Abstract
Currently, the program-target approach, the most important mechanism of which has become state programs, acts as the main paradigm of the public expenditure management system. This method is based on the selection of priority areas of state activity and the development of interrelated measures to achieve them with maximum efficiency and in a given time frame with a certain provision of financial resources. The significance of the study lies in the fact that program-target management is the most progressive and discussed approach to the management of budget expenditures, which is one of the most debatable issues. The solution to the problem of insufficient financial resources is entrusted to economists who are wondered how to use and distribute the available funds most effectively in order to meet the needs of society as much as possible. Based on this need, monitoring and evaluating the effective use of budget funds is an important part of the activities of government agencies in different countries. The paper investigates the essence of the target-oriented method of budgetary resources management; evaluates the effectiveness of the results of the program-targeted approach and identifies the problems of effective use of this method. The directions of its improvement are proposed.
Keywords: Budget expenditures, program-target method, state program, budget resources, budget programs
Introduction
The relevance of the article is due to the fact that the program budget acts as a key tool for managing public expenditures. It provides an opportunity to switch to program budgeting from expensive (resource) methods of budget planning and its execution, which are traditional.
Problem Statement
To date, there is no unified approach to understanding the essence of such a type of budget expenditure management as program-target management. The reason is the breadth and complexity of this term. At the same time, it is worth noting that management itself is a purposeful impact exercised by the subject of management in relation to the object of management, in which various tools, methods and measures are applied. The above method of budget expenditures management consists in the organization of management of these expenditures, which involves taking into account certain objectives in the formation of the expenditure part of the budget. It also provides for further assessment of the results of achieving these goals.
Research Questions
The program budget is the key tool for managing public spending. It provides an opportunity to switch to program budgeting from costly (resource) budget planning and execution methods, which are traditional.
The essence of management consists of three interrelated components - planning, operational management and control. Programmatic method in the framework of budget planning implemented through activities related to the definition of goals, drawing up forecasts, plans, programs for the development of social the economic sphere of the spheres of government - state and municipal, economic sectors, formations of public law character. This activity is focused on solving problems associated with ensuring the national security of the Russian Federation, sustainability development of territories in socio-economic terms.
Since the main purpose of budget expenditures is to meet public needs (Bril, 2018), the peculiarities of the volume and structure of the budget expenditures characterize the strategic priorities of social development, which are implemented within the framework of the state budget policy (Lazarova & Tegaeva, 2019).
The purpose of the program-targeted method of managing budget expenditures is to ensure the connection between the allocated funds and the results of spending these funds. This method implies the need to distribute budget funds between various state programs.
One of the advantages of program budgeting is its focus on solving long-term problems, and its basis is the assessment of expected results in the future, which significantly distinguishes it from the budget, built on items, the basis of which is the experience of previous periods. Thus, for the formation of a long-term economic and social policy of the state, the most effective method of program budgeting. Despite all the advantages of program budgeting, its application, in particular, application at the initial stages, is a rather complicated process. The transition to this type of budgeting presupposes large-scale changes in the public administration system.
Performance evaluation
According to F. Hameed (2010), the assessment of the effectiveness of budget expenditures is a tool for increasing the efficiency, flexibility and efficiency of budgetary resource management, since the integration of the assessment of results into the budget mechanism is aimed at carrying out a continuous analysis of the expected and achieved level of effectiveness of expenditures of the budgets of the budgetary system of the Russian Federation and, on its basis, optimizing the distribution and redistribution and use of budgetary funds, taking into account the criteria for the effectiveness of budgetary expenditures and budgetary activities.
The main principle of the formation and execution of the expenditure side of the budget in the system of program-targeted management of its resources is the measurability of the planned and actual results of budgetary activities in each area and the systematic assessment of the level of effectiveness of budget expenditures in their planning, implementation and control over budget execution, which implies determining criteria for assessing the effectiveness of budget expenditures, budget programs, activities of government bodies, which is manifested in the formation of a system of effective indicators for each budget program of costs, quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the product, efficiency, as well as indicators of direct and final results for assessing the final socio-economic effect of implementation of the budget program.
A systematic assessment of the effectiveness and social efficiency of the use of budgetary resources must be carried out at the level of budget programs, budget expenditures in general and by functional purpose at the level of activities of the main administrators of budgetary funds and the industry as a whole (Benito & Bastida, 2009).
International Experience
Analysis of international experience in managing budgetary processes has shown that there is no universal method for the transition to program budgeting. For more effective implementation of programs, it is necessary to appoint a responsible manager who will have certain powers to be responsible for the effective execution of budget programs and the use of allocated budgetary funds. It is necessary to establish at least one evaluation criterion, which will allow determining the effectiveness and degree of achievement of the goal, which was set by the manager (Bril, 2018; Elokhov & Elokhova, 2019).
The experience of the transition to program budgeting in the UK can serve as a positive example. The first stage of changing the budget system here began in 1980 and lasted 17 years. Such a long period made it possible to develop a procedure to check the effectiveness of the activities of public authorities. The two-step reform of the United Kingdom budget system has led to the creation of a commercial method for managing funds in the public sector of the economy. The German experience in the application of program budgeting allows us to conclude about the flexibility of the studied budgeting system. (Lazarova & Kabaloev, 2019).
Purpose of the Study
Study of the content and tools of program-targeted management of budget expenditures in the system of state strategic planning and forecasting.
Research Methods
The article uses the following research methods: horizontal and vertical analysis, statistical measurements, graphical method and method of scientific generalization.
Findings
The effectiveness of program-targeted management in North Ossetia-Alania
Public expenditure management occupies one of the significant places in the budgetary policy of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania, and is more characterized by the state of the budget process, the procedure for effective planning, budget approval and its execution in terms of expenditures, as well as control over its implementation (Ministry of Economic Development of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania, 2021). The article analyses the financing and implementation of the main state programs implemented in the republic for the period 2016-2018.
In 2016, the volume of budgetary allocations that were allocated for the implementation of activities of the State Programs of the North Ossetia-Alania amounted to 19,899.3 million rubles. In 2017, there was an increase in the volume of funding for state programs, which in actual terms amounted to 955.1 million rubles. or 104.8% of the level of 2016. In 2018, the growth in funding for government programs continued and reached RUB 24,354.9 million. or 116.8% of the level of the previous period.
For the three analysed years, the state programs with the largest amount of funding should be singled out: "Development of education in North Ossetia-Alania", the second position was taken by "Development of health care in North Ossetia-Alania", in third place was "Social development of North Ossetia-Alania".
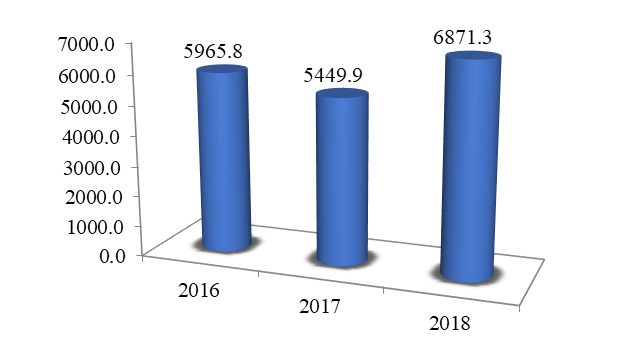
Within the framework of the state program "Development of education in North Ossetia-Alania", during the study period, there was an ambiguous dynamic. The volume of financing under the program in 2017 amounted to RUB 5,499.9 million. Then, in 2018, there was an increase in the volume of financing under the program by RUB 1,421.4 million, and amounted to RUB 6,871.3 million in actual terms. or 126.1% of the level of 2017, which is clearly seen in Figure 1. In general, growth was noted for the period under review.
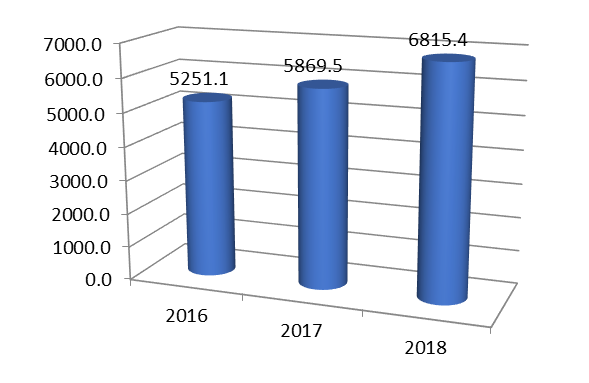
According to the state program "Development of health care in North Ossetia-Alania" during the study period, there was a positive trend. In 2016, the amount of financing amounted to RUB 5,251.1 million. In 2017, the volume of financing under this program increased by 618.4 million rubles. and amounted to 5,869.5 million rubles. In 2018, a similar situation was observed - the volume of financing in absolute terms increased by 116.1%, amounting to 6,815.4 million rubles.
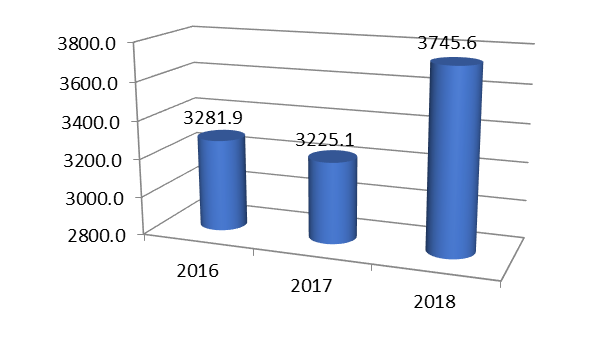
Within the framework of the state program "Social development of North Ossetia-Alania", during the period under study, there was an ambiguous dynamic. Funding for the program in 2017 amounted to RUB 3,225.1 million, a decrease of RUB 56.8 million. In 2018, the opposite trend was observed - the volume of financing increased by 520.5 million rubles. and amounted to 3,745.6 million rubles in actual terms. or 116.1% of the 2017 level, which is clearly seen in the diagram. In general, positive dynamics was noted for the period under review (see Figure 2).
Assessment of the socio-economic efficiency of budget expenditures is aimed at identifying the influence of the expected and actually achieved direct results of budget programs and the activities of the main administrators of budget funds on various spheres of public relations, indicators of the country's socio-economic development (see Figure 3).
It is possible to assess the results of achieving the goals of the state programs discussed above by mastering the indicators, which are their mandatory elements. Each indicator is a quantitative and qualitative characteristic of the implementation of measures of the state program, which takes into account both the sphere of state activity and regional characteristics.
In 2016, within the framework of the state program "Development of Education in North Ossetia-Alania", out of 56 planned indicators, 44 were achieved. Due to the incomplete implementation of 12 indicators, the effectiveness of the program was 78.6%. In particular, the indicator of the share of the number of preschool children, instead of the planned 5%, was fulfilled by 1% due to the lack of appropriate financial resources to support private kindergartens. In 2017, the Program planned to achieve 65 indicators, of which 54 were achieved. Due to incomplete implementation of 11 indicators, the effectiveness of the program was 83.1%. Of the 58 target indicators planned in 2018, fifty-seven were achieved. The effectiveness of the program was 98.3%, as one of the planned indicators was not fully implemented. The level of efficiency of the implementation of the state program during the analyzed period is estimated as average. (Kairova & Gabeeva, 2019)
Under the program "Development of Health Care in RNO-Alania" in 2016, it was planned to achieve 66 target indicators, but the planned values were achieved for 51. Incomplete implementation of 15 indicators reduced the effectiveness of the program to 77.3%. In 2017, 63 of the planned 72 indicators were achieved. Due to incomplete implementation of nine indicators, the effectiveness of the program was 87.5%. In 2018, 66 of the planned 71 indicators were fulfilled, and the effectiveness of the program was 93.0 percent (Kairova & Gabeeva, 2019).
Conclusion
The purpose of the program-targeted method of management of budget expenditures is to ensure the link between the allocated funds and the results of spending of these funds. Having analyzed the problems that arise in the implementation of this approach, it is necessary to identify the main directions of their solution. In order to ensure an increase in the efficiency of the implementation of state programs in the region, a set of appropriate measures is proposed (Premchand, 2005; Vedung, 2017).
- Responsibility for the effectiveness of budgeting must be increased. The envisaged responsibility should be specified.
- It is necessary to form a methodology, on the basis of which the effectiveness will be assessed. This methodology should include sections describing the composition of qualitative and special indicators, as well as a risk map. The risk map should define the composition and content of risks under the program.
- It is necessary to monitor the implementation of programs, and to identify the reasons, due to which the funds provided in the budget for the implementation of the programs are not fully implemented. If it is found that the target programs may not be executed, it is necessary to develop proposals to change the volume of allocated funds, indicating the reasons for the incomplete or untimely implementation of the budget funds allocated to the implementation of programs.
Thus, in order to ensure the unity of budgetary classification, to ensure the effectiveness of the implementation of state programs, to develop budgeting based on program-targeted principles, it is necessary in cooperation with the administrations of urban districts and municipal districts to study the issues related to the implementation at the level of municipalities of the activities provided for by state programs. When the indicators of a state program or subprogram are amended, it is advisable to include intermediate and mandatory indicators as part of the performance evaluation system.
References
Benito, B., & Bastida, F. (2009). Budget Transparency, Fiscal Performance, and Political Turnout: An International Approach. Public Administration Review, 69(3), 403-417.
Bril, D. V. (2018). BOR: foreign experience. Budget, 5, 21-25.
Elokhov, А. M., & Elokhova, T. A. (2019). Productive foreign experience useful for the development of program and target management in Russia. Antro, 1, 233-240.
Hameed, F. (2010). Budget Transparency and Financial Markets’, [unpublished paper]. International Budget Partnership.
Kairova, F. A., & Gabeeva, M. A. (2019). State Programs as a tool for program and target management of budget expenditures of the RSO-Alania. Economics and Entrepreneurship, 11(112), 401-405.
Lazarova, L. B., & Kabaloev, G. K. (2019). Priority areas of social policy. Collection of scientific papers Management of the economic and social systems of the region, 281-284.
Lazarova, L. B., & Tegaeva, Z. E. (2019). Main directions of increasing the efficiency of expenditure of the federal budget, Economics and Entrepreneurship, 11(112), 174-177.
Ministry of Economic Development of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania. (2021). State programs. http://economy.alania.gov.ru/index.php/activity/programs/stateprograms
Premchand, A. (2005). Controlling Government Spending: The Ethos, Ethics and Economics of Expenditure Management. Oxford University Press.
Vedung, E. (2017). Public Policy and Program Evaluation. Routledge.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 September 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-115-7
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
116
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2895
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Lazarova, L., Kairova, F., Abaeva, E., Bibilova, N., & Savlokhova, V. (2021). Program-Target Method Of Budget Resources Management In Social Development Of The State. In I. V. Kovalev, A. A. Voroshilova, & A. S. Budagov (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST-II 2021), vol 116. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 352-358). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.09.02.38

