Prerequisites For A Competency-Based Approach To Evaluating Competencies Of Successful Entrepreneurs
Abstract
This research examines forming key competencies of entrepreneurs, as far as the authors believe that these competencies function as the fundamental factor determining the effectiveness of mastering the various support forms by business entities. The hypothesis of the research is that in modern conditions, especially in the conditions of COVID-19, the business community needs not just support measures, but digital support measures. Therefore, it is advisable to study such aspects as structuring flexible and soft skills or competencies of entrepreneurs. Consequently, the subject of the research is defined as the relationship between professional and supra-professional competencies that determines the forming and development of a successful entrepreneur. This allows us to define the purpose of the research as the identification of key groups of competencies of business entities focused on effective business management. It should be noted that in author's opinion it is necessary for a successful entrepreneur to form meta-competencies in addition to professional (hard skill competencies) and supra-professional (soft skill competencies) competencies. The article gives characteristic of each group of competencies, reflects their relationship with business processes, management system, external and internal environment. This research has mostly a staged nature and indicates the groundwork for further comprehensive research, which involves assessing the expectations of entrepreneurs in the field of digital forms of support and substantiating supra-professional and professional competencies, on the one hand, as dynamic skills and abilities of a successful entrepreneur, on the other hand – as a priority requirement for an effective employee of the "future".
Keywords: Supra-professional competencies, professional competencies, entrepreneur
Introduction
In a market economy the business entities are the main driving force of the country's economic system. They form the economic environment and, to a large extent, they are responsible for the country's competitiveness and innovation activity in the world market. In turn, the public sector should provide an adequate environment for the functioning of business structures, allowing them to maximize their potential.
Currently, the policy of support for business in Russia involves the implementation of various forms that contributes to the development of the target groups entities: financial-credit, property, information-analytical, educational and so on.
In our opinion, in the last decade, the mechanisms and forms of educational and informational support for business have become particularly important due to the following circumstances. Firstly, the modern economy demonstrates the increasing role of the entrepreneur's personal qualities (his or her knowledge, skills and the ability to apply them) in determining the current business performance and its prospects in a highly competitive market. Secondly, the dynamically evolving functioning environment determines the high speed of changes in the competencies necessary for functioning in modern markets, which require prompt and timely updating.
Thus, we can confirm the validity of Lache's (2011) opinion according to whom, competence is «a dynamic concept that involves taking actions, adjusting to the environment and changing the firm's internal and external environment ().
Problem Statement
The modern system of professional education, both for higher education specialists and those, who are at the level of professional training, is focused on obtaining by the entities a specific set of competencies that determine their ability to implement the necessary set of functions.
Competencies, in contrast to skills, have a broader meaning, including in addition to the latter also the totality of the individual's knowledge and his or her direct ability to implement appropriate actions. An analysis of an entrepreneur's potential from the perspective of a competency-based approach will more accurately reflect reality than from the perspective of solely his or her skills. Thus, the issue of this research can be defined as the definition of an entrepreneur's competencies focused on effective business management.
Research Questions
The subject of the research is the relationship between professional and supra-professional competencies that determine the forming and development of a successful entrepreneur.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the research can be fairly defined as the identification of key groups of competencies of business entities focused on effective business management.
Research Methods
The used research methods are desk analysis, synthesis, comparative analysis of literary sources, methods of graphic interpretation.
Findings
As a rule, professional competencies aimed at direct work within the economic operations tend to attract the most attention, however, the importance of the so-called soft skills is also of high significance.
Competence represents a set of knowledge, proficiencies and skills that determine the ability of a person to perform a certain functional activity.
The division of competencies into groups of professional (hard skill competencies) and supra-professional (soft skill competencies) allows you to form a certain set of requirements for the qualification of representatives of the business environment, however, in modern conditions, it is relevant to expand this complex by adding a group of meta-competencies (Cruz-Hinojosa & Gutiérrez-de-Mesa, 2016; Goerzig & Bauernhansl, 2018; Nguyen & Burgess, 2014).
Meta-competencies are a system of knowledge, proficiencies and skills to increase the level of mastering and acquire new supra-professional and professional competencies during the working life, as well as determine the entrepreneur's abilities to anticipate the necessary set of lower-order competencies in advance.
Some authors have proposed the use of the term Contextual Competence (Motamedi, 2018), citing its defining ability of the individual to conduct a full-fledged analysis of the context, namely, a set of factors that have a direct and indirect impact on decisions (including in the long-term aspect).
An entrepreneurial activity is unique in terms of competence requirements (Mattayang et al., 2019). This fact is determined by the specifics of the entrepreneur's activity: the business activity of the entity implies the implementation of a full set of functions for managing and distributing all available resources, as well as timely decision-making and responsibility for them both in the current moment and in the long term (Torres-Toukoumidis et al., 2019).
Thus, the entire set of competencies that an entrepreneur must have in order to effectively run a business can be divided into three groups: Hard Skill Competencies, Soft Skill Competencies, and Meta-competencies.
The first group describes the professional skills of a business entity, reflecting his or her knowledge, proficiencies and mastering the skills of work in specific subject areas: management and personnel motivation, financial management, basic accounting and tax accounting, business planning, management of production resources and process, marketing and sales management, as well as knowledge of the main features of «his or her» sphere (Sudirman et al., 2020). The analysis of the level of mastering this group of competencies can be carried out quite simply even by the entrepreneur himself or herself with the help of a significant number of practice-oriented professional tests in the relevant fields of knowledge. Moreover, entrepreneurs themselves are often able to accurately identify areas in which they have a lack of knowledge in the process of doing business.
The second group-Soft Skill Competencies-determine the personal qualities of an entrepreneur that determine the success of his or her enterprise and are identical, regardless of the size or specifics of the business. This group of competencies includes the skills of goal setting, delegating of responsibility and decision-making, effective communication at all levels, leadership, creative thinking, searching and analysing the necessary information, as well as knowledge of mechanisms and the potential for implementing the described actions. The object that the business entity's attention is focused on when implementing this group of competencies is the social component of its environment, which allows creating effective channels of interaction that open new opportunities for the organization.
In contrast to professional competencies, it is more difficult to measure the level of mastering the general competence (although such attempts are regularly made by scientists from different countries (Riyanti et al., 2016).
Meta-competencies determine the proactivity of a business entity, its adaptability to new conditions of a dynamically changing external environment, as well as its ability to «anticipate» the future market opportunities, consumer requirements and industry trends. This group is the most difficult one for verbal defining as well as for defining its components and their characteristics.
Meta-competencies are the second-order competencies that determine the ability of an entity to master new Soft and Hard Skill Competencies which are necessary for functioning in qualitatively different markets, creating innovative products and forms of business. Based on the results of the analysis, the following competencies were identified within this group: personal time management and personal efficiency, skills of adaptation to changing environmental conditions, the level of development of social intelligence and intuition, skills of analysis and working with trends, as well as identifying future needs of consumers, skills of creating value (sense making).
The result of the analysis made it possible to identify the appropriate pool of competencies that a modern entrepreneur should have (fig. 1). In a dynamically changing environment, this list is not exhaustive, but it defines the most important skills and knowledge that a business entity needs to carry out economic activities.
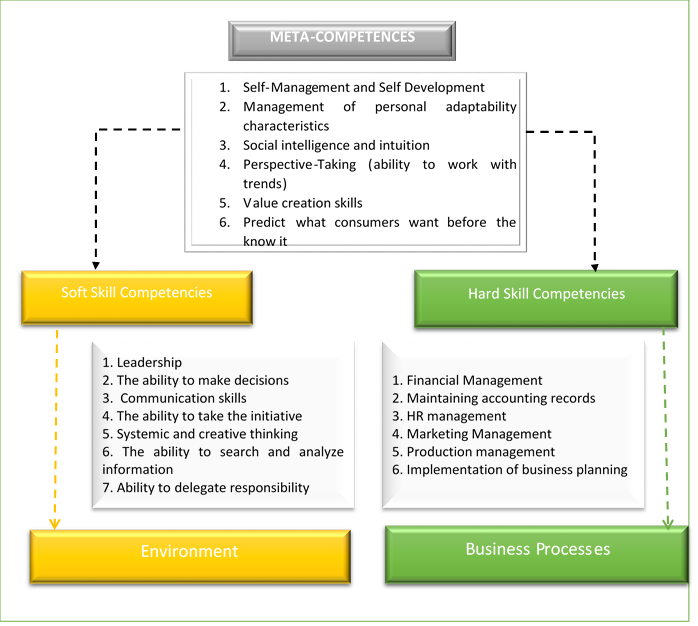
Shown in figure 1 a set of first-and second-order competencies is intended to serve as a target reference at the stage of forming programs for implementing information and educational support for business entities that can effectively compete in the modern market.
Conclusion
The issue of forming entrepreneurial competencies affects the field of scientific interests of many researchers (Leithy, 2017; Riyanti et al., 2016; Sudirman et al., 2020) who consider both aspects of forming entrepreneurial competencies depending on the growth and development of business structures, and attempts to build models of competence matrices of successful entrepreneurs. In this context, we believe that to ensure the necessary level of timely development of relevant competencies by entrepreneurs, it is necessary to form appropriate channels for the transfer of knowledge and skills between subjects and objects of the educational system. Taking into account these requirements, digital forms of support for business development that actively use the opportunities of using information technologies and distance (including online) forms of education will be the most appropriate.
However, the effectiveness of such programs depends not only on the correct channels for transmitting information. This process also requires a thorough analysis and identification of entrepreneurs' expectations and requirements for obtaining specific knowledge and skills that they currently possess in an insufficient level.
References
Cruz-Hinojosa, N. J., & Gutiérrez-de-Mesa, J. A. (2016). Literature review of the situation research faces in the application of ITIL in Small and Medium Enterprises. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 48, 124–138. DOI: 10.1016/j.csi.2016.05.001
Goerzig, D., & Bauernhansl, T. (2018). Enterprise Architectures for the Digital Transformation in Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. Procedia, 67, 540–545. DOI:
Lache, C. (2011). Competence management. The yearbook of the Gheorghe Zane Inst. for Econ. and Soc. Res., 20(2), 123–131.
Leithy, E. (2017). Towards Creating an Entrepreneur Competencies Model. J. of Entrepreneurship & Organizat. Manag. https/doi.org/
Mattayang, B., Syam, H., Akib, H., & Amiruddin, M. S. (2019). Snapshot Level of Principal Entrepreneurs Competency. Proc. of the Inter. Conf. on Soc. Sci. DOI:
Motamedi, K. (2018). Contextual Competence. Int. J. of Busin. and Manag., VI(1), 26–35.
Nguyen, T., & Burgess, S. (2014). A case analysis of ICT for knowledge transfer in small businesses in Vietnam. Int. J. of Inform. Manag., 34(3), 416–421. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2014.02.009
Riyanti, B. P. D., Sandroto, C. W., & Warmiyati, M. T. D. W. (2016). Soft Skill Competencies, Hard Skill Competencies and Intention to Become Entrepreneur of Vocational Graduates. Int. Res. J. of Busin. Stud., IX(02), 119–132.
Sudirman, I., Joko, S., & Aisha, A. (2020). Software entrepreneurs’ competencies based on business growth. J. of Res. in Market. and Entrepreneurship, Ahead-of-print. DOI:
Torres-Toukoumidis, A., Robles-Bykbaev, V., & Cajamarca, M. (2019). Gamified Platform Framing for Entrepreneur Competencies. J. of Entrepreneurship Ed., 22, 1–9.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
17 May 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-106-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
107
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-2896
Subjects
Science, philosophy, academic community, scientific progress, education, methodology of science, academic communication
Cite this article as:
Sinyuk, T. Y., Lobakhina, N. A., Prokopetz, T. N., Komarova, S. N., Zhuravleva, O. G., & Rybalko, Y. A. (2021). Prerequisites For A Competency-Based Approach To Evaluating Competencies Of Successful Entrepreneurs. In D. K. Bataev, S. A. Gapurov, A. D. Osmaev, V. K. Akaev, L. M. Idigova, M. R. Ovhadov, A. R. Salgiriev, & M. M. Betilmerzaeva (Eds.), Knowledge, Man and Civilization - ISCKMC 2020, vol 107. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 1494-1499). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.05.197

