Abstract
The feasibility of adapting modern business to current changes in the world economy is explained by the ability of digital technologies to ensure optimal operation of e-business. But despite the fact that many companies around the world are undergoing the process of digitalization, some of them believe that this process is a threat to their business. Problems such as information insecurity, shortage of personnel, cost of the latest equipment, etc., remain unresolved. Yet fewer industries remain unaffected by the digital revolution. Digital transformation changes the very nature of modern business, thus creating a special ecosystem. In order to successfully transform and further develop business in the current era, companies need to change the way they do business. It is important to note that the terms "digitalization" and "digital transformation" are in one case a means of making high profits, in another case a process of transforming the enterprise according to the latest changes in the economy. For the purposes of this article, the authors conducted a thorough research of the problem on the economic goals of digital transformation of business, since the main subject of research is “digitalization” and “digital transformation” of enterprises. The fundamental works of foreign and domestic authors in the field of the digital economy were also considered. According to the results of the study, the authors of this article presented the Roadmap of digital architecture and the author's concept of digital transformation.
Keywords: Digitalizationdigital transformationinformationbusiness processes
Introduction
We live in a modern society and cannot imagine our life without technologies. The creation of a worldwide Internet was the highest point of the next information revolution’s wave. Thus, the exchange of information on a global scale became possible. In the 1970s the theorist and publicist Daniel Bell (1973) predicted the entry of humanity into a new stage of development characterized by the growth of the tertiary sector of the economy. The author of the “Third Wave” Alvin Toffler had a similar point of view (Platonov, 2019).
General Business Principles are changed by technology. Digital technology is the result of the human development’s process. Indeed, according to many economists, digital technologies are new information technologies, which allow ensuring the optimal operation of e-business structures in the current economy. The process of digital transformation itself can be called as the era of dramatic changes. The role of digitalization is increasing every day, and the result is an economic processes’ simplification. Digital transformation goes ahead. This is an irreversible process which helps to increase business efficiency and accelerate sales revenue growth thanks to new and innovative digital business models.
Problem Statement
Companies all over the world go through a digital business transformation because this leads to the ability to quickly adapt the business to the new challenges of digitalization. This allows you to expand the boundaries of organizations, increase the speed of making management decisions, by replacing or transforming business processes and creating an environment for digital business.
An enterprise using digital technology can take advantage of convergence opportunities in which product data is available at all stages of its life cycle – from development to maintenance. That’s why the management of the enterprise can make more informed decisions, carry out transformations for “quick implementation” in the aspects of entering the market, flexibility, quality, security and operational efficiency, as well as creating new business opportunities (Gribanov, 2017). At the same time, accelerating technology adoption can harm established business models.
Digital transformation has both positive and negative sides, and therefore it is important to ensure information security on the Internet, in corporate and local networks through which digital data is transmitted. Since the Internet is publicly available, hackers can take advantage of this and further implement a number of threats:
- theft of personal data;
- information theft;
- change or destruction of data, etc. (Samuylov, Begishev, Moltchanov, & Andreev, 2019)
Such digital transformation’s problems as information security, staff shortages, lack of the ability to purchase expensive equipment, etc. are the main (Figure
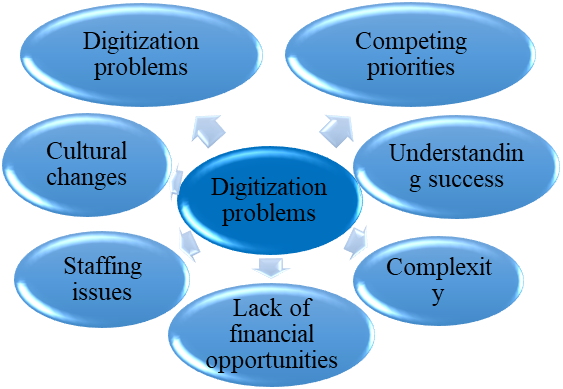
According to the research in this area 25 % Russian companies and 31 % in the world consider the digital revolution as a threat for their business. Risks arise due to the new born digital companies can bring down traditional strong players from the leadership position. In the Russian Federation a quarter of respondents said that changes occurring due to the influence of ubiquitous digitalization threaten their business. In the world 31 % of company representatives made such a statement.
Companies showing the best financial results see a threat in actual changes in the global economy due to digitalization. 64 % of representatives reported this while this statement was supported by only 27 % of the respondents in general.
Despite the problems and difficulties, the topic of digital business transformation remains the most relevant today. The scale and digitization’s rate confirm this. Fewer industries remain unaffected by digital change. Transport, fuel and energy complex, housing and communal services sector, construction, medicine: almost all industries are involved in this process. Digitization influences easier on trade, the financial sector, and government.
It should be particularly noted that the state as a service is the prospect of the next five years. Even today about 4 thousand information sources, 93 thousand organizations are digitizated in the context of the Russian State business system of housing and public services. The Federal Treasury develops the public procurement system, processing about 220 million transactions per day.
Thus, due to the implementation of the Smart Grid concept, Russian energy complex will enter a new phase of existence, which will be characterized by harmonious interaction with the environment, improvement of the quality of life and general economic recovery. Smart Grid networks are upgraded power supply channels using communication and information technologies. The essence of Smart Grid technology in the electric-power engineering is data collection of electricity production and consumption. This allows distributing energy resources correctly, ensuring reliability of their consumption and efficiency of use.
Nowadays utilities deal with enormous challenge. However, they are simultaneously active in an industry where digital transformation can lead to huge cost savings, new offers, alternative pricing models, optimizing customer experience and even radically new ways of “doing business” interacting with customers and their business model itself.
From a technological point of view, the Internet of things, big data and everything connected with the smart play a key role. In addition, investment and innovation in informing customers about their consumption and enabling them to control it in invisible ways expand many opportunities in areas such as ecology / environment and changing supply chains.
The insurance industry also has numerous opportunities for using transformational technologies.
Most consumers, for example, would like to have a sensor attached to their car or home if this leads to lower premiums. However, there are problems to the degree that technology offers tremendous opportunities that are increasingly being used by insurers. An important role is played by the changing expectations of policyholders and other consumers. In addition, there is a lot of work in core business processes, such as managing insurance claims, customer service, and following changing rules.
The digital transformation of healthcare, in particular, is due to the problem of aging / population growth, increasing chronic diseases, increasing costs and changing people's expectations and behavior as a result that digital healthcare is playing an increasingly important role.
Thus, digital transformations provide new opportunities so that enterprises can create new values using old assets. Digital transformations are changing the nature of a modern enterprise by changing the scale of activity, the product and organization life cycle. Consequently, digital technology creates "digital value." Network effects are rapidly spreading throughout the business ecosystem, shaping pricing policies under the influence of data on consumer behavior. Global Consulting and Research Company Gartner, Inc. suggests considering any business as a set of platforms with open borders, and not as a closed system with assets (Sologubova, 2019).
Research Questions
The formation is a key resource in the modern world. Every second, mankind generates huge amounts of digital data which not only occupy a place in storage but also help companies doing business. To take full advantage of the available information, it is necessary to accumulate, structure and analyze it.
The main subject of this research is the digitalization and digital transformation of enterprises, further developed thanks to innovative technology, for example, Big Data (big data) or Artificial Intelligence (AI, artificial intelligence). They are aimed to analytics workflow on the basis of which it is possible to make decisions, adapt offers to specific clients and predict their behavior.
When explaining the terms “digitalization” and “digital transformation”, it is necessary to understand that:
in the first case, it is an art of process of the targeted outcome vide licet flexible production, bringing excellent results to customers, and higher profit to owners. The term “digitalization” is used to describe a transformation that goes further than simply replacing an analog or physical resource with a digital or information one. Revealing the concept of “digitalization”, we should talk not only about the software and hardware complex and tools, but also about the methods of work adopted by the company and the stimulation of innovation.
and in the second case, this is the process of transferring an enterprise to a “flexible” state from the current, from the point of view of the main areas key for a sustainable business. These key areas can be identified using key elements of the business value chain, such as:
Product Lifecycle Management
Production and product management
Business intelligence
Integration and data management
Safety and reliability
Corporate culture and the people behind it
Process and technology measurements
Actually, the goal of digital transformation is not to replace technologies or adopt new models of interaction, but to rethink the enterprise itself and its business processes.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to clarify the nature of digitalization and the digital transformation of business in modern economic conditions. The materials of this article allow not only understanding what exactly is changing dramatically in industries and in their business, but also how these changes will affect how they evaluate their activities. That strengthening the competitive positioning of successful firms does not depend on the technologies they adopt. What should be the nature of subsequent IT investments.
It is necessary to show that digital transformation is a deep transformation of business and organizational activities, processes, competencies and models for the full use of changes and the possibilities of combining digital technologies and their accelerating impact on the whole society in a strategic and priority way, taking into account current and future changes.
The development of new professional qualities depends on the ability to be more flexible, people-oriented, innovative, customer-oriented, orderly, effective and able to stimulate / use opportunities to change the existing situation and use new information and service revenues. Digital transformation efforts and strategies are often more relevant and are present in markets with a high degree of commodification.
Research Methods
As the main research methods were applied:
experimental-speculative methods: analysis of registered statistics, published results of the work of research institutions and Fitch Ratings, information provided by periodical business and scientific publications, including the Internet, in research materials performed by independent analytical organizations, legislative and regulations governing entrepreneurial, innovative and scientific-technical activities in the Russian Federation, studies of international organizations;
general scientific principles of a systems approach;
quantitative and qualitative studies of the main trends and directions in the formation and development of digital business transformation;
analysis methods – logical, comparative, strategic, managerial, etc
Findings
Digitalization sets the vector by which socioeconomic systems of all levels will develop for the long term. This is necessary for scientific process of digital business transformation (Gribanov, 2017).
To understand the studied problem many authors addressed to fundamental works of such foreign authors as Parker, Alstyne Marshall, and Choudary (2016), Bell (1973), and etc.
The development of business structures and their transformation within the framework of the socio-economic system as a whole including in connection with the development of digitalization processes are studied in the domestic authors’ works such as Gribanova (2017), Kapustina, Kudryavtseva, Shishkin, and Shishkin (2012), Avdeenko and Aletdinova (2017), Babkin, Burkaltseva, Kosten, and Vorobyov (2017).
The study of this issue made it possible to determine that the digitalization of processes is relevant not only at the level of individual enterprises: entire industries choose this development path for themselves as the only opportunity to meet the rapidly changing conditions of the surrounding world. As the result the digital transformation of industry, retail, the public sector and other areas are already changing the lives of every person and every company. According to the international analytical agency International Data Corporation (IDC) which is studying the global market for information technology and telecommunications, by 2018, global spending on digital transformation amounted to $ 1.3 trillion, and by 2021 this value will approach $ 2.1 trillion.
The penetration of digital technologies in all business sectors was due to the fact that this transformation accelerates interactions and all business processes, transferring them to real-time mode enhances the mutual influence of all factors, thereby creating a special ecosystem of the enterprise. The enterprise ecosystem is a complex of business development factors. It dictates a completely new algorithm of action
However, in the digital world not every organization is able to form its own ecosystem because in this process the strategy, goals, age, level of development of the organization, etc. But there are also “ambidextra companies” that go through the digital transformation process without any problems (Sologubova, 2019).
We must not forget that the fundamental role in digitalization is not so much artificial intelligence as the human mind.
Every year, large companies such as Forbes Insights, Hitachi Data Systems and others make the research to understand the cost-effectiveness of digital business transformation. A survey of more than a hundred IT managers of the largest companies from various sectors of the economy revealed the main goals of digital transformation (Figure
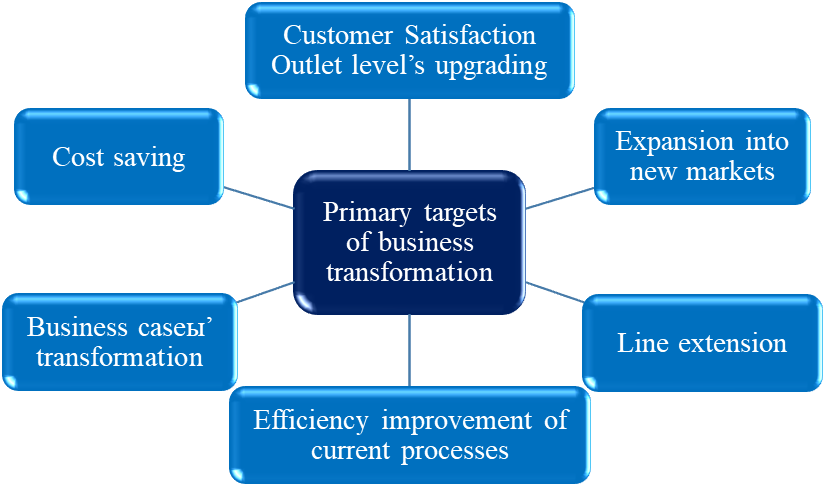
Today we have connected digital technologies as pervasive widespread smart devices, the industrial cloud computing and almost ubiquitous Internet connection. They are powerful enough in combination to unleash that well-known economist Carlota Perez calls the shift of techno-economic paradigm.
Currently "maturing" the digital enterprise is focused on the integration of digital technologies such as social, mobile, analytical and cloud service all conversion processes of the enterprise. In other words, the connected digital technologies require a complete rethinking of what we consider enterprise. Less Mature digital business is focused on the solution of discrete business problems with the use of individual digital technologies, which in our opinion is not quite correct.
According to the authors, the ability to digitally rethink a business is determined primarily through a precise strategy, implemented, as a rule, by the top management promoting the digital culture. The peculiarity of digital transformation is that dealing with risks is already becoming the rule, as more digitally mature companies strive to gain stable competitive positions. To this end, it is necessary to attract competent performers who can organize the correct processes for working with data, control their quality and usefulness, in order to ultimately benefit from the introduction and use of digital technologies.
Below we can see the highlights of the author's findings:
Next, we present the statistics on the digital transformation of the business according to research in this area. Most respondents are IT executives and professionals:
87 % say digital transformation is a competitive tool
88 % say they are in a digital transformation stage
96 % of organizations consider digital transformation critical
50% of executives say they have a clear roadmap for digitalization
39% believe digital transformation has made progress in securing real-time transactions; 32 % say this helped them to leapfrog solution in improving the efficiency of operations; 28 % said it helped them to gain new customers, 25 % said it helped them to leapfrog solution in accelerating product development.
45% of respondents are confident that digitalization will increase business income
25% of respondents believe that digital will provide an opportunity to establish more fruitful relationships with customers.
87 % of companies are confident that digitalization will positively affect the experience of employees in the company as well as on employee productivity
Companies that have already gone through the digital transformation claim that: increased market share – 41 %, there was an increase in customer involvement– 37 %, more favorable working climate – 37 %, more, web and mobile technologies – 32 %.
44 % of CEOs say business knowledge and the ability to understand the transformation of the corporate world through the creation and implementation of new IT technologies is a skill that many companies lack.
Based on the above we line that key challenges for businesses thinking about digital business transformation are:
1. Digital strategy – what to do?
2. Digital transformation – how can we do it?
On the basis of analytical reports scientific articles, opinions of experts, the authors offer the following definition of "digital transformation". It is a cultural, organisational and operational change in the organization, industry, or economic system through appropriate integration of digital technologies, processes and competencies at all levels and functions in a phased manner. Digital transformation using technology to create value for different stakeholders (clients, in the broadest sense of the word), innovation and adaptation to changing circumstances.
Thus, the digital transformation of the corporate world is the transformation of business models, processes, services, activities and competencies for using the opportunities offered in the two directions of global change: globalization has the free movement of people, ideas, goods, equipment and money in a dynamic global economy (the boundaries are blurred between old markets and new markets); in combination with digital technology innovation – joint to stimulate the creation of new business models that generate growing streams of data and revenue from new and desirable products and services.
Globalization and technological innovation at the same time generate new digital industry, the markets and the economy is the evidence of geopolitical and economic paradigm shifts changing all aspects of society.
Conclusion
The article examined the most important aspects of digital business transformation as a deep and accelerating transformation of the corporate world. In other words, it is the use of technology to radically increase productivity. In almost all spheres of activity, they use the achievements of the digital world, such as analytics, artificial intelligence, big data, the Internet of things, augmented and virtual reality, etc. in order to improve the efficiency and competitiveness of the business. Data and information have become major assets, sources of income and essential support tools in the information age.
To succeed in the digital age, it is unnecessary to turn into the new Amazon, Google, or Netflix. However companies may have to change their methods of work in order to create a solid base for the development of their business. There are likely to be obstacles along the way, but it is not about money, about lack of time and not even about the scarcity of resources. It is about the attitude to digital strategy.
Digital transformation projects most often fail because the organization is not ready for the scale of the changes that are necessary for success. To harness the power of new technologies, the corporate world needs to be prepared to accelerate evolution, business agility, customer focus, and all forms of data analysis.
References
- Avdeenko, T. V., & Aletdinova, A. A. (2017). Digitalization of the economy through the improvement of expert knowledge management systems. Science and technical Statement of St. Peter. State Polytechnic University Economic science, 1, 7–18.
- Babkin, A. V., Burkaltseva, D. D., Kosten, D. G., & Vorobyov, Yu. N. (2017). Formation of the digital economy in Russia: essence, features, technical normalization, development problems. Science and Technical Sheets of the St. Peter. State Polytechnic University Economic science, 10(3), 9–25.
- Bell, D. (1973). The Coming of Post-Industrial Society. A Venture in Social Fore casting. Harmondsworth: Penguin Books.
- Gribanov, Yu. I. (2017). Features of the formation of a market for IT service providers as part of the digital economy development program in the Russian Federation. Perm: Publ. House of PNIPU.
- Kapustina, I. V., Kudryavtseva, G. V., Shishkin, V. V., & Shishkin, V. I. (2012). Inertia of trading enterprises as a property of economic functional systems. International Science Journal, 3, 25–29.
- Parker, G. G., Van Alstyne, M. W., & Choudary, S. P. (2016). Platform revolution: How networked markets are transforming the economy and how to make them work for you. WW Norton & Company.
- Platonov, I. N. (2019). International economic relations in the global economy: a textbook for undergraduate and graduate programs. Moscow: Publication House Yurayt.
- Samuylov, K. E., Begishev, V., Moltchanov, D., & Andreev, S. (2019). Networks and telecommunications. Moscow: Publication House Yurayt.
- Sologubova, G. S. (2019). Components of digital transformation. Monograph. St. Petersburg.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
07 December 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-095-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
96
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-833
Subjects
Management, human resources, resource efficiency, investment, infrastructure, research and development
Cite this article as:
Golovina, E. Y., Evloeva, M. V., Yu, J., & Kylie, L. (2020). The Economic Goals Of Digital Business Transformation. In A. S. Nechaev, V. I. Bunkovsky, G. M. Beregova, P. A. Lontsikh, & A. S. Bovkun (Eds.), Trends and Innovations in Economic Studies, Science on Baikal Session, vol 96. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 281-290). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.12.37

