Abstract
Malaysia now stands on the dawn of the 21st century, where the nation facing different challenges. In facing these challenges, most effective instrument is education, since education can equip people with opportunity to improve lifestyle, and contribute to successful members in society and national development. However, in order for the education to be meaningful, education should not only focus on physical and mental growth, but also in the needs and aspiration of developing society. Students in higher-level education are seen as future leaders and expected to accomplish various roles with their competency and performance. Higher education is the key for economic advancement. Therefore, comprehensive research is needed in studying factors affecting the academic achievement in making sure that the institution can produce the best graduates. Thus, today’s curriculum should contain emotional and spiritual intelligence in order to prepare the students to face complex global challenges. Therefore, the objective of this study is to identify the industry expectation for graduates and to propose new research model by using five dimensions, which is knowledge, skills, abilities, emotional quotient and spiritual quotient (KSAESq). The purpose of KSAESq model is to produce holistic graduates by combining five dimensions that will help graduates to be more prepared to meet industry expectation.
Keywords: KSAemotional quotientspiritual quotienthigher educationgraduates
Introduction
Education is important and acts as the key role especially for the development of economic and the development of a country. As education is important for development of a country, there is constantly improvement that has been made in our education system by Ministry of Education. One of the improvements including creating an Education Development Master Plan (Pelan Induk Pembangunan Pendidikan, 2006-2010) and the Malaysian Education Blueprint (Pelan Pembangunan Pendidikan Malaysia, 2013-2025) Which intends to enhance the quality of education in Malaysia in order to meet the requirements of global education in order to develop competitive human resources and have a strong market value. Education is also known as the key to achieve professional goals as in this competitive environment, it offers knowledge to preserve one's self. The National Philosophy of Education (Falsafah Pendidikan Negara) is intended to create intellectually, physically, emotionally and spiritually harmonious and intellectual individuals (Rayung & Ambotang, 2018). This philosophy is enforced through five educational stages that start with pre-school, primary, secondary and secondary or tertiary education before a student goes into work environment (PPPM 2013-2025). The aim is to create a human capital that is balanced and competitive that can meet the requirements of the country. However, today higher education institutions face various difficulties in equipping graduates with the right skills and attitudes that can meet with the business environment requirements. In latest years, it has also been one of the main issues of the country that many graduates do not have the perfect combination of abilities and individual characteristics that employers needed, although some of them may have outstanding educational qualifications. Other than that, traditionally educational institutions have given less attention to other forms of intelligence. Their primary focus is totally on logical and linguistic intelligence. Yet many scholars are starting to argue that intrapersonal and interpersonal skills, or emotional intelligence, could be more crucial to life achievement rather than linguistic or logical intelligence (Tucker et al., 2000). Thus, universities should be focusing on develop the student's entire character, including intellectual, emotional and social abilities that will assist graduates in their future endeavours. Therefore, this study is carried out to identify the skills required by graduates in order to meet the industry expectation.
Problem Statement
Emotional intelligence is one of the main aspects of the national education philosophy. According to Jaaffar et al. (2018), emotional intelligence help students facilitate an efficient response, adapt and react to change the environmental situations to achieve success in areas where they are involved. Universities should focus on developing the entire personality of the student which includes intellectual, emotional and social skills which will help graduates in their future endeavors (Baker et al., 2019). Generally, the single entity of Intelligence Quotient (IQ) is not a guarantee for individual success in life. According to Goleman (1998) IQ contributes only about 20% of success in life whereas Emotional Quotient (EQ) contributes another 80%. It is said that individuals possess some abilities in using emotions in order to enhance thought effectively than others (Jaaffar et al., 2018). Therefore, the levels of emotional intelligence of students need to be studied to help students achieve personal excellence in any field they are involved. Besides, through the national education philosophy, the importance of EQ is very clear and significant as SQ (Yusof, 2012). Therefore, the targeted focus is the student in public and private institution sector as in the Malaysian Education Plan, it aims to produce outstanding students that has a spiritual growth and emotionally healthy so that they are able to contribute to the well-being and progress of the nation. Emotional aspects is prioritized in the development of student (Mohzan et al., 2013). All of these dimensions refer to the manifestations shown by students from non-academic aspects. This is in line with the weakening issue of soft skills among students. Other than that, it can’t be denied that the success of an education system depends on a number of factors and one of the most important factors is the curriculum implemented to achieve the goals. One’s success in life does not depend solely on intellectual intelligence. The inclusion of a focus on EQ and SQ as part of the graduate curricular could lead to a variety of positive personal, social, and societal outcomes. Increasing EQ and SQ may not only facilitate the learning process, improve career choice and likelihood of success, but could also enhance the probability of better personal and social adaptation in general. Thus, today’s curriculum should contain EQ and SQ in order to prepare the students with competencies to face complex global challenges.
Research Questions
The research question of this study is:
What is the industry expectation for graduates?
Purpose of the Study
The main purpose of this study is:
To identify the industry expectation for graduates.
To propose the new research model by using five dimensions which is knowledge, skills, ability, emotional quotient and spiritual quotient.
Research Methods
This concept paper uses secondary source such as published paper, journal, thesis and research work.
Findings
From the discussion above, it shows that graduates with knowledge, skill and abilities only does not fulfill industry requirement, thus following is the propose model (refer Figure
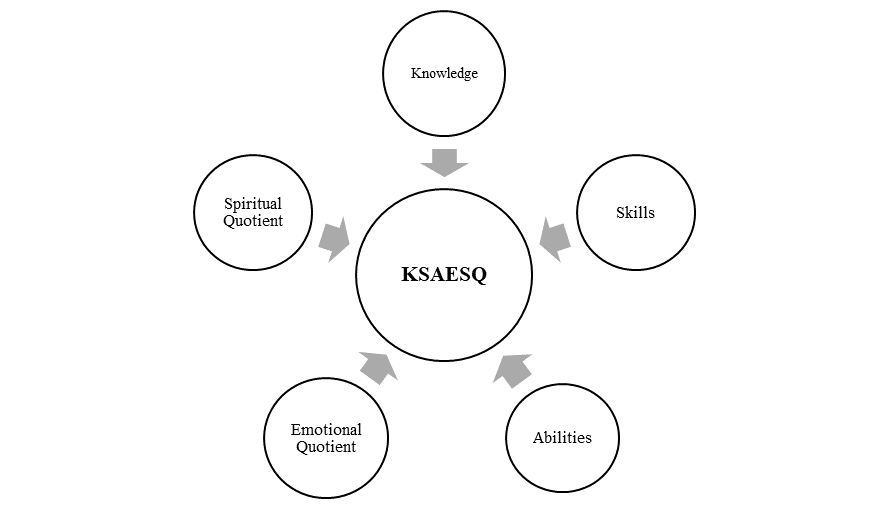
The purpose of KSAESq model is to produce holistic graduates by combining Knowledge, Skill, and Abilities with Emotional Qoutient and Spiritual Qoutoent. Apart from that, KSAESq model could ensure the education outcomes are in line with the requirements of the job market. Graduate who posses high degree of KSAESq usually work more efficient rather than those who are without EQ and SQ (Chanda & Chanda, 2019). According to Lievens and Chan (2017), previous research only focus on KSA model without other attribute. Study by Koizumi (2019), suggested that one of skill that required for industry 4.0 is EQ.This is because the emotional aspects such as high self-confidence, adaptability when facing with problems and obstacles in the workplace, motivate themselves to achieve common goals, work effectively in teamwork and have the skills to deal with the conflicts. In addition, those aspects is needed in the environment of work in order for graduates to improve the performance of a job and adapt with work environment. In addition, Shahroom and Hussin (2018) concluded that spiritual is one of the key factors in order to be successful in Industry 4.0. SQ is important as it is the ultimate intelligence where people address and solve the problems with meaning and value which it is required in the working environment (Akhtar et al., 2015).
Conclusion
One’s success in life does not totally depend on intellectual intelligence. Emotional intelligence is one of the most important elements of the philosophy of national education. Therefore, a good and happy life, coupled with physical and psychological health can be achieved essentially through the interdependence of spiritual intelligence and emotional intelligence. Students ' emotional intelligence levels therefore need to be studied in order to assist them to attain personal excellence in whatever area they are engaged in. Besides, through the national education philosophy, the importance of EQ is very clear and significant as SQ (Yusof, 2012). As for this study, from the findings above, it could be concluded that, KSAs, with focusing on EQ and SQ could result in a multitude of beneficial private, social and societal outcomes. Increasing EQ and SQ will not only promote the learning process, improve job decision and the likelihood of achievement, but may also increase the likelihood of improved personal and social adaptation in overall. Thus, in order to prepare the students with competencies to face complex global challenges, future research shall be focusing on empirical study using this new model (KSAESq) among graduates in Malaysia Higher Education Institutions.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to UNITEN iRMC who has funded this research through BOLD 2025 Research Grant.
References
- Akhtar, S., bin Arshad, M. A., Mahmood, A., & Ahmed, A. (2015). Spiritual quotient and ethical values towards organizational sustainability. International Letters of Social and Humanistic Sciences, 58(1), 1-7.
- Baker, R., Jaaffar, A. H., Sallehuddin, H., & Hassan, M. A. (2019). The Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Affective Commitment: An Examination of Police Officers. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, 8(2S9), 658–665.
- Chanda, M., & Chanda, A. (2019). Spiritual Revival and Management Practices: Modern Approach to Management. In Science and Spirituality for a Sustainable World: Emerging Research and Opportunities (pp. 98-113). IGI Global.
- Goleman, D. (1998). Working with emotional intelligence. Bloomsbury.
- Jaaffar, A. H., Baker, R., Ibrahim, H. I., & Alwi, M. N. R. (2018). Understanding Spiritual Intelligence and Affective Commitment Among Police Officers in Malaysia: The Mediating Role of Work Engagement. The Journal of Social Sciences Research, 404-412.
- Koizumi, S. (2019). The light and shadow of the fourth industrial revolution. In Innovation beyond technology (pp. 63-86). Springer.
- Lievens, F., & Chan, D. (2017). Practical intelligence, emotional intelligence, and social intelligence. In Handbook of employee selection (pp. 342-364). Routledge.
- Mohzan, M. A. M., Hassan, N., & Abd Halil, N. (2013). The influence of emotional intelligence on academic achievement. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 90, 303-312.
- Rayung, M. N., & Ambotang, A. S. (2018). The Influence of Emotional and Spiritual Intelligence on the High School Student Outcomes. Journal of Education & Social Policy, 5(1).
- Shahroom, A. A., & Hussin, N. (2018). Industrial revolution 4.0 and education. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 8(9), 314-319.
- Tucker, M. L., Sojka, J. Z., Barone, F. J., & McCarthy, A. M. (2000). Training tomorrow's leaders: Enhancing the emotional intelligence of business graduates. Journal of Education for Business, 75(6), 331-337.
- Yusof, N. M. (2012). Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and students attitude towards co-curricular uniform bodies in Malaysia. EDUCARE, 5(1).
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
30 December 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-099-0
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
100
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-905
Subjects
Multi-disciplinary, accounting, finance, economics, business, management, marketing, entrepreneurship, social studies
Cite this article as:
Toolib, S. N., Mohamad, M., Daud, S., & Hanafi, W. N. W. (2020). Fulfilling Industry 4.0: Requirements Of Graduates Attributes And Skills In Malaysia. In N. S. Othman, A. H. B. Jaaffar, N. H. B. Harun, S. B. Buniamin, N. E. A. B. Mohamad, I. B. M. Ali, N. H. B. A. Razali, & S. L. B. M. Hashim (Eds.), Driving Sustainability through Business-Technology Synergy, vol 100. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 297-301). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.12.05.31

