Abstract
Now there are practically no commercial organizations that can successfully work without attracting borrowed resources. Current business practice shows a constant change in the ways and forms of attracting borrowed capital. The modern level of information technology development made it possible to successfully organize crowd-investing platforms through which investors (including individuals) got the opportunity to directly enter organizations in need of additional financial resources. As a result, both commercial entities and investors face the problem of agreeing on the parameters of the investment agreement. The agreement of opinions is based on the solution of the financial task associated with the calculation of some key indicators such as the planned revenue from sales, cash flows, borrowing dates, interest rates on borrowed capital, payment schedule, tax burden of both the investor and the organization. The study presents an algorithm for deciding whether to attract the resources of a commercial organization. In it, the authors linked the conditions of the enterprise, arising from the peculiarities of financial and economic activity and the interest of investors (individuals), when choosing an alternative to the use of free financial resources. The assessment obtained in solving the set financial task will provide significant assistance, both in making decisions on investing and in attracting borrowed resources.
Keywords: Costslegal entitiessources of startup financingtaxation of individuals
Introduction
Taking into account the postulates of classical approaches to financial management, the financial and economic activities of the vast majority of companies are practically impossible without attracting borrowed capital at various stages of its life cycle. Efficient use of borrowed funds allows increasing the volume of business activities of a commercial organization. As a result, the efficiency of using the total capital of the company is improved and ultimately has a positive impact on the market capitalization of the company. In the modern world, due to the digitalization of economic relations, the relationship between the enterprise and the investor is undergoing significant changes. Commercial enterprises, based on internal reporting and development plans, put forward their own conditions on the amounts and timing of the receipt of financial resources, but the financial cycle of the cycle of resources dictates their dates of repayment of debts. This process is influenced by the opinions of investors on the conditions for the return of invested resources. Currently, due to the development of various financial platforms and instruments, investors have a large choice of investment directions for temporarily free financial resources. Based on the opinion of various authors (Bogdanov, 2018), we can say that the most significant factors, both for the enterprise and for the investor, affecting the choice of sources of financing of borrowed capital and areas of financing, in addition to its cost, also include: management flexibility, risk level, transaction time, expected additional income and preferences.
Problem Statement
The question is to form a model for financing the introduction of a business idea into the activities of a commercial organization or startup by attracting resources from a wide range of investors. The study under the investor considers only an individual – a resident of the Russian Federation. The parameters of the evaluation model should answer several basic questions:
For what period and at what minimum percentage it is necessary to attract resources for the organization/startup.
Whether it is advisable to invest resources on the part of an investor-individual.
How the cost part will change by taking into account the tax burden in the calculations between the organization and individuals.
In what form it is necessary to provide resources to a commercial organization/startup in order to minimize the risk of financial losses from the investor.
What the minimum price should be for new products (goods, work, service) for the means of calculating and processing data in the accounting management system.
Whether it is advisable to bring products (goods, works, services) to the market, relative to competitors.
What the financial results of the commercial organization/startup are, when introducing a new type of activity, taking into account the use of borrowed resources?
Research Questions
The purpose is to create a model for financing the implementation of a business idea in the activities of a commercial organization or startup by attracting resources from a wide range of investors. The study considers only an individual resident of the Russian Federation as an investor.
Purpose of the Study
In methodological terms, the study is based on general scientific methods of financial management, financial mathematics, accounting and management accounting. The typological features of the problem to which this study is devoted, as well as the wide range of questions related to it, required the authors to systematize continuity in the study. In the process of research, such general scientific methods as comparative analysis, logic-analytical methods, system analysis, as well as the construction of graphical dependencies and the formation of tabular data, were used. The information base of the study was the legislative and regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation regulating the taxation of legal entities and individuals, accounting for costs at the enterprise, data from open sources of the Bank of Russia and the banking community, statistical data of the Federal State Statistics Service of the Russian Federation. The work uses materials from international and sectoral scientific and practical conferences, as well as publicly available information from the global Internet.
Research Methods
In analyzing the question of the effectiveness of attracting borrowed resources in financial and economic activities, on the basis of own experience and information available in the economic periodical (AlfaBank; The Bank "FC Opening"; Sovcombank; Gavrichenko & Luskatova, 2018; Osadchaya et al., 2017; Stunguriene & Urbšiene, 2011), it is necessary to note the dualism of this task, which consists in the presence of diverse points of view. On the one hand, they are consumers of resources – commercial enterprises; on the other hand – investors, owners of material and financial resources. As a result, as a starting point of the study, the authors consider the following facts:
Attracting a bank loan by a commercial organization (small or medium-sized business), in the vast majority of cases, either a pledge or guarantee security of third parties is necessary. Small businesses often lack the necessary collateral.
Investors are interested in constant payments (once a month, once a quarter, once a year a debt repayment scheme or income payment), which is often unprofitable for the company due to the presence of sectoral features of the financial and economic cycle of the enterprise. Therefore, for enterprises, the most acceptable option is to return borrowed funds when there is a necessary and sufficient free flow of money.
The option of expanding or diversifying the business – increasing the authorized capital by attracting new owners, carries the risk associated with the loss of independence of a commercial organization.
Attracting resources not only in cash, but also in material, and the right of ownership remains with the investor. This approach serves as an additional protection for investments in the unfavourable development of the situation when implementing a business idea.
The investor must understand the associated risks of investing in the business. They are related, firstly, to possible full or partial losses of invested funds; secondly, with the emergence of an additional tax burden, which must be taken into account when receiving money.
Findings
Examining this question, we present the process of finding a solution in the form of an algorithm schematically represented in Figure
The form of borrowing. From a practical point of view, two main options can be considered. The first option is classic, attracting capital in the form of funds to the organization's settlement account. The second option is the purchase by the investor on his own behalf and at his own expense of the asset necessary for the implementation of the business idea with the subsequent lease of it.
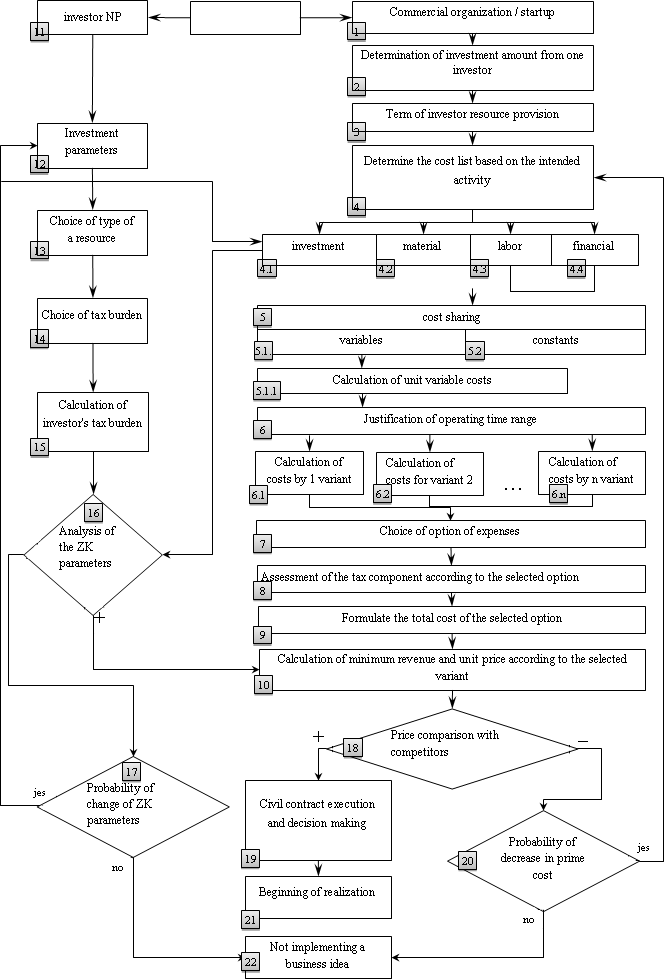
At the same time, the lease agreement may provide for the transfer of ownership of the asset after a certain period of time after the repayment of the debt. This option is preferable for the investor, since it allows you to save to one degree or another invested resources in case of unsuccessful implementation of a business idea.
Formation of tax burden in the organization and the investor. The authors in their studies are of the opinion that in calculations the interest rate on attracted capital should be "net”. In other words, it is necessary to take into account the tax burden when calculating the return on investments. If a commercial organization has costs for the implementation of both the first and second versions according to the accounting regulation (The Bank "FC Opening") increase the cost of products (goods, works, services), then for an investor – an individual, not everything is so unequivocal. If investments in the implementation of the business idea occurred in the form of cash, then interest income is taxed according to paragraph 1 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Sovcombank) at a rate of 13 % (an investor is a resident of the Russian Federation). If the property is leased to a legal entity, then the investor has the opportunity to pay tax on professional income (rate 6 %) (Gavrichenko & Luskatova, 2018). In the presented versions, a different tax base is obtained.
Information that is collected during the joint implementation of these stages should show all the costs of the company in cash equivalent, as well as the timing of their occurrence. The obtained data must be divided into variables and constants in step 5. In this situation, the authors propose to use traditional accounting management systems. This is the use of unit-level cost measures, such as the wage quantity of the main production workers, the number of hours of equipment operation, and the number of units produced (step 6).
At step 10, the minimum revenue is calculated. This calculation is proposed to be made through the break-even point, that is, when the sales volume is equal to the costs of production and sale of products (goods, works, services). Based on the data received, it is proposed to make decisions on the implementation of the business idea or the revision of data on it (stages 17, 18).
For the investor, the main is stage 16. It compares the potential return on the proposed project for the investor with alternative opportunities. There are many investment options, especially taking into account risk. Therefore, the authors, as a criterion for assessing the sufficiency of the estimated yield, propose to conduct a comparative analysis regarding the risk-free rate of return (interest rate). This calculation is presented in the form of formula 1.
, (1)
where:
Di – income that the investor plans to receive in the i-th period of time from investing in the project/startup (taken from the investment agreement).
∑Ti – amount of taxes that the investor will pay in the i-th period of time.
∑ICi – amount of costs incurred by the investor in the i-th period of time (e.g. insurance, account maintenance, etc.).
∑I – total amount of the investor's investments in the project/startup at the initial stage (taken from the investment agreement).
N – number of full years of project/startup implementation or investor participation.
n – number of periods (months, quarters), project implementation or investor participation in it.
R – risk-free interest rate at the time of conclusion of the investment agreement. It is equal to the key rate of the Bank of Russia (Martynova et al., 2019) or the rate of return on investment in an individual investment account (Central Bank of the Russian Federation; Gazprombank; Obraztsova et al., 2017; Rosselkhozbank; Sberbank; Savitskaya, 2018; VTB).
If the condition prescribed in formula 1 is not met, then two recommendations are possible: the first is the refusal to conclude a contract; the second is the revision of the terms of the investment contract
Conclusion
The main feature of the formation of capital of small commercial enterprises or startups is the fact that often the main source of financing is borrowed funds at an interest rate much higher than the market rate. Therefore, based on the practice of economic activity, the implementation of the presented mechanism is a real opportunity to understand the viability of the main business idea. The information base of the presented algorithm is realistic, because in its formation it relies on the initial data of accounting and management accounting. In turn, individual investors have a tool that allows you to assess the effectiveness of investment taking into account the tax burden. This tool allows you to make an investment decision based on your own preferences regarding profitability and risk, on the feasibility and forms of investing money.
References
- AlfaBank. https://alfabank.ru/make-money/deposits/?submitted=true&limit_rub=1000000¤cy =rub&period=
- Bogdanov, A. (2018). Augmented reality apps are storming the AppStore. Appleinsider. https://appleinsider.ru/app-store/prilozheniya-s-dopolnennoj-realnostyu-shturmuyut-app-store.html
- Central Bank of the Russian Federation. https://cbr.ru/
- Gavrichenko, E. V., & Luskatova, O. V. (2018). The industry practice of project financing. Proc. of Higher Ed. Institut.: textile industry technol. ser., 5, 5–10.
- Gazprombank. https://www.gazprombank.ru/personal/increase/deposits/
- Martynova, T. A., Eremeev, D. V., & Knyazeva, I. O. (2019). Financial assessment of the feasibility of using Bank credit at the enterprise. Fund. Res., 11, 100–105.
- Obraztsova, O., Poliakova, T., & Popovskaya, E. (2017). The choice of funding sources for start-ups in a transitional economy: The ability to predict in a national context. Foresight and STI Governance, 11(3), 71–81.
- Osadchaya, N. A., Murzin, A. D., & Torgayan, E. E. (2017). Assessment of risks of investment and construction activities: Russian practice. J. of Advan. Res. in Law and Econ., 8(2), 529–544.
- Rosselkhozbank. https://www.rshb.ru/natural/deposits/dohodniy/
- Savitskaya, G. V. (2018) Updating existing approaches to determining the duration of operational and financial cycles. Econ. anal.: theory and pract., 8(17), 1564–1583.
- Sberbank. https://www.sberbank.ru/ru/person/contributions/deposits_n
- Sovcombank. https://sovcombank.ru/saving
- Stunguriene, S., & Urbšiene, L. (2011). Assessment of construction object financing solutions. Technol.l and Econ. Develop. of Econ., 17(4), 579–594.
- Tax code of the Russian Federation, adopted on 31 July 1998, no. 146-FZ. ConsultantPlus. http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_19671/
- The Bank “FC Opening”. https://www.open.ru/deposits?from=main_menu
- VTB. https://www.vtb.ru/personal/vklady-i-scheta/
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
27 February 2021
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-101-0
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
102
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1235
Subjects
National interest, national identity, national security, public organizations, linguocultural identity, linguistic worldview
Cite this article as:
Eremeev, D. V., Kukartsev, V. V., Tynchenko, V. S., Stupina, A. A., & Martynova, T. A. (2021). Decision-Making On Attracting Additional Financial Resources Of Commercial Organization. In I. Savchenko (Ed.), National Interest, National Identity and National Security, vol 102. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 567-573). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2021.02.02.71

