Abstract
Innovation is a concept that has received much attention in recent years. Innovation leads to the product and process improvement, assists organization to survive, to grow faster, to be more efficient, and ultimately to be more profitable than non-innovators. However, the innovation rate in Malaysia is not yet reaching the full potential. In addition, innovative behavior in Malaysia is still at the infancy stage, especially among SMEs in Malaysia. In order to boost the innovation rate, it is imperative to solve the challenges and issues faced by SMEs. Thus, the enablers of innovation performance are proposed to SMEs in this study. With the enablers proposed, it can lead to a greater innovation performance among SMEs and assist the country’s growth which eventually improve the global innovation index ranking. As such, organizational culture and organizational learning are proposed as potential enablers to improve innovation performance among SMEs. The study also proposed open innovation as a potential mediator with the above relationships. In a nutshell, the purpose of the present study is to propose a conceptual framework which can be utilized to boost the innovation among Malaysian SMEs.
Keywords: Innovationinnovation performancesmall and medium enterprisesMalaysia
Introduction
In today digitalize era, the Industrial Revolution (IR) 4.0 is gaining its popularity. IR 4.0 is being emphasized among SMEs in Malaysia as it has been a long acknowledged that SMEs contribute significantly to the overall economic performance around the world, and Malaysia is not an exception. In fact, SMEs can transform to be better in enhancing organization, management and production capabilities; improving productivity and efficiency; enabling better quality and monitoring; and developing innovators and producers of IR 4.0 technologies (MITI, 2018). However, SMEs in Malaysia are not yet reaching the full potential in improving the performance (Zakaria et al., 2016). Therefore, it is important to understand the drivers that can assist SMEs to fully contribute to the economic performance especially in innovation performance.
According to global innovation index (GII) 2018, Malaysia with a score index of 43.16/100 has been ranked at 35th place in Global ranking and at 8th in SEAO (South East Asia, East Asia and Oceania) ranking. Malaysia used to record a strong GII score between 2011 and 2013 (See Figure
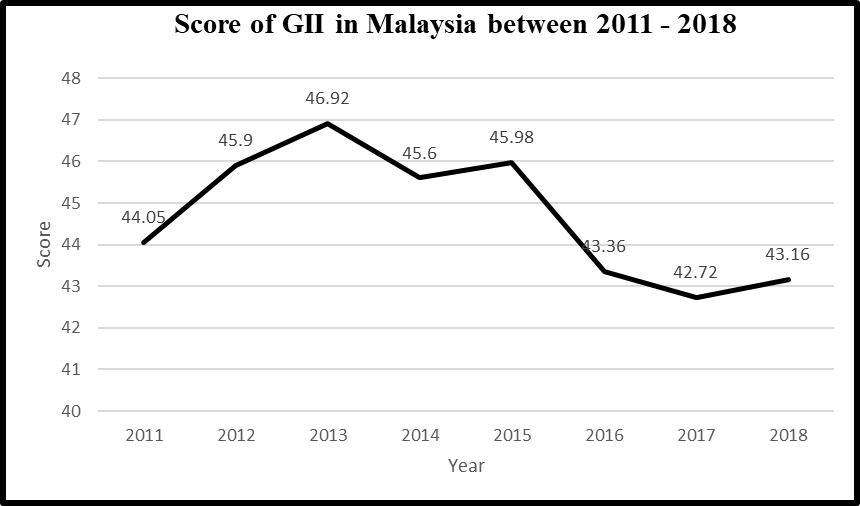
Other than that, SMEs recorded a higher GDP growth of 7.2% in 2017 compared to 5.2% in 2016. Besides that, SMEs has continued surpass the overall GDP growth of 5.9%. The higher SME GDP growth was led by both private consumption and investment activities, contributed by the strong domestic demand, sustained by domestic and foreign tourist spending which partly due to the hosted of Southeast Asian (SEA) Games and also the higher exports demand for products and services of SMEs from ASEAN and other trading partners (SME Corp, 2017). However, by comparing the GDP growth in Malaysia with other Asia countries (The World Bank, 2017), Malaysia is at position which need to push harder in order to enhance the growth of GDP. Even though Vietnam, Myanmar, Philippines, and India are the lower-middle income countries, while Malaysia located in upper-middle income countries, they still leading ahead of Malaysia in terms of GDP growth. Other than that, the SME Masterplan aims to boost the sector’s contribution to the nation’s economy by potentially contribute 41% for the GDP by 2020 in Malaysia (The Star, 2018). However, the recent SMEs GDP contribution has increased to 37.1% as compared to 36.6% in 2016 and 36.3% in 2015 (SME Corp, 2017). Based on the statistics, the increment of SMEs GDP is far from desired. To assure SMEs are able to contribute 41% of GDP by 2020, SMEs should be given a huge attention, support and assistance. Therefore, a research pertaining to innovation of SMEs heed the call in Malaysia.
As moving towards a high-income nation by 2020 through productivity-driven and innovation-led growth, Malaysian SMEs must adopt innovation and technology in their business operation. However, SMEs always faced the challenges in their innovation and commercialization due to lack of integrated support and funding to finance. According to CEO Steinbeis Malaysia Foundation (STMY), Dr. Abdul Reezal Abdul Latif, SMEs have the desired to innovate but the challenges they faced to innovate and transform their organization towards IR 4.0 are capital and time (The Malaysian Reserve, 2018). Besides that, the other constraints that confronted by SMEs are lack of knowledge on competitors and global demand, information on the targeted market, and employee skills (SME Corp, 2017). These problems faced by SMEs have to be encountered as it will affect the tendency of innovation. Thus, there is a need for more extensive research in innovation performance particularly among SMEs. To encourage more involvement of SMEs in innovation, it is important to identify enablers of innovation performance. The present study therefore tends to determine the enablers of innovation performance among SMEs in Malaysia.
Problem Statement
Innovation is a crucial variable as it can help organization to configure the existing resources, products, processes, and systems to adapt to the market (Chen et al., 2018). It has been addressed that with the absence or low level of innovation performance, it will affect the organization and consequently the entire economy. Hence, innovation is a solely needed to be concerned as it is important in sustaining the country growth.
According to our Prime Minster, Tun Dr. Mahathir Mohammad, Malaysia requires to strengthen the innovation capacity and capability in order to improve GII ranking to top 30. As now, Malaysia has ranked at 35th place and the phenomenon of GII score is kept dropping from 2013 to 2018, therefore performance of innovation which need to be concerned especially among SMEs.
Besides that, the increment of SMEs GDP is far from desired based on the statistics. To assure SMEs can contribute 50% of GDP by 2030, innovation performance among SMEs have to be improved. It is believed that with the improvement of innovation among SMEs, it can lead to huge consumption among consumers, and eventually help in improving GDP. Therefore, a research pertaining to innovation of SMEs heed the call in Malaysia.
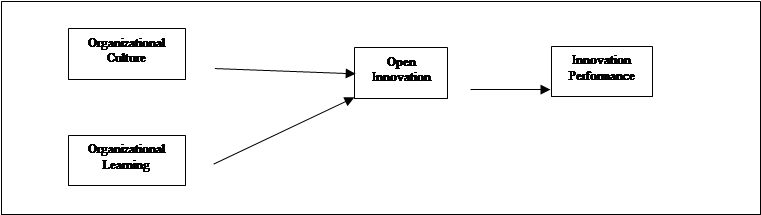
Last but not least, the issues that faced by SMEs such as lack of capital and time, lack of knowledge on competitors and global demand, lack of information on the targeted market, and lack of employee skills must be solved as it will affect the tendency of innovation. Thus, it is important to identify enablers of innovation performance to encourage more involvement of SMEs in innovation. The enablers of innovation performance consist of organizational culture, organizational learning and open innovation.
Research Questions
Research question is one of the critical steps in the research process. In this study, the research aims to answer the questions below:
Does open innovation mediate the relationship between organizational culture and innovation performance?
Does open innovation mediate the relationship between organizational learning and innovation performance?
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the present study is seeking the ways to enhance innovation performance among SMEs. Indeed, SMEs, government and policymakers would be interested to know how to improve innovation performance in organization. By narrowing the context of this study, it should be able to provide a better innovation knowledge to the managers of SMEs. In fact, this study is expected to serve as a guide to managers in Malaysia on how the organization could be increased the innovation activities and improve the innovation performance with the assist of enablers of innovation performance such as organizational culture and organizational learning. With the knowledge provided, managers of SMEs can be organized their business more successfully and stay competitive.
Besides that, the present study aims to provide useful information to the government. It is predicted to provide a greater information related SMEs for government in order to help and solve the issues faced by SMEs. Therefore, the government agencies such as SME Corporation Malaysia (SME Corp), Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MOSTI), Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC) etc. can provide a greater support or assistance to SMEs in enhancing innovation performance and eventually increase the ranking of GII.
The present study also serves as a guide to policymakers to formulate the appropriate measures as well as the policies for SMEs to boost the innovation performance. Through this study, policymakers can propose a better and suitable scheme and support programs or activities to SMEs which can promote the long-term output growth and improve the productivity and eventually can enhance the economy of the country.
Research Methods
In this study, managers of SMEs from five different states in Malaysia namely Selangor, Kuala Lumpur, Johor, Perak and Penang are selected as sample. This is because these five states have the highest concentration of SMEs. According to the statistics provided by SME Corp (2016), Selangor is the highest concentration of SMEs with 19.8%, followed by Kuala Lumpur with 14.7%, Johor with 10.8%, Perak with 8.3%, and Penang with 7.4%. Besides that, the present study will focus on SMEs that have been operating for at least a year. The main reason is many SMEs fail within the first year following start-up (Kee et al., 2019). The resilience and durability of SMEs is crucial and that is where the present study only include SMEs have been operating at least a year. Another reason is innovation can only happen if SMEs have the capacity to innovate. Certain amount of time is needed to observe the exact innovation performance of SMEs. Thus, the inclusion criteria for SMEs are (1) SMEs from five states in Malaysia namely Selangor, Kuala Lumpur, Johor, Perak and Penang; and (2) the organization has been operating for at least a year.
Due to the difficulty to gain voluntary from organization to conduct survey, the steps taken to approach organization should be encountered. Before the distribution of questionnaire, researcher will seek for the permission from SMEs managers to conduct survey based on the list that retrieve from SMEs directory database. SMEs will be approached either with a call or through an email. The purpose of this approaching is to notify the related study is being conducted and requested for the permission from them to be part of respondents. After getting approval from them, a set of questionnaire will be sent to them via email. The questionnaire will be prepared via online form which is Google Form. A cover letter will be attached with the questionnaire to state the purpose of the questionnaire. Moreover, researcher will be assured of confidentiality of the data gathered from respondents. A contact number of researchers also will be provided for respondents in case they have any inquiry.
Findings
The present study proposes two potential enablers of innovation performance among SMEs in Malaysia namely organizational culture and organizational learning. Organizational culture has been highlighted as significant predictor to the innovation success among SMEs 2009). The local researchers, Abdullah et al. (2014) has urged for more studies on organizational culture and innovation among SMEs in Malaysia to enhance the understanding on the dynamic of organizational culture. In addition, a report has indicated that 70% of SMEs has reached to full growth potential as the workplace culture has limited their innovative idea to flourish (MalayMail, 2016). Of which, there were only 33% of SMEs were innovation leaders with skilled in responding any changes, threats, and chances in their markets, 43% of SMEs were innovation businesses which are interested in innovation but under-delivered in practice, and 24% were laggards with no or little interest in innovation plan (MalayMail, 2016). To improve the innovation among SMEs, it requires a mindset change among employees. Therefore, the present study heeds the call by Abdullah et al. (2014) to investigate the relationship between organizational culture and innovation performance among SMEs in Malaysia.
Organizational learning is another important enabler in driving innovation in Malaysia. Raj and Mahapatra (2009) indicated that organizational learning is needed in order to improve labour skill. However, according to Bizsphere Managing Consultant, Mr. Yap Keng Teck, Malaysian SMEs are lack of learning to face the borderless digital economy especially in the IR 4.0 (Business Insider Malaysia, 2018). It is interesting to note that 62.1% of SMEs commented that the greatest challenge for the successful implementation of the IR 4.0 is lack of skills and knowledge among employees (SME Corp, 2017). Therefore, organizational learning is extremely needed among SMEs to sustain and boost the innovation performance. Hence, organizational learning is proposed for Malaysian SMEs in present study.
Open innovation is a proposed mediator in present study. SMEs must facilitate their automation and digitalization to stay competitive. In the SME Survey, 31.8% of the respondents are aware of IR 4.0. Of which, about 69% of them are ready for the Industry 4.0, 66.4% are anticipating that the adoption of Industry 4.0 can enhance the productivity and efficiency, and 62.1% respondents realize that the biggest challenge in implementing Industry 4.0 is the employees’ lack of knowledge and skills (SME Corp, 2018). Other than that, the challenges faced by SMEs are lack of technology knowledge, lack of understanding of digital tool usage, lack of awareness on financing options and limited access to technology (SME Corp, 2018). Besides that, shortage of skilled workers in Malaysia is the greatest challenge as there is a strong demand for a digital workforce (The Star, 2019). Therefore, SMEs must continuously seek for the new and existing technologies in aligning their business with IR 4.0. As an open innovation concept allows the organization to explore outside knowledge and to exploit internal resources to stay competitive (Drechsler & Natter, 2012; Popa et al., 2017), it might be beneficial to solve the problems of lacking knowledge and skills as well as financial issue. Thus, open innovation is proposed to mediate the four enablers toward innovation performance.
As conclusion, the present study proposed organizational culture and organizational learning as the potential enablers that can assist in improving the innovation performance among SMEs. The study also proposes that open innovation as a potential mediator with the above relationships. Hence, this study proposed the use of organizational culture and organizational learning in innovation performance via the mediating role of open innovation. The proposed framework as shown in Figure
Conclusion
Although many empirical studies have already been carried out in innovation performance within the context of SMEs, this study attempts to fill the literature gap in order to benefit both academicians and researchers. As according to Gomes and Wojahn (2017), and Garcia-Morales et al. (2018), scholars urged to examine other factors that related to innovation performance. Therefore, the two enablers of innovation performance namely organizational culture and organizational learning are employed in the present study. With these enablers of innovation performance, it can improve innovation performance among the SMEs and eventually improve the economy in Malaysia. Specifically, this study is expected to assist managers in managing their innovation activities with the strong sources proposed to stay competitive in IR 4.0.
References
- Abdullah, N. H., Shamsuddin, A., Wahab, E., & Hamid, N. A. A. (2014). The relationship between organizational culture and product innovativeness. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 129, 140-147.
- Business Insider Malaysia (2018). Malaysian SMEs are plagued by high costs and insufficient funds, survey finds. Business Insider Malaysia. https://www.businessinsider.my/malaysian-smes-are-plagued-by-high-costs-and-insufficient-funds-survey-finds/
- Chen, Z., Huang, S., Liu, C., Min, M., & Zhou, L. (2018). Fit between organizational culture and innovation strategy: Implications for innovation performance. Sustainability, 10(10), 3378.
- Drechsler, W., & Natter, M. (2012). Understanding a firm's openness decisions in innovation. Journal of Business Research, 65(3), 438-445.
- Garcia-Morales, V. J., Martín-Rojas, R., & Lardón-López, M. E. (2018). Influence of social media technologies on organizational performance through knowledge and innovation. Baltic Journal of Management, 13(3), 345-367.
- Gomes, G., & Wojahn, R. M. (2017). Organizational learning capability, innovation and performance: study in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMES). Revista de Administração (São Paulo), 52(2), 163-175.
- Kee, D. M. H., Yusoff, Y. M., & Khin, S. (2019). The role of support on start-up success: a PLS-SEM approach. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 24, 43-59.
- MalayMail (2016). How SMEs can innovate. https://www.malaymail.com/news/life/2016/10/20/how-smes-can-innovate/1231581
- MITI (2018). Industry 4WRD: National Policy on Industry 4.0. https://www.miti.gov.my/miti/resources/National%20Policy%20on%20Industry%204.0/Industry4WRD_Final.pdf
- Popa, S., Soto-Acosta, P., & Martinez-Conesa, I. (2017). Antecedents, moderators, and outcomes of innovation climate and open innovation: An empirical study in SMEs. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 118, 134-142.
- Raj, S. R., & Mahapatra, M. K. (2009). Growth and productivity performance of small manufacturing enterprises (SMEs) Insights from major states in India. Journal of Indian Business Research, 1(1), 39-56.
- SME Corp (2016). Special Highlights Economic Census 2016: Profile of SMEs. http://www.smecorp.gov.my/images/SMEAR/3_Chapter1.pdf
- SME Corp (2017). SME Developments and Outlook. SME Annual Report 2017/18. http://www.smecorp.gov.my/index.php/en/laporan-tahunan/3342-laporan-tahunan-pks-2017-18
- SME Corp (2018). SME Annual Report 2017/18 - A Connected World: Digitalising SMEs. http://www.smecorp.gov.my/index.php/en/?option=com_content&view=article&layout=edit&id=3342
- The Malaysian Reserve (2018). Lack of capital and time hampering SMEs to innovate. The Malaysian Reserve. https://themalaysianreserve.com/2018/03/15/lack-of-capital-and-time-hampering-smes-to-innovate/
- The Star (2018). SMEs need to rise to the challenge. The Star. https://www.thestar.com.my/metro/smebiz/focus/2018/01/01/smes-need-to-rise-to-the-challenge/
- The Star (2019). Kelly Services: Huge demand for digital skills. The Star. https://www.thestar.com.my/business/business-news/2019/03/28/kelly-services-huge-demand-for-digital-skills/
- The World Bank (2017). World Bank national accounts data, and OECD National Accounts data files. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD.ZG?end=2017&locations=IN-MM-CN-VN-MY-PH&start=2017&view=bar&year_high_desc=true
- Zakaria, N., Abdullah, N., & Yusoff, R. (2016). The innovation-performance linkage: Empirical evidence of Malaysian manufacturing SMEs. Paper presented at the International Soft Science Conference, Langkawi Island, Kedah, Malaysia.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
06 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-087-7
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
88
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1099
Subjects
Finance, business, innovation, entrepreneurship, sustainability, environment, green business, environmental issues
Cite this article as:
Teh, S. S., & Kee, D. M. H. (2020). The Need Of Innovation Among Malaysian SMEs. In Z. Ahmad (Ed.), Progressing Beyond and Better: Leading Businesses for a Sustainable Future, vol 88. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 721-727). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.65
