Abstract
The article explores regular practices of supporting the procurement activities of small businesses. Measures of state support for small business in the field of procurement are summarized. The possibilities of revitalizing small enterprises through the format of supporting purchases of high-tech innovative products are being considered. Thus, it is justified to increase the status of small businesses in the formation of new technology markets. When conducting procurement procedures, large companies with state participation are primarily beneficial. Barriers and restrictions to effective procurement by small business entities have been identified, with the allocation of the sphere of procurement of innovative and high-tech products. Suggested recommendations for the development of formats for supporting innovative, high-tech small business entities. The purpose of procurement procedures is to minimize the overall cost of working with a reliable supplier of the same product. Such support formats as round tables, development of long-term technological partnership, list agreements contribute to improving the efficiency of procurement of large companies from small enterprises
Keywords: Small business, procurement procedures, high-tech and innovative products, round tables, long-term contracts
Introduction
Small entrepreneurship serves as a stabilizer of the socio-economic system of the country, as it provides significant assistance to the employment of the population, smoothing social tension, and contributes to the formation of mobility and flexibility of the economy. In the world system, small business has a significant role in the formation of new technological markets, in the development of high-tech and knowledge-intensive production. Contrary to global trends in our country, small business remains an underutilized resource of the economy. With the support of Russian small business, it becomes a significant driver of the economy. One of the most popular formats of support for small businesses in world practice is the organization of its access to purchases of state organizations and large companies with state participation, which form the markets for the products of innovative high-tech small companies. Small enterprises are considered from two positions: both initiators of the production of high-tech products and consumers of the results of high-tech activities of large businesses.
Problem Statement
In general terms, a service is the result of a certain process occurring in the interaction of the consumer and the supplier on the basis of mutual economic interest (Federal Law of the Russian Federation "On Procurement of Goods, Works, Services by Certain Types of Legal Entities", 2019). Therefore, as part of this study, the regional logistics market is a streaming intraregional system for distributing material, information, service and money traffic between the consumer sector by producing a certain set of services related to processes such as supply, transportation, service support, route optimization, etc. It is services at the current stage of development of this market that acquire a special role, which is associated with the rapid growth in the quality of logistics procedures, including in Russia.
Research Questions
The logistics market has a high degree of proximity to perfect competition, which is certainly reflected in the dynamics of economic development of territorial entities. This fact makes it possible to state the need to improve the logistics industry at the regional level. However, from the point of view of world trends in the development of the logistics services market, the Russian Federation is still at the initial stage of the formation of a highly efficient logistics system, which is primarily due to the regional differentiation of the socio-economic situation of households. In other words, today the Russian market of goods movement is inferior in quality and complexity of services to similar world practices of developed countries (Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 11.12.2014 No. 1352 "On the peculiarities of participation of small and medium-sized enterprises in the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities", 2020). So, if in the foreign market the share of goods transportation services occupies about 68 %, and the share of complex logistics services and management activities – 18 and 12 %, respectively, then in the Russian market the transportation of goods is 88 %, and management logistics is only 1 %, the remaining 11% is other services for shippers and consignees (Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 29, 2015 N 1169 "On the Procedure for Monitoring Compliance of Procurement Plans for Goods, works, services, plans for the purchase of innovative products, high-tech products, medicines, changes made to such plans, assessments of the conformity of the projects of such plans, Draft amendments to such plans to the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation, providing for the participation of small and medium-sized enterprises in the procurement, procedure and timing of the suspension of the implementation of these plans based on the results of such assessment and monitoring ", 2020). From this it follows that the specifics of the modern Russian logistics market lies in its mono-direction, and the key process determining the content of the market is the movement of goods between the supplier and the buyer. Another feature of the industry under consideration in Russia is the absence of logistics intermediaries (Federal Law of December 29, 2015 N 408-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation", 2020). As a rule, economic entities build their own system of goods movement, not using intermediary services, due to the low level of trust characteristic not only of the logistics sector, but also in general for the Russian private sector, especially on a regional scale.
Purpose of the Study
The combination of the above features negatively affects the level of logistics costs. And since the overall assessment of the transport and logistics system of the country consists of separate regional indicators, the study of the logistics services market at the level of the territorial entity of the Russian Federation is considered relevant and, in particular, the experience of developing the logistics system of the Republic of Bashkortostan, a region with favourable conditions for business activities and high potential opportunities in the field of logistics, is interesting.
Research Methods
In this article, the following research methods are used: graphic, comparison method.
Findings
Measures of state support in the field of procurement provide: regulation of access of small enterprises to procurement of goods, works and services for state and municipal needs; Increased access to government-owned companies' orders; mandatory quotas of corporate purchases from small and medium-sized businesses (from 2020 - at least 20% of the total annual volume) (Federal Law of the Russian Federation "On Procurement of Goods, Works, Services by Certain Types of Legal Entities", 2019; Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 11.12.2014 No. 1352 "On the peculiarities of participation of small and medium-sized enterprises in the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities", 2020) creation of a register of specific companies for compulsory purchase of innovative high-tech products from small enterprises (Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 29, 2015 N 1169 "On the Procedure for Monitoring Compliance of Procurement Plans for Goods, works, services, plans for the purchase of innovative products, high-tech products, medicines, changes made to such plans, assessments of the conformity of the projects of such plans, Draft amendments to such plans to the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation, providing for the participation of small and medium-sized enterprises in the procurement, procedure and timing of the suspension of the implementation of these plans based on the results of such assessment and monitoring ", 2020). Establishing a roster of small businesses as potential qualified suppliers of major companies; Establishment of a unified procurement information system (Federal Law of December 29, 2015 N 408-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation", 2020) formation of an up-to-date list of high-tech and innovative products; Organization of training on participation in the procurement procedure (Methodological materials (requirements) for the development of provisions on the procedure and rules for the application (implementation) of goods, works, services that meet the criteria for attribution to innovative products, high-tech products, 2020).
The Institute for Development in the Field of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises has been created - SME Corporation, one of the key tasks of which is to organize access to corporate procurement in accordance with federal law No. 223.
All this together allows expanding the access of small enterprises to purchases of large and largest companies, creating conditions for guaranteed sale of their products, including high-tech, innovative products.
Analysis of cases on procurement practices of small business entities, statistics of a single information system in the field of procurement, expert opinions show the need to further develop the format of relations between procurement participants.
However, small entrepreneurs face challenges and constraints in carrying out procurement procedures directly as both a supplier and a customer. For example, the difficulty of legally supporting the participation of small enterprises in regulated corporate procurement; insufficient organizational and technological readiness to participate in procurement procedures, insufficient skills of specialists, the need for significant financial resources for the purchase of modern office equipment and access to high-speed Internet (Sakleev, 2017).
According to the statistics of the unified information system of the country, the volume of purchases changes unpredictably, poorly regulated (Figure 1). This is primarily due to the fact that the rules for participation in procurement procedures, a high level of uncertainty in the economy and policy, are constantly changing. For 2019, the factor of slowing down the growth of gross domestic income plays a significant negative role.
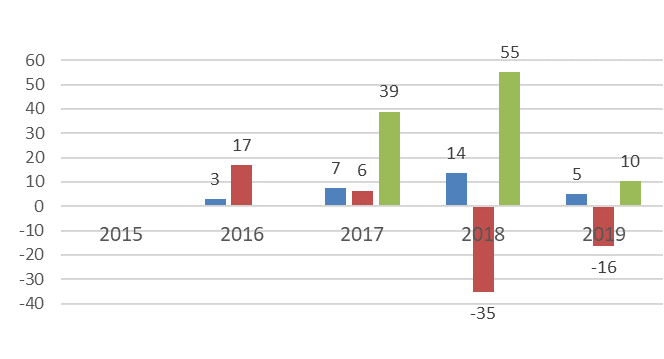
The evaluation of the effectiveness of public procurement by large companies from small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is presented in Table 1 (Site of the Unified Procurement Information System, 2020; Site of the Federal State Statistics Service, 2020).
The share of purchases by large companies from small and medium-sized enterprises for 2019 year amounted to 25.4% (with the established standard 18%) of all purchases in the country, which corresponds to 3.9% of the gross domestic product of Russia. In the global economic system, SME production in various countries ranges from 33 to 67 per cent of the country's GDP.
In the period 2016-2019, the range of procurement is expanding and the number of contracts of large companies with small and medium-sized entrepreneurs is increasing by more than 4 times. The average purchase contract price decreases by 43% from 13.86 million rubles in 2016 to 7.93 million rubles in 2019. The achieved savings of large companies in procurement from small and medium-sized enterprises are more than in general procurement practice. According to 2019, the savings received by large enterprises are 2.2 times higher than this indicator in the framework of general practice for FZ-223 (3.8%). The number of non-competitive purchases is reduced, where the small enterprise is the only supplier.
The listed indicators indicate an effect in favor of large companies. So, the level of competition in procurement with small and medium-sized enterprises is insignificant, it is 2 performers per large customer. The low efficiency of procurement procedures for small enterprises is due to the application of the lowest bid price in order to save the customer's money, which leads to an underestimation of the quality and innovative potential of small enterprises.
In connection with the transition to a digital format of the economy, one of the key goals of state policy is to support business development in the high-tech sector, primarily effective procurement procedures.
Evaluation of the involvement of small and medium-sized enterprises in the procurement of high-tech, innovative products is presented in Figure 2.
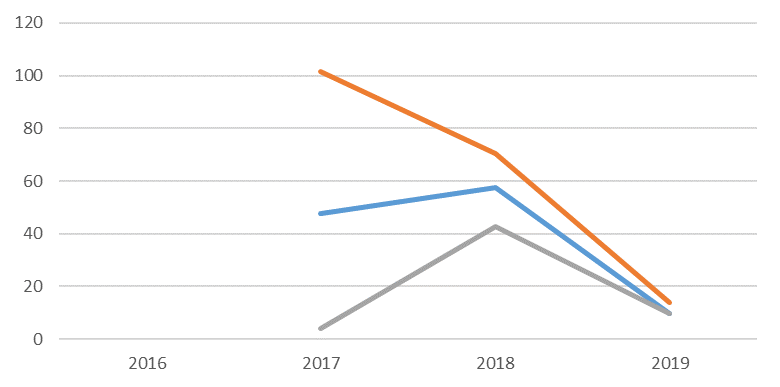
Statistical information attracts attention primarily with a sharp increase in 2017 and then a sharp decrease in the growth rate of purchases of high-tech, innovative products for 2019. The share of purchases of products of the high-tech sector is lowest. Note that in 2019 this represents 12.4% of the volume of purchases from SMEs, 3% of the volume of purchases in the country, 2.1% of the total turnover of small enterprises, 0.4% of the country's GDP (calculated taking into account the data of Table 1).
The main product of the high-tech sector is computer, electronic and optical equipment. In the context of the active digitalization of the company, SME Corporation for 2020 expects that the share of high-tech equipment will be 55.4% (equivalent to the amount of 102 billion rubles), the share of products and services in the field of information technology - 22.5% (41.4 billion rubles) of the total volume of purchases from small and medium-sized enterprises (Website of JSC "Federal Corporation for the Development of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises" (SME Corporation), 2020).
According to the long-term forecast of the country's socio-economic development until 2030, the share of high-tech knowledge-intensive industries in Russia's GDP should be 12% in 2020 (Forecast of the long-term socio-economic development of the Russian Federation for the period until 2030 (developed by the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia), 2020).
Procurement procedures for high-tech, innovative products from small business entities should differ from purchases of standard catalogue goods. The production of products in the high-tech sector and technological processes are based on the results of not only applied, but also basic scientific research. These are industries with a research and development cost share of 8% or more. The small scale of production in a small enterprise causes high overhead costs and high prices for products compared to foreign counterparts. Small innovative enterprises are characterized by lack of business reputation, insufficient experience, non-conformity of the qualification level of applicants to the established requirements. All these circumstances reduce the competitiveness of small enterprises as suppliers.
In world practice, three main models of relations between large business and small enterprises in the field of high-tech production are traced:
- Within the largest company, innovative structural units are formed: scientific and technical divisions, internal innovation centers and venture capital organizations, innovative-oriented matrix structures are used;
- A large company absorbs small and medium-sized innovative firms, acquiring a minority share to familiarize itself with the innovative project, and if the project is of strategic importance, it absorbs the firm;
- a large company cooperates with small innovative firms on the basis of long-term contractual relations, in the format of startups.
The third model ensures the continued independence and growth of small businesses.
The system of procurement procedures implements measures to support small enterprises:
- information, marketing, credit guarantee and legal support of access of small enterprises to purchases of the largest companies with state participation;
- Creation of a Single Demand Window for Innovative Products and a Single Window for small entrepreneurs to submit innovative proposals;
- methodical provision of pricing when purchasing high-tech, innovative products taking into account the costs of warranty and post-guarantee services, market information on resource prices, etc.;
- technological partnership of large customers with small business entities, involving them in the development of technical tasks and design documentation;
- negotiating the conditions for providing high-tech, innovative services and products, synchronizing the development plans of large customers and small performers;
- allocation of procurement of high-tech, innovative services and products into an independent object of procurement activity with subsequent differentiation of procurement procedures taking into account the uniqueness, scientific and technological novelty, complexity, scientific capacity, compliance with priority areas of development of science, technology and technology, availability of patents or know-how, etc.;
- Conduct an audit of the procurement procedure according to the qualification criteria for the selection of innovative, high-tech small enterprises.
Modern innovative economy, characterized by the dominance of horizontal network communications, is distinguished by the logic of creating information and its use through network interactions (Mandel, 2016). Therefore, the key organizing link in the system of procurement procedures is the exchange of information, the creation of new knowledge, and the colorful interaction of procurement participants. The main format of such joint partnerships is the round table. In the context of digitalization of the company, round tables actively conduct online federal trading platforms to explain the standard parameters of procurement procedures (Nielsen, 2017). Large companies regularly organize round tables with potential suppliers, involving leading heads of key departments and services; discuss the prospects of the company's development, regulations for conducting procurement procedures. Holding a modern round table online allows to expand the range of prospective suppliers (Sydney Lazarus, 2018).
With the participation of large and large customers in procurement, small enterprises face many problems not only of a general nature, like the algorithm and characteristics of participation in procurement, the preparation and completion of document forms when receiving financial and warranty support. Of particular importance is the receipt of qualified assistance in the correct and complete preparation of the procurement documentation, which includes the qualification, technical and commercial part of the application based on the technical documentation prepared by the customer. Receiving feedback from the manufacturer allows the procurement organizer to check the prepared technical specifications for the completeness, unification and standardization of the purchased products, this is especially important if the manufacturer proposes to make changes to the technical documentation.
The round tables may discuss the following issues:
- quality and completeness of the customer's preparation of technical tasks for material and technical resources (ETT, OL, TT, etc.); the extent to which they meet the requirements of the procurement procedure;
- proposals for improvement of technical tasks, unification and standardization of procured products;
- the amount of procured goods, based on the annual demand, that the procurement bidder may produce in his or her production, taking into account the current production load;
- minimum terms of production and delivery of products from the date of conclusion of the contract;
- possibility to participate in procurement procedures and to carry out contracts on a long-term basis under list contracts.
Expected positive results from the round tables:
- the better the roundtable participants are prepared, the less loopholes of unscrupulous customers to violate the Procurement Regulations and other local regulations regarding the procurement activities of a large company;
- procurement takes place with high congruence, efficiency and in the minimum time period established by local regulatory documents;
- the interaction between the customer and the supplier is more reliable and understandable for each of the parties.
There may be negative consequences of round tables for participants in procurement procedures - these are anti-competitive agreements, for example, in the form of cartel conspiracies. The most common price collusions during bidding. Prior to bidding, potential competing participants secretly enter into an agreement on conditions for obtaining a contract before the start of bidding and on dividing the market to the detriment of the customer's interests. The signs of such cartel collusion are the following actions of participants in the procurement procedure: potential suppliers submit the most profitable offers at the minimum price sequentially; all, except one participant, submit proposals with violations of the terms of the procurement documentation; There remains one participant who wins a non-competitive purchase; companies that do not win the purchase, in exchange for their "loss," receive another sub-contract from the winning participant or a monetary reward from him (Official website of Ivlev's lawyer S.S., 2020). If the territorial administrations of the antimonopoly service, other regulatory bodies, identify the existence of an anti-competitive agreement, administrative and even criminal liability is provided.
When holding a round table, it is useful to discuss the strategy for the development of long-term relations through procurement, followed by the conclusion of long-term contracts or list contracts with a price limit (Lysons & Gyllingham, 2014). The long-term relationship between buyer and supplier should be most cost-effective. Production and supply of high-quality innovative products cannot be ensured under conditions of one-time transactions (Deming, 2011).
The conclusion of a long-term contract is aimed at achieving a guarantee of supply of the purchased product, at the right time, at the optimal price. Due to the fact that many domestic large companies conduct procurement procedures in accordance with federal law or the Procurement Regulations of the company, the procurement procedures can take several months. With one-time transactions, there is a risk of disruption of deliveries of the product required in production, as well as loss due to company downtime. For a small enterprise, it is also important to have a guaranteed market for complex high-tech products. When concluding a contract, a clause is made on the need for the supplier to implement a risk management system (Deming, 2019; Shaykhutdinova et al., 2015, 2017; Solodilova et al., 2020; Stock & Lambert, 2005; Zagitova et al., 2020) in their production.
Long-term agreements are considered a legal tool for improving the quality of products based on the establishment of deadlines for the implementation of progressive standards indicators. By concluding a long-term contract for a period of more than 3 years, participants establish the conditions for the production of new types of products based on the expansion of the product line (assortment); consider the possibility of step-by-step improvement of certain characteristics of products, production technologies; develop measures to prevent or eliminate the causes of marriage. Contracts providing for a gradual improvement in the quality of the delivered product ultimately lead to the emergence of a competitive product on the world market, which, amid the instability of the world currency and the government's import substitution program, is especially valuable for the market of domestic goods. The use of the long-term contract format leads to the development of specialization and cooperation in all sectors of the economy, which reduces the dependence of the country's economy on the export of natural resources (Biryukova, 2016).
A variety of long-term contracts are list contracts, which are recommended as a valid tool for improving procurement performance in large companies. In the period from 2018 to 2020, the number of procurement procedures with the further conclusion of the long-term list agreement has increased by a multiple. So, for example, according to the TEK-TORG ETP, according to the organizer of the purchase of Bashneft-Production LLC, there were 23 purchases in 2019. - 46, and in February 2020 already 37 purchases (Electronic trading platform of JSC "TEK-Torg," section of PJSC "NK Rosneft.", 2020).
Features of list agreements:
- list contracts are concluded for deliveries without indexation, without volume discount with all procurement participants admitted before the evaluation stage and whose price has a deviation from the minimum price of not more than 15%;
- in case of default by one of the suppliers, its volumes are transferred to the next supplier in ranking without making a question at the procurement commission, provided that the planned value is not exceeded;
- When delivery volumes are transferred to the next supplier, the losses incurred in the form of differences in value will be issued to the first counterparty;
- the main and reserve list agreement is concluded with the simultaneous signing of the List of Prices, at the same time the item items for which the minimum prices are offered are fixed as main items, and prices for which exceed the minimum prices of the winners by no more than 15% are fixed as reserve items;
- in case of non-delivery of the main items, the transfer of the right of delivery to the supplier is initiated, with whom the List Agreement is concluded for the corresponding items fixed as reserve, with the issue of the difference in value without a question at the purchasing commission, provided that the planned value is not exceeded;
- the planned delivery cost for the current year and the projected demand for subsequent years are set; the volumes of goods purchased are indicative and can be changed both to a larger and a smaller direction.
When concluding a list agreement, there are also pitfalls: the price is fixed for 2 years and in the case of the supply of complex or imported equipment, such contracts are not always beneficial to the supplier. Therefore, the role of holding round tables for an open discussion of the above points is very important.
The use of procurement tools such as round tables, long-term and list contracts requires their sharing.
Conclusion
Thus, small business has a large unrealized potential in the field of corporate procurement. State measures on legislative, methodological and technological support for procurement activities contribute to an increase in the purchase of products from small business entities. The practice of evaluating and choosing suppliers on the basis of only a minimum price for their products limits the development of small businesses. The purpose of procurement procedures is to minimize the overall cost of working with a reliable supplier of the same product. Such support formats as round tables, development of long-term technological partnership, list agreements contribute to improving the efficiency of procurement of large companies from small enterprises. Despite the existing risks, the joint practice of holding round tables with manufacturers of material and technical resources, concluding long-term and list contracts is clearly recommended as a valid mechanism in order to achieve a transparent economic result in the conduct of procurement procedures.
References
Biryukova, T. A. (2016). Long-term relations in the system of strategic planning and development of the enterprise. Bulletin of Economics, Law and Sociology, 2. http://www.vestnykeps.ru/0216/4.pdf (In Russian).
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 11.12.2014 No. 1352 "On the peculiarities of participation of small and medium-sized enterprises in the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities". (2020). http://base.garant.ru/70819336 (case date: 13.02.2020). (In Russian).
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 29, 2015 N 1169 "On the Procedure for Monitoring Compliance of Procurement Plans for Goods, works, services, plans for the purchase of innovative products, high-tech products, medicines, changes made to such plans, assessments of the conformity of the projects of such plans, Draft amendments to such plans to the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation, providing for the participation of small and medium-sized enterprises in the procurement, procedure and timing of the suspension of the implementation of these plans based on the results of such assessment and monitoring ". (2020). http://base.garant.ru/71237208 (case date: 20.05.2020). (In Russian).
Deming, E. (2011). The way out of the crisis. Alpina Pablisher.
Deming, E. (2019). New time management. Simple mechanisms leading to growth, innovation and dominance in the market of Alpina Pablisher. LLC.
Electronic trading platform of JSC "TEK-Torg," section of PJSC "NK Rosneft." (2020). https://www.tektorg.ru/ (case date: 22.05.2020). (In Russian).
Federal Law of December 29, 2015 N 408-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation". (2020). http://base.garant.ru/71295402 (case date: 20.05.2020). (In Russian).
Federal Law of the Russian Federation "On Procurement of Goods, Works, Services by Certain Types of Legal Entities". (2019). [Electronic Resource]: from 18.07.2011 No. 223-FZ (ed. From 02.08.2019) //ATP Consultant Plus. http://www.consultant.ru (case date: 20.01.2020). (In Russian).
Forecast of the long-term socio-economic development of the Russian Federation for the period until 2030 (developed by the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia). (2020). from 18.07.2011 No. 223-FZ (ed. From 02.08.2019). ATP Consultant Plus. http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_144190 (case date: 22.05.2020). (In Russian).
Lysons, K., & Gyllingham, M. (2014) Procurement and supply chain management from the 6th English ed. Ewright-Publishing.
Mandel, B. R. (2016). Modern organizational psychology. Modular course: tutorial. Director-Media. (In Russian).
Methodological materials (requirements) for the development of provisions on the procedure and rules for the application (implementation) of goods, works, services that meet the criteria for attribution to innovative products, high-tech products. (2020). https://www.garant.ru/products/ipo/prime/doc/72085960/ (case date: 22.05.2020). (In Russian).
Official website of Ivlev's lawyer S. S. (2020). http://advokativlev.ru/vopros-otvet/kartelnyiy-sgovor-na-torgah-po-44-fz/ (In Russian).
Sakleev, M. A. (2017). Public procurement as a tool to support small business. Public-private partnership, 4(1), 57-66. https://doi.org/10.18334/ppp.4.1.37679 (In Russian).
Shaykhutdinova, G. F., Nikonova, S. A., Karachurina, R. F., Sharipova I. M., Korotkova L. N., & Sultanova, L. F. (2017). Stimulating of entrepreneurs' innovative activity in the Republic of Bashkortostan. Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences, 9(7S), 1005-1015. http://ddoi.org/10.4314/jfas.v9i7s.91 (In English).
Shaykhutdinova, G. F., Zhidkova, E. V., Minisheva, L. V., Nikonova, S. A., & Sharipova, I. M. (2015). Actual problems of youth entrepreneurship at the modern stage. Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 6(2), 379-386.
Site of the Federal State Statistics Service. (2020). https://zakupki.gov.ru/epz/main/public/home.html (case date: 13.02.2020). (In Russian).
Site of the Unified Procurement Information System. (2020). https://gks.ru (case date: 13.02.2020). (In Russian).
Solodilova, N. Z., Malikov, R. I., Grishin, K. E., & Shaykhutdinova, G. F. (2020). Regional business ecosystem: institutional capacity. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences EpSBS. Krasnoyarsk Science and Technology City Hall. Krasnoyarsk, 103-111.
Stock, R. J., & Lambert, M. D. (2005). Strategic Logistics Management. Infra-M.
Sydney Lazarus. (2018). Are Reverse Auctions a Threat to Good Supplier Relationships? https://spendmatters.com/2018/07/12/are-reverse-auctions-a-threat-to-good-supplier-relationships/ (circulation date: 28.01.2020).
Website of JSC "Federal Corporation for the Development of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises" (SME Corporation). (2020). https://corpmsp.ru/ (case date: 10.02.2020).
Nielsen, W. (2017). Technical Report: Policies that Promote SME Participation in Public Procurement. Business Environment Working Group. https://www.enterprise-development.org/wp-content/uploads/DCED-BEWG-SME-Procurement-Report.pdf (circulation date: 14.02.2020).
Zagitova, L. R., Sharipova, I. M., Vyugova, D. S., & Akhmetshina, A. I. (2020). Development of state support for small and medium-sized businesses in the field of innovative procurement. Bulletin BIST (Bashkir Institute of Social Technologies), 1(46), 87-95. (In Russian).
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 September 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-115-7
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
116
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2895
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Sharipova, I. M., & Gareeva, A. (2021). Small Business Procurement Support Formats. In I. V. Kovalev, A. A. Voroshilova, & A. S. Budagov (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST-II 2021), vol 116. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 502-513). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.09.02.56

