Abstract
The results of the study of the existing practice of labor rating in livestock industry are presented and the validity of the applied labor standards is assessed. In the studied organizations, the methodological materials used in the work are analyzed in order to determine labor norms and standards for labor rating and their compliance with the existing reference and normative documentation for the rating of labor processes by the type of work in agriculture. To study the process of rating, the analytical and research method is used, which implies time-based observations of the implementation of technological processes divided into labor operations, techniques and actions. The necessity to take into account the norm-forming factors during the observation of the implementation of the technological process to substantiate the determination of norms and standards of labor is shown. In addition, the necessity to take into account the full set of factors in the organization of labor rating is substantiated. In this regard, the results of the observations are presented, which allow identifying the shortcomings in the planning and organization of work processes, the establishment of norms and standards, the consequences of which are as follows: the increase in unproductive losses of working time, the increase in costs, the distortion of labor productivity, which ultimately negatively affects the results activities of an enterprise as a whole. Possible solutions to these problems are presented. The recommendations on the organization of labor rating processes at enterprises of the agricultural sector are given.
Keywords: Business processes, enterprise management, labor rating, labor productivity, labor standards
Introduction
During the transition from a state direct planned economy to a market economy in the 1990s there was a spontaneous curtailment of the state system of management of organizations and labor rating, which was limited to the development of methodological and regulatory information for state servants. A significant part of the sectoral management and coordination bodies was closed. Practically all the organizations did not carry out work on labor rating. Therefore, today the regulatory and methodological framework is very outdated. Today there is a shortage of qualified specialists in labor rating and there is practically no automated rating.
During the achievement of national goals and strategic objectives for the development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2024, such measures as a faster growth rate of labor productivity, the formation of competitive industries, including agriculture, the increase in non-primary exports, including the increase of operational efficiency (improvement of business processes and product quality, reduction of production time, etc.) are set.
In this regard, business entities need to focus on the enhancement of the role of labor rating as one of the main elements of the economic mechanism that determines the efficiency of enterprises. Agricultural producers and workers are interested in the increase of the amount of production, improvement of their quality and attractiveness for consumers, since this directly determines their income and the wages of workers directly depend on the price, volume and cost of produced and sold goods.
It is possible to achieve it with the help of labor rating mechanism, which is aimed at the increase of its efficiency: increase in labor results in relation to the costs spent to achieve them. Thus, the initial function of labor rating is realized as a process of the establishment of normatively justified time expenditures to perform a unit of specific work.
Problem Statement
The main problems of management in agricultural organizations include a tendency towards a decrease in production efficiency. In this regard, the most important goals of the management mechanism are the reduction of production costs and increase in profitability, increase in production flexibility, establishment of optimal norms and standards and growth of labor productivity by stimulating staff motivation.
The solution to the problem of the reduction of labor productivity is possible with the help of labor rating, which helps to reduce production costs through more rational use of working time. As a rule, the assessment of labor productivity is carried out by the evaluation of the intensity of labor, that is, determination of the direct costs of labor for production (Redikultseva, 2014; Stukach et al., 2017).
The stimulation system in agriculture needs to be improved in accordance with the combination of norms, standards, intersectoral proportions, taking into account the prevailing conditions. The existing regulatory framework of agricultural producers does not fully meet the current level of technology, technique, methods and methodology of labor organization. Legislatively, the work on the organization, regulation and remuneration of labor is referred to the competence of enterprises, which is a positive fact. The protection of the interests of both parties of labor relations, the resolution of contradictions without conflicts is ensured by the regulation of labor rating issues in sectoral and collective agreements.
Along with this aspect, at the state level it is necessary to perform such functions of labor management as the coordination of scientific research on the problems of labor organization, the organization of the development of intersectoral norms and standards of labor, methodological guidance of the design system of labor organization at the stage of the development of projects for new enterprises.
The role of state regulatory research organizations at the federal and regional level has significantly decreased. The network of the state regulatory stations has been practically eliminated. As a result, agricultural producers are not provided with normative materials for labor, including collections of standard norms.
In this regard, the specialists of agricultural enterprises must independently establish, adjust and revise labor standards. Therefore, the important task is to provide agricultural organizations with appropriate methodological recommendations for the regulation and organization of labor, which allow effective activities.
Research Questions
The improvement of agricultural production in such areas as the increase in the level of automation and mechanization of production processes, computerization of technological process control and increase in production flexibility is changing the role of labor rating in agro-industrial enterprises.
Labor rating in this case, must be considered as an element of production management, which, based on the study of the cost of working time, allows establishing reasonable labor standards of rational intensity (Kulkova, 2015; Svechnikova, 2019). Labor rating as a socio-economic category allows using labor standards as a criterion for the assessment of labor discipline, labor productivity, as well as the level of wages of workers (Afanasyev et al., 2018; Bychin & Novikova, 2018; Shumkov, 2016).
In the conditions of market relations, the importance of labor rating system at enterprise increases due to the fact that it ensures that the interests and needs of employees are aligned with the interests and goals of employers (Veselovsky & Abrashkin, 2012).
In recent years, the system of labor rating in our country has undergone major changes. The work on the organization and regulation of labor was legally referred to the competence of enterprises (Sklyarevskaya, 2012). At the same time, it is necessary to note that the introduction of professional standards does not oblige enterprises to obligatory revision of labor standards. At the same time, the regulatory and legal framework formed in the 80s of the XX century has lost its obligatory character and is currently used at the option of the heads of organizations (Blokhin, 2016; Lapteva & Zakharova, 2013).
At present, the standard norms are applied to work carried out according to standard technologies (Wilkinson & Hughes, 2000), used at most enterprises of the industry, which does not reflect the level of technical equipment of production and the individual abilities and capabilities of employees (Marie-Laure Morin, 2005).
During the study of the current state of the system of rating and organization of labor in agricultural organizations, a questionnaire survey of managers and specialists of farms in Omsk region was carried out.
During the survey, it was found that in most of the surveyed organizations (83%), the cost of working time for the implementation of the main production processes is accounted (Figure 1).
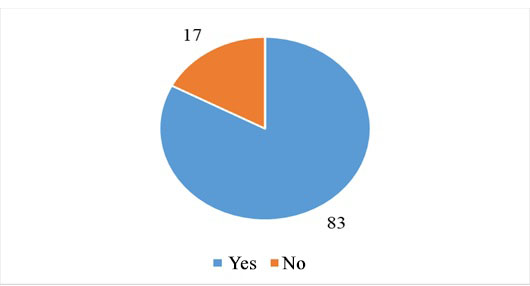
The study showed that not all enterprises in the region develop the processes of rating and organization of labor at the proper level.
In agricultural organizations of Omsk region, the greatest attention is paid to the regulation of labor in the crop growing industry. The largest percentage of all surveyed farms noted that in order to establish production rates, they use a reference book of standards for mechanized field work (2.9%), standard production rates for hand labour in agriculture (2.5%) and uniform time rates for loading and unloading operations (2.5%) (Figure 2).
During the study of the system of labor rating in the livestock industry, it was found that the main method to determine the cost of working time is timing, which was used in most of the studied organizations. 5% of commodity producers noted that a photograph of an employee's working day was used to determine labor costs, while photographic timing of working hours was used in 7% of surveyed households.
Foremen (116 farms) and economists (73 farms) deal with labor rating issues in agricultural organizations. At the same time, the majority of agricultural producers (73%) update production rates only when working conditions change (for example, when purchasing new equipment), focusing on the technical characteristics of the equipment. 27% of respondents indicated that they update the norms annually.
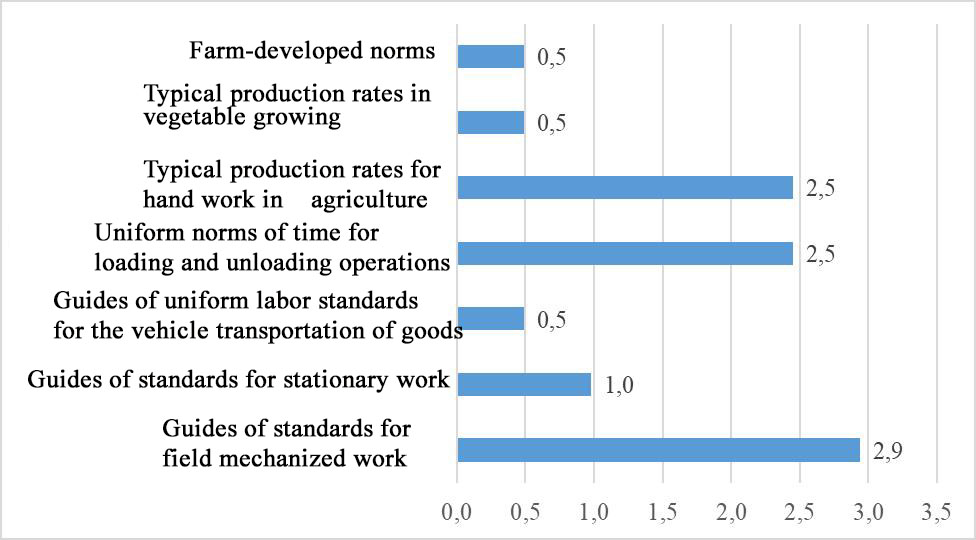
The research showed that many farms were insufficiently involved in labor rating issues. As managers note, with the leave of labor specialists, these processes develop according to the particular situation. From the sources used to determine the standards and labor standards, the methods of 1986-2001 are indicated. There is no doubt that there have been significant changes in the agricultural industry in recent decades. New technologies are being introduced, technology is becoming more productive and the breeds of farm animals differ in productivity. The processes in crop production have changed in the same way. That is why the majority of farms, when setting norms and prices, are guided by their own experience and the experience of other farms.
Thus, the labor standards applied in agricultural organizations should reflect the level of technical equipment of the workplace and the level of qualifications of employees. Labor standards should ensure the e health and maximum performance of employees during the entire shift. At the same time, the activity of employees must ensure the production of quality products with minimal production losses (Swinnerton & Schoepfle, 1994).
Labor rating serves as the basis in the formation of the labor intensity of production, which in turn affects the number of employees and the planned wage fund. In addition, labor rating is a measure of labor productivity, which forms such a level of wages that would ensure the reproduction of the labor force with the optimal intensity of the labor of employees.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to identify the reserves for the increase in production efficiency by the improvement of labor rating and development of recommendations for rating the labor of agricultural organizations in all natural and climatic zones of Omsk region, taking into account the existing experience of labor rating and existing regulatory legal acts in modern economic conditions based on the analysis of the validity of the used standards and standards for the types of technological work in crop production taking photographs of working time and timing.
Research Methods
The standardization of labor in the livestock industry consists in the development of production standards, time standards and standards for animal care. The study of the existing practice of labor rating in the livestock industry of agricultural enterprises in Omsk region was carried out using the main technological processes based on analytical, statistical, expert methods, taking into account the timekeeping data and photographs of working days.
The specificity of labor processes in the livestock industry lies in the fact that the means and objects of labor are living organisms (animals), fodders and products. Therefore, the rating of labor at enterprises is carried out taking into account a number of factors, the main of which are natural, technological, technical, organizational, economic and social ones.
The various combinations of these factors create organizational and technical conditions for the implementation of production processes in animal husbandry. During the standardization of labor in the livestock industry, it is necessary to take into account working conditions, technical equipment of workplaces and qualifications of workers. According to the norm-forming factors, it is necessary to develop and classify the norms of time, norms of service and production norms in animal husbandry.
In all studied enterprises, labor standards in the livestock industry are determined by analytical-calculation or analytical-research method based on the values of the norm-forming factors obtained as a result of certification of dairy farms and complexes. The passport of production conditions contains the following information: the type of premises and their capacity, age and sex groups of animals and their production purpose, methods of keeping animals, animal productivity, types and norms of feeding, mechanization and automation of production processes, work technology and work organization.
In order to study the process of rating, the analytical and research method was used, which involved the conduct of time-based observations of the implementation of technological processes, divided into labor operations, techniques and actions. Being a way to measure the costs of working time for an employee to perform operational work at the workplace, taking into account the requirements of technology, the method of timing allows using the data obtained to monitor the results of employees' activities and identifying unproductive losses of working time at each stage of the production process.
Findings
Together with the Ministry of Agriculture and Food products of Omsk Region, the study of the existing practice of labor rating in the livestock industry by means of questionnaires, surveys and visits to agricultural enterprises of Omsk Region was carried out, which involved 200 farms of the region. According to the survey data, 87% of agricultural producers account the costs of working time for the main types of work. At the same time, they use guides of standards for the types of work published in 1978, 1992 and 2000.
Only seven of the surveyed enterprises have labor standards developed in their livestock. As a rule, in organizations rating is carried out by the economist of an enterprise or the foreman of livestock teams. Service standards are updated when working conditions change in 75% of the surveyed farms, 27% of respondents noted that the update is carried out annually. 20% of enterprises had their service standards revised as a result of the purchase of new equipment. All the enterprises set production rates independently and experimentally, focusing on the factory characteristics of equipment.
The state of labor rating in agricultural organizations of Omsk region is determined by the combination of various conditions and factors: natural, technological, technical, organizational, economic and social. Such factors are considered to be norm-forming. The various combinations of these factors create organizational and technical conditions for the implementation of production processes. The norms of service and the norms of production in animal husbandry are developed and classified taking into account the norm-forming factors and the norms of time.
In general, for the farms of Omsk region, the level of application of scientifically grounded norms developed taking into account certain factors characteristic of a particular organization is rather low. Thus, according to the results of the survey, only 3.4% of producers had the independently developed standards in the field of labor rating, the rest of the enterprises used standard norms. In farms where reasonable time rates and production rates were used, a low level of losses of working time and a high level of labor productivity were noted.
According to the studies, at the moment the main norm-forming factors influencing changes in labor standards are technical and technological. More than 80% of the regional enterprises use outdated equipment and therefore use previously developed standards.
The method of timing allowed identifying unproductive losses of working time due to the choice of irrational methods of the organization of production processes: feeding, animal care. For example, in some agricultural enterprises in the region, the existing service standards for dairy cattle breeders are significantly lower than those determined in the course of the study. The reason for non-compliance with the norms is the irrational use of working time during the day, which is associated with long breaks. The obvious losses of working time for organizational, technical and other reasons range from 10 to 50%, including hidden losses, sometimes exceeding the obvious ones by several times, due to the inability of employees to work in a regulatory and technological mode. This circumstance significantly affects the number of employees of an enterprise, entails a decrease in labor productivity and increase in labor costs, which in turn has a negative impact on the efficiency of production and economic activities.
The results of the study indicate the possibility to improve the labor rating system, managing this process and increasing production efficiency, but only if the process of rating as a whole is approached systematically and organized on a scientific basis.
The efficiency of labor rating for employees of an agricultural enterprise should be based on the presentation of technological procedures as business processes in terms of the assessment of the effectiveness of the rating process. All business processes are carried out on the basis of the principle of saving mode, which can be implemented on the basis of the rating of human, financial, material and other resources.
The study of the content of work on the regulation of labor at enterprises and the study of the concept of “business process” allowed describing the work on the regulation of labor as a business process. The input to the process is human resources. The mechanisms of influence on the regulation of labor as a business process are the labor code, guidelines, methods and ways of the establishment of labor standards, methods for studying the cost of working time and scientific organization of labor (Labor Code, 2001). The direct executors of the process are employees of the department of organization and labor rating. The line managers are responsible for the provision of the necessary information.
The heads of departments are in charge of the coordination and approval of all the developed programs for labor rating.
In general labor rating as a business process is presented in Figure 3.

At the same time, the analysis of the current situation indicates the presence of a number of serious problems that require solution:
First, the arrival of new technical means, the improvement of technology and labor organization dictate a corresponding expansion of normative work and the positions of labor specialists are excluded from the staffing structure of most enterprises in Omsk region.
Secondly, there is no necessary relationship between the technical characteristics of new equipment and regulatory factors, which leads to significant differences in the value of the established standards.
Thirdly, there is still a high differentiation both in the natural and climatic zones of the region and at the level of farms in terms of the level of application of scientifically grounded norms.
Finally, the primary documents of many agricultural producers do not reflect all the norm-forming factors that directly affect the application of labor standards at each workplace during the performance of a specific job.
The introduction of scientifically grounded standards for direct labor costs in planning will reveal unused reserves for the reduction of the labor intensity of production and more efficient use of labor resources. Agricultural producers independently develop their concept of the implementation of reasonable labor standards in order to find reserves for the reduction of production costs, fuller utilization of labor and production potential and increase in production efficiency in general.
Conclusion
According to the results of the study it was found that today effective resource saving can be achieved with the help of information technologies, which allow the most accurate tracking and regulation of the use of all resources in enterprises. The use of information systems in animal husbandry allows increasing the efficiency of the organization of technological processes, optimizing the use of agricultural machinery and working time of performers. The heads of agricultural enterprises independently determine the priority areas of technical and technological development.
The elimination of losses of working time is based on a number of criteria: organizational, technical, sanitary and hygienic, psycho-physiological, social and legal. The implementation of the process approach in the management of labor rating implies the need to separate it as a unique supporting business process, inscribed in the general system of enterprise functioning. This will allow the development of norms and standards, taking into account modern features, the influence of external and internal factors of production and will contribute to the development and improvement of the system of labor rating, both within an individual enterprise and at the industry level.
In accordance with the survey the recommendations were developed and proposed that will allow agricultural producers to optimize and systematize the work on labor rating at enterprises, as well as to increase the interest of workers in the final results of labor, which will contribute to the growth of labor productivity. This, in turn, will ensure a positive dynamics of the financial results of enterprises as a whole and, as a consequence, the consolidation of labor resources.
As a rule, the assessment of labor productivity at enterprises is carried out by determining the direct costs of labor for production, that is, the intensity of labor is assessed. The economic effect of labor rating consists in the reduction of labor costs by the improvement of the organization of labor processes, as well as the improvement of product quality, better use of equipment, saving fodder, materials, energy, and ultimately reduction of production costs and increasing profits. In addition to the economic effect, labor rating also has a social effect, which is expressed in the improvement of the working capacity, maintenance of the health of workers, increase of job satisfaction due to improved working conditions, higher wages and advanced training. Each commodity producer aims for the most efficient use of his available resources and the elimination of losses of working time is an effective and justified method of costs reduction and increase in the productivity of workers.
Thus, labor rating is currently an integral part of the successful functioning of enterprises. Labor rating is an effective way to make optimal use of the material and labor resources, the basis of planning, the regulator of wages and a important factor in the motivation of employees to increase labor productivity.
Acknowledgments
The research was carried out as part of the task of the Ministry of Agriculture and Food of Omsk Region (state contract No. F.2019.268388)
References
Afanasyev, V. S., Abdulov, R. E., & Medvedeva, Y. M. (2018). Forgotten category of economics (to the problem of labor productivity). Political Economy Issues, 3, 29-41.
Blokhin, K. V. (2016). Improving labor standards as the basis for increasing labor efficiency. International scientific journal "Innovative Science", 9.
Bychin, V. B., & Novikova, E. V. (2018). Labor rationing as an element of effective intrafirm management in modern conditions. Labor Economics, 1, 78-85.
Kulkova, I. A. (2015). Methodological approaches to the analysis of the labor rationing system in organizations in market conditions. Human Progress, 1(2), 24-36. https://www.elibrary.ru/download/elibrary_24983199_65163400.pdf
Labor Code. (2001). Labor Code of the Russian Federation (as amended on July 31, 2020). No 197-FZ. December 30, 2001. Retrieved on 30 August, 2020, from http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_34683/
Lapteva, A. M., & Zakharova, M. A. (2013). The role of rationing in the effective organization of labor. Bulletin of the Kostroma State University. ON. Nekrasov, 3, p. 57-60.
Marie-Laure Morin (2005). Labor law and new forms of corporate organization. International Labor Review, 1, 6-27.
Redikultseva, E. N. (2014). Current trends in the legal regulation of labor rationing. Bulletin of VyatSU, 9. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennye-tendentsii-v-pravovom-regulirovanii-normirovaniya-truda
Shumkov, N. Yu. (2016). Labor rationing as an element of effective strategic intrafirm planning. Economy. Control. Right, 2, 23-26.
Sklyarevskaya, V. A. (2012). The current state of the theory and practice of the organization and regulation of labor in Russia and in countries with developed market economies: problems and solutions. Actual problems of social and economic development of Russia, 4, 121-123.
Stukach, V. F., Astashova, E. A., Zinich, L. V., Zinich, A.V., Kuznetsova, N. A., Tetereva, A. M., Nardina, S. A., & Volkova, I. A. (2017). Balance of labor resources in rural areas of the region: monitoring, forecasting, development of human capital. Omsk, Omsk State Agrarian University named after P. A. Stolypin.
Svechnikova, T. M. (2019). Improving the validity of labor standards in agriculture. Moscow Economic Journal, 8, 263-270.
Swinnerton, K. A, & Schoepfle, G. K. (1994). Labor standards in the context of a global economy. Monthly labor review, 9, 52-58.
Veselovsky, M. Ya., & Abrashkin, M. S. (2012). Conceptual aspects of the management of the labor rationing system at the enterprise. Bulletin of the Moscow University named after S. Yu. Witte. Series 1. Economics and Management, 1, 96-103.
Wilkinson, R., & Hughes, S. (2000). Labor standards and global governance: examining the dimensions of institutional engagement. Global governance, 2, 259-277.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 July 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-112-6
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
113
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-944
Subjects
Land economy, land planning, rural development, resource management, real estates, agricultural policies
Cite this article as:
Astashova, E. A., Kondrateva, O. V., & Kuznetsova, N. A. (2021). Labor Rationing As An Element Of Effective Enterprise Management In Modern Conditions. In D. S. Nardin, O. V. Stepanova, & V. V. Kuznetsova (Eds.), Land Economy and Rural Studies Essentials, vol 113. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 394-403). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.07.47

