Abstract
Ecopsychological approaches to the psychological aspects of the interaction between the individual and the environment have been developing in modern science for more than 25 years. The social situation of development is considered an integral characteristic of the environment in which the modern adolescent grows up. The study of changes in the personality traits of adolescents in the conditions of postindustrial society appears to be an important tool for solving relevant problems of sustainable human development. Even though the phenomenon of attitude towards health and ways of its development has been actively researched in recent years, the study of socio-cultural factors and factors of self-preservation behavior of modern adolescents is relevant and understudied. The article presents the results of the study of the variable of locus of control on the scale of internal attitude towards health and motivational preferences on a sample of school and university students from Moscow, Moscow Region, Orsk, Chelyabinsk, and Voronezh. The results of the study revealed that adolescents who live in poorer socio-environmental regions have a more responsible attitude towards health issues. Comparison of 2019-2020 studies of adolescents demonstrated the impact of the external information environment related to the pandemic on the growth of the index of internal locus of control. We also obtained differences between genders showing that exposure to the information environment has a stronger effect on changes in the type of locus of control of young men than of young women.
Keywords: Ecopsychology, health, locus control, social development
Introduction
The research focus on sustainable development includes the issues of preserving the physical (somatic) and psychological health of children from the impact of negative environmental factors ("Ecology of Childhood"). However, at the current stage of psychological science, attention is given to psychological problems of studying human consciousness and individuality, mental development and learning, perception, emotional experiences, and behavior, as well as psychological, mental, and physical health in the context of systemic relations "human – environment (natural, social)" and "individual – life environment" (Panov, 2020). The phenomenon of attitude towards health and the ways of its development has been studied extensively in recent years (Gazizullina, 2018; Semenova, 2018; Yermolayeva, 2018; Solodova, 2018). Many different aspects of educational conditions for the development of attitude towards health in pre-school, school, and higher education institutions have been researched. As of today, despite the great attention from the Government of the Russian Federation and the development of a whole range of strategic and policy documents, the health of the population and the current demographic situation in the regions are characterized by the presence of unfavorable trends. According to official statistical data and the results of numerous targeted physical examinations over the past decade in Russia, there has been a 66% increase in the overall incidence rate among adolescents aged 15-17 (Kuchma et al., 2016, Pogontseva, 2019). The influence of socio-economic factors on the health of the population of different countries is undeniable. Researchers say that health attitudes are an important component of remedial activities aimed at improving children's health (Ermolaeva, 2018; Gazizullina, 2018). Despite a large number of works on the problems of health of school students, there are only a few studies on the influence of environmental and school environment factors, as well as on the lifestyle of adolescents living in different environmental and social conditions (Melnikova, 2018; Perekusin, 2019; Semenova, 2018).
Problem Statement
The locus of control that is used to study the psychological attitude of adolescents towards health issues “was chosen as a personality variable that serves as a predictor of a person's responsible attitude towards various life circumstances, including health, as well as influences a person's understanding of the causes of illness and his or her involvement in recovery” (Pantelev, 1987, p. 279). The locus of control related to health refers to people's perceptions of what regulates their health (Hope et al., 2018; Kassianos et al., 2016). A separate and as of now understudied topic is the development and variability of locus of control. Galvin et al. observe that little is known about how physiological or social factors experienced in adolescence affect the internal/external locus that one perceives with age. It has been suggested that the precursors of locus of control begin to influence a child's life at an early age. Precursors of locus of control type are linked to parenting style, socio-economic background, and childhood experiences (Galvin et al., 2018). The generalized view of the correlation between an action and the environment is pivotal to the locus of control and is consistent with the notion that through the locus of control an individual assesses the environment rather than oneself (Johnson et al., 2015).
In the framework of Vygotsky's cultural-historical theory, “the internal transfer of external social relations between people is the fundamental basis for the development of personality” (Vygotsky, 1984, p. 223). If we consider the personal characteristic of "locus of control" as a form of higher mental functions, then the transition from external to an internal locus of control appears to be natural in the process of personality development. Depending on external circumstances, a person's experience, the maturity of personal standpoint, and cognitive functions, it is possible to alter a person's attitude from the position of internal or external locus of control. Perhaps the manifestation of a person's external attitudes towards certain life circumstances signify not a personality regression, but rather could indicate a stage of mastering more complex forms of behavior, an opportunity to use personal resources to solve difficult problems and to relieve emotional tension in any situations that are not crucial to the person. For example, in the literature on the role of locus of control in human behavior, one may find the term "situational strength" (strong situation), which may weaken or strengthen the effects of locus of control (Galvin et al., 2018). Contemporary research is also focused on exploring the correlation between the group and individual locus of control. For example, a collective or shared sense of control may emerge at the group level, which consequently influences both team processes and outcomes. Moreover, this collective (e.g., more internal) locus of control may be very different from the participants' personal loci (e.g., more external), and differences between team and individual loci may affect performance (Galvin et al., 2018). From our perspective, this factor should be taken into account in large-scale research of people, when their answers may reflect not individual characteristics, but rather a group perception of responsibility, the ability to independently make decisions in a particular sphere of human life activity. More particularly, the information field on the spread of infectious diseases appears to be a component of the external environment, which arranges the social interaction, thus improving the responsible attitude towards the health of people around them. The social situation of development is considered an integral characteristic of the environment in which modern adolescents grow up. The social situation of growing up of children and adolescents in the conditions of post-industrial society, which has distinct signs of transitivity, is characterized by multidirectional influence on their personal and psychological development. The study of changes in personality traits of adolescents in the conditions of postindustrial society appears to be an important tool for solving relevant problems of sustainable human development.
Research Questions
- What are the differences in attitudes towards health among adolescents living in regions with different environmental and socio-economic conditions?
- Has the information environment related to the pandemic influenced adolescents' attitudes towards health?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to examine the factors that influence the responsible attitude towards the health of today's adolescents.
Research Methods
A total of 934 adolescents (394 boys and 540 girls) between the ages of 14 and 20, with an average age of 16, took part in the study of the personality variable of locus of control. The tests were conducted in 2019 and 2020. A total of 385 (192 boys and 193 girls) 9th-grade students from 6 schools from different districts of Moscow and the neighboring Moscow Region (Khimki and Dolgoprudny) participated in the study in the spring of 2019. A total of 549 (202 boys and 347 girls) school students (10th and 11th grades) and 255 college students (1-2 year students) from Moscow, Moscow Region, Orsk, and Chelyabinsk took part in the study which was conducted in February-March of 2020.
The distribution into the relatively favorable sample in terms of environmental conditions and level of socio-economic development (Moscow and Moscow suburbs) and sample with unfavorable environmental conditions and low level of socio-economic development (Orsk and Chelyabinsk) was made on the basis of subjective assessment by the local residents in 2019. In this research, we were interested to learn the opinion of residents on how they assess the environmental condition of the cities in which they live, rather than the actual environmental situation of the regions. According to the website domofond.ru, Moscow occupies the 51st place in the rating of millionaire cities as assessed by local residents, while Orsk and Chelyabinsk occupy the 185th and 186th places respectively (On the state of sanitary epidemiological well-being of the population in the Russian Federation in 2019).
The study of motivational preferences involved 285 respondents of 10-11 grades, studying in schools of Orsk and Chelyabinsk, as well as 1st-year students of Voronezh State Medical University. The study was conducted in 2019-2020 and involved 16-17 year old boys and girls.
Measures and tools
The questionnaire "Level of subjective control" modified by Gretzov was used as the research tool. The results were distributed into 3 groups: "internals" (high scores on the scales – "I"), "undetermined" (average scores – "U"), and "externals" (low scores – "E").
In order to study the motivational preferences of boys and girls we used the questionnaire for high school students "What's the most important thing in life". The purpose of this questionnaire is to encourage adolescents to express their meaningful needs and desires, as well as their life plans. In the idea of one's social and individual future, a person's life plans overlap with such concepts as a life path, life strategy, purpose and meaning of life, etc. These are the concepts that cover the main spheres of a person's life. From this perspective, students were asked what they consider the most important things in life.
Following the goals of our study, the answers were distributed by their content according to qualitative categories, which characterize a certain sphere of preferences (desire to acquire new qualities or abilities, to become a good student, etc.) and desires, which represent the attitude towards one's health and the health of loved ones.
The obtained data were processed with the use of methods of descriptive and mathematical statistics (Student's t-test).
Findings
For the purposes of this study, we present the results of the "Level of subjective control" questionnaire on the scale of internal attitudes towards health and illness. We shall briefly note that the entire sample of adolescents surveyed in 2019 and 2020 is characterized by an "undetermined" locus of control (ranging from 53.4% to 92.9%). We did not find any significant differences in the samples of adolescents with a strong external locus of control on any of the seven scales of the "Level of subjective control" questionnaire. The percentage of adolescents with a strong external locus of control ranged from 0.9% to 6.2%.
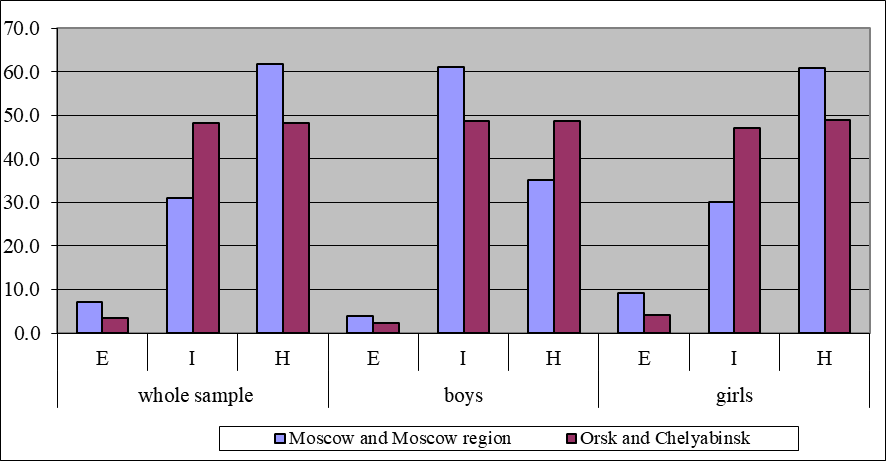
In the group of adolescents with an internal locus of control, the highest percentage was obtained on the scale of internality in relation to health and illness. Comparison of the results between adolescents living in different regions showed that there are almost 20% (17.35%) more adolescents in the South Ural region with a developed internal locus of control in relation to health and illness. Almost half of the adolescents in Orsk and Chelyabinsk have control over their actions with regard to health issues, and they are ready to take responsibility for their health and the health of their loved ones. In the groups of internal and undetermined locus of control, we obtained significant differences between adolescents living in Moscow and the region with respect to Student's test: t=4.125, p<0.01, group "I" and t=3.127, p<0.01, group "U" (see Table 1 and Figure 1).
We did not find any significant differences between young men living in the Moscow region and the South Ural region; however, there is an inverse trend in the total sample: there are 12.2% more young men from the Moscow region with an internal locus than those from Orsk and Chelyabinsk. A comparison of girls from Moscow and South Ural regions revealed an advantage in the frequency of internal locus of control for girls living in Orsk and Chelyabinsk (17% more, t = 3.224, p < 0.01). The percentage of young men and girls in the South Ural region with an internal attitude towards health and illness is almost the same – 48.25% and 47% of the sample. At the same time, there are almost twice as many young men from the Moscow region with an internal locus of control on the scale of attitudes toward health and illness compared to young women (61% and 30% respectively, t = 4.494, p < 0.01). This finding requires additional research, but a comparison of the study samples collected in 2019 prior to the pandemic and on the eve of quarantine restrictions in the spring of 2020 allows us to hypothesize that young men are more susceptible to external environmental influences in comparison to young women.
There are no significant differences between the study samples of adolescents in 2019 and 2020, but there is a trend toward an increase in internal attitudes towards health and illness; the percentage of adolescents with an internal locus of control increased by 5.6% in the spring of 2020. Comparison of values of locus of control types among young men revealed an increase in the internal locus of control by 16.2%, and considerable differences were found between the groups of young men – t=3.075, p<0.01. There are no significant differences among girls, but there is also a tendency for an increase in the internal locus of control from 34.9% in 2019 to 40.6% in 2020 (see Table 2, Figure 2).
The distribution by the locus of control type between boys and girls in 2019 was nearly identical. The difference between loci of control types was 1.4% in the group with an external locus of control (group "E"), 2.4% in the group with an internal locus of control (group "I"), and 3.5% in the group with an undetermined locus of control ("U").
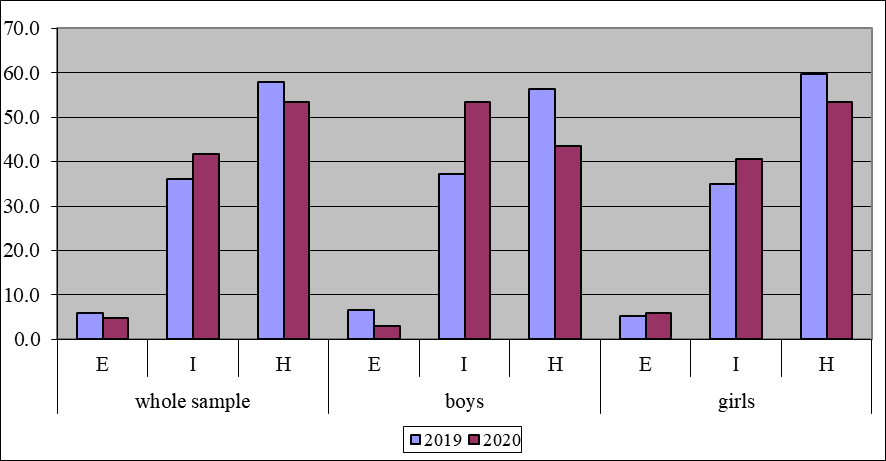
In the study of adolescents in the spring of 2020, we found significant differences between boys and girls – t=2.933, p<0.01. There are 13% more boys with a strong internal locus of control as compared to girls. Therefore, the increase in the percentage of the internal locus of control in 2020 is due to the fact that boys living in Moscow and the Moscow region are more susceptible to the information field associated with the coronavirus pandemic than the girls. In addition, there is a general trend for the entire sample to develop the internal locus of control when there are a deteriorating epidemiological situation and a real hazard to health. Despite the limitations of our study due to the fact that in 2019 the sample was only represented by adolescents living in Moscow and the Moscow region, our data do not contradict the Johnson et al. study, which revealed changes in locus of control indicators depending on the manipulation of people's perceptions about the environment (Johnson et al., 2015). Therefore, the development of psychological and educational measures of influence on the development of responsible attitudes of adolescents towards health issues may be efficient through the influence on the personality variable of locus of control. Information about the epidemiological and environmental conditions of the region where adolescents live may increase internal attitudes towards illness, as well as promote activity for the preservation of health. Bozhovich and Blagonadezyna (1972) point out that leading motivations determine "everything that characterizes the integral appearance of a person with its specific historical features" (p. 3). With this in mind, it is of great interest to study the motivational sphere of modern graduate students under unfavorable epidemiological conditions. During the analysis of the respondents' answers, we found that there were no significant differences in the responses of school students of 10th and 11th grades, so that is why these groups of respondents from each region were grouped into a common group. In total, 1371 responses from boys and girls were collected and then studied. Quantitative data for the surveys conducted in October-November of 2019 for the categories of our interest are shown in Table 3.
Based on the obtained data, irrespective of the region of residence, the most important needs for boys and girls are the development of their own personality, the acquisition of desired qualities and skills. The needs of self-fulfillment and self-improvement of boys and girls aged 16-17 include the acquisition of "New qualities and abilities" (strength, appearance, abilities, skills, personal qualities), "Achievement, success", and the "Learning" category is included as well. Findings show that the least demanded in terms of self-development and self-improvement are the desires associated with the acquisition and improvement of various skills and abilities ("Get a driving license", "Become successful in life", "Get the rank of the Candidate for Master of Sports", "Get an education", "Win a competition"). Along with other skills and abilities the most expressed desire is to know foreign languages, several or one ("To know several languages"), regardless of the place of residence of respondents. In the modern world, adolescents recognize the relevance of mastering foreign languages as a necessary skill.
The analysis of the motivational preferences of graduates of regional schools in Orsk and Chelyabinsk demonstrated that the desire for self-expression and fulfillment (p ≤ 0.001) is prevailing among the answers. Respondents' preferences concerning their own and their relatives' health are of interest to us in this study. The category "Desires that are characterized by attitudes towards health" includes desires addressed to people from their inner circle ("Health of relatives") and attitudes towards their own health ("I would like to be a healthy person). Despite the fact that the desires addressed to people from the inner environment are noticeably inferior in quantitative relation compared to personal needs in fulfillment among adolescents. The results of the study revealed that boys and girls living in less favorable social and environmental regions have a more responsible attitude towards health issues. A study of the statements of 1st-year students majoring in pediatric care showed that respondents expressed more desires towards health not just for the people from their inner circle, and also expressed the desire to help people in general (p ≤ 0.001). The obtained findings require additional study.
Comparison of the results of the 2019 and 2020 surveys conducted among adolescents showed the influence of the external information environment related to the pandemic on the growth of graduates' desires related to personal health and the health of their loved ones. Quantitative data for these categories are shown in Table 4.
According to the results presented in the table, the desires associated with the need for self-fulfillment (p ≤ 0,005) have changed significantly. Significant differences in the category of desires related to people from the inner circle have not been identified, but there is a distinct trend towards an increase in the rate of desires related to people from the inner circle and health in 2020. Among the answers of respondents to this orientation, the desires related to parents and other relatives are slightly prevailing. The wishes refer to the health of relatives ("I want my relatives to be healthy"). As a result of the unfavorable epidemiological situation caused by the outbreak of coronavirus, the percentage of statements concerning the development of a vaccine has increased ("I want all deadly viruses to disappear forever," "The development of a vaccine for all diseases"). There were no statistically significant differences between boys and girls. During the pandemic, the level of anxiety about their own and their relatives' health increased in the respondents' statements, and the hierarchy of motivational preferences of the older adolescents can be observed too. This fact certainly requires further study, but comparing the study samples before the pandemic in 2019 and the eve of quarantine restrictions in the spring of 2020, it is of great interest to investigate the specific impact of the information environment on the motivational sphere of modern older adolescents.
Conclusion
The total sample of adolescents from Moscow, Moscow region, Orsk, and Chelyabinsk is characterized by the prevalence of undetermined locus of control. The frequency distribution of locus of control types revealed a tendency of transition from the undetermined locus of control to the development of an internal locus of control. Our findings may reflect the stage of locus of control development as a higher mental function when external control from others transforms into an internal one, as well as the stage of development of personal attitude towards the ability to have an influence on significant life events, to plan one's actions and to be responsible for one's deeds. At the present time, boys and girls from 14 to 20 years old are at the stage of development of volitional processes, development of self-awareness, self-control, and self-regulation, on the basis of which the personal quality of external or internal locus of control is being developed.
The number of students with an internal locus of control in Orsk and Chelyabinsk is almost twice as high compared to the Moscow region. Our findings suggest that more challenging socio-economic conditions of growing up contribute to the early development of a sense of responsibility for one's life, which can function as a coping strategy for dealing with challenging situations. The evidence supporting this hypothesis can be illustrated by the data on a comparison of the expression of the locus of control type on the scale of internal attitudes towards health and illness, obtained in the spring of 2019 and February-March 2020 when the rate of adolescents with an internal locus of control increased under the influence of the information environment as the epidemiological situation deteriorated. Young people living in Moscow and the Moscow region proved to be the most susceptible to information about the risks associated with a coronavirus pandemic.
The life plans of modern school graduates are characterized by the need for personal development, self-improvement, and self-fulfillment. The similarity in the content of motivational preferences among 16-17 year old boys and girls living in different regions of the country has been identified. Unfavorable epidemiological situation and external influence of information environment in the conditions of pandemic influenced the hierarchy of motivational preferences of graduates and contributed to increasing of anxiety for their own health.
References
Bozhovich, L. I., & Blagonadezyna, L. V. (1972). Izuchenie motivov povedeniya detej i podrostkov [Study of the motivations of the behaviour of children and adolescents]. Moscow: Pedagogy. [in Russ.].
Galvin, B. M., Randel, A. E., Collins, B. J., & Johnson, R. E. (2018). Changing the focus of locus (of control): A targeted review of the locus of control literature and agenda for future research. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 39(7), 820–833. DOI:
Gazizullina, P. G. (2018). Social`no-e`konomicheskie determinanty` zdorov`ya podrostkov v Rossii [Socio-economic determinants of adolescent health in Russia]. Moscow. [in Russ.].
Hope, N. H., Matthew A., Wakefield, M. A., Northey, L., & Chapman, A. L. (2018). The association between locus of control, emotion regulation and borderline personality disorder features]. Personality and Mental Health, 12(3), 241–251. DOI:
Johnson, R. E., Rosen, C. C., Chang, C.-H. (D.), & Lin, S.-H. (J.). (2015). Getting to the core of locus of control: Is it an evaluation of the self or the environment? Journal of Applied Psychology, 100(5), 1568–1578. DOI:
Kassianos, A. P., Symeou, M., & Ioannou, M. (2016). The health locus of control concept: Factorial structure, psychometric properties and form equivalence of the Multidimensional Health Locus of Control scales. Health Psychology Open, 3(2). DOI:
Kuchma, V. R., Yefimova, N. V., Tkachuk, E. A., & Mylinnikova, I. B. (2016). Gigienicheskaya ocenka sily` uchebnoj aktivnosti uchashhixsya 5-10 klassov obshheobrazovatel`ny`x shkol [Hygienic assessment of the strength of the learning activity of students of 5-10 classes of general educational schools]. Hygiene and sanitation, 95(6), 552–558. [in Russ.].
Melnikova, I. V. (2018). Kompleksnaya ocenka faktorov, formiruyushhix zdorov`e gorodskix i sel`skix podrostkov [Comprehensive assessment of the factors shaping the health of urban and rural adolescents]. Angarsk. [in Russ.].
O sostoyanii sanitarno-e`pidemiologicheskogo blagopoluchiya naseleniya Rossijskoj Federacii v 2019 godu (2020) [On the state of sanitary epidemiological well-being of the population in the Russian Federation in 2019] State report. Moscow. [in Russ.].
Panov, V. I. (2020). Ot e`kologii detstva k psixologii ustojchivogo razvitiya. Ekopsikhologicheskiye issledovaniya-6 [From the ecology of childhood to the psychology of sustainable development. Ecopsychological Research-6]. In Ecology of Childhood and Psychology of Sustainable Development. Collection of Scientific Articles. (pp. 10–14). Moscow; Kursk: FBNBU Psychological Institute RAO: University Book. [in Russ.].
Pantelev, S. R. (1987). Metody` izmereniya lokusa kontrolya [Methods of measuring the locus of control]. General psychodiagnostics. (pp. 278-285). Moscow: Moscow university press. [in Russ.].
Perekusin, M. V. (2019). Kompleksnaya ocenka sanitarno-e`pidemiologicheskogo blagopoluchiya obshheobrazovatel`ny`x uchrezhdenij i zdorov`ya uchashhixsya [Comprehensive assessment of the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of general education institutions and the health of students]. Kazan. [in Russ.].
Pogontseva, E. (2019). «Shkol`naya medicina» perexodit ot pilotnoj k shirokomu vnedreniyu [«School Medicine» is moving from pilot to wide introduction]. Retrieved from https:///medvestnik.ru/content/news/Shkolna-medicina-pereditho-mot-pilota-k-shirokomu-nedreniu.html [in Russ.].
Semenova, A. Y. (2018). Vliyanie social`no-e`konomicheskix i demograficheskix faktorov na sostoyanie zdorov`ya naseleniya regiona (na primere Respubliki Kry`m). [Influence of socio-economic and demographic factors on the state of health of the population of the region (using the example of the Republic of Crimea)]. Moscow. [in Russ.].
Solodova, I. E. (2018). Psixologo-pedagogicheskoe soprovozhdenie razvitiya polozhitel`nogo otnosheniya k zdorov`yu v obrazovatel`noj srede starsheklassnikov. [Psychological and pedagogical support for the development of a positive attitude towards health in the educational environment of high school students]. St. Petersburg. [in Russ.].
Vygotsky, L. S. (1984). Pedologiya podrostkovogo vozrasta. Tom. 4. Detskaya psixologiya [Pedology of Adolescence. Vol. 4. Child psychology]. Pedagogy. [in Russ.].
Yermolayeva, S. V. (2018). Vliyanie kompleksa faktorov okruzhayushhej sredy` na pokazateli zdorov`ya detej i podrostkov (Ul`yanovskaya oblast`). [Influence of complex environmental factors on health indicators of children and adolescents (Ulyanovsk oblast)]. Vladimir. [in Russ.].
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
25 June 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-111-9
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
112
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-436
Subjects
Personality, norm, pathology, behavior, uncertanity, COVID-19
Cite this article as:
Begunova, L., Lisichkina, A., Ledneva, V., & Ivannikova, A. (2021). Adolescents’ Attitude Towards Health In Regions With Different Environmental Conditions. In M. Ovchinnikov, I. Trushina, E. Zabelina, & S. Kurnosova (Eds.), Personality in Norm and in Pathology, vol 112. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 297-307). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.06.04.34

