Abstract
The article reveals the essence of innovative management of industrial enterprises and the stages of development. It also reveals the characteristics of innovative development, the analysis of its theoretical foundations and the requirements for innovation. The author argues that innovation incorporates innovations related to human needs that change with the development of society, the processes of their creation, distribution and use. The article also comments on the essence of the economic category "Innovation" in terms of innovation management, the scheme of organization of innovation management in industrial enterprises, the external strategic goals of innovation management and the level of management of innovation management in enterprises. In the practice of innovation management, the term innovation is often associated with "investing in innovation." At the same time, the concept of innovation is the result of intellectual activity on the introduction of innovations in socio-economic relations in the organization of production processes, the characteristics of which are highlighted in the article: novelty, ie new quality indicators; achieving high economic efficiency; improving the competitiveness of the enterprise or product, etc. The article analyzes the characteristics of innovation in the organization of innovation management in industrial enterprises, as an economic category, which is inextricably linked with such terms as "invention" and "innovation". These are: scientific and technical innovation; availability of practical use in the production process; commercial suitability.
Keywords: Innovative management, development, implementation, labor, economic growth, production
Introduction
The period of post-industrial development of the system of economic relations requires the transition of economic development to an innovative path. Innovative reforms will need to cover various forms of public life and management. The effectiveness of the implementation of innovative activities is reflected in the achievement of sustainable economic growth, while ensuring high productivity of the economic system in the country, as well as the creation of appropriate conditions for progressive development. Analysis of the features of innovative development in the economic literature, its theoretical basis shows that the innovation process is becoming increasingly complex, and the requirements for innovation are also increasing. This situation makes it necessary to improve the system of innovative management of economic activity, to study in depth its theoretical and practical aspects. In revealing the essence of innovation management, it is expedient to first analyze the lexical meaning of the term innovation and its definition as an economic category. The term innovation is derived from the English word ‘innovations’, which literally means innovation, invention. In particular, innovations mean scientific and technical achievements and innovations in areas such as engineering, technology, management and labor organization, based on best practices, their application in various fields and activities (Abulkasimov, 2017).
Problem Statement
Innovations in the system of economic relations are the creation or improvement of new products (goods, works, services), the introduction or improvement of new forms of production processes, the introduction of new marketing or organizational methods of doing business, job creation and external relations. is the end result of the innovative activity it incorporates (Vertakova, 2008). In the economic literature, the economic category of "innovation" is described as a real manifestation of scientific and technological progress in potential new products and technologies (Ilenkovoy, 2012). In particular, innovation is the innovation of meeting the changing human needs with the development of society, combining the processes of their creation, distribution and use (Abulkasimov, 2017). At the same time, innovative management is the result of activities aimed at the introduction and popularization of new procedures, methods, patterns and innovations, new types of products, technologies in the production management process (Vertakova, 2008). In its broadest sense, innovation means the effective use of organizational, technical and socio-economic solutions with innovative, production, financial, commercial, administrative or other characteristics such as new technologies, types of products and services. According to international standards, innovation is the end result of innovation in the form of a new or improved product on the market, a new or improved technological process applied in practice, or a new approach to social services (Abulkasimov, 2017).
In innovation management practice, the term innovation is often associated with “investing in innovation”. At the same time, the concept of innovation (innovation, novelty) is the result of intellectual activity for the introduction of innovations in socio-economic relations in the organization of production processes, which can be distinguished by the following features (Vertakova, 2008):
- novation, for instance, new quality indicators;
- achieving an increase in the level of safety and protection of consumers through the introduction of innovations;
- achieving high economic efficiency;
- improvement of the competitiveness of the enterprise or product.
Research Questions
The study of economic relations in the use and application of the nature of innovative management and development stages of industrial enterprises.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of the study is the use and application of the nature of innovative management and development stages of industrial enterprises.
Research Methods
During the study, methods of observation, methods of induction and deduction, time series, economic statistics, analysis and synthesis, statistical grouping, research monograph, structural analysis, comparative analysis and other methods were used.
Findings
In the economic literature, there are many theoretical views on the economic category of innovation, and we believe that the given scientific views (see Table 1) are relevant to the object of our research.
When organizing innovation management at industrial enterprises, most modern economists and practitioners widely use the Frascati Guide and Oslo Guide as a normative document in the formation of their approaches to the concept of innovation (Manual of Oslo…, 2010).
These two normative documents are of constant importance at the international level in the organization of innovation management, innovation assessment, their implementation in practice and are constantly being improved by a group of experts on science and innovation of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. (OECD).
International standards for the collection, processing and analysis of data on science and innovation were first approved in 1963 in Frascati, Italy, and by 1992, methodologies for collecting data on technological innovation were approved in Oslo.
The analysis shows that in the organization of innovation management at industrial enterprises, innovation as an economic category is inextricably linked with terms such as "invention" and "innovation", the following features can be distinguished:
- scientific and technical innovation;
- possibility of practical use in the production process;
- commercial suitability.
According to the results of our research, in a market economy, innovation plays an important role in improving the efficiency of enterprise management, increasing its competitiveness and strengthening its position in the market. This, in turn, stimulates the development of innovative enterprise management, awakening the need to form a modern innovation management system at enterprises.
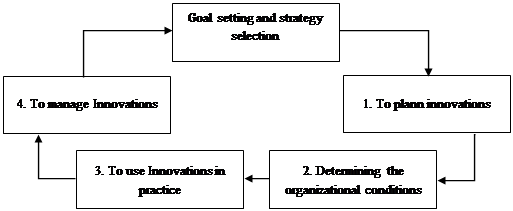
Innovation management is the organizational structure and personnel of innovative activity, which embodies the forms, methods and principles of managing the innovative processes of an enterprise (Ivasenko et al., 2009). Like other areas of enterprise management, innovation management has its own characteristics, which are arranged in the following order (see Figure 1) (Ilenkova & Goksberg, 1997).
First of all, it is necessary to determine the purpose of the organization of innovative activities of industrial enterprises and select the optimal strategy of innovative development.
The next stage includes four stages of development, which will include: innovation planning, identification of organizational conditions for the implementation of innovations, implementation of innovations and innovation management.
The four stages of development listed above will have to address the relevant tasks. Bunda (Ilenkova & Goxberg, 1997):
- the first stage is innovation planning, at which stage the task of network planning of innovations in accordance with the innovative development strategy of the enterprise should be solved.
The second stage is aimed at determining the organizational conditions for the implementation of innovations, at which stage the following tasks should be addressed:
- identification of the necessary resources for innovative development, the introduction of innovations in the activities of the enterprise;
- to provide them with appropriate resources in a timely manner in order to ensure the timely implementation of the work set on the basis of the plan developed in accordance with the innovative development strategy of the enterprise;
- clearly define the responsibilities of employees of the enterprise and control the timely performance of their duties;
- organization of innovative activity of the enterprise.
The next stage is the stage of implementation of innovations in practice, in which tasks must be carried out in accordance with the developed innovation plan, such as the implementation of scientific research, development of scientific and technical developments and ensuring their implementation in practice.
The final stage is the management of these innovations, in which the following tasks must be performed:
- monitoring the innovative activity of the enterprise and analyzing the achieved results;
- the organization of innovative activities of the enterprise, the identification of errors in its implementation and taking appropriate measures to eliminate them in a timely manner;
- evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of innovative projects implemented at the enterprise;
- control over the timely implementation of decisions on the management of innovative activities in the enterprise;
- practical application of innovations;
- continuous improvement of the company's innovative development strategy based on the company's experience in organizing innovative activities.
At this point, economist P.N. It is worthwhile to pay attention to the results of research conducted by Zavlin. In his research, the scientist distinguishes the following three aspects of innovative management of enterprises (Bazilevich, 2009)
- The art of innovation management and related science.
- The type of activity associated with management decision-making in the process of innovation in the enterprise.
- Innovation management staff of the enterprise.
The analysis shows that the art of innovation management and its science-related aspects are reflected in scientific approaches to innovative management of the enterprise, based on the general management theory (Umarov, 2020, 2021).
In the second direction, the assessment of innovation management as a type of activity associated with making management decisions in the process of innovation at an enterprise includes specific technological structures, methods and all related processes of the innovation management process. This situation differs from other types of innovative management as a specific direction of enterprise management, the organization of this type of management process differs from the usual management of stages, their characteristics of efficiency. In the process of organizing innovation management, functions and tasks are determined based on the state of the innovation system of the enterprise and its level of development.
The innovation management apparatus of the enterprise represents the organizational structure of innovation management, which is directly related to the innovation field.
The analysis of the theoretical foundations of innovative management of enterprises shows that the manager of the enterprise must meet the following requirements for the implementation of this type of management (Bazilevich, 2009):
- understand the essence of innovation and distinguish its types;
- understand the features of innovation processes;
- be able to correctly assess the innovative potential of the enterprise;
- be able to analyze the internal and external innovation environment of the enterprise and effectively use its components;
- planning of innovative processes, their implementation and assessment of the amount of necessary financial resources, as well as their target placement;
- to be able to accurately assess the level of risk of innovative activities of the enterprise and make appropriate decisions to reduce it.
The purpose of the innovative management of the enterprise will be inextricably linked with the tasks of the firm, its specific features, including its traditions and its development cycle. In the modern system of economic relations, business entities (enterprises, firms, companies, corporations, etc. with the status of a legal entity) have the opportunity to freely choose the direction of activity, partners, types of property. This, in turn, has a certain effect on the innovative goals of the enterprise, the direction of its tasks (see Figure 2).

The analysis shows that today the external factors influencing the activity of each enterprise and the internal needs associated with its development lead to the formation in the system of goals of innovative management. The system of strategic goals of innovative management of the enterprise in view of the influence of the external environment is specified.
Based on the internal needs of the enterprise related to development, the goals of innovative management are reflected in the following (Ogolevoy, 2002):
- increasing its efficiency through a complete overhaul of the system of production stages;
- increasing the competitiveness of the enterprise on the basis of effective use of scientific, scientific-technical, intellectual and economic potential.
The analysis shows that the goals of innovation management are described on the basis of the following criteria (Ogolevoy, 2002):
- target level (tactical, strategic);
- environment (internal, external);
- the structural structure of the goal (economic, social, political, scientific, technical, technological, organizational, etc.);
- priority (priority, permanent, traditional, one-time);
- validity period (long, medium and short term);
- functional structure (production, ITTKI (NIOKR), personnel, finance, marketing, management);
- stages of the development cycle of the enterprise (formation (manifestation), growth, maturity (flight), decline, termination (bankruptcy)).
It will be possible to observe the implementation of the "goal tree" in the practice of organizing innovative management in enterprises. At the same time, lower-level goals are subordinated to them as part of higher-level goals. The formation of the "tree of innovation management goals" of the enterprise requires an analysis of the levels of innovative management, and the levels of the goal tree are formed in accordance with the levels of innovative management. Most studies distinguish the following two levels of innovation management (Afonin, 2005):
- strategic innovative management - it means the strategic directions of economic growth and development of the enterprise in the long run;
- functional (operational, operational) innovative management - aimed at improving the efficiency of management of innovative activities in the enterprise, which includes processes related to innovative developments, implementation of innovations, production and sale of innovative products.
Given the interrelationship between the levels of innovation management functions, we consider it appropriate to divide the tree of innovation management objectives of the enterprise into three stages (see Table 2). This will further increase the level of complexity and efficiency of innovative management.
The analysis shows that the functions of innovative management include (Afonin, 2005):
- analysis;
- expediency;
- incentives (motivation);
- organizational;
- coordination;
- control;
- regulation.
Conclusion
In our opinion, in order to increase the effectiveness of innovation management in industrial enterprises of the country, it is expedient to formulate development directions for innovative activities for the strategic development of the enterprise, to develop appropriate measures for the implementation of innovations. In this case, the use of the proposed method in the formation of the tree of innovative management goals, along with achieving high efficiency, creates the basis for ensuring the sustainability of innovative development of the enterprise.
References
Abulkasimov, H. P. (2017). An explanatory dictionary of economic terms and concepts. Tomsk: ABU matbuot-konsalt.
Afonin, I. V. (2005). Innovation management. Gardariki.
Bazilevich, A. I. (2009). Innovatsionnyy menedjment predpriyatiya [Enterprise innovation management]. Uniti.
Ilenkova, S., & Goksberg, L. (1997). Innovative management. Banks and Exchange, UNITI.
Ilenkovoy, S. D. (2012). Innovation management [Innovatsionnyy menedjment]. UNITI-DANA.
Ivasenko, A., Nikonova, Ya., & Sizova, A. (2009). Innovative management. KNORUS.
Manual of Oslo: Recommendations on collection and analysis of data on innovations. (2010). Tsentr issledovaniy i statistikinauki.
Ogolevoy, L. N. (2002). Innovative management. INFRA-M.
Surin, A. V. (2008). Innovative management. INFRA-M.
Umarov, I. (2020). Innovative activity of the food industry of Uzbekistan. Economics and Society, 7, 74.
Umarov, I. (2021). Ways To Develop Entrepreneurship In The Food Industry. The American Journal of Applied sciences, 3(01), 153.
Vertakova, Yu. V. (2008). Upravleniya innovatsiyami: Theory and practice. Eksmo.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 September 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-115-7
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
116
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2895
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Sarimsakov, D. Х. (2021). Innovative Management And Development Stages Of Industrial Enterprises. In I. V. Kovalev, A. A. Voroshilova, & A. S. Budagov (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST-II 2021), vol 116. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 717-725). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.09.02.80

