Abstract
Food processing industry has always been taking an extremely important place in the economy of the Trans-Baikal Territory. However, the economic recession affected this field dramatically. Covering the primary needs of the population this field is supposed to have a sustainable future. Stability, dynamic balance and possibility of self-developing are the main factors of its further development. The climate and the remote location of the Trans-Baikal Territory from the central part of Russia determine the stable development of the processing field. The raw materials are grown locally: meat and milk processing, baking and confectionary industries. Dynamic stability involves interconnected development of the food and agricultural industries. As a result, an increase in agriculture may cause an increase in the food processing industry. Stability of the food processing industry is determined by a permanent outlet. The local companies are to take into account not only the local demand but the markets in the nearest regions. The prospective outlets are the nearest constituent entities of the Russian Federation: the Republic of Buryatia and the Irkutsk Region, as well as China. Moreover, the supplied products are to meet all the requirements, transportation and sale features on the external markets. The possibility of self-development involves a reserve of production capacity and investments to equip companies with machines. According to the research, the companies have excess capacity but they need upgrading and extra funding.
Keywords: Agricultural holding, food industry, regional economy, sustainable development, Trans-Baikal Territory
Introduction
Sustainable development of industries that meet all the needs of population is an important condition of a stable economy of any region. In this sense, the food processing industry is the most important one and directly affects the stable supply of a consumer market with food, the structure of consumption, the structure of expenditures of the population and, in general, the standard of living. The food processing industry experiences difficulties later than other ones, but they are much harder and affect final consumption directly. Therefore, the sustainable development of the food processing industry is a prerequisite for the recovery of the economy.
Problem Statement
Due to a number of factors, the food processing industry in the Trans-Baikal Territory is going through hard times. The industry is affected by a decrease in real income of the population, the population outflow and poor development of the agriculture. Moreover there is a great competition with imported products. In this regard, it is necessary to find out the factors that could ensure a sustainable development of the food processing industry in the future. The article is aimed to identify these factors.
Research Questions
The subject of this article is as follows:
- internal reserves and external conditions for the development of the food processing industry in the Trans-Baikal Territory, expressed in a number of factors of its sustainable development;
- long term problems and growth potential of the food processing industry of the region.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the article is to identify factors of sustainable development of the food processing industry in the Trans-Baikal Territory in the current economic conditions.
Research Methods
To make a research, the authors used a method of sequence analysis, a method of graphical data presentation, a method of regression analysis and methods of system analysis of data.
Findings
Negative trends in the national economy have a particularly strong impact on the depressed territories, which the Trans-Baikal Territory has been for a long time. It became evident in comparison with other regions when the Trans-Baikal Territory joined the Far Eastern Federal District (Kichigina, 2019); (Kovalchuk & Kravtsova, 2019). The Trans-Baikal Territory takes the 6th place among all the constituent entities of the district according to the square kilometers, and the 3rd place – according to the number of the population. However, in terms of economic indicators, the region lags far behind other territories: it occupies the 11th last place according to an average income per capita. In terms of an average monthly gross payroll, the territory occupies the 9th place, and in terms of gross regional product per capita - the 10th place. In terms of the agricultural products the region takes the 4th place. This indicates a potential for agricultural development, and as a consequence – for the development of the food processing in the region. However, the possibility and prospects of such growth depend on a number of factors.
The long-term, sustainable development of the food processing has not been observed yet. The very concept of sustainable development implies the presence of stability, immutability, dynamic balance and the possibility of self-development (Tamaev & Shulgina, 2012).
In general, meaning immutability assumes relative stability of the used factors of production and external factors in the long run.
Dynamic balance refers to the balance of factors of production within the system.
Self-development implies the presence of internal reserves of the economic system to increase production volumes and improve economic indicators.
The stability of the system refers to the invariability of the operating conditions of the production system in their interconnection with consumption.
The national standard of the Russian Federation GOST R 54598.1-2015 refers to a sustainable development that meets the current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. A lot of publications are devoted to these issues (Chuprov, 2018; Samarukha & Makarova, 2019). In its most general form, the sustainable development of the food processing industry in the region implies the ability of the system to maintain the existing functioning level and to develop it in the long term period in the context of the limited resources and instability of the environment. In this sense, the industry has all the necessary resources, internal reserves and external capabilities. Let us consider the main factors that determine the opportunities for the sustainable development of the food processing industry in the Trans-Baikal Territory.
Immutability involves constantly operating characteristics inherent in a particular region and industry. The climate and the remoteness of the Trans-Baikal Territory from the central regions of Russia are the irreplaceable factors. We must remember about the sharp continental climate almost all over the territory, the quality of agricultural land, the location of the region and the insufficient development of the infrastructure of the whole region (Chistyakova, 2018); (Sarris, 2015). Historically, the main sectors of the food processing industry, due to some features of the region, are the processing of meat and milk, the production of bakery and confectionery products of non-durable storage. These fields have developed due to the remoteness of the Trans-Baikal Territory from the central regions where the great number of agricultural raw materials for industrial processing is grown: sunflower, durum wheat, melons and vegetables, sugar beets and others. Transportation of raw materials for processing to the region is not economically feasible due to high transportation costs, high electricity tariffs in the Trans-Baikal Territory and rather high salary. Although some raw materials are still partially imported to the region, a significant number of agricultural raw materials are grown in the Trans-Baikal Territory. For example, in 2018, they received 177.1 thousand tons of grain, potatoes - 161.1 thousand tons, melons and vegetables - 22.2 thousand tons, cattle and poultry for slaughter - 49.4 thousand tons, milk - 330.9 thousand tons, eggs - 64.7 million pcs. Thus, the perspective directions of sustainable development of the industry are limited by the sectors mentioned above (Shishkina et al., 2020).
Dynamic balance implies the integration and interdependence of the development of the food processing industry and agriculture. It is worth mentioning that the number of enterprises in agriculture, hunting, fishing and fish farming is declining annually. In 2017 there were 855 enterprises, and in 2018 - only 841 (Trans-Baikal Territory – 2018, 2019). A number of enterprises processing food, on the contrary, increased slightly during this period from 156 to 160 companies. In comparison with 2006 the decline is dramatic. In 2006 there were 2058 agricultural enterprises and 294 food processing enterprises. The general economic downturn also affected the sectors producing essential goods for the population.
For many years the local producers supplied the Trans-Baikal Territory with basic food products, such as meat, milk, bakery products, sweets, and drinks. Raw materials for the production were grown locally; then they were processed and consumed. Agriculture and food industry developed in close interconnection. Since 2013, there has been a steady decline in the both fields, agricultural cultivation and processing (Figure 01).
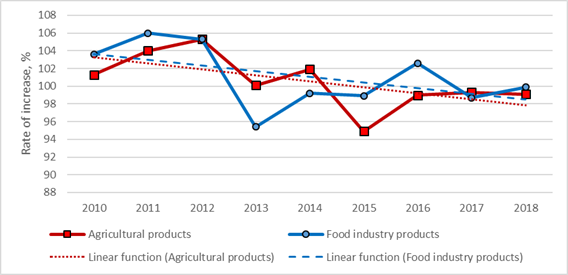
During the period of 2013 - 2018, the average annual growth rate of the physical production volume of both types is almost the same and amounts to 99%. Despite the fact that there is a direct correlation between the production volumes of the food industry and agriculture (pair correlation coefficient was 0.7), the dynamics of actual production volumes in current prices of the corresponding period shows different orientation (Figure 2).
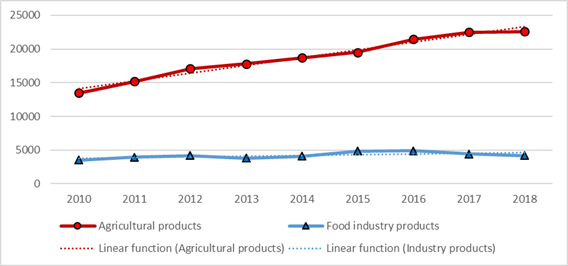
This indicates an imbalance in the prices for products: during the period, a price increase of agricultural products was higher than a price increase of food products. In 2018, the price index of the agricultural producers was 111.9%, and the price index of the food producers was only 101.3%. The reason of this imbalance is the structure of agricultural production. In recent years, the volume of cultivation of industrial crops, rapeseed in particular, has increased greatly. Its main outlet is China. The area occupied by industrial crops increased from 7.2 thousand hectares in 2012 to 18.4 thousand hectares in 2018 (Trans-Baikal Territory – 2018, 2019). A sale price of rapeseed imported to China is much higher than that on the domestic market.
Currently, rapeseed cultivation in the Trans-Baikal Territory is carried out by the Breeding Plant “Komsomolets” with the cultivation volume of about 15 thousand tons in the Chernyshevsky, Krasnokamensky and Sretensky districts, and by the Trans-Baikal Agricultural Holding LLC, which has its sown areas in the Krasnokamensky district (Taskaeva & Shishkina, 2019). The Far East Development Fund planned to invest 600 million rubles in a project for the cultivation of rapeseed on the farm. As a result, the volume of rapeseed cultivation is planned to be increased up to 50 thousand tons per year, and the cultivated area – up to 100 thousand hectares. It will give not only the possibility to get extra income by the Komsomolets Breeding Plant but it will increase the number of the rapeseed processing enterprises in the Trans-Baikal Territory.
In general, the development of the processing sectors depends on the state of agriculture which is a source of raw materials in the remote regions of the country. Thus, a development of the food processing industry in the Trans-Baikal Territory may be caused by a rise in such sectors as growing grain, legumes, melons, berries, vegetables, cattle, sheep, poultry, and bee breeding.
The stability of the food processing industry in the region is determined by its geographical location and by a constant sales market. Food processing enterprises are closely related to the final consumption market. This is especially true for industries that are most developed in the Trans-Baikal Territory, such as meat, milk, and bakery products. The food products of the Trans-Baikal Territory are of high quality and are in demand on the local market. They could successfully replace imported products, but they are not convenient for sale in large retail chains (Gladkikh, 2017). The food products lag behind its competitors in terms of packaging and transport characteristics. All this, as well as small volumes of production and a high level of competition on the food markets, determine the outlet, mainly in the territory of the Trans-Baikal Territory. It should be noted that the population of the Trans-Baikal Territory has been gradually decreasing for more than 30 years mainly due to the migration outflow of the population. Thus, on January 1, 2012 the population of the region was 1099.4 thousand people, then on January 1, 2019 - only 1065.8 thousand people. It also limits the market for products, although there is growth potential. Imported products from other regions are widely represented on the local market. They often have a wider range and different quality characteristics. In the future, the local producers may occupy this niche with a competent range policy and an increase of production volumes.
On the contrary, a part of confectionery, drinks and sausages is sold in small volumes in the markets of the Republic of Buryatia and the Irkutsk Region, as well as in China. For a deeper penetration into the markets of the nearest regions, local producers need to improve product characteristics, to develop cooperation with the owners of large regional retail chains and increase their production volumes.
It’s worth mentioning that the most important development factor is a neighborhood with China. The negative trends of recent years testify an increasing dependence of the Trans-Baikal Territory on external supplies, including the most necessary food products. At the same time, the changes taking place in the Chinese consumer market make it possible for the Russian producers to expand the supply of food products to this country (Kravtsova, 2017); (Popova, 2018). In recent years, the standard of living and incomes of the Chinese population have grown significantly. The average monthly salary in 2018 in Hong Kong was US $ 2592, in Beijing US $ 1336, in Shanghai US $ 1374, in Guangzhou US $ 1023. Compared with an average level of wages in the Trans-Baikal Territory, in 2018 it amounted to $ 647 in terms of US dollars, and $ 695 in Russia as a whole. Of course, the income level in China varies greatly in different provinces; however, the overall increase in wealth is noticeable. It contributes to a greater mobility of the population of China, the emergence of the opportunity to travel and changes their consumer preferences. The Chinese are increasingly interested in buying food products from Russia and, in particular, the Trans-Baikal Territory. They associate them with high quality, natural ingredients and absence of harmful additives. As it was noted earlier, confectionery, meat processing products, and soft drinks are currently exported to China in small quantities. This direction is promising in every sense; it must be developed and maintained on the national level.
Opportunities for self-development. The next factor of a sustainable development of the industry can be considered an availability of reserves of production capacities, their development and investment in the technical equipment of enterprises (Shupletsov & Nechaeva, 2015); (Tertyshnik, 2017). National statistics shows that there are free capacities in almost all areas of food processing. In particular, in 2018, the level of production facilities in the production of sausages amounted to 48.6% flour production - 21.3%, bakery products - 61.9%, pasta - 47.6%, confectionery - 59.9%. A significant increase in the output can be obtained if they are involved in production. An obstacle to this is a lack of raw materials. As it was said above, the processing enterprises in the Trans-Baikal Territory use mainly local raw materials. The deterioration in agriculture is directly reflected in the performance of the food processing industry. Currently, 80-95% of all agricultural products are grown in households. Under these conditions, the purchase of raw materials from the population, especially from the distant settlements, creating a network of procuring organizations, will allow the population to sell their products, and increase production of the processing plants. These measures will provide food enterprises with raw materials.
On the other hand, the volume of investments in the economy of the region and in the food industry has been extremely insufficient and has been declining annually for many years (Sukhodolov & Geniatulina, 2019) (Figure 3).
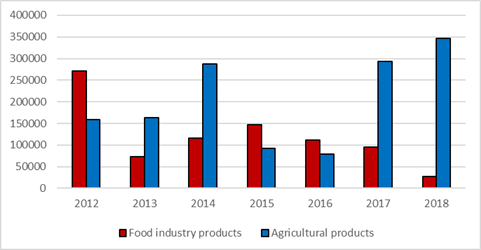
In 2012 the volume of investment in fixed assets amounted to 271.382 thousand rubles, then in 2018 - only 26.718 thousand rubles. The volume of investments in agriculture, on the contrary, increased from 159.199 thousand rubles in 2012 to 286.386 thousand rubles in 2018. Thus, the technical equipment of the food processing industry is aging faster than that in agriculture. If the current trend continues in the future, the processing of raw materials will be economically useless or even impossible. It is necessary to provide support at the state level for agricultural enterprises and processing companies. There are projects and some agro-industrial holdings in the Trans-Baikal Territory, including agricultural and processing enterprises. In particular, they include the Makkaveevsky Food Processing Plant OJSC, the Daursky Meat Processing Plant LLC, Chita Dairy Plant LLC. This is especially promising, since related industries will support each other's development and contribute to the strengthening of the agro-industrial holding on the market.
Conclusion
The conducted research shows that the development of the food processing industry in the Trans-Baikal Territory can become a flagship for the development of the consumer market and provide a solid basis for the recovery of the economy. The development of agriculture and infrastructure, the creation of agro-industrial holdings, the development of the procurement sector, and the increase in investment in fixed assets of the industry are necessary conditions. Food processing enterprises still have a certain amount of production capacity and human resources. However, the lack of proper attention to these industries and the lack of funding may lead to their complete elimination in the future.
References
Chistyakova, O. V. (2018). Production and technological infrastructure of innovative business in resource regions. Baikal Research Journal, 28(4), 682-693.
Chuprov, S. V. (2018). Adaptability of the sustainability and innovative development management system of an industrial enterprise. Production operator, 26(1), 23-33.
Gladkikh, O. V. (2017). Import substitution mechanisms in the implementation of the national procurement regime. Scientific Bulletin of Baikal State University, 27, 67-76.
Kichigina, I. M. (2019). The Trans-Baikal Territory joining the Far Eastern Federal District: an assessment of the cross-border development. Russian and Chinese studies, 3(1), 23-33.
Kovalchuk, L. B., & Kravtsova, S. A. (2019). The entry of the Trans-Baikal Territory into the Far Eastern Federal District: territories of priority development and the “Chinese factor” as tools to smooth out inter-regional differences. Russian and Chinese studies, 3(2), 64-73.
Kravtsova, S. A. (2017). Prospects for the export of Russian grain to China. Border region in historical development: partnership and cooperation: materials of the international scientific conference. (pp. 65-75) Chita: Trans-Baikal State University.
Popova, E. M. (2018). Investment cooperation between Russia and China as an integral component of a strategic partnership. Russian and Chinese studies, 2(1-2), 16-25.
Samarukha, A. V., & Makarova, G. N. (2019). Designing the industrial technological revolution on the principles of sustainable development, taking into account counteraction to unfair competition. Baikal Research Journal, 10(2), 9-9.
Sarris (2015). Food security stocks and emergency reserves from a European Union cap perspective. St Petersburg University Journal of Economic Studies (SUJES), 1, 37-68.
Shishkina, N. P., Klinnikova, N. V., & Rodionova, S. N. (2020). Role of agricultural processing for food security of the Trans-Baikal Territory. BIO Web Conf. 17. https://www.bio-conferences.org/articles/bioconf/pdf/2020/01/bioconf_fies2020_00211.pdf
Shupletsov, A. F., & Nechaeva, E. S. (2015). Role of the resource potential and business structures of municipal entities of Irkutsk Oblast in effective development of regional economy. Baikal Research Journal, 6(4), 9-9.
Sukhodolov, YA. A., & Geniatulina, I. R. (2019). The importance of Chinese investment for the socio-economic development of the Trans-Baikal Territory. Russian and Chinese studies, 3(2), 74-84.
Tamaev, R. F., & Shulgina, L. V. (2012). Adaptive Strategies for Sustainable Industry. Journal "Proceedings of VSUET», 1, 174-176.
Taskaeva, M. P., & Shishkina, N. P. (2019). Agricultural development as the basis of food security. Journal of Economy and entrepreneurship, 9(110), 100-104.
Tertyshnik, M. I. (2017). Assessment of reserves and imbalances in production capacity of enterprises. Innovative Clusters in the Digital Economy: the VIII scientific conference. St Petersburg University, 410-415.
Trans-Baikal Territory – 2018 (2019). Chita. Stat. Sat Transbaikalkraistat
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 July 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-112-6
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
113
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-944
Subjects
Land economy, land planning, rural development, resource management, real estates, agricultural policies
Cite this article as:
Shishkina, N. P., Ermakova, T. F., & Rodionova, S. N. (2021). Factors Of Sustainable Development Of Food Processing Industry In The Trans-Baikal Territory. In D. S. Nardin, O. V. Stepanova, & V. V. Kuznetsova (Eds.), Land Economy and Rural Studies Essentials, vol 113. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 907-914). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.07.108

