Abstract
Amid the implementation of the tax federalism principles, tax administration can be considered in two aspects: a general aspect being tax administration at the country level with regards to its administrative-territorial units and a narrow aspect being tax administration within one administrative-territorial unit of the country. The result of the effective functioning of the current tax administration mechanism is an increase in tax and levy receipts to the budgets of all levels. Based on the analysis of tax payments to the consolidated budget of the region, the results of accounting and reporting and other tax control measures being one of the functions of tax administration, we can conclude that tax administration is the most important element of managing the tax system. The generation of tax revenues of regional and local budgets largely depends on the quality of tax administration, which is especially important amid the socio-economic situation in the Russian Federation characterized by a structural budget deficit. The high level of tax relations results in a high level of tax revenues. Insufficient tax payments to the budget lead to various socio-economic problems in society. Consequently, the development of the entire state economy depends on harmonious tax relations. The solution to this problem is to increase the level of financial and tax literacy of taxpayers, develop a patriotic attitude towards the obligation to pay taxes, ensure trust on the part of the taxpayer in the process of collecting taxes to replenish the budget and carry out expenses on them.
Keywords: Revenues, tax, tax administration, tax control
Introduction
Tax administration is one of the factors influencing the overall level of revenue from taxes and fees. It ensures effective management of tax relations arising in the process of establishing introduces and collects taxes and fees on the territory of the Russian Federation, exercises tax control, tax planning and forecasting.

Problem Statement
Amid the implementation of the tax federalism principles, tax administration can be considered in two aspects: a general aspect being tax administration at the country level with regards to its administrative-territorial units and a narrow aspect being tax administration within one administrative-territorial unit of the country. The result of the effective functioning of the current tax administration mechanism is an increase in tax and levy receipts to the budgets of all levels (Malis, 2018).
Depending on the level of tax revenues, new short and long term tasks of tax administration are determined, the results of the activities of tax authorities are assessed, tax incentives are developed, and the tax burden on the regions is leveled (Basnukayev, Khadzhieva et al., 2020)..
Research Questions
Quantitative indicators of the ax administration efficiency are as follows:
- the amount of taxes and fees received to the regional budget;
- the total number of taxpayers registered with the territorial tax authorities;
- the amount of tax payments assessed and collected by the audit in the course of control measures;
- the amount of unpaid tax as well as taxes, fees and fines liabilities.
Let us consider the efficiency of the taxation system of the Russian Federation with regard to these indicators as exemplified by the Chechen Republic. To assess the dynamics of taxes and fees return in the budget system as well as the impact of the control results and accounting activities of tax authorities on the level of tax payments collection, let us analyze the statistical and analytical reports of the Office of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the Chechen Republic presented on the official website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia and obtained directly from structural divisions of tax services.
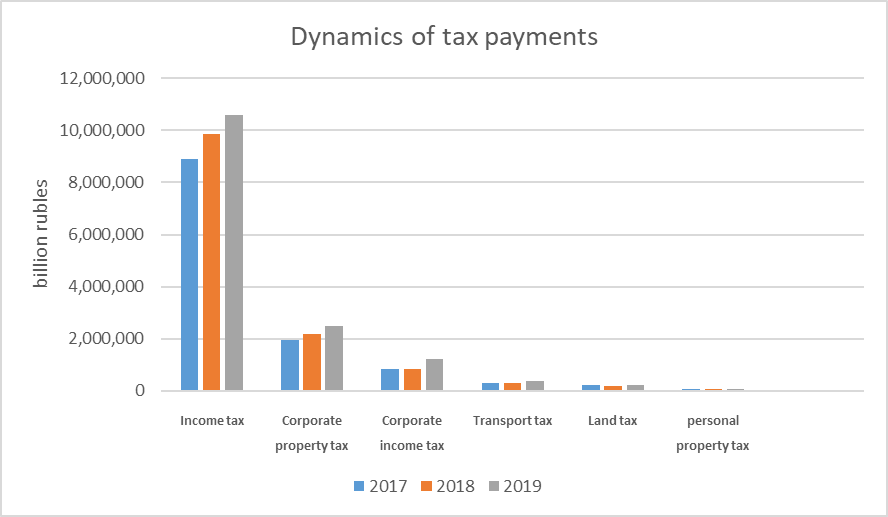
Thereafter, let us consider tax control and its role in improving tax revenues collection of the budgetary system of the Chechen Republic. The main compulsory tax payments that generate the regional and local budgets of the Chechen Republic are personal income tax and property taxes. At the same time, despite the fact that personal income tax is a federal tax, part of the proceeds from this tax is credited to the consolidated budget of the Chechen Republic. Tax payments for property tax of individuals and land tax go to local budgets. Figure 1 shows the dynamics of the main budget-generating taxes return to consolidated budget of the Chechen Republic in 2017–2019.
Over the past years, the leading position in the structure of republic’s tax revenues has been occupied by personal income tax. The main tax payers are tax agents, who bridge individuals receiving income and tax authorities. According to official data received from the Office of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the Chechen Republic, the number of registrants being tax agents-employers in the republic is 9,778 organizations and 18,991 individual entrepreneurs. To achieve high rates of personal income tax, officials of the tax authorities of the Chechen Republic hold weekly committee meetings devoted to wages legalization and debts settlement in order to induce taxpayers to voluntarily pay the assessed taxes.
Raids with law enforcement agencies aimed to identify individuals engaged in non-registered occupation as well as other tax control measures regularly implemented by tax authorities affect the growth of personal income tax revenues.
The second budget-generating tax being of particular fiscal significance for the regional budget is the tax on the corporate property tax. The tax authorities credit property taxes based on the information provided by the executive authorities responsible for the registration of vehicles, cadastral registration, maintenance of the real estate register and official registration of real property titles within the authority specified in Article 85 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The dynamics of the corporate property tax revenues was influenced by the legislative factor. The amendments made to the regional tax legislation by the authorities of the Chechen Republic led to the repeal of certain tax reliefs for corporate property tax for a large number of budgetary organizations.
One of the main elements of corporate income tax administration, which influences the increase in revenues in addition to improving the organizations’ bottom-line, is tax control. The main form of tax control over this tax is office and field tax audits. The most frequently detected errors during tax audits are the following:
- reduction of the tax base covering expenses that cannot be deducted;
- not including non-operating income to the tax base;
- incorrect depreciation accrual.
The head of the relevant tax authority of the Chechen Republic initiates a field tax audit of corporate income tax in the following situations:
- organization’s expenses over several tax periods exceed income;
- organization’s constant unprofitability in comparison with its peers;
- failure to provide information upon the request of tax authorities.
Thus, tax control over organizations’ activities becomes crucial under present-day conditions. Revenues from corporate income tax largely depend on the effectiveness of tax control measures.
Local taxes round out the above histogram. Their role in the overall tax revenues structure is minor. The table provides information on the tax base and structure of land tax accruals in 2019.
According to the data presented in Tables 01 and 02, 274,992 units of land plots located on the territory of the Chechen Republic were subject to taxation in 2019. The number of taxpayers obliged to pay the calculated amount of tax was 232,713, benefits were provided to 49,367 taxpayers.
200,586 taxpayers paid the personal property tax, incentives were provided to 18,243 taxpayers. Budget revenue for this tax was planned in the amount of 137,259 million rubles.
Thus, the inspectorates keep records of individuals’ and legal entities’ asserts subject to taxation.
In accordance with Article 21.1 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs”, 174 organizations were de-registered from taxation for the same period due to the following: cessation of business – 156 organizations, change in location – 18. The main reasons for the termination of activities were the following:
- tax liabilities;
- lack of profit and payback;
- debt on loans and borrowings;
- bankruptcy.
According to the report 1-UCH, as of 01.01.2020, 1,409,892 of individuals were registered with tax including 8,422 foreign citizens. The corresponding figure for the same period last year was 1,332,264, the increase amounted to 77,628 individuals or 105.8 %.
Since the self-employment tax was introduced on the territory of the Chechen Republic, 3,335 self-employed persons registered at the tax authorities at their place of residence. Of these, 3,333 were registered in 2019 and 2 – in 2018.
To assess the role of tax administration in tax revenues generation, it is also necessary to consider the statistics of additionally assessed amounts by tax inspectorates in the course of control activities.
In the course of control activities, the tax authorities of the Chechen Republic introduced additional charges on tax payments for the year 2019 (Table 04, table 05). Additional charges distributed by the types of tax audit are shown in Figure 02.
Compared to the same period in 2018, the total amount of additionally charged tax increased by 3.5 million rubles or 101.2 %.
During 2019, the republic tax authorities carried out 80,605 office tax audits, which in absolute terms was 14,554 audits less than in 2018, or 0.84 %.
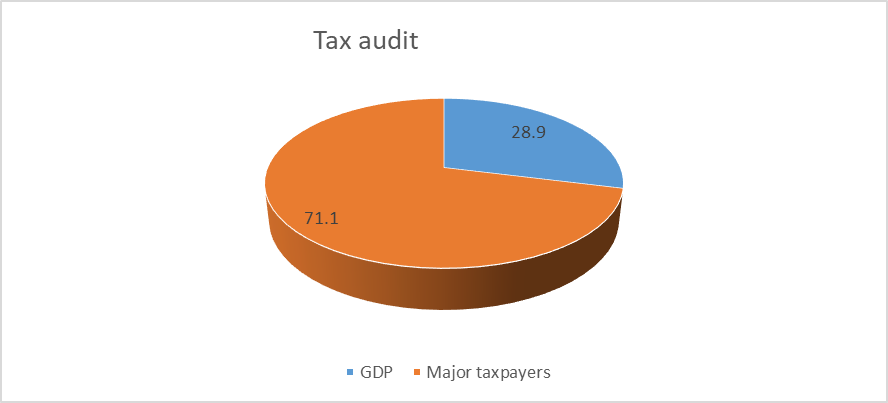
The proportion of additional charges based on the results of tax audits in 2019 is shown in Figure 03.
The presented diagram (Figure 03) illustrates the ratio of additional charges made in the course of the office tax audits to the field audits. The proportion of additional charges based on the results of the office tax audits was much higher, which proves the effectiveness of this tax audits type.
Thus, based on the analysis of tax payments revenues to the consolidated budget of the Chechen Republic, the results of accounting and reporting and other tax control measures being one of the functions of tax administration, it can be concluded that tax administration is the most important element of tax system management (Figure 04). Generation of tax revenues of regional and local budgets largely depends on the quality of tax administration, which is especially important in the context of the socio-economic situation in the Russian Federation characterized by a structural budget deficit.
It has long been known that a high level of tax revenues is the result of high level tax relations. Tax gap leads to various socio-economic problems in society. Consequently, the development of the economy of the entire state depends on harmonious tax relations (Basnukayev, Isanbaeva et al., 2020).
It has been stated that one of the major problems while generating region’s tax revenues is tax evasion, which takes the following forms: deliberate evasion, fictitious bankruptcy, concealment of taxable items, falsification of documents for claiming a refund of VAT, negative psychological attitude of the country’s population to taxation, etc. (Goncharenko & Melnikova, 2017).
The problem solution involves increasing the level of financial and tax literacy, developing a patriotic attitude towards the obligation to pay taxes, ensuring trust in the process of collecting taxes to replenish the budget and incur expenditures. All of the above qualities of the subjects engaged in tax relations are formed by the tax culture.
Tax discipline is the main element of the tax culture. Tax discipline is understood as the activity of the subjects engaged in tax legal relations, taking the form of generation and development of ethical and financial behavior when fulfilling their tax obligations. Indicators of the tax discipline level are as follows:
- debts on taxes and fees;
- number of identified tax violations;
- electronic interaction between taxpayers and tax authorities.
To determine the level of tax discipline in the Chechen Republic, we have studied the total amount of tax debt to the budget, the dynamics of growth and the reasons for its generation. The data are presented in Table 03.
Purpose of the Study
One of the main problems in the process of generating tax revenues in the region is tax evasion, which has various forms: deliberate, fictitious bankruptcy, concealment of objects of taxation, falsification of documents for accepting VAT for refund, negative psychological attitude of the country population to taxation, etc. The solution to this problem is to increase the level of financial and tax literacy of taxpayers, develop a patriotic attitude towards the obligation to pay taxes, ensure trust on the part of the taxpayer in the process of collecting taxes to replenish the budget and carry out expenses on them.
Research Methods
Within the framework of the study, the following methods were used: analytical and comparative methods, comparison method, methods of scientific classifications, etc.
Findings
The growth dynamics of debt presented in the table enables to judge that tax and duties liabilities in the Chechen Republic are due to various reasons and in general they tend to increase. In 2019, the total debt of taxpayers in the Chechen Republic amounted to 3,951,644 rubles and decreased by 899,540 rubles compared to 2018.
This decrease was achieved by the following measures:
- debt repayment as a result of enforcement collection;
- debt settlement by offsetting overpayments on account of debt repayment, etc.
Nevertheless, despite the decrease in 2019, the total debt is consistently high. The main reason why the debt level in the republic does not decrease is the annual increase in personal property tax liabilities. Thus, we can conclude that tax discipline is at a rather low level and requires measures to increase it.
Conclusion
After analyzing the above information on the revealed tax violations in the course of tax audits by tax authorities of the Chechen Republic, we can conclude that in 2019, in relation to previous years, both in office and field tax audits, the number of tax legislation violations significantly decreased. The number of audits decreased as well, which indicates an increase in tax discipline in 2019 compared to the prior-years.
References
Basnukayev, M. Sh., Isanbaeva, D. V., & Tashanova, Z. Ya. (2020). Regional tax policy as a structural element of social and economic policy. Bulletin of the Academy of Knowledge. Economics and management of the national economy (by industry and spheres of activity), 28(2), 44–49.
Basnukayev, M. Sh., Khadzhieva, Kh. Kh., & Chandaeva, M. D. (2020). Features of building a reasonable regional policy in the depressive republics. Bulletin of the Academy of Knowledge. Economics and management of the national economy (by industries and spheres of activity), 28(2), 49–53.
Goncharenko, L. I., & Melnikova, N. P. (2017). On new approaches to the policy of applying tax benefits and preferences in order to stimulate economic development. Economics. Taxes. Right, 2, 96–104.
Malis, N. I. (2018). Improving tax policy at the regional level: main directions. Financial journal, 1, 51–60.
Tsindeliani, I., Kot, S., Vasilyeva, E., & Narinyan, L. (2019). Tax system of the Russian Federation: current state and steps towards financial sustainability. Sustainability, 11, 6994.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
29 November 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-116-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
117
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2730
Subjects
Cultural development, technological development, socio-political transformations, globalization
Cite this article as:
Basnukaev, M. S., Mambetova, A. A., & Musostova, D. S. (2021). Tax Administration For Ensuring Tax Revenues. In D. K. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in The Context of Modern Globalism, vol 117. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 223-230). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.11.30

