Abstract
Global transformations that happen in all spheres of human life require people to response to them timely and adjust to the new conditions of living. Globalization and rapid development of information technologies make universities to develop and get ready for tough competition for a potential student. The university in modern conditions has to show its capacity and effectiveness both to the consumer of services and to the state represented by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation. This article considers the main problems that a modern educational system faces such as: providing innovative development of education; using ICT in the learning process; personnel security; commercialization of a university; awareness of the importance of a university. The authors consider solving these issues by the example of the Chechen State University. We came to the conclusion that the formation of the university as an equal participant in the development of the region and the country requires adapting to the modern economic trends. At the same time, there has to be a balanced approach to solving this problem. Initially, we should recognize the priority of the educational cycle over the economic and other aspects of the university's activities. The main efforts of all the processes should be aimed at the effectiveness of the educational process.
Keywords: Globalization, higher education, learning process, modern conditions, modern economy
Introduction
Global transformations taking place in the world in all spheres of human life require constant monitoring of these processes, timely response to them and the ability to adapt to them. Greater openness of borders for interaction and the rapid development of information and communication technologies promote and push universities to the transition from a period of stagnation to development, to readiness for tough competition for a potential student, to ensure their “attractiveness” for the consumer of services, the employer. The university must show its capacity and effectiveness of the chosen vector of development both to the consumer of services (student, employer) and to the state represented by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation. All this forces educational organizations to be more open. Universities should become open systems that closely interact with the external environment. Greater openness also presupposes a greater influence of external factors on intra-university processes, which predetermines the impossibility of developing a university in isolation from the socio-economic development of the region. A situation arises when the scientific potential of universities and graduating specialists should contribute to the successful development of the region, while regional employers interested in scientific support of their projects and in highly professional personnel are interested in strong universities in their region. Based on the need for a close relationship between the university and the employer at the state level, the need for employers to participate both in the educational process itself and in the development of educational programs is enshrined in regulatory documents. The possibility of creating appropriate joint departments at enterprises has been secured. The digitalization of the activities of organizations and institutions, to which much attention is paid at the federal level, is called upon to become an effective toolkit in solving these challenges of our time. As part of the implementation of the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated May 7, 2018 No. 204 “On national goals and strategic objectives of the development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2024”, including with the aim of ensuring the accelerated introduction of digital technologies in the economy and social sphere, the national program “Digital Economy of the Russian Federation” was prepared by the Government of the Russian Federation and approved by the minutes of the meeting of the Presidium of the Council under the President of the Russian Federation for Strategic Development and National Projects No. 7 dated June 4, 2019.
Problem Statement
An important factor that ensures the competitiveness of the university in modern conditions, its attractiveness for school graduates is both the use itself and the efficiency of using modern ICT in the educational process and in other areas of its activity, as well as the degree of development of innovative activities in the educational sphere of the university.
Research Questions
In accordance with the new trends, the development of the University should be primarily innovative. Innovative activity in education implies the functioning of a system of interrelated actions aimed at reforming education, solving problems existing in the education system. Characterizing the target settings implemented by innovative activities, let us turn to the Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation”, which notes that it is “focused on improving the scientific and pedagogical, educational, methodological, organizational, legal, financial and economic, personnel, material and technical provision of the education system” (On Education in the Russian Federation, 2012). This task is especially acute for regional universities, claiming to be the leading university in the region. It should accumulate all the advanced ideas in a particular area. It should be a generator of ideas that ensure the stability and prosperity of the region, and the country as a whole. To be the main supplier of highly qualified, competitive-ready professionals.
Purpose of the Study
Of course, the university will not release a 100% ready-to-work specialist. It is unlikely that this is the main purpose of training. In our opinion, the main task of an educational institution is to prepare a specialist who is able to think, analyze, generalize and draw the correct conclusions, prepared to substantiate and implement innovative projects in various fields. In fact, at the present stage, education is focused not so much on the transfer of knowledge as on the mastery by students of basic competencies that allow them to find the necessary knowledge.
In our opinion, today, several problems arise before the education system in the light of the tasks that it faces:
1. providing innovative development of education;
2. effectiveness of using ICT in the learning process;
3. personnel security;
4. commercialization of a university;
5. awareness of the importance of a university, as one of the active participants in work with youth and in the formation of a comprehensively developed personality.
Research Methods
The most acutely identified problems are manifested in the post-crisis situation. How to deal with them? How to solve these problems? Consideration of these issues is given by the example of the Chechen State University.
Innovative activity in education is primarily a system of interrelated actions aimed at changing, improving the established practice of education, at solving problems existing in the education system. The Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation” notes that it is “focused on improving the scientific and pedagogical, educational, methodological, organizational, legal, financial and economic, personnel, material and technical support of the education system” (On Education in the Russian Federation, 2012). One of the key questions in training a specialist is when to start training? With the choice of a narrow specialization? From the first year? The answer is obvious. From school.
Now there is a lot of criticism in the university environment of the Bologna system. What is it connected with? A careful study of the criticism shows that it is not the fundamental principles of the Bologna system that are mainly criticized, but the mechanisms and results of its application.
Findings
Another very important aspect is half-heartedness in decision-making in this area. As a result, at a certain stage, some “roughness” appears in the process of “grinding” the new system to fit the traditional education system, to its methodology, which is more focused on the unconditional authority of a scientist and teacher, on a combination of a student and a teacher, on the methodology in which the university, the ministry decided what, when and how to study the student. In conditions when high-quality training of a specialist began only after choosing a specialization, this was the only correct way to prepare a graduate. The long leadership of the USSR in various scientific fields is a confirmation of this. However, with greater openness of borders in various areas, including the declared desire of European countries and Russia to create a single educational space, which is facilitated by the development of new information technologies and the possibility of their effective application, makes us reformat structurally and methodologically. This is where the first methodological crisis arises. In accordance with the Bologna system, the student himself determines his so-called “scale (trajectory) of learning”. But is our freshman ready for this? Unfortunately, more often than not. As a result, we get a kind of hybrid: not a full-fledged Bologna system, and not a traditional form of education.
One of the key points in solving this problem, in our opinion, is the creation of a fully functioning scheme: “school-university-production”.
An example of the effectiveness of the “school-university” scheme is the Moscow State University, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology and other leading universities of the country, which have been working in this direction since Soviet times and, not to a small extent, thanks to this scheme, have achieved such high results. By projecting this scheme onto our region, we would add “production” here as well. This is due to the need for an urgent restoration and creation of a modern production sphere of the republic designed to meet both the present and future needs of the region. Taking into account the role and importance that was assigned by the Head of the Republic, Hero of Russia R.A. Kadyrov to Chechen State University, the rigid linking of the “school-university” scheme to production is, in our opinion, logical and justified. At the same time, this scheme “spurs” various branches of production to create sectoral training programs, taking into account their development programs, stimulates their more active participation in the preparation and education of students. It will help to move away from formalism in this matter. Certain steps in this direction are already being taken. In addition to participating in the implementation of the educational process in accordance with the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standards, representatives of potential employers are invited as “observers” when passing the final attestations. Often, they also select specialists there. This is in addition to the traditional annual job fair. Active work is being carried out among high school students. An important role is played by attracting schoolchildren to the work of various workshops at the faculties. In addition to the already traditional university Olympiad among schoolchildren, research is also carried out in the form of a questionnaire to determine the existing priority trends in the choice of a profession among high school students. Here are some illustrations of such a sociological study conducted among graduate schoolchildren by the career guidance department of the Chechen State University:
of this sociological study is to analyze the reasons that influence the choice of a university and the direction of study of students.
is 11th grade students of general educational institutions of the Chechen Republic.
is the factors that a student operates when choosing a university and a direction of study.
Sociological research objectives are:
- to determine what is the motive for obtaining higher education;
- to identify the criteria by which applicants are guided when choosing a university and a field of study.
of collecting information is a survey through an online survey.
of the Chechen Republic took part in the online survey. The total number of students in grade 11 in all secondary schools of the Chechen Republic is, of whichtook part in the online survey. As we can see, the coverage of the target audience is almost 100 %.
The online survey included 10 questions. Here we will give answers to just a few of them:
“Do you consider education at a university a prerequisite for a successful career?” the students responded as follows (Figure 1).
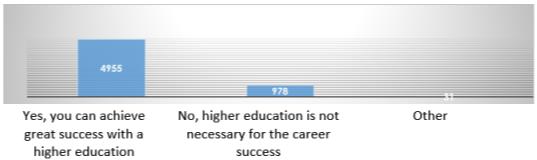
- Yes, you can achieve great success with a higher education (90 % of the respondents);
- I prefer to get secondary vocational education (9 % of the respondents);
- I do not plan further education after school (1 % of the respondents).
“What are you guided by when choosing the university you want to enter?” the students responded as follows:
(This question had one or more answers)
- High quality education (4820 people).
- The prestige of the university (1560 people).
- Availability of budgetary places (1502 people).
- University rating (755 people).
- Research activities of the university (599 people).
“What sources of information do you trust more when choosing a university?” the students responded as follows:
(This question had one or more answers)
- University website (2597 people);
- Social networks (877 people);
- Print media (357 people);
- Television (326 people).
“What higher or secondary vocational educational institution of the Chechen Republic do you plan to enter?” students answered as follows (Table 01).
From this table it follows that about 50 % of the respondents plan to enroll in the Chechen State University.
The answers to the question turned out to be interesting: What areas of training are you considering for admission? It turned out that the most popular areas of training among 11th grade students are:
- Biology (570 people);
- Economy (490 people);
- Jurisprudence (368);
- State and municipal administration (363 people);
- General medicine (355);
- History (334);
- Chemistry (271);
- Business Informatics (234);
- Linguistics (215);
- Philology (209);
- Dentistry (204).
It was unexpected for us that in the first place among the demanded directions was “Biology”, and the top ten included “History”, “Chemistry” and “Philology”. The possibility of further employment also played a significant role in choosing a profession. It is here that the provision of close interaction and full-fledged functioning of the “school-university-production” scheme comes to the fore.
Another element designed to adapt our education system to world standards is the network form of educational programs (On Education in the Russian Federation, 2012), which is receiving great attention at the present stage, since this form of interaction provides greater academic mobility and a wider range of knowledge in the required areas. More fully characteristics and tasks of network learning are given in (Vesna & Guseva, 2013):
Characteristics:
- “is organized mainly according to promising educational programs, as a rule, of an interdisciplinary nature, in order to train personnel for large industry, scientific and other projects;
- allows forming unique competencies that are in demand, first of all, in rapidly developing sectors of the economy;
- provides the possibility of using in educational activities along with the resources of educational organizations, material and human resources of other organizations: scientific, industrial, medical, cultural organizations, etc.”
Tasks
- “training of personnel with unique competencies in demand in the labor market of priority sectors of the sectoral and regional economy and the labor market;
- improving the quality of education by integrating the resources of partner organizations in priority areas of sectoral, inter-sectoral and regional development in accordance with international standards;
- introduction of the best examples of domestic and foreign practices in the educational process for the development of applied research for the needs of enterprises in the industry and the region.”
The work (Vesna & Guseva, 2013) fully reveals the whole paradigm associated with the network form of learning. However, the mechanisms of its implementation cause some fear and caution. It is important here that a university that is not basic in a network for a particular educational program does not withdraw itself from the development of this educational program on its basis, despite its “status” in this combination. Despite the external attractiveness and validity of this form of interaction, there is a certain danger here for regional and peripheral universities. The desire to report on their cooperation with one or another top university for the momentary satisfaction with “work” in conjunction with a leading university should not be a priority. Blind following as a follower can lead to the gradual “extinction” of key fundamental directions. Regional universities should be interested in supporting and developing these areas on their basis. Universities should progress towards development. An important role in ensuring the innovative development of the university is played by the full functioning of the management adapted to modern realities in the educational environment. The key role in ensuring the relevant goals and objectives is played by the education quality management system (QMS) created by the order of the Federal Agency for Education “On the development and implementation of an intra-university education quality management system in higher educational institutions” (No. 304 as of 03.12.04). The main task of the QMS is to become a universal management tool to ensure high efficiency of the University's activities, which implies high-quality “products” at the output, which correspond to the modern world conjuncture. A number of events at the federal and regional levels devoted to this issue have shown that two approaches are noted in solving this issue:
1. Formal. Such a service is created under the subordination of the vice-rector for academic affairs and is engaged in purely ensuring control over the educational cycle.
2. Informal. A similar service is being created under the direct subordination of the rector, and it is a key tool in the management of the organization.
The priority of the second approach is obvious, since the activities of all services, including financial, personnel, economic, are aimed at improving the quality of education. This education quality management service is essentially designed to organize, manage and monitor the effectiveness of all processes at the university. Organize and provide methodological support to the processes. Test the existing management structure and, if necessary, submit proposals for the management's consideration to adapt this system to newly emerging external changes.
The achievement of the declared goals of the university depends on the efficiency of the functioning of this system. It should be noted that the Chechen State University was the first in the Republic and one of the first in the North Caucasus Federal District to introduce a full-fledged QMS system.
Thus, innovativeness in education for us is not just a declared concept, but a vital condition for the formation and further development of the republic's economy.
One of the important criteria in assessing the stability of a university is the level of ICT development. This formulation of the issue is becoming increasingly relevant in the light of the latest documents of the Government of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education aimed at digitalizing the economy in general and education in particular. The goal of digitalization of education is to ensure greater accessibility to information and digital resources and the use of digital technologies in the educational process. The role of ICT development in education during a pandemic was especially vividly expressed. Forced leaving for distance learning showed that where initially much attention was paid to information and computer technologies, the transition to distance learning was less painful. A striking example of this is the Chechen State University. After the corresponding order of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education, the university was able to switch to distance learning without major problems. This was achieved thanks to active work in previous years to create an appropriate material and technical base, which is based on new technological approaches with an emphasis on computerization.
One of the main features of a university in a post-crisis situation is “staff shortage”. Routine work in this area under normal conditions, for us, is of paramount importance and requires the full mobilization of resources and potential. At the same time, an important role is played by the understanding of this problem on the part of the regional executive power, as the main consumer of our services. One of the first decisions of the Head of Administration of the Chechen Republic A-Kh. Kadyrov, was a restoration of the republic's universities in the city of Grozny, which was extremely important from the political side as well. The task of the earliest possible restoration of the entire education system was defined as the primary one. At the cost of the incredible efforts of Kadyrov A-Kh., the universities were preserved and restored.
In these conditions, the leadership of the Republic aimed the universities at preserving the personnel potential that still remained in the Republic.
The significance and role assigned to universities in that period was paramount. In the conditions of the complete absence of secondary specialized educational institutions, universities were called upon to lure as many young people as possible into their walls in order to fence them from the harmful influence of the street and various kinds of extremist movements. The next stage is full-fledged staffing and technical support, in order for students to receive full, high-quality knowledge.
In this direction, two solutions are justified:
- involvement of experts from outside
- training own personnel
Of course, the second way is the priority. However, it requires long time. At the moment, both paths are actively used. Scientists and teachers from the leading universities of the country are attracted to work in universities. Part-time professors work with Moscow State University, RUDN, SFedU, KBSU. At the same time, all conditions are created for full-fledged work for specialists who are moving to work at ChSU on a regular basis. A prerequisite is the training of young personnel. The Head of the Republic, Hero of Russia Kadyrov pays much attention to the training of highly qualified personnel for the republic’s universities. In the frame of his training program, about 300 students were sent to European universities. After receiving higher education in Germany and Great Britain, all of them were employed in their specialties. At the same time, the Head of the Republic set the task for them to actively engage in science and work on further improving their professional level.
As noted above, taking into account the experience of leading Russian universities, we, together with the Ministry of Education and Science of the Chechen Republic, are working on the preparation of schoolchildren. 3 schools were taken under the patronage. The main emphasis is placed on training students in the mathematical and natural blocks. Additional attention is also paid to classes in ICT and foreign languages.
In our opinion, it is this kind of work that is designed to contribute to a more harmonious adaptation of a graduate of the school to the university, when he systematically visits the university, its laboratories. Learns the inner life of a particular faculty. All this just brings him to meaningful actions from the first year, to greater independence in the process of organizing his studies in accordance with the Bologna system. To ensure continuous education, the university has a lyceum, two colleges (one of them is medical) and an institute of additional vocational education.
More thoughtful actions on the part of students in terms of organizing their studies at the university and more flexible reciprocal action of the university in terms of ensuring the rights of students in the field of education, the ability and will of the university to move away from certain stereotypes will contribute to the preparation of our students in accordance with world standards, at the same time, not allowing blind copying of European methods. A systematic approach to innovations in the educational sphere is needed, guided by a course to improve the quality and content of education. Keeping the best of our traditional training system. One of the good methodological practices was the student's cross-cutting work on one scientific topic, starting with the coursework and ending with its final qualifying work. Unfortunately, at this stage, this pattern is rarely observed. One of the main indicators of the university's efficiency in general and effective personnel policy in particular is the availability of dissertation councils for the defense of doctoral and master's theses. Thanks to the creation of an appropriate base, 6 (six) dissertation councils are functioning at ChSU:
- 07.00.02 – National history (historical sciences);
- 08.00.05 – Economics and management of the national economy (economic sciences);
- 12.00.01 – theory and history of law - state; history of doctrines about law and state (legal sciences; 12.00.08 – criminal law and criminology; penal law (legal sciences);
- 13.00.01 – General pedagogy, history of pedagogy and education (pedagogical sciences); 13.00.08 – Theory and methodology of vocational education (pedagogical sciences);
- 25.00.36 – Geoecology (by industry);
- 10.01.02 – Literature of the peoples of the Russian Federation (North Caucasian literature); 10.02.02 – Languages of the peoples of the Russian Federation (North Caucasian literature).
Another problem of higher education, in our opinion, is the commercialization of the university. The terminology of commercialization and market relations has already become a persistent attribute of the educational sphere. An important issue is understanding the priority of educational goals and objectives over market ones, the ability to maintain a balance between these areas, understanding that the main thing in a university is an educational paradigm that meets the challenges of the 21st century. At the same time, the development strategy of the university cannot be successful without taking into account market realities. To solve educational problems, the university must have money, good management, marketing, appropriate advertising and consumer orientation.
As noted in (Asaul & Kaparov, 2007), “the economic function plays the main – after the educational – role within a Russian university and is generally inherent in both state and private Russian universities...” (p. 52). One of the elements of this function is the commercialization of education. A sharp decrease in state-funded places makes it almost impossible to study at a university for many talented graduates of schools and technical schools. Moreover, this trend continues. Higher education turns out to be affordable only for the elite. Certainly, higher education should be elite; however, elitism in this case should not imply the possibility of educating financially secure students, but the elitism of education itself, its quality, and a high level of educational services provided. The solution to this problem is possible with an integrated approach.
Along with the quality of the educational services provided during the period of tough competition for students, household issues also play an important role: accommodation, leisure, etc. To solve this problem, a modern university campus is being built at ChSU on an area of 1 hectare. A modern residential complex was put into operation. There are two university swimming pools. All this raises the attractiveness of ChSU for applicants, including the so-called “contract soldiers”. Another factor in the attractiveness of a university is the presence of a partner university from top domestic and foreign universities, the possibility of obtaining a second diploma.
An important component of the innovative activity of the university is the work on the formation of a socially active personality with a high spiritual and moral culture. In the messages of the President of Russia Putin to the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, it was emphasized, that “the spiritual unity of the people and the moral values that unite us are as important a development factor as political and economic stability ... and society is only able to set and solve large-scale national tasks when it has a common system of moral landmarks, when the country maintains respect for the native language, for the original culture and for the original cultural values, for the memory of their ancestors, for every page of our national history. It is this national wealth that is the basis for strengthening the unity and sovereignty of the country, serves as the basis of our daily life, the foundation for economic and political relations.” In this regard, the educational functions of the university are being strengthened. The task is daunting due to the fact that the formation of the views and behavioral structure of the younger generation is significantly influenced by the media and various Internet resources. In such conditions, it becomes necessary to develop and implement a conceptual model of state policy for the effective work of the “state-university” tandem. This issue is especially relevant in the post-crisis regions, where the struggle for the minds of the younger generation is most acute. This problem has been partially solved in the field of education. Unfortunately, the current concept is focused on general education. Deep awareness of this problem and the will to solve it was demonstrated in the Chechen Republic, where, on behalf of the Head of the Republic, Hero of Russia Kadyrov, where successfully operates the developed program “A single concept of spiritual and moral education and development of the younger generation of the Chechen Republic” (A single concept of spiritual…, 2013). The main goal of the Concept is upbringing and providing socio-pedagogical support for the formation and development of a spiritual and moral, responsible, educated and creative citizen of Russia in the Chechen Republic. The basic values in the concept are the civil, national and religious values of the peoples of the Chechen Republic. The document reflects the following: rationale for the need for such a Concept; characteristics of the principle of secularity of spiritual and moral education and development of the younger generation; priorities in spiritual and moral education and development; interethnic and interfaith relations in the context of spiritual and moral education and development; methods and technologies for the implementation of the Concept; creating conditions for improving the quality of work on spiritual and moral education and development. The Concept defines the tasks of state and municipal authorities and civil society institutions. Within the framework of this program, it was possible to consolidate all social institutions, including universities, which in one way or another influence the formation of the worldview of the younger generation. In addition, in the Chechen Republic such Internet resources as websites “Chechnyatoday.com” and “Grozny-inform” have been created, which are an effective form of countering extremist propaganda, contributing to the educational, cultural and spiritual development of citizens of the Chechen Republic. The Center for Spiritual and Moral Education and Development is functioning.
At the moment, the federal authorities are aware of the need for a more thought-out youth policy. Over the past ten years, a number of documents have been adopted at the federal level designed to raise work with youth to a higher quality level (Fundamentals of the state youth policy…, 2014; On youth policy in the Russian Federation, 2020; Patriotic education of citizens of…, 2015). Various scientific studies are being carried out in this area, according to the results of which specific steps are proposed in the framework of youth policy in Russia (Danilyuk et al., 2014; Kalimullin, 2013; Pokatylo et al., 2014).
Conclusion
In a situation of tough, competitive struggle in the economic, political, and ideological spheres, an uncompromising struggle is going on for the minds of the younger generation. And our task is not to let their brains get clouded and direct them along the path of creation and development. Everything is intertwined here: both education and educational work.
Thus, the formation of the university as an equal participant in the development of the region and the country presupposes the comprehensive development of an educational organization adapted to the new economic trends of the 21st century. At the same time, there must be a balanced approach to solving this problem. Initially, there should be an understanding of the priority of the educational cycle over the economic and other aspects of the university's activities. The efforts of all processes should be aimed at the effectiveness of the educational process.
References
A single concept of spiritual and moral education and development of the younger generation of the Chechen Republic. (2013). Grozny.
Asaul, A. N., & Kaparov, B. M. (2007). Management of a higher educational institution in an innovative economy. Humanistics.
Danilyuk, A. Ya., Kondakov, A. M., & Tishkov, V. A. (2014). The concept of spiritual and moral development and education of the personality of a citizen of Russia. Second generation standards. Prosveshcheniye.
Fundamentals of the state youth policy of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2025. Order of the Government of the Russian Federation of 29 November 2014, no. 2403-r. Moscow. Retrieved from: http://publication.pravo.gov.ru/Document/View/0001201412080039
Kalimullin, R. Kh. (2013). Spiritual and moral education of youth is the path to the development of tolerance. Fundamental research, 11-5, 1035–1039.
On Education in the Russian Federation. Federal Law of 29 December 2012, no. 273-FZ, Article 15.
On youth policy in the Russian Federation. Federal Law of 30 December 2020, no. 489-FZ. Retrieved on 2nd of August from http://publication.pravo.gov.ru/Document/View/0001202012300003
Patriotic education of citizens of the Russian Federation for 2016–2020. State programs. Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation, no. 1493 as of 30.12.2015.
Pokatylo, V. V., Shigabutdinova, L. R., & Volkova, A. V. (2014). On the need for moral education of youth. Young scientist, 4, 1066–1068.
Vesna, E. B., & Guseva, A. I. (2013). Models of interaction of organizations in the network form of implementation of educational programs. Journal Modern problems of science and education, 6.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
29 November 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-116-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
117
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2730
Subjects
Cultural development, technological development, socio-political transformations, globalization
Cite this article as:
Kutuev, R. A. (2021). The Development Of A Higher Educational Institution In Modern Conditions. In D. K. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Social and Cultural Transformations in The Context of Modern Globalism, vol 117. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 903-914). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.11.121

