Abstract
This article deals with the conditions for combating international terrorism. The authors analyze the factors of international terrorism, as well as their relevance in the medium and long term. Cultural and religious differences of civilizations and their influence on the international terrorism are analyzed. For example, some differences in the values of Western and Islamic civilizations are explored. At the same time, an assessment of the concept of S. Huntington is given, who was one of the first to declare the influence of civilizational differences on the process of radicalization of population, in particular, in the Middle East. The authors analyze the economic factors of international terrorism. The article shows the level of uneven economic development of countries, as well as social inequality on a domestic scale. The link between inequality of States and social strata as well as international terrorism is revealed. In addition, the authors’ reasoning also concerns the issues of the relationship between social justice and terrorism, the influence of values of young people, which form the basis of terrorist organizations, on protest sentiments expressed in the form of a terrorist struggle. The terrorist struggle is one of the types of protest against the contradictions caused by modern trends in globalization. The authors conclude that the international community cannot achieve the desired results in the fight against international terrorism unless the causes of international terrorism, including poverty, inequality, lack of social justice, the desire to preserve cultural and religious identities and values are addressed.
Keywords: Terrorism, civilization, international, inequality, economy, state
Introduction
Many states representing different civilizations are currently faced with the problem of terrorism. Among them are the states of the West, India, China, Russia, the countries of the Near and Middle East, etc. Therefore, nowadays the world community recognizes international terrorism as one of the most significant global threats to humanity. This is stated by political leaders of states, international and public organizations, scientists and representatives of culture at various levels. The fight against international terrorism, judging by the statements of the leaders of states, as well as the practical measures taken by the governments of the countries, has been in place for at least several decades. This fact creates the prerequisites for the preliminary results of this struggle and also the results in the medium and long term.
Problem Statement
Currently there is no consensus in the scientific community regarding the factors of emergence and development of international terrorism. Of course, this does not contribute to solving the issue of the effective counteraction to this phenomenon. International terrorism needs a comprehensive assessment that would contain such elements as the state and trends, objective factors of its emergence and development. This approach will make it possible to predict the effect of fight against international terrorism.
Research Questions
1. Terrorism in the world.
2. International terrorism development trendsа
3. Objective factors influencing the emergence and development of international terrorism.
Purpose of the Study
The aim of this work is to establish the factors of efficient fight against international terrorism.
Research Methods
The methodological basis of the work is the objectivity concept regarding key global issues. Their research involves the use of methods of comparative analysis, world-systems approach.
Findings
At present, we can state the fact that in spite of the calls against terrorists around the world, the level of this phenomenon has not dropped in recent years to the level of the threshold, allowing us to say that the world community has radically changed the situation in the fight against terrorism. According to the annual data of the Global Terrorism Index prepared by the Institute of Economics and Peace (IEP), the number of people killed in terrorist attacks had decreased from 2015 to 2019 (as shown in Figure 1). However, if we compare the number of deaths from terrorism since the United States declared war on international terrorism, supported by virtually the entire world community, the number of deaths from terrorist attacks has grown significantly.
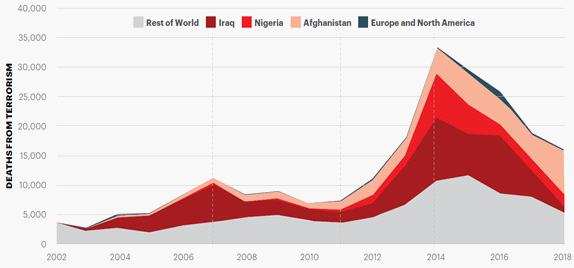
At the same time, in 2018, a fairly large number of people died at the hands of terrorists, i.e. 15,952 people. It is important to note that the number of countries where terrorist attacks occurred, as a result of which people had died, increased from 67 to 71. It has to be stated that this is one of the highest rates since the early 2000s.
Thus, currently, one can state, firstly, the presence of an intention on the part of states, primarily of the major powers, to overcome international terrorism. The second tendency suggests that global terrorism remains at a critically high level and, as before, threatens humanity. Thus there is a subjective desire to fight terrorism, and there are objective realities that contradict it, which means that this threat still exists. This study will not dwell on the problem of the effective actions of international coalitions of states in the fight against terrorism, the contradictions they face in the course of this struggle and geopolitical interests that are put above the task of defeating terrorism. These problems are extremely important, but at the same time, in our opinion, they are the subjects to be discussed separately. We will dwell on the objective factors of terrorism that contrary to the goals of the states get on the way to win the victory over the international terrorism.
Considering that terrorism is a widespread phenomenon, it is necessary to deal not only with the perpetrators of terrorist acts, destroying or imprisoning them. Indeed, the elimination of the most dangerous terrorists of the XXI century – Osama bin Laden, Sh. Basayev, as well as the leader of IS Al-Baghdadi – did not significantly affect the solution of the issue of increasing the effectiveness of the fight against international terrorism. Obviously, over the past 15 years, many leaders of bandit groups have been eliminated and even individual terrorist organizations have been suppressed. But at the same time, the goal of eliminating the causes of international terrorism and its ideological foundations was not set at the political level. Therefore, it is extremely important to determine the patterns of the emergence and development of international terrorism as a phenomenon in time and space, its factors and ideological foundations. Otherwise, states will be doomed to fight individual terrorist organizations, their leaders and sponsors, but not the phenomenon as a whole.
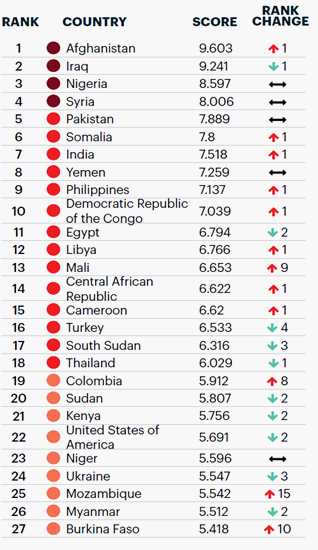
In order to better understand the nature of such a phenomenon as terrorism, it is necessary to pay attention to the countries that are more affected by terrorism and where the activities of terrorist organizations have gained the greatest scale (Figure 2). Of course, these include regions such as the Middle East and North Africa. States such as Iraq, Afghanistan, Syria, Nigeria are currently the leaders in the number of terrorist attacks. If we talk about Syria, then, undoubtedly, the explosion of terrorism in this country can be attributed not only to the presence of complex social contradictions, but also to an external factor. Indeed, we are talking about terrorist invasion of this state by IS, which is globally recognized as a terrorist organization. Moreover, it is quite probable that the support of terrorism in this country from state structures pursuing their geopolitical interests is possible. However, as it was mentioned above, the topic of support for terrorism by foreign states requires a separate careful study and consideration. We will focus on the domestic premises of terrorism.
In the context of globalization the world is compiled of contradictions that periodically turn into the form of protest actions, conflicts, including armed ones. Terrorism is also a consequence of certain contradictions in the world as a whole, and in the individual states, in particular, a form of people’s protest against injustice and inequality. The nature of this protest can be understood by delving into the cultural and economic dimension of the modern world.
Thus, the world is divided into civilizations that differ from each other, first of all, in terms of culture, religion and values, and only then in terms of technologies. The technologies of the West – the most technologically advanced – civilization are willingly borrowed by the rest of civilizations (Chinese, Islamic, Indian, Russian, etc.); however, the cultural influence – Westernization – is perceived rather painfully around the world. At the same time, opposition takes completely different forms: from condemnation and moral censure to the most radical ones, including terrorism.
It should be noted that such terrorist organizations as Al-Qaeda, IS put anti-Americanism and resistance to cultural Westernization as the basis of their ideology. On this basis, new members are being recruited for gangs. Obviously, the values of a consumer society and individualism are in sharp conflict with collectivism and religious values, for example, in the Arab world, where future members of terrorist organizations are actively recruited. It should be said that the majority of members of society cannot afford to live within the framework of the material culture delivered by the West. The destruction of basic values is perceived in the East as a threat of degradation of society, destruction of the traditional way of life, which allows one to survive in the complex realities of the modern world. Undoubtedly, Western values penetrate the Islamic civilization and enthrall a part of society with a comfortable and luxurious lifestyle.
Peoples and states at all times have been fighting for freedom, which has been and still is in the possibilities of choosing values, religion, limiting the penetration into society of those values and attitudes that can harm the development of society and people, subordinate it to the rule of other peoples and states. Currently, the same process is taking place in the countries of the Near and Middle East, China, India, and Russia. Parties, social and political movements, leaders and leaders of states oppose Western values. In the West itself, there is a fairly massive anti-globalization movement. And this is not surprising, since peoples, social groups and individuals have the right to independently make a choice in favour of one or another ideology, views, religion, culture. Obviously, the stronger the spiritual bonds in society, the stronger the rejection of Westernization in different parts of the world. Especially if Western values contradict the attitudes of the peoples of other civilizations and states. At present, the Islamic civilization, like all other civilizations, willingly borrows Western technologies, attributes of a comfortable life, but at the same time painfully perceives the American values. The West is now mostly called the ‘godless’, the ‘spiritless’ by spiritual and political leaders, representatives of intelligentsia of Islamic states.
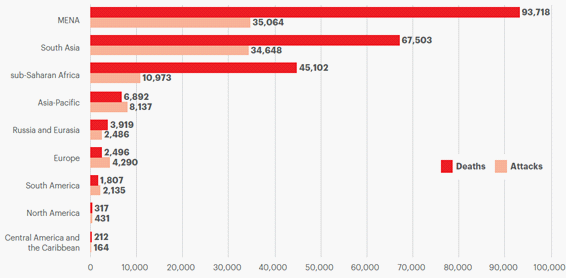
The contradictions of modern Western and Islamic civilizations are most evident (Figure 3). And this is easy to explain. The fact is that the peoples of the Islamic civilization for the most part live in a traditional, religious way. In the West, a secular society was built. Of course, the United States and its allies (first of all, the EU countries) strive not only for military, political, financial and economic domination, but also for cultural domination. And they succeed to a large extent due to the dominance in the world media.
The problem lies not only in the fact that Muslims do not want to adopt Western values and the way of life, but in the fact that they lack real opportunities for appropriate borrowing (Koibaev, 2019). In fact, only a small part of society can benefit from the Western lifestyle standards in Islamic civilization, and it represents large and medium-sized businesses, high-ranking officials, bureaucrats, and the military. Yes, this part of society in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan can live according to Western economic and even cultural standards. But at the same time, the majority of society in these countries lives at the poverty level and a significant part is desperately poor (Byazrov, 2016).
Poverty implies not only the lack of opportunities for a certain level of consumption, characteristic of developed and developing countries, but also the lack of opportunities to purchase food. Thus a big part of population is simply underfeed. For example, according to independent Pakistani experts, 38% of Pakistan’s population – over 67 million people – was constantly starving (Kamenev, 2014).
Another leader in terms of the number of terrorist acts committed on the territory of the state is Afghanistan, as of the end of 2009, in the human development index (level of literacy, education, longevity, access to clean drinking water, etc.) from 182 countries of the world occupied the penultimate position. Moreover, about half of the country population’s income was one dollar a day. Currently, the situation of the people of Afghanistan has not changed. This means that about 12 million people in Afghanistan (of which three million are children) live in poverty (Okimbekov, 2016).
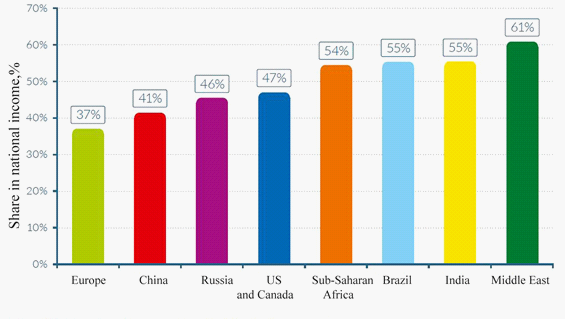
The conflict in the Islamic society is associated with different levels of access to social benefits: education, medicine, real estate, work, income. The wealthiest stratum of the population, which is negligible in the scale of society, has enormous advantages in relation to the overwhelming majority of people. This social contradiction is clearly enough manifested in the share of the richest 10 % in the national income. In the countries of the Middle East this figure reaches 61 % (3). At the same time, this indicator in Europe and Russia is 37 % and 46 % (3), respectively (as shown in Figure 4).
Another country with a high level of terrorism is Nigeria. According to the IMF, as of the beginning of 2019 Nigeria occupied the 140th position in the world ranking according to such an indicator as GDP per capita (5). And according to the human development index, Nigeria takes 158 position (6). Iraq is ranked 90 (5) and 120 (6) in terms of GDP per capita and the human development index, respectively.
Conclusion
The objective factors contributing to the emergence and development of international terrorism include inequality and lack of social justice, as well as cultural and religious contradictions. Growing inequality is a global trend that has characterized the humanity over the past few decades. Currently, there are no effective mechanisms for solving this problem both on a global level and individual states. The cultural influence of the West is a consequence of the global hegemony of the United States and its allies. Obviously, as long as the world is unipolar, there will be, on the one hand, a center dictating its will to the periphery, and on the other hand, there will be an increase in discontent with imposed economic and cultural standards in different parts of the world. Despite the efforts undertaken by the major powers (China, Russia, India), currently there is no reason to talk about the formation of a multipolar world with the centres of power comparable to the United States. In connection with the foregoing, it can be said that in the medium term there are no opportunities to eliminate the objective factors of the emergence and development of international terrorism. This means that the world community for the next 10-15 years will not be able to radically change the situation in the direction of increasing the effectiveness of the fight against international terrorism.
References
Byazrov, A. V. (2016). Poverty and inequality as factors of international terrorism. Strategic anti-crisis management: global challenges and the role of the state. Coll. of VI Int. Sci. and Pract. Conf.
Kamenev, S. N. (2014). Economic Development of Pakistan (1947–2012): Macroeconomic Analysis. Inst. of Oriental Stud. RAS.
Koibaev, B. G. (2019). Christians and Muslims of Western Europe in the second half of the twentieth century: problems of dialogue. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 58, 550-559. DOI:
Okimbekov, U. V. (2016). Economy of Afghanistan (production infrastructure). LLC “Publ. house MBA”.
Visionofhumanity (2019). Global terrorism index. http://visionofhumanity.org/app/uploads/2019/11/GTI-2019web.pdf
WID (2018). World Inequality Report. General Provisions. https://wir2018.wid.world/files/download/wir2018-summary-russian.pdf
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
17 May 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-106-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
107
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2896
Subjects
Science, philosophy, academic community, scientific progress, education, methodology of science, academic communication
Cite this article as:
Byazrov, A. V., Koybaev, B. G., Kosov, G. V., & Usova, Y. V. (2021). Prospects For Combating International Terrorism. In D. K. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Knowledge, Man and Civilization - ISCKMC 2020, vol 107. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 301-308). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.05.41

