Abstract
Regional and local taxes mainly consist of property taxes, whose revenues are insignificant. Thus, they are deliberately not included in federal budget revenues. Revenues from key, budget-generating taxes are subject to transfer to the federal budget. Regional tax policy is a part of the financial policy of the state to provide the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The economic growth of the region largely depends on a competent regional tax policy, since it affects the economic activity of business entities. Stimulation of the economic activity of economic entities in the region should lead, on the one hand, to an increase in their profits, and, on the other hand, to an increase in tax revenues to the budget. In this regard, the ongoing regional tax policy serves as one of the effective tools for achieving sustainable economic development in the region. The mechanism for calculating and levying regional and local taxes generate their own sources of income for the regional budget. Although the mechanism has a number of shortcomings, it can provide a stable financial base for sustainable development of the region on condition of the correct regional tax policy. The role of tax administration and tax culture is increasing every year not only in the process of tax levying but also for sustainable economic growth in the region. Improving the quality of the tax administration mechanism and increasing tax levying are priority areas for the tax policy development.
Keywords: Budget, revenues, region, tax, tax administration
Introduction
Currently, regional budget revenues are directly dependent on federal legislation, whose provisions aim to centralize all financial resources at the federal budget level. At the same time, the regional budget is characterized by the predominance of non-repayable revenues from the federal budget over its own revenues. Regional and local taxes mainly consist of property taxes from individuals and legal entities, whose revenues are insignificant (Goncharenko & Melnikova, 2017). Thus, they are deliberately not included in federal budget revenues. Revenues from key, budget-generating taxes are subject to transfer to the federal budget.
Problem Statement
It is known that high tax revenues to the budget are achieved by increasing powers decentralization. It is due to the fact that, as a rule, more efforts are made to ensure income from their own revenues than when collecting taxes exclusively for the federal budget in the territories of the constituent entities. Thus, fiscal decentralization, i.e. giving the executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation quantitative and qualitative powers in the field of taxation, is required.
Thus, to ensure economic growth and improve the financial situation in the constituent entities, it is required:
- to improve regional tax legislation;
- to expand the powers of regional authorities in the field of taxation;
- to increase the amount region’s income in the structure of regional budget revenues.
Research Questions
Tax relations in the regions should be based on the principle of realizing an organic connection with the development of production activities, increasing the number of business entities, i.e. implementation of tax regulation over the activity of business entities (Basnukayev et al., 2020).
The main processes having a negative impact on the generation of the financial base in the regions are as follows:
- low rate of enterprise production;
- uneven distribution of the tax burden between economic entities;
- decrease in the profitability of many industrial sectors;
- significant amount of unprofitable enterprises, enterprises insolvency;
- heavy debit debt, which leads to tax liabilities;
- annual increase in tax liabilities.
Regional tax policy is a part of the financial policy of the state providing the constituent entities of the Russian Federation with financial resources by regulating elements of taxation for regional taxes, tax legal relations and regional tax legislation (Malis, 2018).
The economic growth of the region largely depends on a competent regional tax policy, since it affects the economic activity of business entities. Stimulating the economic activity of economic entities in the region should lead, on the one hand, to an increase in their profits, and, on the other hand, to an increase in tax revenues to the budget. In this regard, the ongoing regional tax policy serves as an effective tool for achieving sustainable economic development in the region (Boboshko, 2011).
Let us consider the main prospects in the field of tax policy of the regions for the period 2018–2021:
- development of human capital, attraction of investments to the region;
- implementation of a closer connection between accounting and tax accounting;
- improving property taxation being the main part of regional taxes;
- improving the efficiency of the applied financial instruments.
Let us consider the personal property taxation in more detail. In the context of the need to strengthen the revenue component of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, property taxes have significant potential as the main source for replenishing the region’s own revenues (Maslennikova, 2020). In this regard, in order to ensure high revenues from these taxes, it is necessary to establish an effective mechanism for the regulation and administration of property taxes, both from individuals and legal entities. The most relevant areas for improving property taxation in the subjects are the following:
- effective social policy regarding property taxation;
- analysis of the tax base to ensure the growth of the property tax potential;
- increasing the collection of property taxes;
- elimination of the problem of excessive tax burden in the process of adopting a cadastral basis for tax collection.
According to the analysis of tax revenues in the Chechen Republic, the tax on the property of organizations has the greatest fiscal effect for the consolidated budget of the Chechen Republic. In recent years the exemption from taxation of the organizations’ movable property has become the main change in the organizations property tax. This implies that now the organizations not having movable property are not liable for property tax and are not required to declare reporting on this tax. As a consequence, tax revenues from this type of tax have decreased by 180 billion rubles. As well, in addition to a decrease in the amount of tax revenues, the risk of re-qualification of real estate into movable property increases. Its prevention is a new task for tax administration.
Real estate includes all objects of property related to land, whose transportation is practically impossible without causing incommensurate detriment to their established purpose. In addition to land properties, aircraft and sea vessels, inland navigation vessels and other objects that can be attributed to this type of property are also recognized as real estate (Kuzimov et al., 2020).
Thus, the abolition of the tax on movable property has the following consequences:
- stimulating the acceleration of the introduction and development of technologies in the domestic industry;
- reducing the burden on small and medium-sized businesses, as compensation for the increase in the VAT tax rate;
- reducing the part of the tax revenues of regional budgets.
Despite a number of progressive changes in the structure of corporate property taxation, the problem of interaction between tax authorities and registration authorities remains acute. Due to incorrect information contained in databases, only 60 % of real estate objects are bound by taxation. This situation is unacceptable and requires the adoption of measures to change the procedure for interaction with the registration authorities, which will significantly raise revenue from this type of tax.
Additionally, the problem of the growing tax burden is aggravated. From our perspective, it can be solved in the following ways:
1) return to the taxation of real estate with a downward change in tax rates, which will eliminate the existing disagreements regarding the classification of property into movable and immovable,
2) abolish ineffective tax incentives and establish a list of property items that are exempt from taxation depending on their belonging to a particular depreciation group.
In addition, in the future it is expected that all property taxes from individuals and legal entities will be replaced by one tax called “real estate tax”. However, today there are no necessary economic and legal conditions for this kind of global changes in property taxation. It is assumed that the introduction of one property tax replacing all the others will improve the quality of the current tax system and will fully meet the needs of the market economy development.
The second most important source of the regional budget replenishment is the vehicle tax. In the Chechen Republic, revenues from this tax are obtained predominantly from individuals. To determine the prospects for improving the transport tax, it is necessary to consider the following problems associated with its calculation and collection:
- primarily, it is necessary to note the environmental problem. The existing rates of the vehicle tax depend on the engine power and do not take into account such characteristics as the vehicle size and the volume of emissions that pollute the environment when determining the tax base;
- the established progressive taxation scale, depending on engine power, cannot be regarded fair. Due to one horsepower included in another group of established rates, the taxpayer is obliged to pay the tax amount several times more. The executive authorities of the regions can increase or decrease the rates established by tax legislation but not more than 10 times;
- the third problem of transport taxation is associated with the lack of intended use of revenue. In our opinion, it would be more expedient to create special road funds aimed to centralize the received tax revenues to be spent on improving the road infrastructure of Russian highways, since it is known that vehicles are a source of increased danger.
Considering all of the above shortcomings in the calculation and collection of the transport tax, many experts propose to abolish this tax and include the excise tax on fuel products in the products’ price. A number of positive and negative aspects can be distinguished with this regard. The positive aspect is a less complicated procedure of tax collection, since the tax is already included in the price of gasoline. This will significantly increase tax collection, eliminate the reasons for debt creation due to respite payment, and prevent tax evasion.
However, along with positive aspects, there are also negative ones. These include the following:
- an increase in the fuel price, since in addition to the amount of excise tax, a tax will also be included in the cost of fuel, which will incur taxpayers’ displeasure;
- reduction of the regional budget’s own revenues. Considering that the excise tax is a federal tax, and the transport tax is subject to transfer to the regional budget, the regional authorities will forfeit the right to establish certain elements of taxation. Namely, when setting tax rates, regional features of the economy will not be taken into account;
- an increase in prices for gasoline and diesel fuel will have a negative impact on other segments of the population who do not own vehicles and do not pay this type of taxes, since fuel and gasoline are also used for other purposes, for example, for electric generators.
Thus, in our opinion, the Russian system for calculating the transport tax has a number of disadvantages. To eliminate some of them, the following methods can be applied:
- due to the lack of a unified information base for the tax authorities and the traffic police, irrelevant data are often used to calculate taxes. To eliminate such errors, it is necessary to enter cards for vehicle owners, which they will fill out when registering vehicles. The cards will contain information about the identity of the vehicle owner, car brand, horsepower and other characteristics. After filling out, the cards will be transferred to the relevant tax authorities;
- elimination of large intervals between tax rates for smaller ones. The number of rates will increase but the distribution of the tax burden will be fair;
- provision of certificates of non-indebtedness from the tax authority during re-registration and passing the technical inspection of vehicles.
In our opinion, the third method is preferable, since the current rules provide for a fairly frequent passage of technical inspections and does not increase the tax burden on taxpayers but only contributes to debts elimination and timely tax payment to the budget.
The third tax classified as a subject tax is the tax on gambling business. According to the analysis, the budget of the Chechen Republic does not have receipts from this type of tax due to the absence of gambling zones on the territory of the region. This tax replenishes the budgets of only those regions on whose territory it was introduced. Consequently, with the exception of four constituent entities of Russia (Altai and Primorsky Territories, the Kaliningrad Region and Sochi), in which this tax is levied, it does not fulfill the intended fiscal function for all other budgets of the constituent entities.
Property taxes also prevail with regard to local taxes that go to the consolidated budget of the Chechen Republic. Revenues from personal property tax, both in the Chechen Republic and in other regions of the North Caucasus Federal District (Ingushetia, Kabardino-Balkaria) are insignificant. This is primarily due to the fact that many individuals who own taxable items for this type of tax enjoy tax incentives. In our opinion, the above list of privileged individuals in the Law “On Personal Property Tax” should be reduced, since incentives are given to such categories of persons who have a sufficient level of solvency to fulfill their obligation to pay tax. The second reason for the low income is that for a long time the taxable items and rates on them have not changed and, thus, require revision.
The next problem of personal property tax is a too simple and short list of taxable objects. In our opinion, this list should be supplemented with such elite properties as penthouses, townhouses, multi-level apartments and set rates different from the existing ones.
Land tax levied from both individuals and legal entities can become a stable source of revenue for increasing local budget revenues in Russian regions. In the structure of tax revenues of the budget of the Chechen Republic, its amount exceeds the amount of tax revenues on personal property.
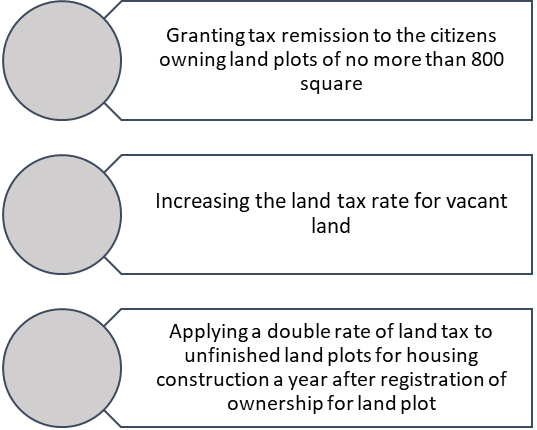
In Russia, paid land use has existed for twenty years. At the present stage, the financial and legal aspects of land use are being developed and supplemented. In particular, changes are taking place in the indicators of the cadastral value of land, the structure and composition of land use. In recent years, systems have been actively developed for compiling an electronic database of all land plots on the territory of the Russian Federation. It is proposed to solve the problem of reliability of data on land plots received by tax authorities by interacting not only with Rosreestr authorities but also with other executive authorities.
Figure 01 shows the measures to improve land taxation in Russia.
The introduction of a trade tax has been a novelty in local tax legislation in recent years. The objective of this tax introduction is to support regional budgets in the event of a crisis and structural deficits. The administration of the trade tax will be subject to improvement for more than one year, and it is quite possible that the proceeds from this tax will serve as a source of covering the regional budget deficit.
Purpose of the Study
To address these issues, it is necessary to improve the tax control system and increase the efficiency of the tax authorities. At the same time, the improvement of the tax control system does not imply total control over taxpayers. It is urgent with this regard to improve the conditions for taxpayers for the convenience of paying taxes and to maximally prevent tax evasion.
Research Methods
Within the framework of the study, the following methods were used: analytical and comparative methods, methods of scientific classifications, etc.
Findings
The study identifies the main factors influencing the generation of tax revenues in the budget of the Chechen Republic being tax administration and tax culture. The role of tax administration and tax culture is increasing every year not only in the process of tax collection but also for sustainable economic growth in the regions. Improving the quality of the tax administration mechanism and increasing tax collection are priority areas for the development of tax policy in 2018–2021.
Conclusion
Thus, it can be concluded that the mechanism for calculating and levying regional and local taxes form their own sources of income for the regional budget. Although the mechanism has a number of shortcomings, it can provide a stable financial base for sustainable development of the region if the correct regional tax policy is applied.
References
Basnukayev, M. Sh., Isanbaeva, D. V., & Tashanova, Z. Ya. (2020). Regional tax policy as a structural element of social and economic policy. Bulletin of the Academy of Knowledge. Economics and management of the national economy (by industry and spheres of activity), 28(2), 44–49.
Boboshko, N. M. (2011). Assessment and control in the system of property taxation: theory and methodology [Monograph]. String.
Goncharenko, L. I., & Melnikova, N. P. (2017). On new approaches to the policy of applying tax benefits and preferences in order to stimulate economic development. Economics. Taxes. Right, 2, 96–104.
Kuzimov, A. S., Lavrov, S. V., & Pavlenko, S. P. (2020). Movable or immovable property. Tax policy or practice, 1, 50–54.
Malis, N. I. (2018). Improving tax policy at the regional level: main directions. Financial journal, 1, 51–60.
Maslennikova, E. I. (2020). On the procedure for the application of tax incentives for the tax on the property of organizations. Tax policy and practice, 1, 35–38.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
29 November 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-116-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
117
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2730
Subjects
Cultural development, technological development, socio-political transformations, globalization
Cite this article as:
Basnukayev, M. S., Musaelyan, A. K., & Sugarova, I. V. (2021). Regional Tax Revenues As Basis For Territory Financial Independence. In D. K. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in The Context of Modern Globalism, vol 117. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 216-222). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.11.29

