Abstract
Timely identified and stated problems of teachers’ professional activities are an essential condition for ensuring the efficiency of the functioning of the scientific and methodological support system, both at the regional and institutional levels. In particular, reliable information about the nature of secondary school teachers’ problems in implementing the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard for general education and organizing professional activities in accordance with the professional standard allows educational authorities and educational organizations to make informed management decisions, develop methodological materials necessary for teachers, provide them with individual assistance measures, implement efficient advanced training programs and personal educational trajectories. This article presents an attempt to formulate the problem field of scientific and methodological support for secondary school teachers’ activities on the basis of a diagnostic study of teachers' willingness to work in the conditions of introducing the professional standard for teachers and the need for their individual scientific and methodological support. This is precisely the vector that is set by the Federal Project ‘Teacher of the Future’ of the National Project ‘Education’, which stipulates that by 2024 at least 70% of teachers under the age of 35 should be involved in various forms of assistance and support. The article is prepared as part of the research work of the state assignment of the RANEPA for 2020 ‘The Development of the Personalized Support System for Teachers in the Framework of the National System of Teachers’ Professional Growth’.
Keywords: General educationprofessional activity of a teacherprofessional standard for teachers
Introduction
The fact that the quality of education is ensured, primarily, by the teaching staff members’ qualifications, upgrading which educational organizations of various types and levels are currently engaged in, is an axiom. These are, for example, centers for continuing professional development of pedagogical workers, teachers’ professional skills and qualifications assessment centers, regional competence centers, scientific and methodological centers for accompanying teachers, educational organizations of higher, secondary and further professional education, secondary schools and other institutions, and pedagogical communities. Within their competence, each of them is aimed at creating a set of conditions for the implementation of teachers’ personal educational trajectories; the organization of scientific and methodological support for their professional growth; the implementation of mentoring in secondary schools, as well as the introduction of innovative forms and methods of supporting teachers, providing them with necessary and efficient assistance. Among these conditions, an important role belongs to the organization of monitoring and diagnostic activities, which allows having objective information on which personal or collective problems of which specific teachers are to be solved and which actual professional needs are to be satisfied. This article continues a series of developments of methodological foundations for teachers’ scientific and methodological support (Tarasova & Pastukhova, 2017). The problem field of scientific and methodological support for school teachers is activities on the basis of a diagnostic study of teachers' willingness to work in the conditions of introducing the professional standard for teachers and the need for their individual scientific and methodological support.
Problem Statement
In the theory of activity, a problem is considered an obstacle (difficulty, barrier) to achieving a goal. For this study, it is fundamentally important that the conditions for a successful solution to the problem are: its correct statement, analysis, evaluation, development of ideas and concepts for finding a solution, their verification and confirmation in practice (Gritsanov, 1998).
In case when these conditions are met, problems become a kind of impetus for a person (or a collective as a whole) to development, improvement, professional and personal growth, and mastering innovations. Problems (difficulties, tasks, barriers), as a psychological phenomenon, perform stimulating and creative functions, which are manifested in the design and dynamization of activities, the mobilization of energy and creative resources such specialists as Maralov (2015), Lewin (2000), Prigozhin (1993), Shakurov (2001), including such teachers as Glushanyuk (2005), Kuzmina (1990), Mitina (2004), etc. At the same time, scientific research of Vinogradova (2018), Pastukhova (2017), Proyanenkova (2009) and the practice show that untimely detected and unresolved problems in teachers’ professional activities can become a serious obstacle to the achievement of the results planned at the Federal State Educational Standard.
The whole range of relatively stable problems that a particular teacher or a pedagogical team faces in the process of professional activity, requiring a certain attitude and an adequate solution, forms a problem field. Moreover, the problems that form the structure of a problem field (domains), as a rule, differ in the degree of intensity. Nevertheless, all of them are, in one way or another, significant for each member of the collective and are manifested in certain thinking, anxiety, worries, feelings, amplified under the influence of both external and internal factors. Operationally the problem field gives both researchers and managers the opportunity to systematize knowledge about the problems experienced by teachers, analyze and evaluate them, develop ideas and concepts for their solutions, and then check the efficiency of the decisions made in practice.
Research Questions
When developing a research tool, it is necessary to be guided by the methodological provision that any scientific measurement should be aimed at identifying the true value of the measured quantity. In this case, these are the real values of certain signs of problems in teachers’ professional activities in accordance with the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard of general education and the professional standard for teachers. Thus, timely identified and stated problems of teachers’ professional activity are an essential condition for the functioning of the scientific and methodological support system, both at the regional and institutional levels.
Purpose of the Study
Identification of the problem field of scientific and methodological support for secondary school teachers’ professional activities in the context of implementing the Federal State Educational Standard for general education and the introduction of the professional standard for teachers.
Research Methods
In the course of work, methods of theoretical research, systematization and classification, methods of comparative research, the system and activity approach were used.
Findings
The research sample was based on the theory of the sampling method, according to which the sampling population can be thousands of times smaller than the general population. In addition, it was taken into account that the levels of the readiness for work in accordance with the requirements of professional standards for teachers and the need for scientific and methodological assistance according to the criteria and indicators established in the methodology can vary significantly among different groups of teachers. Ultimately, the study sample was 1158 teachers from 30 secondary schools from 10 subjects of the Russian Federation: Moscow, Irkutsk, Nizhny Novgorod, Tula, Chelyabinsk, Astrakhan Regions, Stavropol Krai, the Republic of Tatarstan, Chuvashia, Sakha (Yakutia).
The sample of this study was three-stage, i.e. formed in three stages. At the first stage, large units of observation were chosen, which were secondary schools included in the Federal Institute for Education Development (FIRO) RANEPA network experimental site. At the second stage, teachers representing various subject areas were selected. At the third stage, the surveyed teachers were selected. Thus, at the first stage the units of selection were schools, at the second one they were subject areas, at the third – the surveyed teachers.
The representativeness of the sample is ensured by the fact that it reproduces the main characteristics of secondary school teachers: taught subject areas of general education; teaching experience, age. In addition, groups of teachers from both urban and rural schools are represented in the sample.
As follows from the data in the table and the pie chart, the majority of respondents are teachers of the Moscow Region (40.6%) and Stavropol Krai (30.3%). This is due to the fact that secondary schools of these constituent entities of the Russian Federation are the most active participants in the network experimental site of the Research Center for Socialization and Personalization of Children Education of the FIRO RANEPA.
The survey involved teachers of all subject areas and levels of general education, the distribution of which is presented in figure
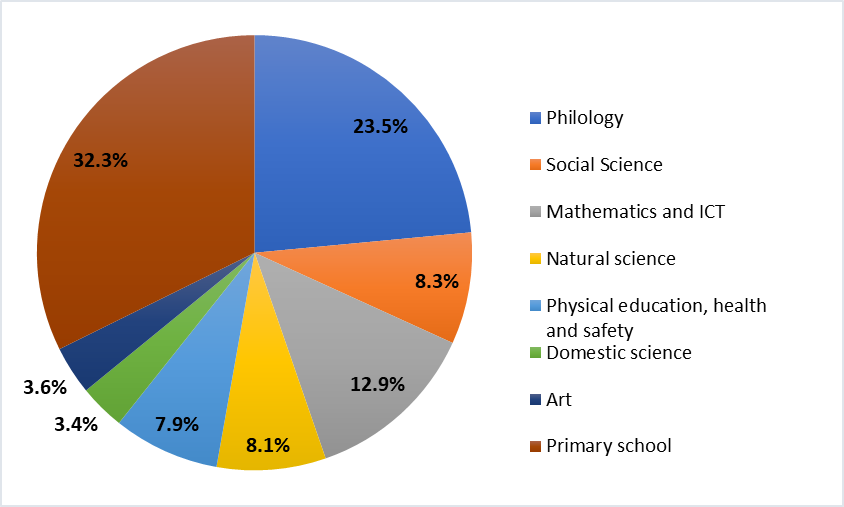
This distribution of respondents by subject area corresponds to the ratio (share) of subject areas in the curricula of educational organizations of general education.
The distribution of respondents by their teaching experience in the general education system is presented in table
As follows from the data in the table and the pie chart, a significant proportion of respondents were teachers with more than 20 years of work experience (44, 9%). The proportion of teachers with less than 5 years of teaching experience was 16.9%. It is alarming that teachers with professional experience from 5 to 15 years account for only 26.4% of the total number of respondents. This means that in ten years schools will face the acute problem of teacher shortages. The distribution of respondents by age is presented in figure
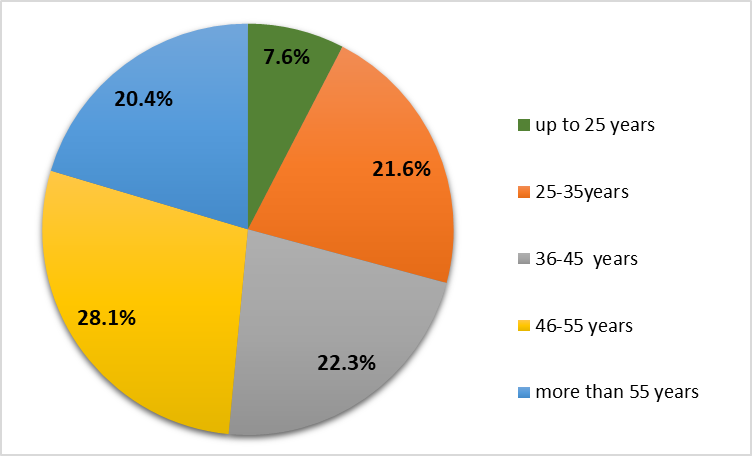
As follows from the above data, the largest group of respondents appeared to be teachers at the age range of 36 to 55 years (50.4%), which, according to modern psychological studies, refers to the second period of human maturity and is characterized by qualities such as: a high level of professional motivation, adequate self-esteem, self-sufficiency, vitality, social maturity, tolerance, adaptability (Voyushina, 2017). Due to the fact that during the study identifying the problem field of scientific and methodological support of professional activity was in store, it was necessary to find out whether teachers need such support, including mentoring and individual routes of professional growth. The survey results were analyzed according to the criteria: ‘General pedagogical function. Training, ‘Educational activities’ and ‘Developing activities’. The analysis showed that most teachers need scientific and methodological assistance on certain issues of performing labour functions of the professional standard. In particular, when performing the labour function ‘General pedagogical function. Training’ 47% of the surveyed teachers need help. When performing labour activities within the framework of the TF ‘Educational activities’, 52.4% of teachers need assistance. Teachers carrying out developing activities need help most of all - 63.2%.
Based on the analysis of the teachers’ obtained self-assessment data on their readiness for professional activity under the conditions of introducing the professional standard for teachers and the need for individual scientific and methodological assistance, the following components of the problem field of scientific and methodological assistance and support for teachers’ professional activity of the general education system were identified.
The first problem of scientific and methodological support of secondary school teachers’ professional activities is the differentiation of the content, forms and methods of methodological assistance in accordance with the specificity of the labour functions performed by teachers. In addition, such assistance should be differentiated by subjects of assistance, taking into account their age, teaching experience and subject areas taught (figure
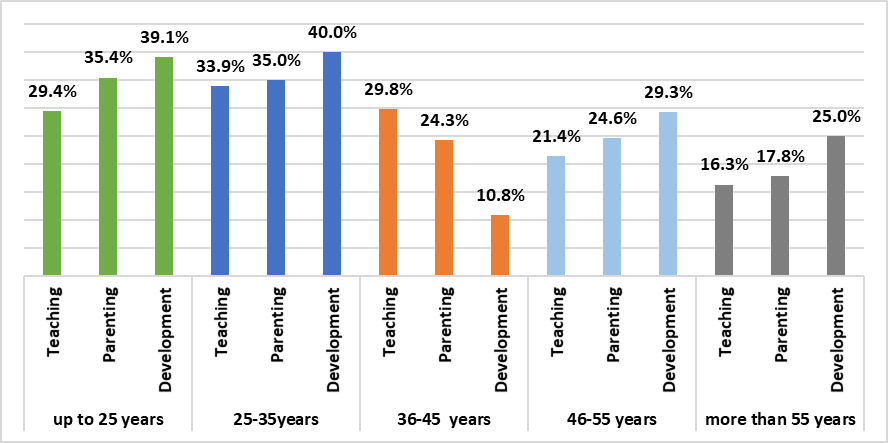
As follows from the data given in figure
As the data in figure 05 show, the highest level of the need for methodological assistance in all three labour functions is experienced by teachers with work experience of under 5 years. It should be noted that this age group included not only recent graduates of professional pedagogical universities and colleges, but also teachers who came to a secondary school without a specialized pedagogical education and took vocational training courses. They are, in particular, health and safety (OBZH), ICT, foreign language teachers. A high level of the need for methodological assistance is also noted among teachers with 5 to 10 years of professional experience. It can be assumed that this is a consequence of a decrease in the quality of pedagogical education, which is, in essence, the root problem of secondary school teachers professional activity.
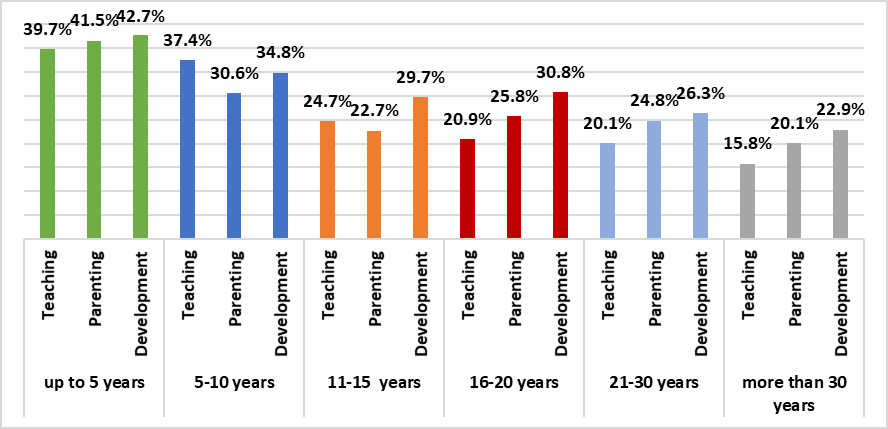
In general, confirmation was once again received that teachers need scientific and methodological assistance, regardless of age or professional experience. At the same time, 62.7% of respondents consider mentoring necessary at school. 19.7% of teachers admitted that they need a mentor. 25.9% are ready to become mentors for their colleagues. At the same time, 56.6% of teachers believe that they do not need a mentor.
It seems important to note that 25.9% of the teachers surveyed are ready to become mentors for their colleagues. Obviously, we can recognize that the statements in the media and social networks about teachers’ inertness, sluggishness, indifference and inability to effectively interact and co-create have no serious basis and have an emotional connotation.
The second problem of the scientific and methodological support of teachers' professional activities is the organization of mentoring in the general education system, including questions of its normative support, the selection and training of mentors, etc.
The third problem is related to the implementation in the general education system of such a form of teachers’ scientific and methodological support as an individual route for professional growth. 46.7% of respondents consider it possible to implement individual routes for teachers’ professional growth at school, and 24.2% of teachers recognize the need for this form of scientific and methodological support. At the same time, 8.7% are doubting the possibility of its practical implementation. 30.7% do not feel the need to use an individual route for their professional growth at all.
The fourth problem of scientific and methodological assistance for teachers' professional activities is related to the individualization of supporting their willingness to work in accordance with the professional standard. In fact, we are talking about the competence of teachers in the field of solving specific educational problems in accordance with the labour functions and labour activities established in the professional standard. Let us illustrate this with the example of the labour function "General pedagogical function. Training (A/01.6)". 48.6% of the teachers surveyed believe that they are fully ready to perform the labour function "General pedagogical function. Training". However, 46.3% indicated that they need individual assistance on certain issues related to performing certain labour actions. Only a quarter of teachers are sure that they do not need any help.
Specification of the level of labour activity proficiency within the framework of the labour function "General pedagogical function". The researching indicate that teachers have a rather high need for individual scientific and methodological assistance, as evidenced by the rating of labour actions, in the performance of which teachers have various difficulties:
- systematic analysis of the efficiency of training sessions and training approaches (52%);
- development and implementation of training programs within the framework of the basic general education program (50.8%);
- implementation of professional activities in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard of general education of the corresponding level (48.6%);
- formation of skills related to information and communication technologies (47.9%);
- formation of motivation for learning (45.5%);
- formation of universal educational activities (44.4%);
- organization, monitoring and evaluation of academic achievements, current and final results of mastering the main educational program by students (43.4%);
- planning and conducting training sessions (36.9%).
It is evident that, in each particular case, it is necessary to find out exactly what aspects of the performance of labour actions teachers have difficulties with and in what form it is better to help them. Despite the fact that pedagogical councils and methodological seminars are held for each of the indicated actions in schools, due to their collective nature they cannot fully compensate for teachers’ real professional deficits. And this means that the fifth problem of the scientific and methodological support of teachers’ professional activity arises — the formation of an efficient system for diagnosing and monitoring professional deficits, which requires the development of convenient, easy, and projective tools.
Conclusion
Thus, the following components of the problem field of the scientific and methodological assistance of teachers’ professional activities in the general education system can be identified.
1. Differentiation of the content, forms and methods of scientific and methodological assistance in accordance with the specificity of the labour functions performed by teachers taking into account their age, teaching experience and taught subject areas.
2. Organization of mentoring in the general education system.
3. The implementation of such a form of teachers’ scientific and methodological support as an individual route of professional growth.
4. Individualization of scientific and methodological support of teachers' readiness to work in accordance with the professional standard.
5. Formation of an efficient system for the diagnosis and monitoring of teachers’ professional deficits.
Secondary school heads, methodological services employees’ familiarization with the results of this study will allow a comparative analysis of the article’s data with data on their educational organizations. A thorough, comprehensive and deep analysis will serve as a basis for:
- understanding the general picture (problem field) of secondary school teachers’ readiness to work in the context of the introduction of the professional standard for teachers and their need for individual scientific and methodological support;
- identification of teachers' readiness to work in the context of the introduction of the professional standard and the need for scientific and methodological support of specific (single) problems of a particular school amid common problems for all secondary schools;
- designing models of the system of teachers’ scientific and methodological support, including mentoring and individual routes for teacher professional development, taking into account regional and institutional features of educational organizations;
- discussing the results of diagnostic research on pedagogical and methodological councils, conducting a SWOT analysis to develop a school strategy for performing the tasks of the Federal Project ‘Teacher of the Future’, as well as relevant regional and local documents;
- planning the content, forms and methods of collective, group and individual scientific and methodological work in secondary schools, including the use of the network and remote interaction capabilities.
Acknowledgments
The article was prepared as part of the research work of the state assignment of the RANEPA for 2020 "Development of the Personalized Support System for Teachers in the Framework of the National System of Teachers Professional Growth".
References
- Gritsanov, A. A. (1998). Noveyshiy filosofskiy slovar [Newest Philosophical Dictionary]. Publishing House V.M. Horse.
- Glukhanyuk, N. S. (2005). Psihologiya professionalizacii pedagoga [Psychology of Teacher Professionalization]. Publishing House Ros. state prof. University.
- Kuzmina, N. V. (1990). Professionalizm deyatelnosti i lichnosti prepodavatelya i mastera proizvodstvennogo obucheniya [Activity and Personality Professionalism of a Teacher and a Master of Vocational Training]. Higher School.
- Lewin, K. (2000). Razresheniye socialnih konfliktov [Resolving Social Conflicts]. Speech.
- Maralov, V. G. (2015). Problema baryerov samorazvitiya lichnosti v otechestvennoy psihologii. [The Problem of Personal Self-Development Barriers in Russian Psychology]. Almanac of Modern Science and Education, 1(91), 72 - 76.
- Mitina, L. M. (2004). Psihologiya truda i professionalnogo razvitiya uchitelya [Psychology of Labour and Teachers’ Professional Development]. Academy.
- Pastukhova, I. P. (2017). Problema formirovaniya metodicheskoy kompetentnosti prepodavateley v kontekste vnedreniya professionalnogo standarta pedagoga: Sredneye professionalnoye obrazovaniye. [The Problem of the Formation of Teachers’ Methodological Competence in the Context of the Introduction of the Professional Standard for Teachers]. Secondary Vocational Education, 2, 3 - 9.
- Prigozhin, A. I. (1993). Novovvedeniya: stimuli i prepyatstviya [Innovations: Incentives and Obstacles]. New School.
- Proyanenkova, L. A. (2009). Metodicheskaya podgotovka budushih uchiteley k resheniyu tipovih zadach organizacii uchebno-vospitatelnogo processa po fizike: problema, koncepciya, model: Monografiya. [Future Teachers’ Methodological Training for Solving Typical problems of Organizing the Educational Process in Physics: Problem, Concept, Model: Monograph]. Moscow State University.
- Shakurov, R. K. (2001). Baryer kak kategoriya i ego rol v deyatelnosti. [Barrier as a Category and Its Role in Activities]. Psychology Issues, 1, 3 - 18.
- Tarasova, N. V., & Pastukhova, I. P. (2017). Problemi i zatrudneniya uchiteley pri ispolzovanii novih pedagogicheskih tehnologiy obucheniya [Teachers’ Problems and Difficulties When Using New Pedagogical Teaching Technologies]. Proceedings of the Russian Academy of Education, 4(44), 87 - 95.
- Vinogradova, A. P. (2018). Pedagogicheskiye usloviya preodoleniya professionalnih zatrudneniy uchiteley v postroyenii obrazovatelnogo processa v osnovnoy shkole [Pedagogical Conditions for Overcoming Teachers' Professional Difficulties in Building the Educational Process in Secondary School] (Doctoral dissertation). https://search.rsl.ru/ru/record/01008707307
- Voyushina, E. A. (2017). Podhodi k opredeleniyu kriteriyev zrelosti lichnosti: Aktualniye voprosi sovremennoy psihologii: materiali IV Mejdunarodnoy nauch.konf. [Approaches Defining Personality Maturity Criteria: Actual Issues of Modern Psychology]. Materials of the IY International Scientific Conference. Krasnodar: Novation, 11-14
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
15 November 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-093-8
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
94
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-890
Subjects
Psychology, personality, virtual, personality psychology, identity, virtual identity, digital space
Cite this article as:
Tarasova, N. V., Pastukhova, I. P., & Chigrina, S. G. (2020). Problem Field Of Scientific And Methodological Support Of Teachers' Professional Activity. In T. Martsinkovskaya, & V. Orestova (Eds.), Psychology of Personality: Real and Virtual Context, vol 94. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 779-788). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.11.02.95

