Abstract
The article discusses the need for informatization of small businesses in the Russian Federation. The current state of informatization of small businesses and features of implementation and use of information technologies in this economic sector were described; the concept “small business” was defined; its criteria were identified. The types and causes of the staff turnover were identified. Taking into account theoretical aspects of staff management, effects of the staff turnover on the current state and dynamics of development of small businesses were analyzed. Economic problems depending on the staff turnover rate were identified. Small business is a social, legal and economic category including legal entities and individual entrepreneurs with a small number of employees and low incomes. Business analysis methods can be used for assessing business risks. Thus, in addition to continuous monitoring as an analytical basis for timely identification of problems, business analysis allows for identification and assessment of risks and threats and development of measures aimed at their elimination.
Keywords: Business analysismonitoringentrepreneurshipsmall businesses
Introduction
The feature of the current stage of economic development is the global change in conditions and formation of new factors that ensure efficiency of business structures. Analytical data are collected in all areas of business and used to predict business efficiency. Information and analytical support for management processes is in demand, since it contributes to business performance and development of rational business strategies.
Competent analytical processing of data on the state and development of the business entity is crucial. These data are important for business negotiations or transactions. However, data collection is only the first step followed by data processing. In practice, analytical data processing can be of two types: operational analytical processing and data mining which precede the decision-making process (Usenko, Chernysheva, & Goncharova, 2013).
Problem Statement
Today, analysis is a creative type of management. Analysis identifies or prevents problems in a timely manner, finds ways to solve them, contributes to business performance and predicts its results.
Thus, in the market economy, management focuses on the use of the internal potential of a business entity, and the economic rationale of management decisions. It requires modern analytical information processing techniques. Foreign companies consider analytical studies as an integral part of business activities. All important decisions are based on the detailed analysis of a problem. In the market conditions, small businesses are more flexible and dynamic. Small businesses provide the market with goods and services, contribute to the employment, i.e., solve a number of crucial economic and social problems (Small and medium-sized entrepreneurship in Russia, 2017).
Research Questions
With a 1,6-fold increase in the number of business entities over the last seven years, the number of unprofitable business entities increased 1.6-fold. In other words, the share of unprofitable organizations does not decrease. It amounts to about 20 % of the total number of small enterprises. Similar trends are typical of the individual entrepreneurship. In Russia, the number of closed individual and farm enterprises is significant and exceeds the number of registered ones. According to the Russian Statistics Agency, only 3.4% of small enterprises conduct business for more than three years.
Russian small business is characterized by a low number of employees per one business entity. According to research, while the acceptable number of employees is 15 people, the actual average number is 3–5 times smaller. Small enterprises with an acceptable number of up to 100 people have 83–85 employees. Thus, many categories of small businesses are micro enterprises (Sinyaeva, Dodorina, & Gerasimova, 2013).
Small business is a social, legal and economic category including legal entities and individual entrepreneurs with a small number of employees and low incomes. According to the legislation, small business is a type of entrepreneurship characterized by a small number of employees (up to 100 people), average profit (up to 800 million rubles per year) (Kuznetsov, 2016), and equity. A distinctive feature of small businesses is their organizational form, average number of employees and a maximum profit rate.
A decrease or an increase in the average number of personnel can generate situations when the company does not meet criteria of a small enterprise. This will change the legal status of the company, reporting procedures and the tax base. The latter directly affects the level of income, and profitability.
In order to eliminate these problems, it is important to improve the staff management efficiency in small businesses.
In general, staff management is a targeted impact on staff in order to use their resources. Staff management involves planning, organization and control of various activities aimed at achieving company goals and respecting staff goals and interests.
If the staff goals are not achieved, the employee will search for a new job. It causes the staff turnover. The staff turnover is the number of employees quitting the job for a certain period. The staff turnover rate describes the number of employees who leave the company compared to the number of people who continue working. It is undesirable to have a high turnover rate. This means that the office consists of new employees who have no experience in working for this company. As a result, new employees need training which can be expensive and time consuming (Small business in Russia: figures and facts, 2020).
There are several types of staff turnover: internal and external, voluntary and involuntary. The staff turnover rate can be reduced by expanding opportunities for career advancement, increasing salaries and benefits. There are several types of the staff turnover. For example, the internal staff turnover refers to employees who leave one position to move to another one within one company. The lack of benefits (paid holiday, medical insurance and retirement plans) can increase the staff turnover rate. In addition, employees want to feel invaluable, so it is necessary to inform them of company projects, train, praise, satisfy their professional needs (Figure
Along with promotion opportunities, these aspects can reduce the staff turnover rate and company operational costs in the long run. There are the following causes of the staff turnover (Ivashko, 2017):

It is necessary to develop and implement labor pool programs. The staff turnover increases costs for in addition (Figure
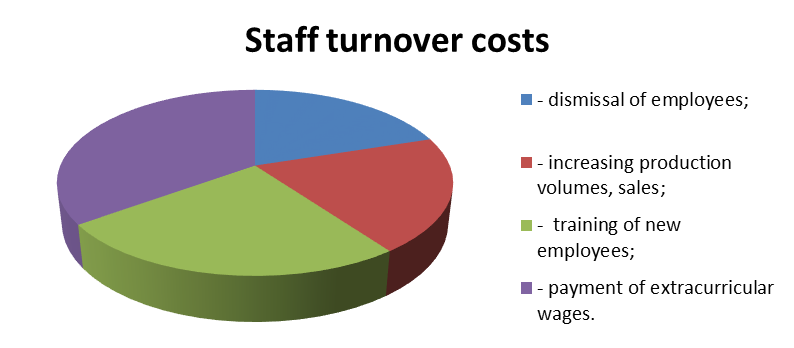
Some authors believe that the staff turnover has both negative and positive effects on business. Possible risks for small enterprises are a decrease in performance of workers (inefficient workers do not quit their jobs), a technological lag (there is no influx of new ideas and technologies, employees are not in demand in the labor market), “synchronous aging”, wavy dismissal of employees, and payroll inflation.
For small businesses, the average staff turnover rate causes moderate expenses for staff selection and adaptation, and reduces labor productivity.
The high staff turnover rate decreases productivity, increases costs for selection and adaptation, causes loss of management continuity (if the staff turnover affects the management team), reduces company's ability to implement a long-term strategy and motivate employees for long-term goals.
Thus, analysis of the staff turnover rate is important for small businesses as it reveals the problems of staff, identifies promising directions for development of staff management in order to eliminate financial, legal and organizational risks. Small businesses have to develop and implement measures to improve working conditions, enhance motivation for efficient work and reduce the staff turnover rate.
Economic instability, crisis phenomena in the economy change the external environment of business entities associated with availability of funds and real estate objects, staff performance, behavior of buyers and suppliers, and administrative and criminal pressure.
Therefore, it is necessary to identify causes of the current situation, and use possibilities of analytical data processing when making management decisions (Idigova, Yusupova, Salgiriyev, & Eskerkhanov, 2015).
The most important features of the economy are quality of information and analytical support for businesses which have a significant impact on social and economic development of society. According to international experience, this issue is a mandatory strategic attribute that helps increase business efficiency. For foreign businesses, analysis is an important and integral part of business activities. Crucial management decisions are preceded by in-depth and detailed research.
In Russia, business analysis is less widespread. Some analytical functions are distributed between departments. In practice, they are often reduced to control functions or financial analysis. However, businesses, especially small ones, need information on causes of business problems, ways for further development with minimum risks (Figure
Insufficient use of business analysis opportunities is due to the underestimation which is especially characteristic of small enterprises and the lack of qualified analysts possessing business analysis techniques recognized by the world analytical practice, etc (Table
Purpose of the Study
Analysis of the current state of informatization of small businesses and features of implementation. Taking into account theoretical aspects of staff management, effects of the staff turnover on the current state and dynamics of development of small businesses were analyzed.
Research Methods
In the course of studying this issue, the directions of small business development in the Russian Federation were considered. Methods for studying theoretical material – the study and synthesis of material, analysis and synthesis. These research methods allow to conduct a study of the collected facts, develop concepts and judgments, draw conclusions and theoretical generalizations of this study, namely, analyze the direction of small business development in the Russian Federation. Identify the problems and prospects of small business development in the Russian Federation.
Findings
Over the last years, in Russia and abroad, business analysis has become an integral part of business activities. It aims at implementing changes that will be beneficial for the business entity by identifying needs and justifying solutions and describing ways to implement these changes (Rybalkina, 2012). Business analysis helps identify true causes of business problems and develop and implement programs for solving these problems. If there are no problems, business analysis can develop rational strategic directions for further development.
Conclusion
There are 50 business analysis techniques. The business analyst must have a flexible mindset, an ability to choose one or another research method that ensures effectiveness in each specific situation. A mandatory business analysis procedure is business efficiency assessment. It ensures usefulness and practical significance of the business analysis methods (Mikhaylova & Popova, 2015). Business risks have to be analyzed and assessed. Business analysis methods allow for assessment of business risks. Thus, in addition to continuous monitoring as an analytical basis for timely identification of problems, systematic business analysis allows for identification and assessment of business risks and threats and development of measures aimed at eliminating them.
References
- Analytical data on small business (2020). Retrieved from: http: //www.giac.ru/
- Idigova, L. M., Yusupova, A. Sh., Salgiriyev, R. A., & Eskerkhanov, R. Z. (2015). Scientific order: approach to personnel assessment as a factor of efficiency increase. Moscow: Dashkov dokhod and K.
- Ivashko, A. S. (2017). Problems of staff turnover. Bulletin of Ulyanovsk State Technical Univerversity, 4, 58–59.
- Kuznetsov, D. A. (2016). Staff management: nature, problems and new solutions. Leadership and Management, 3(3), 159–170.
- Mikhaylova, A. V., & Popova, L. N. (2015). Analysis of the “swing door index”. Modern problem of science and education, 4, 66–75.
- Rybalkina, Z. M. (2012). On the issue of financial and economic stability of construction enterprises in modern conditions. News of higher education institution Ser. Economy Finance and Production Management, 1, 68–75.
- Sinyaeva, L. P., Dodorina, I. V., & Gerasimova, E. A. (2013). Staff turnover as an indicator of enterprise management efficiency. Concept, 4, 31–35.
- Small and medium-sized entrepreneurship in Russia. (2017). Small and medium-sized entrepreneurship in Russia. Moscow: Rosstat.
- Small business in Russia: figures and facts (2020). Small business in Russia: figures and facts. Retrieved from: http://xn--b1ae2adf4f.xn--p1ai/article/26003-kak-zhivet-malyy-biznes-v-kpizis-tsifpy-ifakty.html
- Usenko, L. N., Chernysheva, Yu. G., & Goncharova, L. V. (2013). Business analysis of the company. Moscow: INFA-M.
- Zhangalieva, E. S. (2016). Measures to reduce staff turnover at industrial enterprises. Econominfo, 25, 29–32.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
07 December 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-095-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
96
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-833
Subjects
Management, human resources, resource efficiency, investment, infrastructure, research and development
Cite this article as:
Gavrikova, E. I., Skomorokhov, V. V., & Ilyashevich, D. I. (2020). Directions For Small Business Development In The Russian Federation. In A. S. Nechaev, V. I. Bunkovsky, G. M. Beregova, P. A. Lontsikh, & A. S. Bovkun (Eds.), Trends and Innovations in Economic Studies, Science on Baikal Session, vol 96. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 251-257). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.12.33

