’s brand – National brand index. Simon Anholt worked out the concept of competitive identity which he proposed in the form of a hexagon represented by the six element factors of the contemporary territory brand (Figure 01).
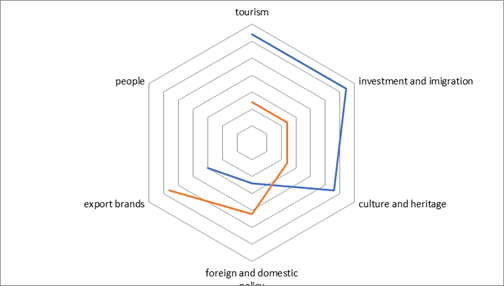
- Tourism. Tourism is one of the highest priority areas when building a territory brand. Territories, like product brands, compete with each other to attract tourists. The decisive role in attracting tourists to the region is played by the region image; how competently the image of a particular territory, its advantages and opportunities are conveyed to the target audience. The competitive advantage is what distinguishes the branded territory from other regions of the same orientation.
- Investment and immigration. Investment policy of the country, opportunities for attracting investments, international brands.
- People. The people living in a given country, famous personalities, movie stars, politicians and sports stars form a certain image, their behavior, life, and cultural values, as well as form the country image, the population lifestyle, and etc.
- Culture and heritage. The country’s activity in the field of culture and promotion of its cultural heritage: a world tour of the national opera, books by a famous author, and victories of the national team in a particular sport.
- Foreign and domestic policy. The country’s political course, decisions made by the country’s leadership, the image of politicians.
- Export brands. A country that exports its goods and services with the designation "Made in" forms its image. The quality of the country’s main brands will positively affect all the manufactured goods of the brands.
Problem Statement
The problem of choosing a suitable territory brand approach.
Russian cities are also developing their own brands based on the achievements of global city brands. Territory brand is a relatively new direction for Russia which is formed as a result of trial and error. Many agencies for creating a brand of cities in the Russian realities make a number of basic mistakes. Primarily, this seems to be like copying the brand of cities from Western counterparts when it is essential to adopt the experience of successful territorial brands. However, full copying cannot be effective due to national and territorial characteristics (Silvia, 2007). The second but no less important mistake is that the agencies involved in brand development are different in level and approach to brand building. For instance, one agency might develop a logo, another might develop a slogan, and etc. The fragmentation of the main elements of a single brand, as a rule, negatively affects the formation of the brand.
Research Questions
Importance of place marketing and territory brand.
Place marketing is a set of activities aimed at improving the image of these territories; it is the creation of a certain image to attract capital. In the case of regional branding, the main goal is economic and social development by creating and improving the main advantages of the region.
The main task of place branding is to attract investment to the territory (Cleave, et al., 2016). Many factors affect the attraction of investments and the aim of brand management is to use the appropriate mechanism to achieve the inherent indicators.
Territorial branding has many interpretations and classifications.
Territorial brands are divided into three types in terms of coverage: local, national and multinational.
1) Local are brands of companies, goods and services that are allocated in a specific geographic area. A local brand is a brand of a limited area within a city, district or territory. The Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation gives its definition of local brands: brands of Russian cities and regions which act as a marketing tool for territories in order to attract investment and human resources, as well as brands of goods and services localized in a specific geographic area. Local brands include city brands, resorts, tourist centers (Dubai, Nice, Amsterdam, and etc.).
2) A national brand is carried out at the level of one country and requires large investment and financial investments. It is a brand of the whole country which is promoted in the world market. The most famous national brand is considered to be “Brand America”, based on the brand of the United States of America by Simon Anholt and Richard Hildreth. They examined the significance of national brands in contemporary conditions and the popularity reasons of the US national brand.
3) A multinational or global brand is based on the same strategic principles in the field of positioning and marketing on a global scale.
Purpose of the Study
Development of a territory typology for building a branding of the region.
High competition between countries, cities and regions predetermines the development of new mechanisms of territorial branding to attract consumers. Competition of territories is a crucial aspect for attracting medium and large companies, investments, and capital.
However, not all territories have the same conditions for attracting such investments. The factors that large companies need to locate their offices and production facilities vary significantly. The conditions are so incomparable that when it comes to one city, companies compete with each other for the right to locate their production or office, while other territories that belong to the second type, on the contrary, compete for the attention of these companies. Thus, it can be divided into two types:
1) FIRST TYPE – companies are fighting for the right to locate their business in a convenient territory offering significantly better conditions for the city. The office location in such cities and countries has a positive effect on the company's image, on its reputation as a major player. The more such companies are located in a given territory, the more its attractiveness becomes. Such cities have great advantages, a reputation formed over the years, a good location, proximity to other large economic centers, when the territory acts as part of a cluster of cities with similar economic and social orientation, and many other factors. All of the above conditions contribute to the efficient development of the city and country.
2) SECOND TYPE – these are territories that do not have existing special conditions in contrast to the first category. There are no starting advantages for attracting investments and customers, the image and reputation of an economically successful city or country; there are also a relatively small number of medium and large companies operating in the territory. In the case of the first type, territory brand does not require much effort and is simplified in terms of promotion. The situation is essentially opposite for the second type of territories for which the development of a special virgin mechanism for promoting this territory is required. However, this does not mean that territories belonging to the first type should not promote their own brand. All territories need branding regardless of whether they belong to the first type or to the second. More and more cities are joining the fight for the consumer which requires improving the territory brand. A successful territory brand implies a well-articulated positive image that evokes clear associations. It should also be clarified that there is a difference between the brand of a country, city and region – each requires a special approach, a mechanism based on the appropriate analysis (SWOT analysis, analysis of the competitive environment and target audiences, and etc.).
Application of the successful experience of other similar territories (cities, countries and regions):
A brand is considered prosperous if a positive image of the territory is formed causing clear associations. Here are the examples of a successful brand of cities and their associative range:
1) A famous example is the “Bilbao Effect.” The transformation effect of the entire city was seen in the Basque country due to one significant construction of the Guggenheim branch by Frank Gehry’s project and the city of Bilbao. A special role is assigned to the key building in Bilbao but it is important to take into account that integrated evolution is required for the certain image formation and the city transformation, and the development of complementary measures aimed at the integrated progress and transformation of the territories. The construction of the New York branch of contemporary art in the Basque country in 1997 played a decisive role in the city brand formation of Bilbao. The city has become one of the tourist centers of the country.
Other similar examples of city brands:
2) London (UK): associations – business capital, economic center
3) Dubai (United Arab Emirates): associations – capital of luxury and leisure
4) New York (USA): associations – freedom, youth culture.
5) Amsterdam (Netherlands): associations – creativity, innovation, quality of life, art.
The problem of choosing a suitable territory brand-approach.
Russian cities are also developing their brands based on the achievements of global city brands. Territory brand is a relatively new direction for Russia which is formed as a result of trial and error. Many agencies for creating city brands in the Russian realities make a number of basic mistakes. This is a copying of the city brands from Western counterparts when it is necessary to adopt the experience of successful territorial brands. However, full copying cannot be effective due to national and territorial characteristics. The second but no less significant mistake is that different agencies in terms of level and approach to brand building are engaged in brand development. For instance, one agency might develop a logo; another might develop a slogan, and etc. The fragmentation of the main elements of a single brand, as a rule, negatively affects the brand formation.
Research Methods
Experience of Russian cities and regions in building a territorial brand:
The following can be distinguished as the most famous ones:
1. Murmansk. When developing a brand, the city authorities focus on the territorial location of the city taking into account the economic potential and the development of Arctic tourism under the slogan “Murmansk is an outpost of Russia in the Arctic” (Figure 02).

2. Saint Petersburg. The city authorities focus on the city’s logo which emphasizes the tourist orientation and marks its main attractions: the logo showing the Peter and Paul spire and drawbridges, the lion’s head giving accent to the city architecture with the slogan “Welcome to Saint Petersburg” by the Volga-Volga agency. It was decided to determine the winner of the competition through a survey of the urban population. The German agency Damm und Lindlar was engaged in the brand of St. Petersburg which worked in the field of image-making for a relatively short time.
In recent years, various agencies that have had varying success have been dealing with the St. Petersburg brand (Figure 03). To date, the approved city logo is a design from the St. Petersburg Tourism Committee:
3) Perm. Promotion of the Perm image has become one of the most discussed among city residents. The project with three Ps "prosto poniatno povtoriaemo” which had been developed by the designer Artemy Lebedev, curator of the Perm Center for Design Development, received positive feedback from branding specialists. However, not all Perm residents approved the logo. The logo design of the Perm Territory (Figure 04) is based on the official emblem of the region.

4) Kazan. The capital of Tatarstan is one of the pioneers in the tourism direction in Russia. The slogan “Kazan – where Europe meets Asia” was actively promoted, but over time, the development of a new slogan took place – “Kazan – Russia’s third capital” (Figure 05).

5) Kaliningrad Region. The Kaliningrad Region is one of the successful examples of Russian territorial brand. The project authors are the studio of Artemy Lebedev who had developed the symbols of Perm. The logo emphasizes the main wealth of the region – amber which is highlighted in the logo texture. Abbreviations underline the historical name of Königsberg.
Findings
The development of the territory symbolism has a long history. Since the Middle Ages, it was known that there were coats of arms of territories, mottos of European countries, cities, castles, and places. Such mottos and coats of arms (symbols) emphasized the identity and special uniqueness of these places. According to their purpose, the coats of arms then served the main purpose, namely, attracting finance. The symbols, depending on the purpose, were intended to highlight the main advantages of the territories. The special historical direction “heraldry” is well-known and studies coats of arms and traditions of their use.
A special place in brand management is given to the concept of territorial positioning of brands – the direct brand dependence on the place of development and production. Consumers subconsciously focus on the place of the product production due to many factors when choosing a particular product. It is generally accepted that goods, a product of a certain category produced in a particular place (country, city, and etc.) is a quality guarantor.
Conclusion
Place branding is becoming more and more relevant depending on the origin place of goods. The number of consumers who prefer to choose a product due to the corresponding criteria is increasing. Therefore, there is a direct dependence between the country brand and the product brands produced in the territory of this country or region.
References
Ankholt, S. (2004). Branding: road to the world market. KUDITS-Image.
Cleave, E., Arku, G., Sadler, R., & Gilliand, J. (2016). The role of place branding in local and regional economic development: bridging the gap between policy and practicality. Regional Studies, Regional Science, 3(1), 207-228.
Eskiev, M. A. (2019). Brand management as a Science of Brand Control. In: Z.A. Saidov (Ed.), Impact of the new geopolitical reality on public administration and development of the Russian Federation. Materials of the II All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference (pp. 220–223).
Eskiev, M. A. (2020). Brand Expansion: Importance and Role for Company Development and Competitiveness. Subbrands, Vertical and Horizontal Brand Expansion. FSI Science, 4(20), 187–191.
Silvia, P. J. (2007). How to write a lot: A practical guide to productive academic writing. http://www.amazon.com
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
29 November 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-116-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
117
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2730
Subjects
Cultural development, technological development, socio-political transformations, globalization
Cite this article as:
Eskiev, M. A. (2021). Territory Branding As An Opportunity For The Region Development. In D. K. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in The Context of Modern Globalism, vol 117. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 531-539). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.11.70

