Abstract
The article examines the problem of certain identification and systematization of the production cluster’s life cycle parameters. Based on the established criterion, a system of positive and negative factors is identified within balanced scorecard strategic projections. To provide metrological support and improve the efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises, a correlation analysis of the economic potential of the production cluster (resulting indicator) and the key leading life cycle factors influencing it is carried out when elaborating the integration model of balanced scorecard parameters. The additive model of the financial and economic potential of the production cluster is elaborated using deterministic factor analysis. A comprehensive generalized assessment of the economic potential development of cluster-forming enterprises and the production cluster is formulated. The integration model of balanced scorecard parameters for evaluation and management of the economic potential efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises is proposed taking into account the key leading factors and vectors of sustainable cluster development.
Keywords: Management model, balanced scorecard parameters, cluster-forming enterprises
Introduction
In the conditions of regional production clusters’ stagnation and the spread of the innovation and network economic paradigm the variety of digital clustering effects determines the emergent properties of cluster-forming enterprises (McCann & Ortega-Argiles, 2013). In the absence of prerequisites for stable economic growth, the emergence and the financial and digital activity of cluster-forming enterprises become the leading drivers of innovative development and metrological support for the economic potential efficiency of the production cluster. At the same time, the processes of digitalization of the economy, based on the introduction and implementation of technological initiatives for innovative support of business strategies for the organizational development, are prerequisites for the revival of production industries and cause factors of their new life cycle (Utkin & Speransky, 2019). Taking into account the parameters of the cluster life cycle in the unstable realization of its economic potential allows us to eventually overcome the uneven levels of efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises and reflect the vectors of sustainable cyclical production development (Sumarsih et al., 2020).
Problem Statement
The comprehensive evaluation and management of the efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises to ensure innovation and digital development of the life cycle of the production cluster are possible only when elaborating the integration model of balanced scorecard parameters for evaluation of the sustainable development of cluster potential. In relation to cluster-forming enterprises, the balanced scorecard concept allows us to determine the prospects of the performance of business processes and the exposure of cluster life cycle factors to economic risks (Benson, 2016; Koshovets, 2019; Mardas, 2007). In the conditions of a stagnant economy, the life cycle factors of industrial production cannot be corresponded with the generally accepted model (Odei et al., 2020). They should be constantly taken into account as part of the projections of the balanced scorecard to reflect the cyclical development of the innovation and digital cluster system. In this regard, the balanced scorecard is the most acceptable innovation method that evaluates the specific features of the state of cluster-forming enterprises and provides a metrological support of the flexibility of the strategic management of financial resources. It should forecast trends in the production cluster development and the life cycle system through key direct and indirect indicators of the financial and economic potential of cluster-forming enterprises.
The problem of the research consists in the identification and systematization of the life cycle parameters of the production cluster when taking into account within the projections of the integration model of the balanced scorecard for evaluation and management of sustainable cluster development. In the context of the metrological support and improvement of the efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises, it is necessary to form projections of the unified integrated balanced scorecard that generate the cluster life cycle factors, followed by the construction of the efficiency management model.
Research Questions
In 2010-2018, the inability to reorganize the industrial complex by ensuring a balanced budget determined the negative effect of digitalization processes, which is expressed in the economic transformation of the regional innovation and production cluster into the digital cluster (a set of “misaligned” and “over-reactive” business objects focused on information and technological “abrupt” changes). The resulting uneven innovation development of cluster sectors and the revenue potential of the budget led to a decrease in the innovation and economic efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises. At the same time, uneven innovation activity not only exacerbated the problem of the lack of multi-level production, but also determined the inefficiency of realizing the economic potential of existing cluster-forming enterprises.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to elaborate the integrated management model of balanced scorecard parameters for evaluating the efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises, followed by the management of the economic potential of the production cluster in the conditions of digitalization.
Research Methods
The fundamental principle of constructing projections of the balanced scorecard for metrological support of the economic potential efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises should be considered the difference in the levels of innovation activity of the economic systems of these organizations with the disclosure of the conditions of competitive advantages. In this case, the identification of the key leading life cycle factors that have the greatest impact on the cluster potential should be carried out through correlation analysis.
The positive and negative factors including in the strategic projections combine the “points of growth”, opportunities, threats and problems of the economic development of the production cluster. The internal balance between the production and innovation efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises and the socio-economic stability of the economy as a whole became the criterion (feature) for identifying the cluster life cycle factors within the balanced scorecard projections, which made it possible to identify and divide the parameters into seven analytical factor groups. This unified criterion was elaborated by us through the modification of the factor analysis of cluster processes used in a number of Russian and foreign methods for evaluating the efficiency of cluster functioning (Kobushko et al., 2020; Mironov & Konovalova, 2019). At the same time, the factors belonging to a particular group were determined by the current conditions of behaviour of cluster-forming enterprises and the possibilities of structural transformation of the economy into a network of interconnected industries.
The correlation analysis of the economic potential of the production cluster (resulting indicator) and the key leading life cycle factors allowed us to determine the most significant parameters that have the greatest impact on cluster development and form the integration model of the balanced scorecard for metrological support of the efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises (Table 1).
The compiled matrix of correlation coefficients shows that the maximum risk zones and the greatest impact on the economic potential of the production cluster are manifested in the interaction of factors X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6 (the closest relationship is close to 1).
These results indicate the need to use the obtained key leading factors for the formation of vectors of the integration model of the balanced scorecard parameters in the metrological support and management of the efficiency of cluster development.
Findings
Figure 1 shows the surface of possible correlations between the most significant key leading factors “Financial stability” (X4) и “Balance of internal processes” (X5).
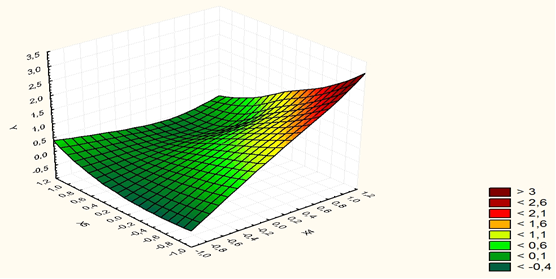
The presented matrix, which reveals the total financial and economic potential of the innovation cluster () as a resulting indicator, combines factor-generating strategic projections (financial stability (), balance of internal processes (), customer satisfaction (), innovation development ()) and their elements (factor features). In this regard, using deterministic factor analysis, the integral value of the economic potential of the production cluster is expressed in the form of an additive four-factor model (with elements of a multiplicative relationship):
(1)
In the elaborated additive model, the distribution of coefficient parameters is determined by the levels of significance of the influence of strategic projections on the resulting integral indicator of the financial and economic cluster potential (from the highest significance of the projection “Financial stability” (0.8) to the lowest significance of the projection “Innovation development” (0.5)). The influence of projections “Financial stability”, “Balance of internal processes” and “Innovation development” on the aggregate potential is fundamental and has a positive character due to the maximum disclosure of the strategic priorities of the economic cluster development in the forming factor groups. However, the impact of projection “Customer satisfaction” should be considered exclusively negative due to the generation of the total economic risk by factor groups ( ).
The positive factors of the economic potential of cluster-forming enterprises and the sustainable development of the production cluster are groups of life cycle factors that form projections with a positive impact on the resulting indicator:
- factors of industrial leadership and competitive advantages,
- factors of innovation positioning and benefits of scaling up,
- factors of survival and dominance in the cluster economy.
The correspondence and correlation of the cyclical vectors is reflected in the integration model of the balanced scorecard parameters, which demonstrates the process of forming methods and directions for improvement of the efficiency and functionality of the economic potential of the production cluster taking into account the factors of its life cycle (Figure 2).
The factor group of the competitive intensity, which mainly forms a negative (risk) projection “Customer satisfaction”, has negative consequences for the efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises. The conflict situation caused by these factors when interacting enterprises and industries in the production cluster exacerbates the unevenness of their innovation and economic development and does not allow to make a transition to a stable cyclicity of the sectoral functioning of the economy.
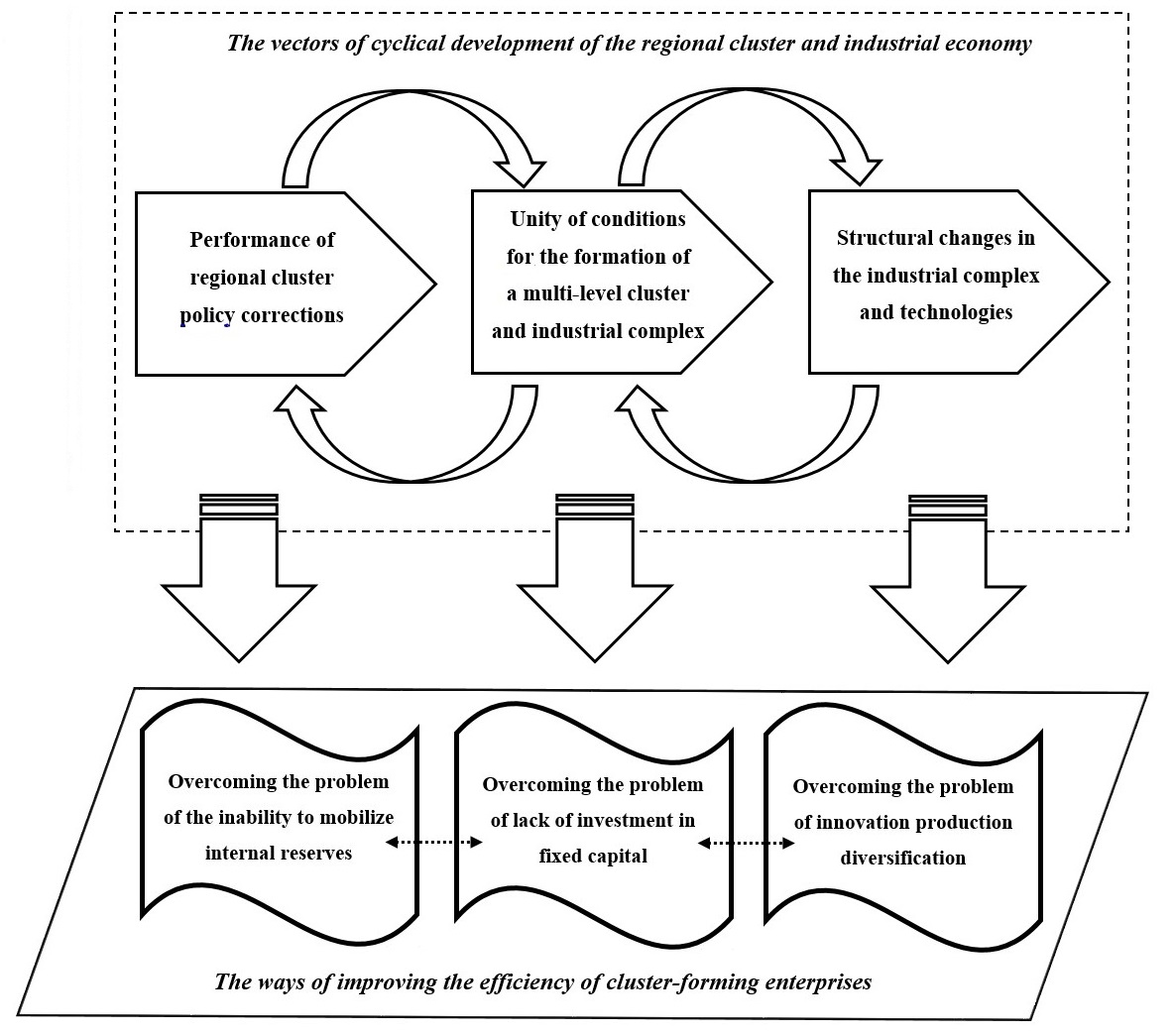
Based on the deterministic factor analysis, a comprehensive generalized assessment of the development of cluster-forming enterprises and the economic potential of the production cluster is formulated:. The key vectors for increasing the efficiency (cyclicity) of cluster-forming enterprises and improving the cluster state should be three directions:
- performance of cluster policy corrections,
- achievement of full coverage of socio-economic, technological and innovation conditions for the formation of a multi-level cluster and industrial complex,
- regulation of changes in the structure of industries and technological innovations during the industrial life cycle.
Thus, the identification and metrological support of the life cycle factors of the production cluster allowed us to propose vectors and ways to improve the cluster efficiency. The elaborated model for management of the efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises links the target settings of cluster processes.
Conclusion
- In the elaboration of the integration model of the balanced scorecard parameters for evaluating sustainable development of the production cluster with the goal to manage the efficiency of cluster-forming enterprises it is important to minimize the negative impact on the aggregate economic and financial cluster potential by projection of customer satisfaction and forming group of the life cycle factors, which will reduce the economic risks of cluster and industrial development.
- The presented results of the research will be of practical importance in the processes of the creation of a strategy for “bringing the cluster economy out of the crisis”, the development of plans for the production complex reorganization and the diversification of management tools for stimulating the implementation of production strategies.
- In the context of the need for metrological support of the production cluster reorganization, which involves increasing the viability of less stable organizations and making the transition to an effective multisectoral economy, the proposed integration model reflects the vectors and directions of development that provide a compromise in the interests of cluster-forming enterprises and standalone sectors of the cluster economy.
References
Benson, I. N. (2016). The impact of institutional environment on wealth and economic development: cross-country comparisons, St Petersburg University Journal of Economic Studies, 3, 38-55.
Kobushko, Ia., Kobushko, I., Starinskyi, M., & Zavalna, Zh. (2020). Managing team effectiveness based on key performance indicators of its members, International Journal for Quality Research, 14(4), 1245-1260.
Koshovets, O. (2019). Making progress horizontally: current practices of economic knowledge production, Social Sciences, 3(50), 58-74.
Mardas, A. N. (2007). The econometric approaches to setting balanced scorecards, St Petersburg University Journal of Economic Studies, 3, 110-118.
McCann, P., & Ortega-Argiles, R. (2013). Modern regional innovation policy, Cambridge Journal of Regions, Economy and Society, 6(2), 187-216.
Mironov, V. V., & Konovalova, I. D. (2019). On the relationship of structural changes and economic growth in the world economy and Russia, Voprosy Ekonomiki, 1, 54-78.
Odei, S. A., Prokop, V., & Stejskal, J. (2020). Innovation collaborations of firms: the case of Hungarian multinational companies, Economy of Region, 16(1), 257-267.
Sumarsih, D. H., Maupa, H., & Kadir, R. (2020). The Strengthening of Industrial Competitiveness through Industrial Fundamental Factors and Information Technology. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, (177), 8-21.
Utkin, A. I., & Speransky, S. N. (2019). Income potential management of the cluster-forming enterprises of Ivanovo region, Proceedings of Higher Education Institutions, Textile Industry Technology, 3(381), 14-20.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 September 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-115-7
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
116
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2895
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Utkin, A. I. (2021). Management Model Of Balanced Scorecard For Improving The Efficiency Of Cluster-Forming Enterprises. In I. V. Kovalev, A. A. Voroshilova, & A. S. Budagov (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST-II 2021), vol 116. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 857-864). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.09.02.96

