Abstract
The personality formation and development are the main goal of the modern educational system. The conditions in which the formation and development of personality take place have changed. This change is due to the fact that modern society carries out its activities in terms of interaction with a dynamically changing information field. The flows of information that a person constantly encounters have both a positive developmental and negative impact on a person. A person’s susceptibility to the negative influence of the information field depends on how personal senses are formed and realized on the personality, which can be enriched with new, important meanings positive for the person and resist a negative influence. One of the factors influencing the formation and development of an individual is ethno pedagogical theory. It gives a person the possibility to develop in ethnocultural space that allows ethnocultural identity to be formed on the basis of ethnocultural customs and traditions of a pedagogical character while cultivating tolerance and respect towards the world cultural process. The current stage in ethno-pedagogical theory development is characterized by the active development of a new direction – ethno didactics. It studies the fundamentals of the ethno pedagogical process development in technological terms. The basis of ethno pedagogical theory is the concept of ethno pedagogical system. The hierarchy of goals of the ethno pedagogical system allows us to trace the features of its implementation.
Keywords: Ethnos, education, culture, personality, pedagogics, ethno didactics
Introduction
Modern society carries out its activities in rather difficult conditions. Changes in all areas of life, the flows of information faced by a modern man, the rapid progress of technology and science entail changes in the personal sphere. A man changes in the process of interacting with the information field. Information and ownership of it in the modern world is becoming a factor determining the ability and readiness of an individual to work effectively. All this determines the changes that occur in the personality and in its activities. The ability of a person to withstand the information that can destroy a person, have a negative impact on its personal meanings, change the world’s picture in a negative direction, depends on how stable personal meanings and the entire personal sphere are, how strong personal beliefs and views of a person are. The problem of a person’s worldview and its stability, the ability to resist the information that can negatively affect a person, is connected with the problem of upbringing, with the ethnic characteristics of the person, with the level of culture, with the general level of personality formation. In this context, the use of ethnic culture and ethnic traditions in the formation and development of an individual represents an urgent problem. The ethnic basis has always determined the way a person looks at the world. The ethnical experience transmitted from one generation to another always contains the generations’ experience, which is composed of the best tradition of upbringing based on ethnic culture. In this regard, it seems to us that any theory of education should be based on ethno pedagogical theory containing conceptual provisions that allow the use of the ethnocultural and ethno-pedagogical experience of generations in the young people education. The experience of public education, which was developed in ethno pedagogics today, needs theoretical understanding, conceptualization, and generalization from the standpoint of the modern scientific picture of the world. Ethno pedagogics allows you to consider popular education from a theoretical point of view, find common points, identify differences, differentiate moments characteristic of individual ethnic groups. The identification of general theoretical principles, the interpretation of numerous facts of public education from a scientific point of view, their systematization, and justification of the principles of their use increase the effectiveness of ethno pedagogical theory implementation in practice.
Ethno pedagogics in modern science
The theoretical base of ethno pedagogics, which has been founded by great teachers and others proved continuity in questions of education, necessity of use of generations’ creative heritage and ethnic educational experience. They promoted ethno pedagogics formation as a branch of modern scientific knowledge. The great scientists mentioned above have paid attention to the fact that national educational ideas can be structured and represented as systems. However, not only teachers were at the origins of ethno pedagogy. Philosophers also contributed to the development of this science. For instance, the Russian religious philosopher N.A. Berdyaev (as cited in Builo, 2020) defined the dialectic correlation of universal and national as follows.
1. The presence of each individual person, traits of a member of the human race in general, and traits inherent in each individual nationality in particular.
2. The unity of the fate of an individual with the historical fate of the people and of all mankind.
3. The dependence of the reality of all mankind on the reality of nationalities.
4. The interconnection of national and universal culture, which is not abstract, but specifically national, and thereby ascending to universal humanity (Builo, 2020).
This correlation remains a key concept in modern ethno pedagogics. The founder of ethno pedagogy, academician Volkov (1999) considers the subject, essence and content of ethno pedagogy in dialectical unity. The subject of ethno pedagogy is folk pedagogy, public education. The essence of ethno pedagogy is revealed in three qualities:
- Firstly, it is considered as the pedagogy of the ethnos survival. Ethnic customs and traditions, which form the basis of ethno pedagogy, are that basis without which an ethnos cannot exist, because it distinguishes one ethnos from another.
- Secondly, as the universal wisdom of education. Wisdom is universal; therefore, it is the foundation of education.
- Thirdly, as the pedagogy of universal love. The pedagogy of love means that the interaction between a teacher and a student is based on the principles of love, cooperation, and mutual understanding.
The content of ethno pedagogy is determined by the system of ethno pedagogical knowledge in its various directions and manifestations, such as historical ethno pedagogy, regional ethno pedagogy (Arsaliev, 2019a), analytical ethno pedagogy (Volkov, 1999), preschool ethno pedagogy, ethno pedagogy of the game, aphoristic ethno pedagogy, family ethno pedagogy, ethnopedagogical anthropology , ethno pedagogical education (Kharitonov, 2020), ethno social pedagogy, comparative ethno pedagogy, sub-ethnic pedagogy.
Overcoming of the modern education system crisis caused by the discrepancy of rates of global, technological, ethnic, cultural, and educational processes development in the transition to an information society is connected with the solution of the formation problem and the development of a new type of person. Deep changes at the present stage of development of a society make new demands to the formation of the person in the educational space. The person of the new type should be ready to live in a polyethnic space to intercultural dialogue to creativity in practical and intellectual activities (Arsaliev, 2019a).
Revealing of ways and means of decrease in spontaneity elements in the ethno pedagogical process, an establishment of the most effective forms and methods of coordination of objective and subjective factors of national education allows improving the last in modern conditions. One of such ways is the use of the synergetic approach in the ethno pedagogical phenomena studying. Its appearance is connected with changes in a general scientific picture of the world.
Problem Statement
The research problem consists in
- Identifying and formulating the theoretical foundations of ethno pedagogical theory.
- Соnsidering ethno didactics as a new branch of ethno pedagogics.
- Considering its methodological basis as a set of scientific approaches.
- Considering ethno pedagogics as a factor of personality formation and development.
Research Questions
In our study, we attempted to analyse the ethno pedagogical system as a component of the regional education system and to define what place in the ethno pedagogical system is occupied by ethnic culture. Furthermore, we tried to reveal the specifics of the methodological base used to consider the phenomenon of ethno pedagogical system and to explain how the ethno pedagogical system is influenced by information in modern society. Another research question relates to ethno didactics as a direction in ethno-pedagogics.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the work is to consider ethno pedagogical theory as a factor in the formation and development of a successful personality. It is necessary to determine the potential of ethno pedagogics and the role of ethno pedagogical technologies in the formation of personality. Another purpose is to define the influence of information on the ethno pedagogical system and its development and to consider the features of the ethno pedagogical system functioning in conditions of its interaction with information space.
Research Methods
At the initial stages of this work, in order to determine the object and subject of research, we used the method of obtaining primary information, which consists in studying literature, documents and the results of ethno-pedagogical activity. Questionnaires and observation methods were used to obtain information on the typicality of some aspects of the phenomena studied. The method of studying and summarizing pedagogical experience was aimed at analyzing the state of ethno-pedagogical practice, identifying elements of a new activity of ethno pedagogues, the effectiveness and accessibility of relevant recommendations. Experimental training, which made it possible to verify in practice the theoretical principles obtained, acts as a complex method (Arsaliev & Taaev, 2019).
Using the totality of the research methods listed above made it possible to put into practice the most important conditions for any pedagogical research – the inclusion of the researcher himself in direct communication and direct interaction with teachers and students in a system where experimental work is carried out to verify theoretical positions; theoretical analysis of literary sources, official documents; study of reports, documents of meetings, conferences, publications in periodicals. The methods of the system-structural approach, analysis, synthesis, modeling, design, forecasting, observation, study, and analysis of the results of activities were used; pedagogical experiments. In substantiating the methodology of ethno didactics, we cannot rely on the theoretical positions of any particular science. Considering the interdisciplinarity of ethno didactics, we turned to the fundamental principles of philosophy and ethnophilosophy, pedagogy and ethno pedagogy, psychology and ethnopsychology, sociology and ethno sociology; analyzed their internal and external relations (Stambach, 2019). Having studied their dialectics, we concluded that the decisive factor in substantiating the methodology of ethno didactics is the combining universal and national principles in education.
If we talk about the research methodology, we used systemic, competence-based, cultural, and technological approaches. In accordance with the system approach, all the phenomena we study are considered as systems consisting of certain components and connections between them. For example, we consider a teacher’s professional culture as a system of competences, pedagogical system etc. We present ethno pedagogic technology as a system of operations (actions) etc. Competence approach involves the consideration of the knowledge, skills and abilities possessed by the individual as competencies that make up the competences system of an individual (Cohen-Scali, 2012; Wuttke & Seifried, 2017). Technological approach means that all actions and operations of teacher are presented not only as a system but also as a set, a sequence of operations. Ethno pedagogical technology represents the ethno pedagogical process, its base, principles, ideas, operations, contents etc. The cultural approach involves the consideration of the individual as part of culture and an active carrier of cultural knowledge (Kharitonova, 2020; Yakubovska, 2019). The formation and development of personality always takes place in a certain cultural space, which creates favourable conditions for personality formation and development.
Findings
As a result of our study, we examined the ethno pedagogical theory in modern conditions. The key concept of ethno pedagogical theory is the ethno pedagogical system, which is a set of elements that ensure the implementation of the ethno pedagogical process, and the relationships between them. The main goal of the ethno pedagogical system is to implement pedagogical goals based on the use of ethnocultural moments in the formation, development and upbringing of an individual.
Ethno pedagogical system as the basis for the functioning of ethno pedagogical environment
In our opinion, the system-forming element of the ethno-pedagogical system is ethnos, since it determines the features of this type of system (Pisarenko & Arsaliev, 2019). In this case, the ethnic group acts as a carrier of national characteristics, national character, national culture, including pedagogical elements. Therefore, the ethnic group is located in the centre of the system, providing all the connections of the remaining elements of the system. Each ethnos (collective of people), adapting to the conditions of life, develops its own stereotype of behaviour, therefore, the stereotype of behaviour can be considered as the foundation of an ethnic tradition, including cultural and ideological foundations, forms of dormitory and economy. In the personality of the teacher, we are primarily interested in the level of formation of ethnocultural competence, allowing the teacher to organize and to control the ethno pedagogical process.
In the student’s personality, we are interested in the initial level of ethnocultural knowledge formation, which will further develop and improve. The level of a student’s ethnocultural competence formation represents the goals of the ethno pedagogical process. The goals of the ethno pedagogical process (Fig. 01) are formulated in accordance with the competencies that the ethno pedagogue is going to form, develop and improve in student’s personality.

Characterizing this hierarchy of goals, we note that it considers all the features of the modern educational space and implements the unity of goals of the state, society, and the individual, the observance of which is one of the conditions for the success of any pedagogical system. The essence of ethnocultural competence, which is the systemic goal of the ethno pedagogical process, is that a person possesses knowledge, skills and abilities, identifies himself as a carrier of experience and knowledge in the field of ethnic culture and interethnic communication. The means by which it will be formed relate to the information technology support of the ethno pedagogical process. The information technology component includes:
The information component or ethnocultural content of training and education, which is the information component of ethno pedagogical technologies; a set and description of ethnocultural competencies (formed personality traits), the formation, improvement and development of which will be carried out in the course of the implementation of ethno pedagogical technology.
A technological component that contains everything related to the procedural part of ethno pedagogical technologies: the forms of organization of ethno pedagogization of the educational process; methods of forming ethnocultural competence (Lipsett-Rivera, 2018); control methods; means of ethno pedagogization of training and education; algorithms of the procedural part of ethno-pedagogical technologies that reproduce the sequence of actions in the ethno-pedagogical process.
Features of the ethno pedagogical system in the information society
The functioning of the ethno pedagogical system in modern society has a number of features related to the general orientation of modern society to interact with the information field. It is determined by the following:
- The uniqueness of the ethno pedagogical system of the region is determined by regional, ethnic and national characteristics.
- The development of regional ethno pedagogical system depends on the level of development of the regional educational system.
- The fundamentals of the regional ethno pedagogical system are defined by personal meanings characteristic of a given ethnic group.
- The level of openness of the regional educational system allows it to communicate with another regional education systems. The oopenness is the main condition of the system effectiveness.
- The level of security with access to information and means of its receipt has to be observed.
- The level of informational competence of a teacher and a student allows to make the interaction with the information field more effective.
Ethno didactics as a component of the ethno pedagogical system
The functioning of the ethno pedagogical system is carried out in a regional educational space. The ethno pedagogical system functions not only in the educational process. The uniqueness of this system lies in the fact that it functions constantly and everywhere. Indeed, the ethno pedagogical functions of the system are realized in a variety of ways. For example, if a child sees a woman dressed in a national costume on the street, reflecting the customs and traditions of this ethnic group, this will also be an ethno pedagogical situation, which must be used by the adult who is next to the child at this moment. This may be a teacher, parent, older brother or sister, grandmother, etc. Or another example – a child prepares dishes of national cuisine with his mother at home – this is also an ethno pedagogical situation. Based on the criterion of the emergence of ethno pedagogical situations, such situations can be spontaneous or specially prepared. And then it is necessary to include absolutely all the people who surround the child in the subjects of the ethno-pedagogical system. Thus, based on the criterion of spontaneity or preparedness of ethno-pedagogical situations, the component composition of the system will vary. The component composition of the ethno-pedagogical system that we offer is focused on the preparedness of the ethno-pedagogical process.
The uniqueness of the ethno pedagogical system lies in its focus on the persistent organization and use of ethno pedagogical situations. This is the complexity of the ethno-pedagogical process, which can occur and proceed spontaneously, or can be a prepared event. Ethno pedagogical interactions and relationships can be specially organized (knowledge, skills, experience acquired by the student during the educational process, participation in lectures, discussions, conferences, joint events, etc.) and spontaneous (knowledge, skills, experience obtained in educational situations that arise spontaneously, without preparation and development, or partially organized (knowledge, skills, skills and experience acquired every hour by a child in domestic and family relationships, in relations with peers, the older generation, various other people, other social institutions, in games and work, from the media, etc.) Educational institutions are called upon to influence the younger generation of the social environment, to communicate scientific, reliable knowledge aimed at creating a positive attitude towards their and other peoples, their history, cultures. The skill of an ethno pedagogue is manifested, first of all, in the ability to organize an ethno pedagogical process and its effective implementation. But even greater skill requires the use of spontaneous ethno-pedagogical situations for educational purposes. The ability to orient oneself, to feel the possibility of using ethno pedagogical moments, competence in the field of ethno culture, awareness of the traditions and customs of the ethnos, pedagogical instinct and a sense of responsibility for the younger generation are the keys to the effective use of any spontaneously arising situation for educational purposes. If we are talking about some cultural issues, the ethno pedagogue should be able to explain them, have knowledge of their origin, consider the age of the pupils when explaining and their possible awareness of these ethnocultural phenomena (Orsini-Jones & Lee, 2018).
If we are talking about a specially organized ethno pedagogical process, here the ethno pedagogue should turn to ethno didactics. Ethno didactics is one of the youngest areas of general didactics, engaged in the study of the experience of teaching. The concept of "ethno didactics" was introduced into science by Yalalov (2017) in a monograph published on the basis of many years of historical, pedagogical and experimental – experimental research, performed on the material of the peoples of the Middle Volga and Urals. It should be noted that ethno didactics in Russia has an almost centuries-old history. Back in the 30s of the XX century, S. Stebnitsky organized training for children of the peoples of the North in accordance with their ethnic nature, which in a short time of training yielded impressive results.
In modern conditions, the ethno didactic approach of the three-component structuring of the content of ethno-national education is successfully applied as an invariant methodology by the national education establishments. Ethno didactic teaching methods and techniques are used in teaching individual subjects as a technology of practice-oriented teaching.
Ethno pedagogics in system of factors influencing the personality formation and development
The problem of the personality and its development has various aspects. Therefore, it is considered by different sciences: philosophy, psychology, pedagogy, age physiology and anatomy, sociology, jurisprudence, etc. In particular, the problem of personality is one of the central in psychology. Personal development is one of the most complex and key issues of pedagogical theory and practice. The person is interesting for psychology from the point of view of its internal structure, patterns of occurrence, formation and development. Pedagogy studies and identifies the most effective conditions for the harmonious development of personality in the process of training and education. One of the most important professional qualities of a teacher is the ability to see each student as a person in his development, growing up, and becoming. Depending on what conditions prevailed in a particular theory of personality development, in psychology and pedagogy on this issue there were three main areas: biological, sociological (social) and biosocial (Culture and Personality, 2020).
- Representatives of the biological direction, considering the personality to be a purely natural being, explain all human behaviour by the action of needs, instincts and instincts inherent in him at birth (Z. Freud and others). Moreover, a person, obeying the requirements of society, constantly suppresses natural needs, "playing" the necessary social roles.
- Representatives of the sociological direction argue the opposite: although a person is born as a biological being, the main influence on his development is exerted by those social groups with which he communicates; it is social situations that determine behaviour and, accordingly, human development. Moreover, the lower the level of development of a personality, the brighter and sharper its biological features, instincts, etc. are manifested in it.
- Representatives of the biosocial direction, at first glance, reconcile two opposing points of view, believing that mental processes (sensation, perception, thinking, etc.) are of a biological nature, and the orientation, interests, and abilities of a person are formed as social phenomena. However, at the same time there is an artificial division of the personality, which cannot explain in any way either its behaviour or its development.
Modern science considers personality as a single whole, in which the biological is inseparable from the social. The development of the personality, as a process, is determined by both the psychophysical characteristics of the individual and the social situation in unity, as well as by the measure of his own activities aimed at self-development and self-improvement (Borovitskaya, 2020; Effendi, 2020).
The relations of social and biological in the formation and behaviour of an individual are extremely complex and have a different effect on them at different stages of human development, in different situations and types of communication with other people. The stages and patterns of development in each direction are theoretically and experimentally investigated in the corresponding sciences. In the educational process, these results are merged into a single system of multilateral development of students, which is mediated by the capabilities of the individual, the influence of the environment and the focused activities of adults. Thus, three general factors of personality development are distinguished: heredity, environment and education. The result of personality development depends on the coordination of actions of all three factors (Fig.02). In the diagram, point A0 conditionally indicates the harmonious development of the personality under the influence of all three, coordinated factors. Points A1 and A2 illustrate the inharmonious (distorted) development in case of insufficient influence of one and excessive action of another factor. Finally, point A3 characterizes the situation of insufficient development of the hereditary personality data both in the environment and in education. Therefore, personality development is a single biosocial process in which both quantitative changes and qualitative transformations occur, the birth of the new and withering away or transformation of the old. Factors of personality development are: heredity, environment and education. Heredity is the transmission of species features from one generation to another. Bearers of heredity are genes. It should be borne in mind that hard-coded signs are enough for the survival of animals, but not humans.
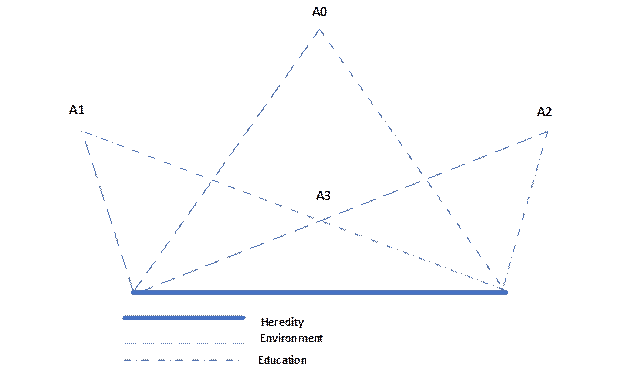
From a psychological and pedagogical point of view, it is important to remember that it is not human abilities that are inherited, but only inclinations. In addition, we must not forget about the existence and unfavourable for the development of personality inheritance, due to various reasons (parental alcoholism, drug addiction, radiation exposure, adverse environmental environment, etc.). Therefore, when considering hereditary traits, the main thing is to create equal conditions for the development of personality. The environment is a complex system of external circumstances necessary for human life and development (geographical, social, informational, ...) (Manyeruke & Cakici, 2017). A person is not born a personality, he becomes it in the process of interaction with the social and natural environment, with the material and spiritual circumstances of his life and work.
Among the social circumstances that play a leading role in the formation of personality, the following can be distinguished:
- Macro-social environment – the social system, the level of development of society and its capabilities to ensure the life and work of people, the impact of the media, socio-political, ethnic, religious conditions in society, etc.
- Microsocial environment – the environment of direct contact interaction of a person: family, friendly company, school class, student group, labour collective, etc. – social interaction in all its varieties, primarily activity and communication with other people.
- Artificial environment – modern technology, technologies for its production and operation, by-products of modern production, information technology environment created by radio, television, the Internet, etc. (The nature and extent of this impact on humans is only partially studied at the moment nevertheless, the importance of this circumstance in the modern development of society makes us single it out into a separate category).
The personality herself plays a special role in his formation and development as one of the most important conditions for the manifestation of all external and internal influences on a person. Therefore, when studying the impact of the environment, it is necessary to consider two points: the nature of the impact of external circumstances and the activity of the personality itself, responding to them. It is necessary to form the correct attitude to internal and external conflict, to develop a person’s resistance to external negative influences (Batarchuk, 2019). Parenting is a specific factor in the development of personality that can correct the influence of the environment and heredity (Nedogreeva, 2017). Unlike factors of heredity and the environment, acting unconsciously, education is a specially organized process of the formation and development of a person, which is based on the consciousness of a person and requires his participation. This is both the strength and weakness of the educational process.
To understand the value of each factor of personality formation and development we have made a survey among school teachers, students and teachers of higher educational institutions of the Chechen Republic had to answer only one question:. The results are presented in Table 1.
The survey has shown that all three categories of respondents believe that the environment is more important than heredity and upbringing. Higher school teachers approach the question more professionally, one might say, even more scientifically.
If we consider these three factors that influence the formation and development of the personality, in terms of their connection with the ethno pedagogical theory, then we can determine that all three factors are closely related to it. Heredity is based on ethnically determined characteristics (Maffini & Wong, 2015). The environment surrounding the person is the environment of the region, an environment that has all ethnic and national characteristics. Parenting is a process that is also based on the use of national and ethnic traditions and customs of upbringing.
Conclusion
At the present stage, ethno pedagogical theory is one of the factors influencing the formation and development of personality. The ethno-pedagogical space in which the formation and development of personality takes place has a potential based on national and ethnic customs and traditions. Ethno-cultural experience, transmitted from generation to generation, contributes to the formation of personal meanings, which form the basis of views, behaviour, worldview (Small, 2016; Stefanenko & Kupavskaya, 2010).
In ensuring the successful functioning of the ethno pedagogical space of the region, it is always necessary to consider the ratio of universal and ethnic values. A major role in this is played by the successful development of ethno pedagogical theory, which offers a scientific and theoretical systematization and understanding of ethnocultural phenomena that have educational potential.
The scientific approaches and research methods used allowed us to consider the ethno pedagogical space as a system, the ethno pedagogical system in its composition, the ethnocultural competence of the individual as a result of the functioning of the ethno pedagogical system (Arsaliev, 2019b).
We have determined the following functions of ethno pedagogical theory in the formation and development of personality in the region:
- Systematizing, it lies in the fact that the ethno pedagogical theory combines the facts and phenomena of public education with the aim of systematizing, explaining and justifying them;
- Consolidating, it consists in the fact that ethno-pedagogical theory becomes the basis on which the rallying and unification of representatives of an ethnic group takes place to preserve their ethnic and national identity;
- Generating, the meaning of which is that an ethno pedagogical theory, analysing ethnocultural facts, substantiating them from historical, pedagogical and ethnographic points of view. generates new scientific knowledge, providing researchers with the opportunity to cognize and at the same time creating conditions for the further development of ethnic culture;
- Communicative, based on the idea that an ethno pedagogical theory is capable of serving the interaction, unification, mutual enrichment of nations and ethnic groups based on constant contacts.
As the study showed, the leading factor in the successful formation and development of personality is the environment. However, the universality of ethno-pedagogical theory lies in the fact that it is directly related to all three factors that determine the success of personality formation. Ethnic and pedagogical features of the upbringing of the young generation are passed on through heredity from generation to generation (Kuzmina & Danilova, 2016). The environment is an ethno pedagogical environment in which the formation of personality takes place. Education is carried out again using ethno pedagogical techniques and technologies.
References
Arsaliev, S. (2019a). Ethno Pedagogical Technologies In Regional Education Environment. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioral Sciences, 58. DOI:
Arsaliev, S. (2019b). Personality Formation And Development In Ethno Cultural Proces. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioral Sciences, 76. DOI:
Arsaliev, S., & Taaev, I. (2019). Ethno cultural competence in professional development of teachers. ICERI 2019, Proceedings. DOI:
Batarchuk, D.S. (2019). The Role Of Ethno-Cultural Knowledge In The Development Of Multicultural Student’s Personality. DOI:
Borovitskaya, J. V. (2020). Revival of Folk Crafts as a Factor of Students’ Ethno-Cultural Competencies Formation in the System of Additional Education. Ethnic Culture, 1(2), 30–33. DOI:
Builo, B. (2020). N. Berdyaev about the main trends of Russian intellectual thought in XIX century. The human. and soc.-econ. Sci., 111(2), 20–24. DOI:
Cohen-Scali, V. (Ed.). (2012). Competence and Competence Development. DOI:
Culture and Personality. (2020). Encyclopedia of Personality and Individual Differences (pp. 977–977). DOI:
Effendi, M. (2020). Strengthening of National Identity Through Personality Development Based on Ethno-Pedagogy at Higher Education. Int. J. of Psychosocial Rehabilitat., 24(04), 2548–2559. DOI:
Kharitonova, S. A. (2020). Ethno-Cultural Education in the Republic of Buryatia: Problems and Prospects of Solution. Ethnic Culture, 1(2), 53–57. DOI:
Kuzmina, E. K., & Danilova, O. A. (2016). The development of ethno-cultural competence of the students in non-language high school. Turkish online J. of design, art and communicat., 6(JLYSPCL), 1027–1031. DOI:
Lipsett-Rivera, S. (2018). The Culture of a Multi-Ethnic Colony. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Latin American History. DOI:
Maffini, C. S., & Wong, Y. J. (2015). The Culture of a Multi-Ethnic Colony. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Latin American History. DOI:
Manyeruke, G., & Cakici, E. (2017). Ethnic identity formation, self-esteem and psychological symptoms among third culture individuals. PONTE Int. Sci. Res. J., 73(8). DOI:
Nedogreeva, N. G. (2017). Ethno-Cultural Approach to the Formation of Personality of Students. Philosophy. Psychol. Pedag., 17(4), 483–487. DOI:
Orsini-Jones, M., & Lee, F. (2018). Intercultural Communicative Competence (ICC) Revisited. Int. Communicat. Competence for Global Citizenship, 2, 7–23. DOI:
Pisarenko, V., & Arsaliev, S. (2019). Use of ethno cultural elements in educational process. INTED2019 Proceedings. DOI:
Small, S. (2016). Culture, structure and black youth diversity. Ethnic and Racial Stud., 39(8), 1445–1449. DOI:
Stambach, A. (2019). Ethnology Unboxed. Ethnologies, 40(2), 111–129. DOI:
Stefanenko, T. G., & Kupavskaya, A. S. (2010). Ethno-Cultural Competence as a Component of Competence in Communication. Psychol. in Russ.: State of Art, 3(1), 550. DOI: 10.11621/pir.2010.0027.
Volkov, G. (1999). Ethno pedagogics. Publ. center “Academy“.
Wuttke, E., & Seifried, J. (2017). Competence, Teacher Competence and Professional Error Competence: An Introduction. Professional Error Competence of Preservice Teachers, 1, 1–14. DOI:
Yakubovska, M. (2019). Cultural Paradigm of Modernity: the Basic Formation of Culture of Personality. Sci. Notes of Ostroh Acad. National Univer.: Psycholo. Ser., 1(8), 35–39. DOI:
Yalalov, F. G. (2017). Ethno-didactic method of organization of teaching. Alma Mater. Vest. Vysshey Shkoly, 9, 90–93. DOI:
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
17 May 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-106-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
107
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2896
Subjects
Science, philosophy, academic community, scientific progress, education, methodology of science, academic communication
Cite this article as:
Arsaliev, S. (2021). Ethnopedagogical Theory As A Factor In Personality Formation And Development. In D. K. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Knowledge, Man and Civilization - ISCKMC 2020, vol 107. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1879-1891). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.05.249

