Abstract
Problems, associated with accounting policy formation processes in globalization context, financial and large-scale capital mergers and state economy progressive transformation, adequate demands to current level of modern market conditions were researched and represented in earlier publications. However, risk classification generalization, analysis, up-to-date socio-economic and financial problems solutions management and negative impact of stochastic circumstances to business are lesser known, so it is very important for further investigation. Large-scale business development modern trends are financial and educational holding capitals merger and FLSB formation with participation of various industries economic units and financial institutions. These processes are sustained by tangible monetary resource stockpiling that can be rated as the positive phenomenon for innovative projects investments. The article discloses risk factors classifications determining contemporary conceptual approaches. It is suggested accounting policies improving peculiarities as effective risk management tool for financial and educational large-scale systems (educational holdings) conditions. Also financial and large-scale capital merging modern conceptual approaches are researched in the article. It is suggested scientifically based proposals on processing, engineering and management for large-scale business risk and profitability with banking institutions involvement.
Keywords: Educational holding, large-scale business, management
Introduction
Modern economic relations are characterized by high level of external instability, internal benefits variability, stochastic and risk factors increasing that drastically worsen entities financial positions. Statement, which was mentioned above, illustrate that new business lines development is noteworthy today. It must be based on capitals of financial and educational large-scale business (educational holdings) combining principles and banks involving. Financial and large-scale business structure (FLSB) has power to influence on processing, engineering and management of business activities and state economic stability even in high risks conditions, caused by geopolitical crisis. However these levers are also insufficiently explored and topical for further researches.
Problem Statement
Problems, associated with accounting policy formation processes in globalization context, financial and large-scale capital mergers and state economy progressive transformation, adequate demands to current level of modern market conditions were researched and represented in earlier publications. However, risk classification generalization, analysis, up-to-date socio-economic and financial problems solutions management and negative impact of stochastic circumstances to business are lesser known, so it is very important for further investigation. Large-scale business development modern trends are financial and educational holding capitals merger and FLSB formation with participation of various industries economic units and financial institutions. These processes are sustained by tangible monetary resource stockpiling that can be rated as the positive phenomenon for innovative projects investments. Applying of innovations is a specific mean to increase enterprises potential for the global competition. Experts note this one is the main way for nowadays crisis overcoming (Aven, 2014). Innovative projects implementation deferred costs are related to increasing uncertainty, risks negative impact and economic entities lower returns. Financial institutions can reduce these affects and make business activity more predictable and effective. Financial institution which is Federal Tax Service (FTS) participant has valid cash flow levers management system for stochastic and entropic internals and externals.
Research Questions
- To research risk factors classifications determining contemporary conceptual approaches.
- To suggest accounting policies improving as effective risk management tool for financial and educational large-scale systems (educational holdings) conditions.
- To disclose financial and large-scale capital merging modern conceptual approaches.
- To suggest scientifically based proposals on processing, engineering and management for large-scale business risk and profitability with banking institutions involvement.
Purpose of the Study
Processing, engineering and management of large-scale business risk and profitability with banking institutions involvement (for educational holdings).
Research Methods
The base for the materials that are represented in the article was accumulated on information of outcomes on particular researches (Aven, 2014; Barr, 2018; Creswell & Creswell, 2018; Dickeson & Ikenberry, 2010; Frohnhoefer & Pangilinan, 2019; Fullan & Quinn, 2015; Haimes & Sage, 2015; Hayden, 2020; Lavland & Redding, 2021; Levenson, 2015; Manners-Bell, 2020) and methods on approaches of modern analysis and processing, engineering and management, functioning of financial and educational institutions.
Findings
Financial and educational holdings systems functioning and determination of risks impacts on business activities are top-points of scientific interest for many experts. Those problems solutions methodic approaches are given below. Experts (Aven, 2014; Barr, 2018; Creswell & Creswell, 2018) note that in the XIX century with information society creation it is forming risk society. Its main goal is to withstand political conflicts, technical and natural risks (disasters, epidemics, famine, etc.) which were regular and extremely dangerous for preindustrial period. Nowadays stochasticity and risk of undertaken commitments are increasing in modern geopolitical conflicts conditions. Experts point out: management risk of partial capital losing, thereby exposing danger to company economic interests during taking economical decision in instability. Ignoring risk negative consequences can turn effective business unit into bankruptcy (Dickeson & Ikenberry, 2010). Mentioned above caused IFRS IAS 37 «Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets» offers taking into account risks and uncertainties connecting to various events and circumstances for optimal resources evaluation. Risk regulating can increase liability amount. It is important to be circumspect and cautious in taking decisions in stochastic externals and not to inflate revenues and assets and not to reduce costs and liabilities (Frohnhoefer & Pangilinan, 2019). Expert notices that modern economic analysis completely changes its paradigm from evaluative and statistical approach to disquisition and practical one with optimal decisions choice for management in uncertainty and risk conditions. Therefore business units risk determination and evaluating analytical researches are at the foreground. It is clear that most modern econometrics can’t solve that problem, but readiness in implementing countermeasures to achieve expected success is crucial. Risk evaluating should be based on equal basis, expanding risky operations participant field and reduces failure case disappointment.
There are scholars and practitioners different opinions about risk classification (Aven, 2014; Barr, 2018; Creswell & Creswell, 2018; Dickeson & Ikenberry, 2010; Frohnhoefer & Pangilinan, 2019; Fullan & Quinn, 2015; Haimes & Sage, 2015; Hayden, 2020). This is due to the fact that risk is rather multifaceted concept that combines legal, financial and economic characteristics. Any processing, engineering and management of business unit is impacted by risk, regardless of its activity type. Risks exist before economical operation or project implementation, during its process and after it. Even if company does not carry out any activity, it is in unused opportunities risk field (Fullan & Quinn, 2015).
It is not possible to avoid risks totally in economic activity; this causes its reducing or neutralization require. To solve this problem it is necessary to foresee different risk types, analyze them, and resume results to control them during processing, engineering and management at business. There are a lot of risk definition interpretations in economic literature, which generally characterize adverse events occurrence probability associated with business structures revenues non-compliance and society economic security reducing. Risk factors formation mechanism researching is inextricably connected to economic relations that occur at functioning in process system of educational holdings. Scientific research analysis notes that the very system is formed, developed and further operated with influence of various risk factors which are inherently immanent to economic structures. As an economic category, risk is reflecting actual existing uncertainty and conflict in business processes. Factors are divided into external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous) groups. External risk factors indicate state of economic entity conditions and surroundings; they are independent of enterprises. Internal factors associated with business activity and they are considered to be reliant. These common features as externals and internals are not unique and are determined depending on systems levels. Each higher level system forms internal environment that can develop only in unity with appropriate system level surroundings.
National economy should be considered as the highest level, its socio-economic and scientific-technical direction and state legal regulation of accounting (external factors). The second level is economical, organizational, technical and accounting policies of specific business system (internal factors) in their processing, engineering and management processes. This indicates that externals and internals of mentioned systems are very relative. Each surroundings can be both external and internal. Their conditional distribution depends on considered system level.
Thus, lower rank object external risk factors are internal factors of system, which includes this object. Separate external risk factors for peculiar business of financial and educational holdings system are internal. It can be identified political, economic and banking risks in the most generalized risk groups. Political risk due to political changes, and military conflicts in the world and different states, which are causative to development of such negative phenomena as inflation, capital outflows from the country, high crime rates, etc. Criminalization is legal and regulatory assets violation, implementing business transactions risk, fraud, that lies in accounts primary documents and accounting records and statements manipulation and falsification, accounting records deliberate changes, which distort financial and business operations essence with aim to violate legislation or company's accounting policies, deliberately misprice assets and their write-off methods, original records or documents deliberate omission or concealment, deliberately transactions content concealment, illegally obtained property, displaying incorrect account entries. All these increase risk probability and affect economic processes.
Economic risks are processes associated with negative consequences probability in case of random economic decisions relating to business factors use, liquidity, risky innovative projects investment. These solutions are connected to unforeseen projects, business activities and transactions financial losses risk. Expert (Aven, 2014; Barr, 2018; Creswell & Creswell, 2018; Dickeson & Ikenberry, 2010; Frohnhoefer & Pangilinan, 2019; Fullan & Quinn, 2015; Haimes & Sage, 2015; Hayden, 2020) note that this definition is common to the group of risks arising from capital circulation different stages caused by competitors, suppliers and other contractors actions, market conditions changes, technological errors, etc. Banking risks linked to economic ones, but they have their own specifics, which is typical for banking sector: interest rate changes, credit, currency and price operations, technologies, security, etc. Modern banking market is inconceivable without risk, which contained in any operation, and can be scaled and recompense differently. It would be highly naive to search banking options, which completely exclude the risk beforehand and guarantee some profit or loss (Haimes & Sage, 2015).
Considered risks are closely connected to strategic and tactical objectives. Thus, factors are evaluating for each business system strategic and tactical solutions at processing, engineering and management. Information of factors is primarily classified according to various criteria that reflect economic activity particular area and impact accounting process organization. New strategic goals can be changed or determined at the strategic level only. They refer to product selection, sources funding, business, markets, technology and process analysis, assets acquisition or disposal and other events that could lead to statutory requirements revision. Operational risk factors appear at the tactical level and relate to economic units resources (labour, material, equipment) rational use possibility; also it is set FLSB and evaluation criteria for activities efficiency of its departments.
Nowadays experts suggest using break-even analysis to substantiate domestic economy solutions for internal and external stochasticity, which is based on fixed and variable costs and gives possibility to forecast basing on sales profit operating. Margin and operating leverage are the main risk indicators there. The safety margin (safety zone) shows economic unit reduction amount maximum threat to get into financial loss area. Economists note that if the safety factor is below 30 %, it is high risk indicator. Operating leverage (commercial leverage) allows to control fixed and variable costs optimal ratios for operational risk management. It should be noted that risk factors peculiarities analysing shows that identic factors can be interpreted as positives for one business system and negatives for other. Business processes increased automation for processing, engineering and management requires enlarging amount of high skilled support personnel. There also are situations where factors show positive indicators, but business system regresses. This can happen when it is made negative factors value erroneous interpretation and they are assumed as positives. Thus, raw materials low cost can cause productive resources norms further growth. There were business systems praxis cases that exemplified positive factors indicators negative affection. Factors impact margin is very important. Peculiar factors has period of positive trend in system functioning than it changes to negative one. There can also be reverse sequence.
Current assets stockpiling is the reason for turnover deceleration that also has negative impact on financial ensuring level of business but reserve accumulation minimizes financial and commercial risks (e.g. equipment, goods and business lifecycle processes). It should also be emphasized that risk factors are not always completely understood and formulated, but always arising from interests of individuals, economic units, investors, corporations, non-profit organizations, political parties and national interests. Investors are very reluctant to direct their resources into risky industry. Multinationals research and take into account numerous factors before invest business projects. The main of them include: political system; national political, social and economic stability; local market capacity and accessibility; geographical location, natural resources and labour availability; currency risk; capital return rate; project life cycle; capital return period; investors security and protecting; government regulation (taxes, benefits, regulations stability); market infrastructure availability. Risk management analytical framework is necessary for threats and uncertainty minimizing on partnerships formation stage, investment projects implementation, contracting.
Particular attention should be paid to accounting policies compliance to economic situation influenced by risk and uncertainty internal and external factors. It refers to different risk degrees occurrence depending on special assets future realization probability and accounting policies adjust necessity during peculiar year that requires appropriate financial statements explanations. Deferred charges assets are especially vulnerable in case mentioned above. Prepaid expenses on business system processes realization should be distinctly monitored, because their costs are more dependent on future probabilities and trends evaluation than all other costs value. Achieve results failure risk is relatively higher in this case than in other assets ones. There is high need to reduce negative impact of risks mentioned above on economic activity. It is necessary to form correct type of accounting policy, identify core assets and set their disposal period. These actions strengthen administrative documents supervisory functions.
These classification criteria do not cover risk factors multiple that negatively affect business system processes. There are newest geopolitical problems, economic conditions and technological progress triggers. They influence factors that can become more or less stronger in their impact ability. Risk factors analysis that is given in this article allows identifying regularity and correlations of financial and educational holding capital taking into account internals and externals. International experience shows that investment project's cash flows amount must be less than 15 % of total assets to reduce future risks of innovations. Thus, economic units’ business systems achieve effective results only in enlarged groups of financial and educational holdings.
Main feature of the problem which was mentioned above is that it includes few directions of scientific researches on financial and educational holdings capital merger and large-scale business formation, business activity risks and risk management, banking economic risks. Previous publications enclose these blocks are listed below. The most of them are focused on bank institutions risk management internal problems. Also it was suggested operational risks classification and commercial bank operational risk management effective system formation. It was described banks risk assessment approach including not only operational and technological risks, but also externals caused ones – price, inflation, investment withdrawal, and reinvestment. These risks types are common to all economic structures and large-scale businesses. It was not solved the task of large-scale business (educational holdings) risk management with banking institutions involvement.
Development progress that is stipulated by unification of capital flows in interaction of financial institutions and educational holdings adduces to complexity of business control in accumulation and inspection. This task can be solved with specific implementation of peculiar control structure for financial flows. Framework of bank can provide effective tools for structure that was mentioned above. It also takes into account that such capital merges which appear in the process of unifications of capital flows are characterized by large-scale size. Bank supplies multiple services for finance support and becomes unification center for business interaction of strategic business units of FLSB including their connections to any processes on insurance and investing.
Banks have the leading position in efficient monitoring and control of FLSB practices and business connections. In that processes defined core bank institution becomes main incorporated and crediting agent for educational holdings. This bank provides loans for long periods and play crucial role in economic activity of any kind of business at FLSB. Also it collects control and operating data on each educational holding, participates in its management. Management structure is grounded on specific policy of FLSB that integrates operations on financial flows and accounting that proffer opportune effective adjustment for capital, minimizes various risks. These flows are involved to different solutions in risk management, outlay and liquidity areas. Institutions of banks are active participants of global business interactions and support multiple projects on innovations. That gives comprehensive background for banks connected to FLSB risk transference in interstate control and international commitments for countries with social, political and economical instability. The core element of global business is operations at monetary and credit areas beyond interactions of economic units. Economists specify that interstate monetary correlation is specific kind of intermediaries for states, areas, business entities, bank institutions and costumers during process of products and services transfer (Levenson, 2015). This correlation is characterized with high level of stochasticity and various risks. Results on different analysis in economy illustrates that interstate risks are inherent to any country and destructively influences on projects in investing in each state. Recurring risks becomes main hindrances for investors abroad who make solutions on investments to peculiar business of defined state. Damages of bank institutions appear during FLSB remittance via interstate boundaries and liability of residents of states abroad. The very element of global risk is risk on transference on financial flow that appears in the period when paying of debtor is fixed in his state currency during international transfer. There is need to find for banks the very centers for responsibility of business operations including front and back offices, accounting and treasury that provides effective risk and profitability management (Figure 1).
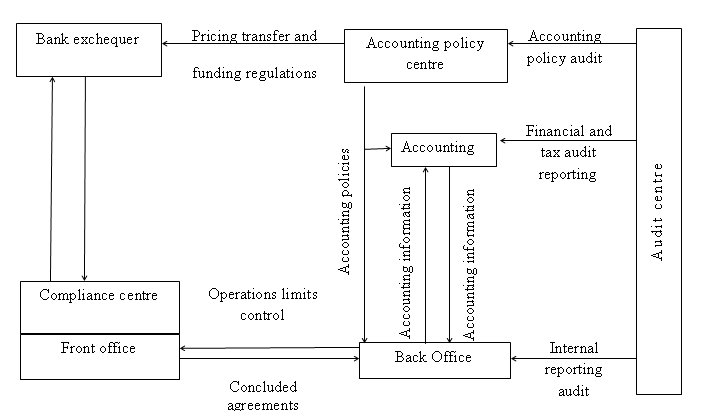
The operations of front office activity at the bank include accords and arrangements. Back office makes evaluations, computations, risk assessments, verifies remittances and regulates approved financial limitations. Unified function of treasury and back office endorse financial arrangements. (E.g.: When it is necessary financial flow at front office for actual validе transference it requests treasury. Treasury makes loan for front office on agreed time with conformed rate on it. Back office monitors terms of limitations and conclusions). Boarders of limits are peculiar requirements to services and operations of bank. Limitations for risks depend on capital amount and returns on investments. Limitations for complicated operations comprise determinations for specific tasks on predictions for bank institution at its financial state including key performance indicators on current and future indices of operations, conclusions of arrangements, outer frames, contracts, documents, requirements of Central Bank, control specific, strategic maps, etc. Characteristics of business operations define measurers and their weights for each part of activity and services, taking into account profitability, return on investment, etc. Accounting office keeps accounting records.
Back office also operates in area of financial management and accounting control, draws up reports. It is special link between different structures of the bank, outer units of FLSB and financial flows system. Accounting office plays core role at correlation of inner divisions of bank institution and Central bank authorities. This office also works on documentation for financial monitoring, support and control, risk management and policy for accounting for peculiar bank. FLSB makes modern mechanism for adequate price formation, profitability control and risk minimization in the terms of correlation and integration of financial flows of bank institutions and educational holdings. This mechanism is valuable element of accounting total management. It also includes pricing for various exchequers, products and services in different conditions of agreements beyond FLSB during its operations. It has different levels, the first one includes pricing in specific strategic business unit at FLSB (e.g., bank), the second one connects pricings in different units (e.g., economic units, bank institutions, insurance offices, etc.). This approach is the most convenient for FLSB. Resource management for such structure is correlated with strategy plan of banking institution, and period of financial plans should be less that strategic ones.
Costs of these centers of responsibility estimates for financial periods, it includes resource base availability. Main capital markets form on this base; they provide credits on different periods. Pricing for mentioned credits are individual and fixed in financial plan of banking institution as legislative norm. Pricing for exchequers and expenses is evaluated for each period of financing separately. Treasury of banking institution charges proceeds to centers of benefits which amass mentioned exchequers from outer environment and convey expenses to centers of outlays that place resources to external surroundings at the close of period of financial plan. All the evaluations are based on data of current and future periods. Transposition of pricing is very important for different economic units of FLSB. It demands specific monitoring, support and control of activities of FLSB units and their administrative expenses. Estimation for costs is grounded on their characteristics and features and also centers of outlays. Administrative inspection entrusted to centers of responsibilities. Hereafter special matrix (Table 1) is suggested for analysis of outlays. Its lines are centers of responsibilities, and columns represent programs of business development with high profits and returns on investments. Data on outlays are summed up by lines at this matrix. Outcomes are numeric information on exchequers of centers of responsibilities. These data represent costs of business program which is required for definition of costs of various services and evaluation of profitableness. Unified codes for centers of outlays and profits (that are structures of FLSB) let to fund values of different economic units.
Optimization for effects provides different options: option 1 – growth of positive outcomes based on under exchequers, option 2 – growth of positive outcomes based on the same level of exchequers, option 3 – growth of positive outcomes is faster than increasing of exchequers, option 4 – positive outcomes have the same level, level of exchequers reduces, option 5 – speed of outcomes reducing less than exchequers. These options illustrate that target of FLSB activities is the growth of outcomes.
Description is given at the Table 1.
Experts mentioned the growth of effectiveness of common and renewed suggested approaches is represented for FLSB at Figure 2.
In the best option any structure becomes lucrative but it is very complicated to attain these states at praxis. Transposition of pricing should lead to support and progress of weak economic units of FLSB. It implements innovations to FLSB structures at processing, engineering and management.
Conclusion
Information that is revealed in this article disclose peculiarities of major risk factors occurrence and their impact on business system processes for financial and educational holding capital merging conditions. The main conclusion of this article is that risks phenomena should be predicted and analysed with management process methodology and taken into account peculiar economic units specific in processing, engineering and management. In researched case it is FLSB activity and its accounting policy. This approach extends accounting policies tools aimed at business monitoring. It gives such benefits as management decisions risk reducing, efficiency increase, economic entity profitability and system optimality. Research results that are revealed in this article disclose financial and educational holdings capital merger conceptual approaches and banking structures role in risk and profitability management for large-scale businesses conditions. It was determined that banking institutions are main indicators of risk factors there. It manages not only operational and technological risks inherent to the banking sector, but also global risks that are related to large-scale business transnational obligations and all market relations participants. Banking institution is the central link in system of financial and educational holdings, it reallocates financial resources and reduces negative risk factors and increase FLSB funds efficiency. Information that was given in the article can be applied as guidance at praxis of control on risks at economic units at large-scale area.
Acknowledgments
This work is self-initiated and self-financed. Authors thanks committee of conference for participation possibility.
References
Aven, T. (2014). Risk, Surprises and Black Swans: Fundamental Ideas and Concepts in Risk Assessment and Risk Management. Routledge.
Barr, C. A. (2018). Budgets and Financial Management in Higher Education. Jossey-Bass.
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. SAGE Publications, Inc.
Dickeson, R. C., & Ikenberry, S. O. (2010). Prioritizing Academic Programs and Services: Reallocating Resources to Achieve Strategic Balance, Revised and Updated. Jossey-Bass.
Frohnhoefer, R. W., & Pangilinan, J. (2019). Risk Assessment Framework: Successfully Navigating Uncertainty. PPC Group, LLC.
Fullan, M., & Quinn, J. (2015). Coherence: The Right Drivers in Action for Schools, Districts, and Systems. Corwin.
Haimes, Y. Y., & Sage, A. P. (2015). Risk Modeling, Assessment, and Management (Wiley Series in Systems Engineering and Management). Wiley.
Hayden, E. (2020). Critical Infrastructure Risk Assessment: The Definitive Threat Identification and Threat Reduction.Rothstein Publishing.
Lavland, A., & Redding, S. (2021). Managing Performance Strategically in Education Agencies: A guidebook for Strategic Performance Management. Information Age Publishing.
Levenson, N. (2015). A Better Way to Budget: Building Support for Bold, Student-Centered Change in Public Schools. Harvard Education Press.
Manners-Bell, J. (2020). Supply Chain Risk Management: How to Design and Manage Resilient Supply Chains.Kogan Page.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 September 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-115-7
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
116
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2895
Subjects
Economics, social trends, sustainability, modern society, behavioural sciences, education
Cite this article as:
Lukyanova, Y., & Gorobets, D. (2021). Management Of Risk And Profitability In Educational Holding With Banking Institutions Involvement. In I. V. Kovalev, A. A. Voroshilova, & A. S. Budagov (Eds.), Economic and Social Trends for Sustainability of Modern Society (ICEST-II 2021), vol 116. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 2325-2334). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.09.02.259

