Abstract
In the article it is investigated the modern requirements for methods of estimating the management. Features and nuances of requirements for assessing efficiency are comprehensively considered. It is revealed a plot of main indicators of functionality in the framework of the proposed technology and also it is placed a great emphasis on a balanced scorecard as an effective and multipurpose tool of management. During the studying a balanced scorecard, there are revealing the technology of such a system usage, two main directions of its work, its advantages and disadvantages. It is considered conditions of successful implementing the system and requirements of objective appraisal for main indicators of functionality. It is investigated a balanced scorecard of marketing and its compatibility with already existing systems of an enterprise to remove its contradictions.it is considered ways of connection between a balanced scorecard of marketing and a balanced scorecard. It is taken into account a principle of creating a balanced scorecard of marketing and niceties of major perspectives. It is developed a concept of introducing and using a balanced scorecard of marketing. To the end of the research, there is using main indicators of achievement to estimate obtained result at all levels of the system.
Keywords: Strategic planningbalanced scorecardindustrial activityenterprise
Introduction
The balanced scorecard (BSC) is produced the management of organizing a multipurpose mechanism which considers a mission and a strategy of an enterprise through a set of interrelated detectors (Solovyova, 2006). The needed case of creating a balanced scorecard is developing a company strategy (Raven, 2002).
The developing a strategy is a main step of development and the beginning of the process means the corporate maturity and the high achievement is enough. But, without a clear strategy the developing a balanced scorecard is impossible (Tynchenko et al., 2019). Therefore, a desire to introduce it and the trying to figure out a business and its perspectives entail the necessity of developing a strategy (Kukartsev et al., 2019).
An object of research is industry realized marketing activity. A subject of the study is a process of managing the marketing of foundry. A goal is the development of estimating the marketing of foundry.
To get the goal there is aiming and solving tasks:
The developing a methodology of creating a balanced scorecard of the marketing of foundry.
The developing a methodology of determining major detectors of achieving the company marketing.
The testing a methodology of a system of estimating efficiency of the marketing of foundry using a concept of a balanced scorecard.
Problem Statement
In an opinion of many researchers, indicators of estimating efficiency should comply with certain requirements. There is:
The minimality. It needs to choose about small number of detectors of estimating efficiency. Otherwise, natural limits of absorbing information will be exhausted and it will be lost.
The profitability of forecasting. Non-financial indicators have to predict forthcoming financial result, in another way, non-financial indicators have to be determining detectors of efficiency but financial one has to be lag indicators, that is, it should summarize result as it will be available. Non-financial indicators which are not revealed itself as determining one might be rejected if it is not needed mandatory indicators in adjustment, ethics and safety control ways for an enterprise.
A comprehensive character. Perfect indicators comprise the whole enterprise, it means it can be used everywhere. In the case, indicators of efficiency of the enterprise marketing have got three main advantages over highly specialized indicators. It can be detected from the lowest to the highest one of enterprise levels stepwise. So, people can see interrelationship between own result and result of an enterprise.
Stability, a system of management has to be a stable one. Indicators should change stepwise to get aware of long-term goals for staff and way of behaviour gets predictable.
Applicability of compensation. Perfect indicators have to be based on the compensation which staffs obtain for work (according financial result or the base of non-financial indicators influenced financial result).
These requirements are not exhaustive. In the way, the next one is important.
Firstly, information presented in the system of indicators of the foundry marketing should be available to apply and transform. Therefore, special attention is paid for clearness as a system characteristic. The feature of scorecard should preclude the data to be neglected just because there is no data or some part of the data is aggregated to the detriment of different information.
Secondly, the scorecard of efficiency of the foundry marketing has to support strategic decisions at the operational level and inform about actual ways of achievement. Moreover, needed information has to be separated from nonessential one.
Thirdly, the scorecard of efficiency of the foundry marketing has to be an individual. In the marketing it is important because of differentiation in relation to competitors and consumers.
Fourthly, the main is the scorecard of efficiency of the foundry marketing has to include major factors for the enterprise marketing. A major indicator of functionality is a factor, which is critical for providing the future success of an enterprise. Moreover, major indicators of functioning (major success factors) are chosen on the base of harmony, stability and, that is, balance.
Research Questions
The authors are faced with questions of analyzing the ideas and concepts of the authors who worked on systems for evaluating the effectiveness of the company, evaluate all the positive aspects and shortcomings of these concepts, show the advantages of one over the other, and based on them propose a technology for implementing and applying our own system of strategic planning of marketing activities, offer methods of evaluating these systems with access to their own methodology for evaluating the activities of the enterprise in organizing the processes of creation, promotion and product provision
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to develop a model for evaluating the marketing activities of an industrial enterprise.
To achieve this goal, the following main tasks were set and solved:
Developing of the methodology for the formation of a balanced system of indicators for the marketing activities of an industrial enterprise.
Developing of the methodology for determining key indicators of achieving the results of the marketing service of the enterprise.
Testing of the methodology of the system for evaluating the effectiveness of marketing activities of an industrial enterprise using the concept of a balanced scorecard.
Research Methods
The most famous set of major indicators of functioning is a balanced scorecard suggested by Kaplan and Norton (2004). A balanced scorecard is an effective and multipurpose tool for managing for stepwise direction of actions (activity, performance) of people group (organization, enterprises, institutes, areas, subunits, project group, etc.) for achievement.
Balanced scorecard directions
BSC has two basal directions. Firstly, it acts vertically, it means it connects the managing an enterprise with others hierarchical levels. Secondly, it acts horizontally it means it takes financial tasks to the “language” of a certain activity (Kaplan & Norton, 2004; Kaplan & Norton, 2007). In BSC it is generally taking into consideration several indicators related four coordinates of business:
Market/clients (consumers): it shows how consumers perceive an enterprise.
Inner business processes (an inner coordinate): it shows where an enterprise exceeds competitors.
Innovation and education indicate if an enterprise could continue improving and creating value.
A financial coordinate: it shows how an enterprise looks in eyes of stockholders and competitors.
A condition of successful implementing BSC for estimating the company marketing during interaction with consumers is a dynamic monitoring major indicator of functionality. The interaction with consumers is a reactive type phenomenon: an action – a reaction – adjustment – an action. A deciding factor is responsibility towards the success. The subcomponents might allow providing efficiency of the monitoring (Meyer, 2004).
To get an objective assessing major indicators of functioning should meet the next requirements.
Firstly, a clear and unambiguous determining criterion allowed every employee to understand it equally. Secondly, relying accurate data from company staff that are not always able to recognize importance of obtaining information sent a huge amount of information about consumers. Thirdly, a focus on data, which is easy to obtain. If it is possible, major indicators of functionality should be based on data which is appeared in the process of managing interrelationship. Fourthly, an acceptable level of accuracy at which there is no opportunity for fraud that it is especially important if major indicators of functioning act as a target or it is a part of a circuit of stimulating interaction. Fifthly, consistency that is immediately checked in the point of obtaining information for guaranteed accounting data required for indicators and the place of obtaining it. Sixthly, setting up basic characteristics for factual indicators with involving lower levels of primary information (Sedera, Gable, & Rosemann, 2001).
These requirements are provided BSC the next advantages (Sharma, 2009; Wu & Hung, 2007). Firstly, BSC let avoid the information excess because of a point is directed to these parameters, which are main. Secondly, BSC met requirements almost eliminates suboptimization induced managers to take into account operational indicators comprehensively. Thirdly, BSC requires managers to convert statements of common way of an organization to a set of certain parameters which reflect strategic factors of development (Chzhan et al., 2019). The core of concept of a balanced scorecard is generally known. Along with other main factors, the compatibility of BSC of the marketing (BSCM) with the existing indicator system is essential, the system of existing indicator is used in different subdivisions of an enterprise. In the way, it is needed to provide the coinciding goals of BSC of the marketing with goals determined in higher systems. In addition, it is necessity to keep an eye on indicators of BSCM not to contradict indicators set up in different systems in the similar level. There is, for example, considering systems of marketing indicators of other subdivisions of an enterprise or indicator systems of different functional spheres (Brown, 2007; Kaplan & Norton, 2004; Niven, 2003).
In many publications of considered problem there is developing BSCM in the way of enterprise perspective “Relation with clients”. The implementing the perspective is often viewed as a task of marketing in an enterprise. It is needed to agree with the opinion of A. Praisner (Nili, Adame, & Cennerley, 2003). There would think that a goal of marketing is exceptionally more detailed analysing control parameters related interaction with clients. Then by analogy the perspective «Internal business processes» would be exclusively related to foundry processes, the perspective «Education and growth» would be related to the personnel department and the perspective «Finance» would be related to the financial department and the enterprise management. In the way it is overlooked important relations existed between these departments. For example, sales activity might influence to the reducing common time cost of business processes (the perspective “Internal business processes”) but more flexible production is able to provide increasing consumer satisfaction, etc.” (Nili, Adame, & Cennerley, 2003).
The using BSC included the assessing the marketing suggests that in every certain way it might use more or less amount of perspectives (directions of estimating the marketing) with changing its plot. There is no a mathematic theorem which could prove that four components of BSC are important and sufficient. It is more important to check every perspective to be more significant in every concrete case. Table
Main principles of using BSC in estimating efficiency of the marketing of managing foundry:
BSC is a controlling tool related strategic and operational level.
BSC let track multipurpose tasks (primarily it is regards interaction with clients and finances) to conduct stepwise.
BSC is a flexible system and it easily adapts to the using in different enterprises and different conditions.
Success of the using BSC is determined not by the compliance of technicalities but by the understanding goals of all employees of an enterprise.
Compliance of these principles can allow avoiding potential conflict situations both a horizontal one (conflicts of indicator systems of the same level) and a vertical one (conflicts of indicator systems of another level) and harmonizing BSCM with BSC of an enterprise.
The union of BSCM and BSC
Harmonizing BSCM with BSC of an enterprise is able to do in two ways (Olven, Petreyk, Roye, & Roye, 2005; Praysner, 2007).
Firstly, there is a way “top down” at which perspectives of a corporate-wide BSC are copied and transferred to the marketing level. Secondly, a “native” way, according the way, it is needed to determine when the marketing is in its “harmony state”. Necessary perspectives are determined on the base of critical factors of success.
In all ways, it has to observer the main principle of designing BSCM, it is all perspectives have to be in casual interrelationship and comprise the more part of marketing spheres which are important for developing an enterprise. The system is essential only if indicators of perspectives “Internal business processes” and “Educational and growth” influence on perspectives “Finance” and “Interaction with clients”.
In other words, BSCM is a set of some hypotheses of reasons and result. The system of assessing should clear provide interactions (hypotheses) between goals and criteria of achievement in different conditions to be real and it is able to manage. Every indicator included in BSCM has to be an element of the chain of the causality which informs all employees of an enterprise about the meaning of its marketing. According the above, it might propose the next general methodical circuit of building BSCM using the “native” method of harmonizing BSCM with BSC of an enterprise. To achieve the goal, it is needed to recognize a place of BSCM in the system of marketing planning in an enterprise (figure
According to figure
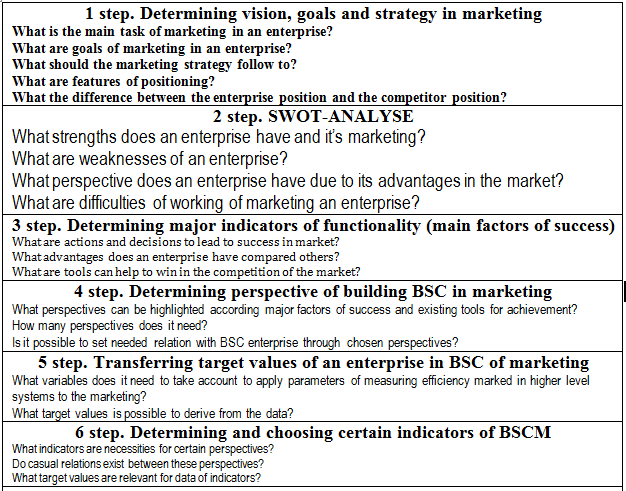
Taking into account the compliance between the indicator system and the planning process, it is possible to developing a concept of introducing and using BSCM. Therefore, the indicator system with regard to marketing is able to develop in an enterprise. The concept is consisting of eight particular steps which are able to integrate in certain ways. It is important that every step will be taken into consideration.
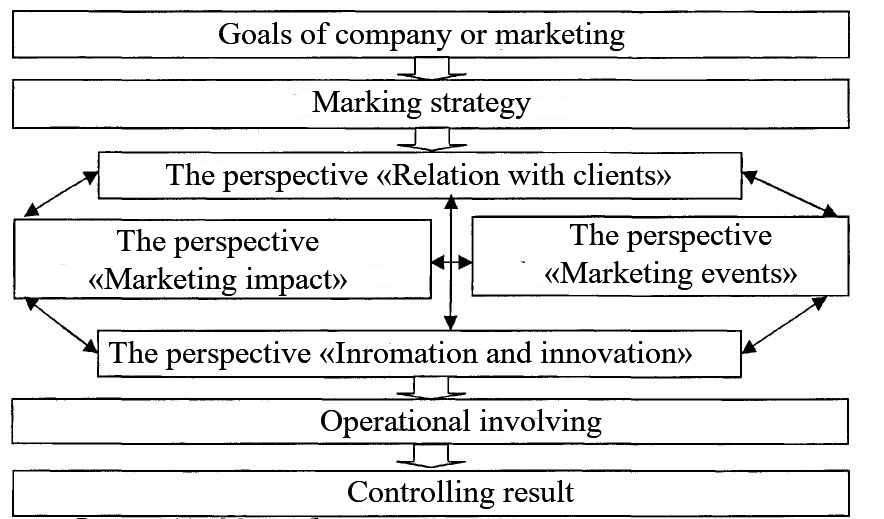
Figure
Without indicating these factors, it is impossible to figure out what result is. Except it, at early steps with just indicators it is impossible to assess how successful marketing strategy of an enterprise is. Conversely, these factors as duration of a time cycle without result indicators might help to achieve short-term operational improvements but not reflect its influencing the client base state and accordingly financial result. Well-developed BSCM should include achievement of the future result (indicator of done work).
While developing BSCM, there is a question about a number of indicators included in the system. If every of perspectives of BSCM has got from four to seven different parameters, in the BSCM there will include an average of 25 indicators. How it was in the practice, employees of an enterprise are distrustful towards statement that there is no more than two dozen for effective assessing the operational activity. In a sense, it might be right but the problem is there is no the difference between diagnostic indicators, which can be used to figure out the business, is controlled and can be signed about extraordinary situations required to immediately take steps and strategical situations determined a development strategy.
Enterprises might have got hundreds and thousands number of indicators which control business processes and sign any failure in the system, but it is not decisive factors of obtaining final results. These parameters can be considered as helping an enterprise to carry out the activity, it is a diagnostic indicator.
BSCM includes major indicator of implementing an enterprise strategy. Therefore, if it is considered BSCM as a combination of more than two dozen of indicators, the working with it is too difficult for any enterprise.
BSCM is not substitute of a system of assessing obvious parameters. System indicators are chosen to make managers and employees of an enterprise to focus on marketing factors, which might lead to major achievement in competition of the market.
During developing and introducing BSCM there is arising a question why financial indicators are included in the system.
A comprehensive system of the assessing and the managing should indicate how improving the marketing is related with improving the financial activity through increasing sales, operating profit, accelerating a capital turnover, reducing operational costs. The balanced scorecard has to save a focus on financial results. In the end, the causality of all indicators has to be linked to financial target. The system keeps all advantages leaved financial indicators as the final result; however, without the exaggeration and misrepresentation which inevitably rise when the exclusive emphasis is directed to improving short-term financial indicators. As soon as BSCM id developed, it becomes the base of creating a balanced scorecard for departments and certain employees of an enterprise. A goal and a strategy of it are determined in the scorecard of efficiency of operating entity.
The system of major indicators of achievement
To assess achievement of each department and every employees of an enterprise correctly it is needed to determine single, fair, understandable and “clear” major indicators of achievement (MIA) by each employee. Major indicators of achievement are directly derived from a mission, vision and main roles of employees. By the opinion of H. K. Rampersad, it is “related to financial sustainability (how much it is possible to provide financial needs), relationship with others (relationship with a life partner, children, friends, an employer, colleagues and other people), internal processes (the state of health and psychological stability) and also knowledge and training (your possibilities or skills and ability to learn)”.
In table
Managers of departments develop own MIA which is completely fit goals and marketing strategy of the whole enterprise and adequate BSCM. The answering an essential question, which is it is needed every employee to get his major indicators of achievement, is positive in the way if an employee has a goal, a strategy but a department where he is working has clients (internal and external) and also an internal business process which let attain the goal and implement the strategy.
Findings
In general, the success of introducing BSCM is defined by the next factors:
Guaranteed supporting top-management (an enterprise at all and also heads of marketing).
Engaging top-management to implement important steps of the development process (creating a coordination group).
Informing and training staff who are responsible for making a decision and also other members of the process (for example, conducting seminars required the attendance).
Choosing suitable project managers and their advance preparation.
Trainings for moderators which act as intermediaries and involve decisions in certain departments (specialists and heads of these departments can be moderators).
The abidance of established review processes marked in the project concept.
Sharing experience and knowledge obtained in the training process, further for developing subsequent scorecards in an enterprise.
The compliance of BSCM with scorecards of functioning directions as well as corporate-wide MIA.
Conclusion
In the studying it is analysed many nuances of BSC and BSCM and features involving these systems in foundry. Steps of the involving were considered. The marketing is so sophisticated and complex science, therefore, there are ways of investigating it, however, there are certain addictiveness and correlations for using certain systems for certain enterprises. It was analyzed ideas and concepts of many authors worked on systems and it was developed the implementation and application technology of BSCM based on it; also, it was assessed ways of estimating data of systems. In the framework of the proposed technology for the use of BSCM in strategic planning of production activities of the enterprise, a methodology of forming a balanced scorecard of marketing of foundry was developed. A methodology of determining major indicators of achieving result of marketing department was developed. It was conducted the approbation of methodology of the assessing efficiency of marketing system with using a concept of a balanced scorecard.
References
- Brown, М. G. (2007). The balanced scorecard: in the implementation way. Moscow: Alpina business books.
- Chzhan, E. A., Tynchenko, V. S., Kukartsev, V. V., Fedorova, N. V., Yamshchikov, A. S., & Krivov, D. A. (2019). Essence and classification of the agribusiness organizations competitive strategies. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth and Environmental Science, 315(2), 022106.
- Kaplan, R. S., & Norton, D. P. (2004). The balanced scorecard. From a strategy to an action. Moscow: Olymp Business.
- Kaplan, R. S., & Norton, D. P. (2007). An organization oriented to a strategy. In: How organizations used a balanced scorecard are succeed in the new business area. Moscow: Olymp Business.
- Kukartsev, A. V., Boyko, A. A., Kukartsev, V. V., Tynchenko, V. S., Bukhtoyarov, V. V., & Tynchenko, S. V. (2019). Methods of business processes competitiveness increasing of the rocket and space industry enterprise. IOP Conf. Ser. Materials Science and Engineering, 537(4), 042009.
- Meyer, M. V. (2004). Business perfomance estimates. Moscow: The Peak.
- Nili, A., Adame, К., & Cennerley, М. (2003). The efficiency prism. Dnepropetrovsk: The Balance Club.
- Niven, P. R. (2003). The balanced scorecardstep by step: maximum increasing efficiency and fixing the result. Dnepropetrovsk: The Balance Club.
- Olven, G., Petreyk, Y., Roye, G., & Roye, S. (2005). The balance between strategy and control. Saint Petersburg: Piter.
- Praysner, А. (2007). The balanced scorecard in the marketing and sales. Moscow: Grebennikov publishing house.
- Raven, D. (2002). The competence of modern society: revealing, development and implementation. Moscow: Cognito center.
- Sedera, D., Gable, G., & Rosemann, M. (2001). A balanced scorecard approach to enterprise systems performance measurement. ACIS 2001 Proceedings, 573–584.
- Sharma, A. (2009). Implementing balance scorecard for performance measurement. ICFAI Journal of Business Strategy, 6(1), 7–16.
- Solovyova, Y. N. (2006). The theory and the methodology of providing marketing competence in the system of managing strategic alliance. St. Petersburg: SPbSUEF.
- Tynchenko, V. S., Fedorova, N. V., Kukartsev, V. V., Boyko, A. A., Stupina, A. A., & Danilchenko, Y. V. (2019). Methods of developing a competitive strategy of the agricultural enterprise. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth and Environmental Science, 315(2), 022105.
- Wu, S. I., & Hung, J. M. (2007). The performance measurement of cause-related marketing by balance scorecard. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 18(7), 771–791.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
07 December 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-095-2
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
96
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-833
Subjects
Management, human resources, resource efficiency, investment, infrastructure, research and development
Cite this article as:
Fedorova, N. V., Lobkov, K. Y., Eremeev, D. V., Tynchenko, S. V., Danilchenko, Y. V., & Shamlitskiy, Y. I. (2020). Strategic Planning Of Enterprise's Industrial Activity Using A Balanced Scorecard. In A. S. Nechaev, V. I. Bunkovsky, G. M. Beregova, P. A. Lontsikh, & A. S. Bovkun (Eds.), Trends and Innovations in Economic Studies, Science on Baikal Session, vol 96. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 765-774). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.12.100

