Abstract
The effective management of university resources becomes more important when solving the task of developing the management system of higher education. The development of higher education requires the development of better ways to manage financial flows in this area. Strengthening the competitive position of universities is ensured through a combination of centralized and decentralized management, the organizational and financial models for the activities of departments, the optimal ratio of public and private financing of education. As the financial model of each structural division of the university is an integral part of the financial system of the university as a whole, it seems appropriate to develop the process of budgeting academic subdivisions within the organizational and financial model of the university. The study presents a financial model of the university division, designed to decentralize the budgeting process in the university to form an independent plan of financial and economic activities of the department. The transfer of authority and responsibility for expenses to subdivisions ensures financial independence and increases the accuracy level of planning. This allows making effective management decisions that provide the activities of the main academic units. The proposed approach is planned to be fully integrated into the overall planning and budgeting process at Vladivostok State University of Economics and Service. The budgeting system helps the authority not only to make an operational assessment of the results of its activities, to predict indicators for the future but also contributes to making decisions aimed at reducing costs and increasing profits.
Keywords: Budgeting system, higher education institution, university, deconcentrated budget
Introduction
During the strategic development of higher education institutions, the issues of mechanisms of influence of the financial factor on the state and development of universities are actualized. The improvement of the financial and economic activities of universities becomes obvious. (Lauder et al., 2015).
The Federal Government Budgetary Institution of Higher Education (hereinafter referred to as VSUES) is a leading university in the Far Eastern region of the Russian Federation, focused on the socio-economic development of the territory. It is a competitive regional university that corresponds to the transformed model of a traditional university. The educational institution keeps partnership relations with organizations and business community, closely interacts with the regional authorities, and actively integrates innovative models and technologies of training through the embeddedness of learning with scientific and practical activities (Urasova, 2016).
Problem Statement
Since the financial model of each subdivision of the university is an integral part of the financial system of the university as a whole, it seems appropriate to develop the process of budgeting academic subdivisions within the organizational and financial model of the university.
The planning system in a budgetary institution is made through budgeting.
The components of the budgeting system of The Vladivostok State University of Economics and Service are shown in Figure 1.
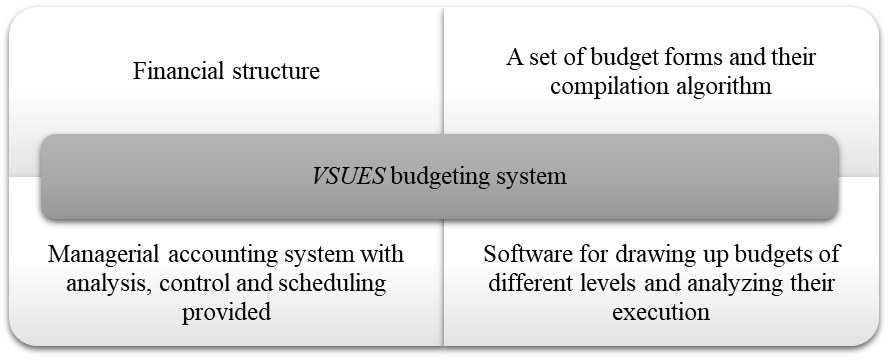
Research Questions
The effective management of university resources puts forward the task of developing the management system of higher education. Special attention should be paid to the financial processes of universities (Gadzhiev, 2016). In VSUES, the method of budgeting by activity types and processes is used. (Varpaeva & Treushnikov, 2018).
Financial Responsibility Centers (hereinafter referred to as FRCs) are responsible for their budgets, taking part in their planning and execution. Table 1 shows the functions of the main subjects of the budgeting system of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution VSUES.
For several Financial Result Centers (hereinafter FRC) and Revenue and Outlay Centers (hereinafter ROC), the elements of the incremental planning method are applied, taking into account the increase in the income plan by a certain percentage to the actual income of the previous period (Borisov et al., 2017). For FRCs that deal with administrative and economic activities, as well as for investment areas, the method of zero-base budgeting (annual statement of expenses need) is used. The financial structure is created based on the current organizational structure, taking into account the types of income-generating activities and expenditure directions, as well as the established hierarchy of subordinated structural divisions (Miroshnikova et al., 2019).
In VSUES financial structure, depending on the financial responsibility area, the following types of financial responsibility centres are distinguished:
1. A Financial Result Center (FRC) is a FRC responsible for achieving the planned financial result of its activities (innovative business incubator, branches).
2. A Revenue and Outlay Center (ROC) is a FRC responsible for the approved revenue plan, implementation and optimization of costs in the range of income received and the selected part of the centralized budget of VSUES (departments and institutes).
3. Outlay Center (OC) is a FRC responsible for the effective implementation and optimization of expenditures within the allocated part of the centralized budget (administrative, managerial and auxiliary FRCs that are nonearning).
The financial structure of VSUES has three levels that are in the relationship of subordination. It is shown in Figure 2.
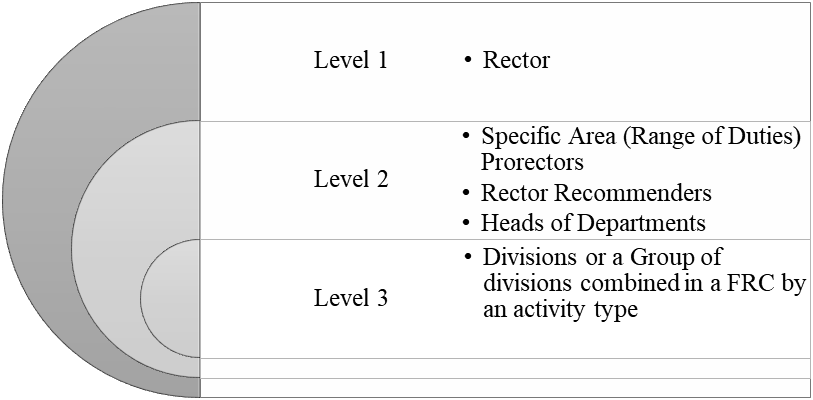
According to the figure, the third-level FRCs are part of the FRC second-level. Second-level FRCs are part of the FRC first-level.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to develop a financial model of the university subdivision designed to decentralize the budgeting process in the university to make up an independent plan for the financial and economic activities of the subdivision.
VSUES basic budgeting model is a based budgeting activity, ABB).
The key characteristics of the model include:
-Transition to self-financing of individual financial responsibility centres (FRC) with the stimulation of annual income growth;
- Annual calculation and approval of budgets of financial responsibility centres;
-Partial decentralization of FRC budgets by allocation (payments) of a certain amount of revenue in VSUES central budget;
- detailing budgets at all levels of the financial structure with the possibility of drawing up separate local budgets according to the type of activity within FRC (Losev et al., 2017).
Research Methods
As part of the development of a decentralized model, the authors formulated the budget revenue classification features (See Figure 03).
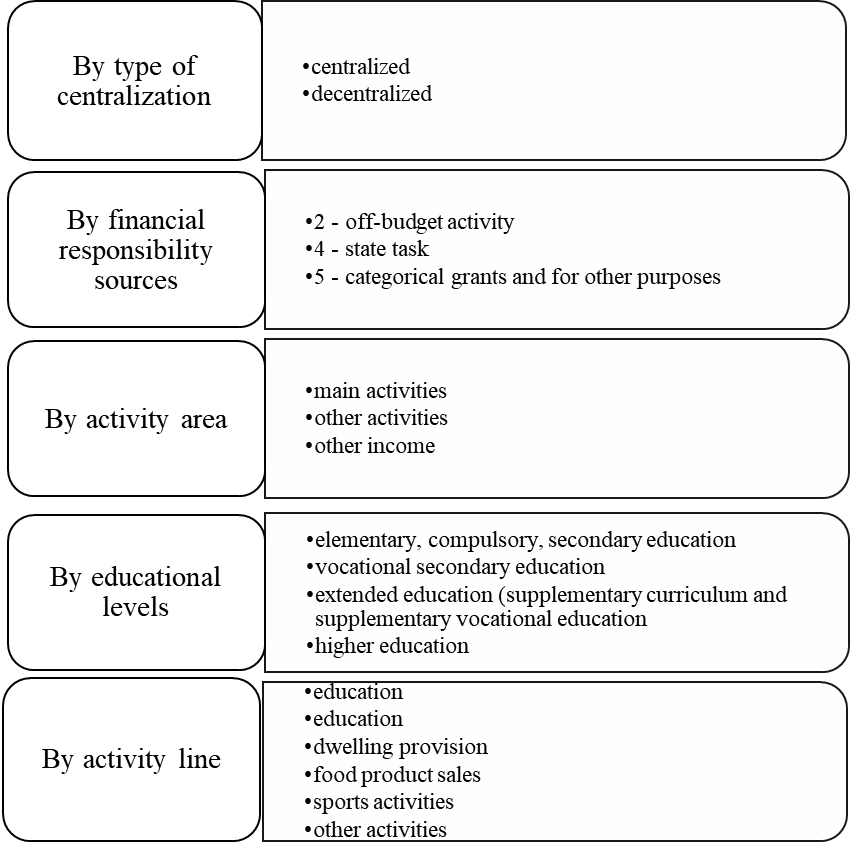
The earnings of these departments from additional professional courses and additional general education courses, from scientific and other activities, go to the decentralized budget after payments to the centralized budget of the university. In turn, the revenue received from the main curricula of higher education (HE) and advanced education (SVE) is distributed to the centralized budget.
The authors offer to group the income of the university and its divisions according to the sources of financial support by the financial support codes:
2- income-generating activities (income from own business);
4-aid grants to perform the government (communal) procurement;
5- aid grants for other purposes (other income funded through the budget).
By the types of activity, the income gained by VSUES can be divided into three groups:
- income from the services that constitute the primary activities according to the Charter;
- income from the services for other activities;
- other receipts.
It should be emphasized that in addition to education, the primary activity includes research activities. Revenues in the research activities mean decentralized revenues. 7% is allocated to the centralized budget. (Lukman et al., 2010).The university expenses are grouped in the following areas (see Table 2):
According to the type of centralization, outlays are divided into centralized and decentralized (Pronina & Rebezha, 2010). Centralized expenses are expenses of the university that are subject to funding from the centralized budget. Decentralized expenses are expenses that are subject to funding from funds earned by the department independently. According to the purpose, the costs can be divided into current and capital. According to the sources of financial stability, VSUES expenses of, as well as the income, are divided into three groups under the financial security codes:
Code 2 includes expenses for the primary types of activity. They are salary, travel allowance, purchase of goods, works and services, payment of taxes, construction and repair, and other expenses.
Code 4 includes expenses funded through the budget, such as salary, public utility charge, and other purchases of goods, works, and services.
Code 5 includes other costs funded through the budget, including capital repair, upkeep of property and scholarships.
Findings
At the final stage of the university budgeting, a final document is drawn – a business and financial performance plan (hereinafter referred to as BFP plan or BFPP) of the state-financed establishment. The university financial responsibility centres make local cost estimates for certain types of activities related to the decentralized university budget. The estimates do not contain information about the financial position of a particular FRC. Therefore, it is not possible to estimate the balance between income and expenses of FRC. For a more detailed treatment of financial figures, it is worth drawing a local BFPP of a subdivision that includes the total of income and expenses of the division, including indirect expenses that cannot be directly attributed to the result of the division activities.
To develop a decentralized model for planning the income and expenditure part of the department of the university, it is necessary to draw the income part of the plan of financial and economic activities of the subdivision and its expenditure part (Bilkisu &Abu Bakar, 2017). The decentralized income will include the income gained by FRC, fully or partially kept by them after the allocation of a part to the centralized budget of the university. Decentralized expenses will include expenses that are subject to funding from the own funds of the department. In the study, income is equated with cash receipts. The authors suggest considering the method of drawing the revenue part of BFPP, according to which the main components of the sources of financial security are classified into:
- income for financial support of the state assignment in;
- income-bearing activities (income from own business).
Aid grants for state assignment represent income from curricula of higher education (HE) and advanced education (AE). The income from own business consists of that from HE and AE curricula, income from additional curricula and research works. Since BFPP is calculated according to the cash-basis method, and the income for the main curricula is calculated by the accrual method, it is necessary to adjust the income for inflows and outflows of accrued expenditures (debts and advance fees). The financial model of budgeting of a subdivision implies that when planning the expenditure part of BFPP, it is necessary to determine which expenses will be direct and indirect. The direct expenses of the educational subdivision include centralized expenses of the university and decentralized budgets of the department.
The centralized ones include:
expenses for the salary paid to the academic staff and clerking employees;
- accrued items for the remuneration of labour;
- purchase of equipment and supplies for the arrangement of the education process.
The decentralized ones include:
- payments to the staff formed according to the estimates of additional curricula, research works;
- equipment and supplies;
- special tax and other payments.
Indirect costs include those related to the university support service performance.
When determining the number of expenses that need to be included in BFPP, it is necessary to distribute them according to the bases of allocation. The authors choose a distributive system of a major group of indirect expenses, i.e. target items, type of expenses codes (TEC) and FRC by units and groups of expenses. At the initial stage, it is necessary to consider only the centralized expenses of the university, and then determine the indirect costs for FRC based on the special-purpose items and TEC. For example, the expense group Maintenance of university areas includes expenses for ensuring the functioning of university areas, expenses for utilities, security, and rent. The basis for distribution is the area occupied by the divisions of the university and the conditional cost of 1 square meter. At the final stage of the university budgeting, a final document is formed, i.e. the business and financial performance plan BFPP).
Conclusion
In the presented model, it is assumed that the Business and Financial Performance Plan of the educational department of the university will be developed directly by the subdivision. Planning will be carried out iteratively. At the first stage, the income of the subdivision is drawn and the revenue part of the plan is built. Then it is handed to the Department of Economics and Planning for verification. At the second stage, the head of the department (director of the Institute) draws up the expenditure part of the plan. After the completion of the department (institute) BFPP planning, it is handed to VSUES Department of Economics and Planning for agreement.
The introduction of the budgeting system of the subdivision of the university will ensure financial independence and increase the efficiency of management decisions of academic divisions by optimizing costs and increasing revenues in the performance of their functions, as well as significantly increase the financial interest in the results of financial and economic activities (De Pillis & De Pillis, 2001). Budgeting is a continuous process of management based on financial figures, on the one hand, and is an integral part of management accounting on the other. According to the integrated approach, it is necessary to take into account that both directions interact and influence the efficiency and business agility of managerial decisions made.
References
Bilkisu, M. E. M., & Abu Bakar, N. E. (2017). Optimal budget allocation for university research and publication agenda through integer programming. Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology, 8(1), 18-27.
Borisov, S. A., Kolesov, K. I., & Plekhanova, A. F. (2017). Upravleniye zatratami i kontrolling. Nizhniy Novgorod [Cost management and controlling]. R. E. Alekseev Nizhny Novgorod State Technical University. [in Russ.].
De Pillis, E. G., & De Pillis, L. G. (2001). The long-term impact of university budget cuts: а mathematical model Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 33(8–9), 851-876. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895717700002855
Gadzhiev, N. G. (2016). Sovremennyye podkhody k finansirovaniyu obrazovatel'nykh programm vuza [Modern approaches to the financing of educational programs of the university]. Bulletin of AGTU. Series: Economics, 2. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennye-podhody-k-finansirovaniyu-obrazovatelnyh-programm-vuza [in Russ.].
Lauder, A., Sari, R. F., Suwartha, N., & Tjahjono, G. (2015). Critical Review of a Global Campus Sustainability Ranking: GreenMetric. Journal of Cleaner Production, 108, 852-863. DOI:
Losev, A. G., Korolkov, S. A., & Tarakanov, V. V. (2017). Model' finansovogo obespecheniya vypolneniya tselevykh pokazateley effektivnosti raboty vuza [Model of financial support for the implementation of the university performance targets]. University Management: Practice and Analysis, 21(6.112), 49-57. [in Russ.].
Lukman, R., Krajnc, D., & Glavič, P. (2010). University Ranking Using Research, Educational and Environmental Indicators. Journal of Cleaner Production, 18(7), 619-628.
Miroshnikova, T. K., Epifanova, V. I., & Kharlamov, A. V. (2019). Developing a project of an integrated supply chain planning and establishment of budgeting. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 8(6), 837-844.
Pronina, A. M., & Rebezha, O. O. (2010). Organizatsiya i metodika byudzhetirovaniya raskhodov v sisteme upravleniya predpriyatiyem. [Organization and methodology of budgeting expenses in the enterprise management system]. Theory and practice of the service: economics, Social Sphere, technologies, 4(6), 162-169. [in Russ.].
Urasova, A. A. (2016). The role of performance-based budgeting in the socio-economic development of the region. Development of territorial socio-economic systems: theory and practice [The role of result-oriented budgeting in the socio-economic development of the region. Development of territorial socio-economic systems: questions of theory and practice]. Collection of scientific articles of the XIV International Scientific and Practical Conference of Young scientists, 341-343. [in Russ.].
Varpaeva, I. A., & Treushnikov, R. V. (2018). Byudzhetirovaniye deyatel'nosti vuza v ramkakh proyektno-tselevogo podkhoda k upravleniyu [Budgeting of university activities within the framework of the project-target approach to management]. International Accounting, 21(1.439), 30-44. [Russ.].
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
21 June 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-110-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
111
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1168
Subjects
Social sciences, education and psychology, technology and education, economics and law, interdisciplinary sciences
Cite this article as:
Miroshnikova, T. K., Varkulevich, T. V., Bedrachuk, I. A., Chudaev, E. Y., & Blinov, M. P. (2021). A Generated Model Of Business Performance In A Higher Education Institution Subdivision. In N. G. Bogachenko (Ed.), Amurcon 2020: International Scientific Conference, vol 111. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 663-670). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.06.03.89

