Abstract
The research aims at solving a multidisciplinary scientific problem – justification of modern forms of development of domestic tourism of the ethnic region based on a combination of historical, cultural, gastronomic, sociological and economic approaches. The object of the research are internal and external tourists and local residents. The directions of development of new non-industrial types of activities in depressive territories of the Republic of Karelia aimed at improving the quality of life of the population alienated from the receipt of economic and natural rent have been substantiated. This article presents an empirical study using the sociological method of exploratory type (formalized interview) and questionnaire survey method. The development of ethno-cultural tourism on the basis of culinary specialties is a perspective direction of domestic tourism as a factor of socio-economic development of border regions. The development of innovative modern forms on the basis of national identity contributes to the development of regional community, as well as diversity and strengthening of interethnic relations, which leads to the development of Russian society. As a result of the research, the authors draw conclusions about high attractiveness and significance of culinary tourism for the region's residents and incoming tourists. The article presents recommendations for the interested parties on increasing attractiveness of their tourist objects. According to the majority of respondents, from the economic point of view, it will positively influence the development of the Republic of Karelia.
Keywords:
Introduction
Looking at the socio-economic condition of Russian peripheral regions, it should be noted that their industrial potential is quite low. In the Republic of Karelia, which belongs to this category, there is a decline in population, its rapid aging, underdeveloped infrastructure, and social vulnerability (Kozyreva et al., 2018).
These problems are an argument for finding new directions in the development of this territory. Statistics on population and number of organizations by regions of the Republic of Karelia for 2015-2018 are presented below (Figure
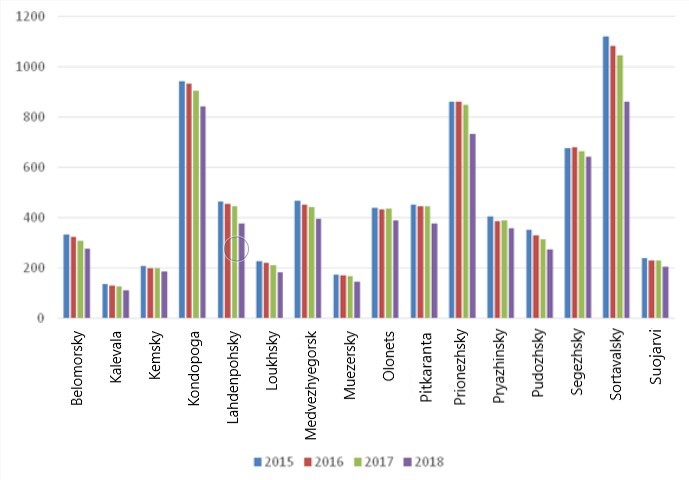
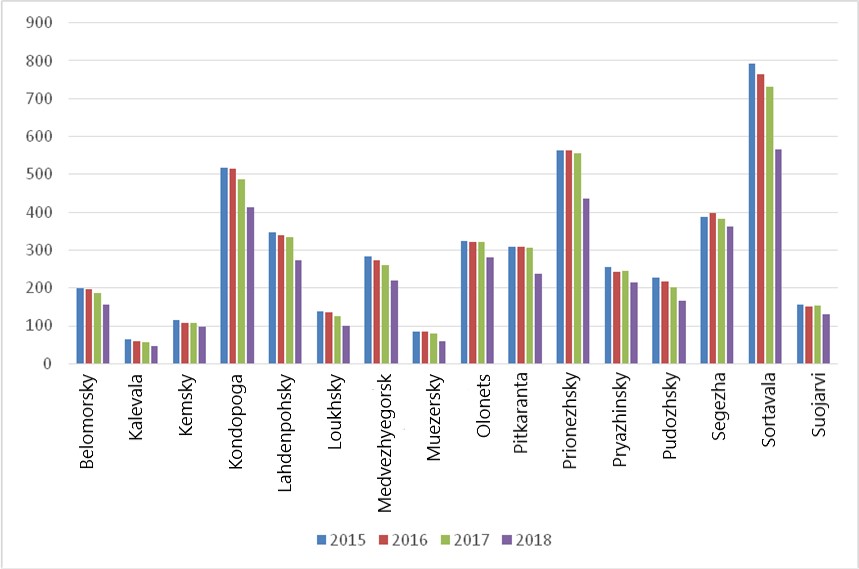
As we can see in Figure
This research considers culinary tourism one of the promising areas in the Republic of Karelia. Because of active development, tourism is called an economic phenomenon of the century. In many countries it plays a significant role in the formation of GDP, additional jobs, employment. Tourism has a great influence on various branches of economy (e.g., construction, agriculture, transport). It acts as an accelerator of social and economic development. Perhaps tourism will be the economic stimulus that can revive interest in regional identity, help local agricultural producers to establish new ties and markets for their products, improve the welfare of small local businesses.
Problem Statement
Tourist business in the Republic of Karelia is represented mainly by non-residents – these are Moscow and St. Petersburg companies. Local agents occupy secondary positions. At the same time they could occupy a legitimate niche in the market by joining the development of culinary tourism.
In the conditions of inequality of Russian regions and weak economic development the growth of popularity to the topic of gastronomic tourism is an urgent issue. But the institutional environment in Karelia is not conducive to this development. Companies that participate in public procurement by the seller of goods are not divided into local (RK) and external (other regions of Russia) market agents. All participants in such purchases are equal. It is necessary to strengthen the position of regional companies from the legislative side. One of the options to support initiatives may be to develop a system of benefits and incentives for local producers and travel agencies in this area. The following options are proposed:
Development of "culinary tourism" considering that tourists prefer to get acquainted with the culture with a help of national cuisine (no matter if they eat in a restaurant or buy local products in a shop).
Development of "culinary tourism", includes tastings and master classes, various forums for advanced training and introduction to new recipes.
Gastronomic tourism involves not only national dishes tasting, but also full acquaintance with cooking technology. Some professional participants of the culinary market consider the purchase of gastronomic tour as an opportunity to improve their skills and undergo professional training. As a rule, foreign tourists in Russia are offered to visit specific restaurants and cafes, take part in tasting dishes and drinks of the cuisine of Russians (Generalova, 2018). Some tourist firms offer foreign travelers to visit agricultural enterprises. The purpose of such events is to form a belief in complete ecological safety of products. Some Russian cities have opened thematic museums with tasting rooms. Possibilities of culinary tours allow local producers to promote their products on the market (Morozov, 2019).
An event or festival culinary tour aims to visit a specific event or gastronomic festival that is periodically held all over the world and is very popular. They play an important role in introducing tourists to local traditions, providing an opportunity to feel the authenticity of the local lifestyle in a pleasant atmosphere (Nekhaeva & Terekhova, 2015).
In the last two decades, Russian citizens have been visiting various Western and Eastern countries where culinary tourism is quite developed. Domestic tourism is gaining popularity at an active rate. Russia is rich in a variety of different ethnocultures, and each has its own peculiarities and culinary traditions (Berketova & Polyakova, 2018).
The development of gastronomic tourism in Russia is hindered by the lack of interaction between tourism companies and producers (Bogatyreva, 2016). Creation of necessary infrastructure for tourism development requires investment from companies. In some regions, including Kazakhstan, one of the problems for the development of culinary tourism is the lack of a common topic for organizing tours.
At the moment, festival forms with an ethnic orientation are actively developing. Within the framework of these festivals, there is a practice of organizing fairs by both large and small farms. It is culinary tourism that can make any tour more attractive, so it is a certain quintessence of national cultural traditions, history of the region, etc. However, there is a big problem – the lack of modern tourist infrastructure (Stepanova & Shulepov, 2018b).
In the Republic of Karelia the situation with the development of gastronomic tourism is in its infancy. There is a need for tourists to study local cuisine because of the simplicity and habituality of the ingredients that make up local dishes. Interest in the original culture of the region and wildlife of Karelia is steadily growing. If earlier this territory was associated exclusively with "wild tourism", now organized tourism is gaining popularity. In 2017 780 thousand organized tourists visited Karelia, which is 3% more than in 2016 (according to the data of the Tourism Department of the RK and KareliaStat).
Culinary festivals are now held in Karelia, which have an element of culinary tourism. In particular, a major holiday is held in the city of Sortavala called "Karelian Gate", which is held since 2014. In 2015, an attempt was made to bake the largest gate in the world. Another interesting festival is the "Kindasovo" festival of humor, which also includes a culinary part. Every year in Petrozavodsk there is a fish festival "Kalakunda", where a tourist is provided with conditions not only for fishing, but also for tasting various fish and other dishes. Many district festivals have a culinary element.
Actively developing fair activity is known in Karelia for a long time. Examples include fairs in Veskelice, Zaonezhye (Shunga, VelikayaGuba), theVeps culture festival "Tree of Life" and so on. That is, culinary brands of small territories are gradually being created (Maximenko & Komarevtseva, 2017). Separate methods of cooking (e.g., fish in milk) and food preservation techniques were borrowed from the local population and this shows very significant gastronomic experience (Nikolskaya, 1989). It should be also noted that it was planned to allocate 463 million rubles from the budget of Karelia for the development of the agro-industrial complex in 2019 (according to the Ministry of Agriculture of Karelia). It is expected that part of these funds will become a good stimulus for the development of culinary tours, in particular, one of its directions – excursions to production.
If we talk about international cooperation, the Republic of Karelia has an export support center on the basis of the Karelian Development Corporation (KDC). According to the Deputy Director of KDRC, now in the field of culinary science there is a program aimed at developing the export of standardized blueberry extract to Korea. Firms "Mama Karelia", "Berries of Karelia", "Fair" and others are actively working on export. There are many cooperation programs with Finland, Sweden and so on. During the last decade many commodity producers have appeared in Karelia, which offer local products. Unfortunately, financial support of these companies from the region is not enough (Stepanova & Shlapeko, 2018a).
Research Questions
The subject matter of the study is socio-economic, socio-cultural inequality of regions, as well as lack of competent institutional environment.
At present, Russia is experiencing stagnation in its socio-economic development. There is no good reason to speak of an increase in the standard and quality of life of the population, real incomes, housing provision, overcoming poverty, and an acceptable level of socio-economic inequality. Russian regions demonstrate significant territorial differentiation due to natural conditions and geographical location, unequal distribution of productive forces, inefficient budget policy and weakness of regional authorities. Successful regions have formed a vast segment of depressed territories, which concentrate entire enclaves of socially depressed areas. Despite the presence of natural resources, there are processes of decline in living standards, marginalization and degradation of the population. The economy is disconnected from local communities. Businesses operating in such areas have a 'colonial' policy (Kozlovsky, 2019).
It should be noted that many travel agencies in Karelia are not residents. The legal address of the vast majority of travel agencies are located in Moscow and St. Petersburg, and, consequently, tax payments are not allocated to the regional budget. Over the past 100 years, the culture of Karelia has lost much of its identity. Development of culinary tourism can become an excellent practice of popularization of knowledge about the cultures of indigenous peoples of Kazakhstan, as well as create conditions for self-identification and pride in their small homeland. Over the past twenty years, the number of Karelians, Veps and Finns in the Republic of Karelia has been declining rapidly and, therefore, any support for elements of the national culture of the region is positive. The development of culinary tourism may lead to increased interest in the indigenous cultures of the region, to strengthening of regional identity, which will attract new flows of tourists. Besides, its development can contribute to the development of small business and agriculture in the region.
Purpose of the Study
The main objectives of the research are to study the necessity and role of gastronomic tourism and its impact on the economy of the region and to prepare recommendations for stakeholders on the development of their tourism services.
Research Methods
With the help of the logical method, the necessity of development of tourist destinations on the basis of gastronomic peculiarities of the region has been investigated.
Findings
In 2019 a sociological survey on the development of culinary tourism was implemented, a database was created and registered. The aim of the survey is to assess the demand for the product of culinary tourism. The survey was conducted in the Internet on GoogleForms platform among the residents of Karelia, some regions of Central and North-Western Russia, as well as neighboring countries, in particular Finland, Estonia, CIS countries and others. The total number of respondents is 250 people.
The sample of respondents participating in the poll is presented in the table
Among the total number of respondents, about one third regularly eat dishes and products of Karelian, Veps, Pomeranian, Finnish and Sámi cuisine. Half of the respondents have tried such dishes. A quarter of the respondents have never tasted such dishes.
Figure
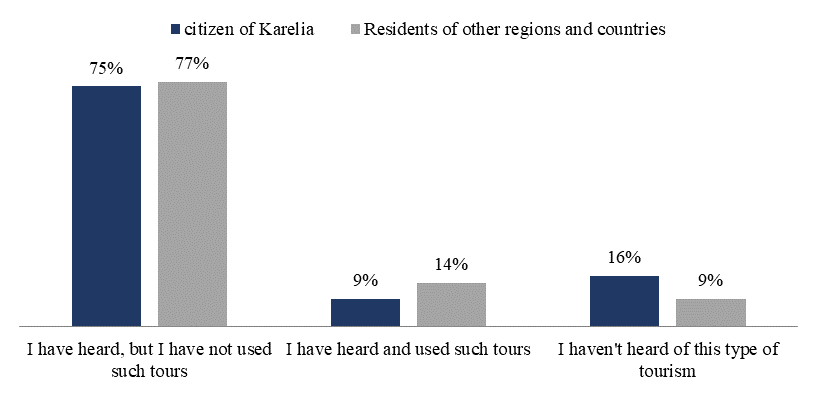
The survey results show quite a high percentage of respondents' awareness. Thus, 76% of respondents have heard something about this type of tourism. At the same time, the share of consumers of gastronomic tourism products among informed respondents is only 9% from Kazakhstan and 14% from other regions. In general, 16% of local residents of Karelia and 9% – from other regions have not heard anything about this type of tourism.
As the survey results show, the main motive for respondents to participate in gastronomic tours is to study local culture and traditions through national cuisine (Figure
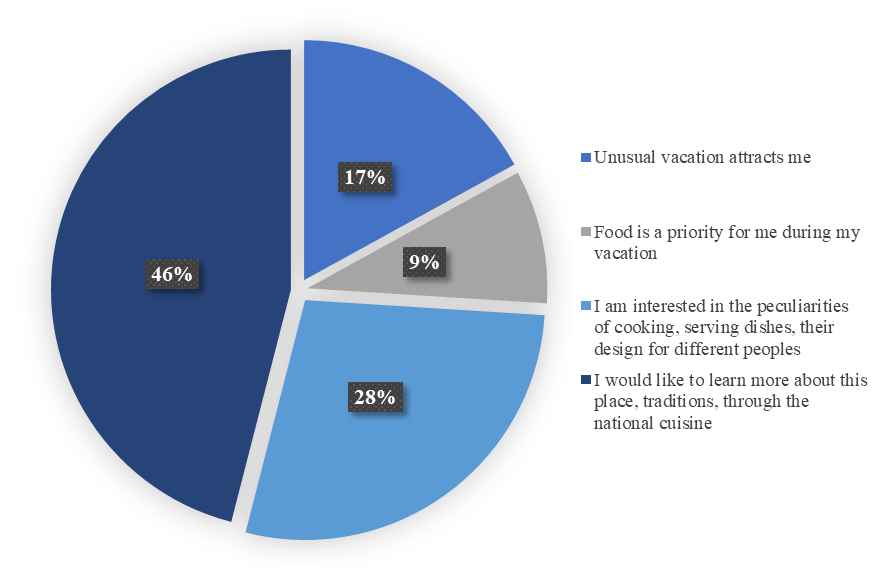
Features of cooking, familiarity with the recipe is of interest to the surveyed tourists in 27% of cases. Culinary tourist product gives an unusual holiday experience. This option is noted in 18% of responses. And only in 9% of answers potential tourists are attracted only by "food". Thus, for the majority of respondents culinary tourist product is not just a means of meeting the need to "feed one's hunger ", but is associated with interest in the local culture and is the reason to talk about the demand for it among tourists visiting the Republic of Karelia.
As it was mentioned above, the development of culinary tourism may become a stimulus for the development of agricultural businesses in the Republics of Karelia (Figure
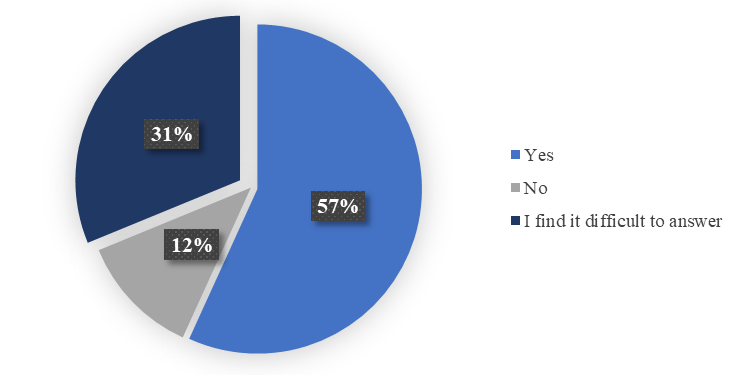
As it can be seen from Chart 5, more than a half of respondents (57%) believe that the development of this kind of tourism can indeed have a positive impact on the position of local agricultural producers. Unambiguously "no" was answered by 12% of respondents. A considerable number of respondents (31%) found it difficult to answer. This distribution of answers corresponds to the real situation on the market of tourist services, based on the ties established for many years in the system of gastronomic business. In many regions, the restaurant business tends to have its own supply connections, and purchases are made through large chains. Local farmers, being able to offer a higher quality natural product, are losing out in the "cost of the question".
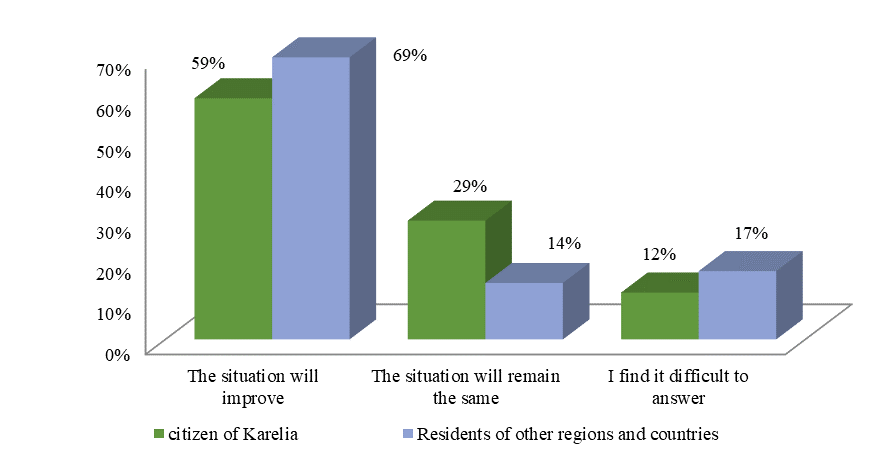
In this context, the question arises as to how the development of gastronomic tourism may affect the economy of the Republic of Karelia (Figure
The survey results show that the majority of respondents both in Karelia and other regions believe that economic situation in the region will improve. However, residents of other regions were more optimistic than local residents (69% vs. 59%). Almost 1/3 of respondents from Karelia supported the assessment "the situation will remain the same". Among respondents from other regions only 14% hold this position, i.e., almost twice as little. 12% of Karelia residents and 17% of respondents from other regions found it difficult to answer.
Acceleration of the culinary activity of the tourist business in the region will not have a significant effect on improving the economic condition of the Republic of Karelia. Nevertheless, the growing demand for gastronomic tourist products may give an impetus to local companies. When asked whether it is necessary to develop culinary tourism in the Republic of Karelia, 82% of respondents answered affirmatively. Of these, 76% believe that local residents will use such tours. In other words, there is a need for such tours among the local population. At the same time, some comments on the Internet showed that this question is not unambiguous. There is a widespread opinion that the influx of tourists may affect the ecological situation in the region, harming lakes, rivers and forests.
Infrastructure component is important in organization of gastronomic tours (figure
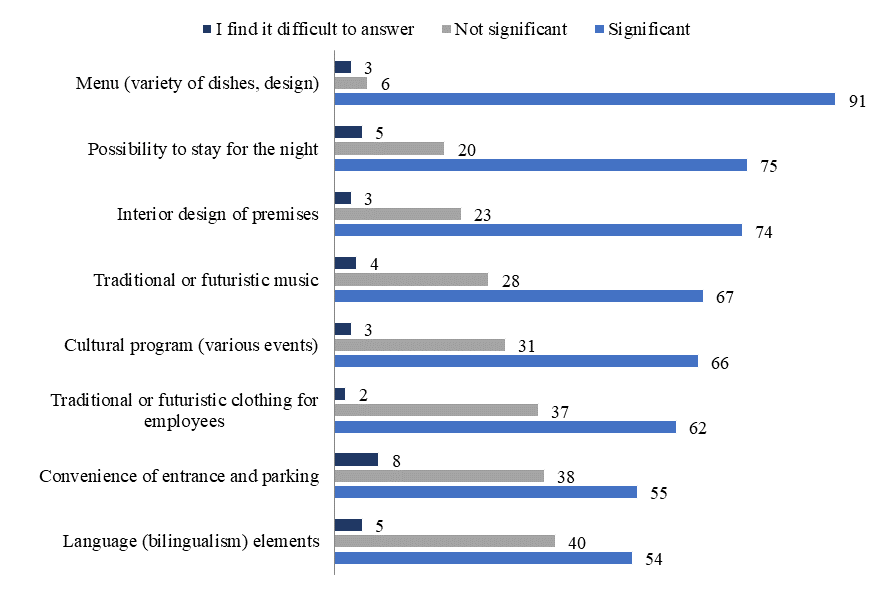
As can be seen from the survey, almost all elements of infrastructure are important for respondents. According to the survey data, the most important element is the design of the kitchen itself – variety of dishes, design, etc. This position was supported by 91% of respondents. For many respondents (75%) it is important to be able to stay overnight. For 74% it is important to design rooms. The Karelian or Vepsian decoration creates additional comfort. A good example is the restaurant "KarelskayaGornitsa" in Petrozavodsk, which attracts tourists with its interior, music and northern cuisine. More than half of the respondents are interested in providing gastronomic tours in 2 languages.
Conclusion
There is an opinion that a delicious gift brought from a tourist trip can bring a person back to where he bought it. That is gastronomic tourism is one of the activities that forms repeat tourists. The sphere of tourism is one of the fastest growing in Karelia. Regional policy should be focused on the preservation of national identity, which is perfectly embedded in gastronomic tourism. Taking into account the interest of the Scandinavian countries, nowadays it can become a competitive advantage over other regions of Russia.
At the same time, institutions supporting culinary tourism are still developing. If we exclude Moscow and St. Petersburg, we can say that culinary tourism in Russia is at the initial stage of development, which is due to the small experience of tourism companies in organizing this type of recreation. But this type of tourism is now actively gaining momentum.
One should not forget about older tourists (50 years and older). For entrepreneurs, attention to this age category may be interesting, due to the fact that these people are more calm, perhaps less active (minimizing the cost of a type of active recreation), but at the same time solvent.
As a development of excursion activity, some travel agencies and organizers of tourist routes should negotiate with large companies producing culinary goods about small excursions to production. This will be an interesting practice, both for entrepreneurs and tourists.
The development of ethno-cultural tourism on the basis of gastronomy is a promising direction of domestic tourism as a factor of socio-economic development of the region. The stimula of this direction are representatives of the regional community: regional authorities, socially responsible business, active social and professional groups, carriers of cultural symbols (Benner, 2019; Guerreiro, 2019). The development of innovative modern forms based on national identity contributes to the development of the regional community, as well as to the diversity and strengthening of interethnic relations, which leads to the development of Russian society (Moneva et al., 2019).
The development of culinary tourism can contribute to the diversification of the economy of the region's municipal areas with agricultural elements, thus preventing stagnation, as well as to the development of the Russian society:
to increase the flow of tourism and the growth of capital inflow to Karelia;
to stimulate infrastructure development;
to stimulate the development of small and medium enterprises;
to support the cultural heritage of the region;
to promote indigenous cultural elements, etc. (Golovneva, 2013).
The research justifies the directions of development of new non-industrial activities in the depressed territories of the Republic of Karelia aimed at improving the quality of life of the population alienated from receiving economic and natural rent. To assess the need to develop gastronomic tourism and its compensatory role in solving the problems of territories with low industrial potential, a toolkit was developed and a sociological survey was conducted. The analysis of the data obtained from the questionnaire survey has shown the need of the local population and tourists in some culinary tours in the Republic of Karelia, as well as elements of gastronomy in "wild tourism". In addition to menus and dishes, the tourist also needs an organized exterior environment. To develop interest in catering places, the business needs to apply elements of indigenous cultures in the interior, music, staff clothing, etc. In turn, this will not only add to the interest of tourists, but also become an instrument to support the region's indigenous cultures. The main task for tour operators is to make tours more diverse and rich, which could potentially increase the flow of tourists to Karelia.
Acknowledgments
Study was conducted within the Government Task “Institutes and Social Inequality in Global Challenges and Regional Limits”, No. 0218-2019-0090
References
- Benner, M. (2019). The spatial evolution-institution link and its challenges for regional policy. European planning studies (pp. 1-19).
- Berketova, L. V., & Polyakova, A. A. (2018). Unusual dishes and traditions of different cuisines of Russia. Proc. of the First Int. Sci. Conf. (pp.468–477).
- Bogatyreva, E. V. (2016). Culinary tourism in Russia as a perspective direction of the internal and incoming tourism. Physical culture, sports, tourism: scientific and methodical support. Coll. of mater. of young sci. and students of All-Russ. Sci.-pract. Conf. with int. participat. (pp. 88–90). Publ. house PSPU.
- Generalova, A. A. (2018). Peculiarities of demand for gastronomic tourism. Econ.environment, 3(25), 81–85.
- Golovneva, E. V. (2013) Regional identity as a form of the collective identity and its structure Labyrinth. J. of Soc. and Huma. Studies, 5, 42–50.
- Guerreiro, M. (2009). Sustainable destination management: a commitment for the future of world tourism. Worldwide hospitality and tourism themes, 11(6), 658-691.
- Kozlovsky, V. V. (2019). Transformation of Mono-profile Regional Industrialism in Northwest Russia.Prospects of Socio-Economic Development of Border Regions.Proc. of the 6th Int. Sci. and Pract. Conf. (pp. 160–166). KarSC RAS.
- Kozyreva, G. B., Morozova, T. V., & Volkov, A. D. (2018). Investigation of the institutional factors of the socio-economic development of the depressive northern border ethnic region. Discussion, 6(91), 38–47.
- Maximenko, A. G., & Komarevtseva, N. A. (2017). Gastronomic brand of the region. In collection: Regional geographical research. Collection of scientific works (pp. 60–64). Krasnodar.
- Moneva, J. M., Bonilla-Priego, M. J., & Ortas, E. (2019). Corporate social responsibility and organizational performance in the tourism sector. J. of sustainable tourism. Channel view publication. Engl.
- Morozov, A. A. (2019). Culinarytourism in the North-West of Russia (on the example of the Republic of Karelia). National interests: priorities and security, 15(5), 851–869.
- Nekhaeva, N. E., & Terekhova, Y. S. (2015). Gastronomic tourism as a perspective direction of development of Russian regions. Natural and Mathemat. Sci. in Modern World, 34, 82–87.
- Nikolskaya, R. F. (1989). Karelian cuisine (2rd ed.), correct.and supplemented. Editorial note. Miner D. I. Karelia.
- Stepanova, S. V., & Shlapeko, E. A. (2018a). Trends of cross-border trade in the Russian-Finnish borderland. Baltic reg., 4.
- Stepanova, S. V., & Shulepov, V. I. (2018b). Tourist infrastructure of the region in municipal context: approaches to assessment. Bull. of Volga Reg. State Univer. of Technol. Ser. Econ. Andmanagm, 4(40), 5–16.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
27 February 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-101-0
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
102
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1235
Subjects
National interest, national identity, national security, public organizations, linguocultural identity, linguistic worldview
Cite this article as:
Morozov, A. A., & Kozyrevа, G. B. (2021). New Non-Industrial Activities In Russian Regions: Culinary Tourism In Karelia. In I. Savchenko (Ed.), National Interest, National Identity and National Security, vol 102. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 629-640). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.02.02.79

