Abstract
The strong bonding between SMEs and nation’s economy caused the rise of attention towards the SMEs’ development. However, SMEs in Malaysia are not developed in the full strength. Organizations that are not developed well will suffer and struggle in surviving in this competitive market as the commerce is changing rapidly. It is believed that the value and resources that carried by knowledge could help, guide and lead organization in gaining competitive advantage in the market. As such, knowledge works as the asset and capital in driving the organization’s success. Besides knowledge, innovation helps organization to reshape and reinvest themselves that could standstill in the competitive emerging market. Innovation works in producing a new and creative idea in implementing new products or enhancement on the existing products which could help to improve the organizational performance. This study examines the relationship between knowledge management and export performance among SMEs in Malaysia, mediated by innovation. This paper focuses on the manufacturing industry of SMEs. There are three dimensions of knowledge management in this study, namely, knowledge acquisition, knowledge dissemination and knowledge application. This study anticipates that the three dimension of knowledge management are critical antecedents on the export performance which could lead to positive relationship with the export performance of SMEs. The findings of the study provide an insight towards the organizations which could lead them in identifying effective strategies and helps in improving their export performance.
Keywords: SMEsknowledge managementknowledge acquisitionknowledge disseminationknowledge applicationexport performance
Introduction
Export performance help to determine the wealth of a kingdom and play an essential role in helping an organization to create the positional benefit in the market (Porter, 1985). Besides that, manufacturing industry emerge as a speeding altering industry and performs a necessary function towards the country. The competitive market and fast changing technology in the market stressed the manufacturing industries to create more value and resources to the customers. In order to continue to be in the competitive market, organizations begin to reinvest and reshape themselves. In conjunction with this, a quantity of studies highlighted product and process innovation in exploring innovation.
Besides that, knowledge management is extensively used within the business market to the extent of export performance or business performance (Suraj & Ajiferuke, 2013; Tseng, 2014; Yang et al., 2012). Nazari and Emami (2012) mentioned that knowledge management allows the organization to get the knowledge and utilize the information and data well. Knowledge management is likewise regarded as the most integral asset for organization as knowledge is vital for business to gain positional benefit in the aggressive market (Sarkindaji et al., 2014). Daud and Yusoff (2010) mentioned that the concept of knowledge management started to enforce in Malaysia at some stage in the late nineties when Microsoft delivered in knowledge when they start their business in Malaysia. In conjunction with this, Malaysia government implemented Knowledge Economy Master Plan in order to achieve the aim in remodelling Malaysia into a knowledge-based economy.
In addition, a few SMEs are still confronted the loss of utility, information and capabilities, restricted to admission of applicable facts on era and dependency on bad and obsolete technology. Moreover, SME’s viable to innovate is constrained to knowledge and available facilities are insufficient and inefficient. Other than that, the perception at the results of KM in the direction of the business performance is still present process development wherein further research is needed to develop the expertise of KM in the direction of business overall performance. Therefore, it is vital to decide how knowledge management is executed among SMEs and how the knowledge management and innovation affect the export overall performance in SMEs.
Hashim and Abdullah (2000) pointed out that the definitions of SMEs in Malaysia is based on the quantitative measure such as number of workers, volume of capital and sales. Therefore, SMEs in Malaysia are classified into several group such as Micro, Small or Medium depending on their number of workers, sales and capital.
SME Corp 2018 defined manufacturing region in SMEs Malaysia which involved the sales turnover not exceeding RM 50 million in addition to the total-time employees is not greater than two hundred employees. Besides that, Mustapha et al. (2011) mentioned that there are several activities within the manufacturing sectors of SMEs Malaysia including manufacturing and processing of uncooked materials, petroleum, chemical, rubber and plastic products, meals, drinks and tobacco products, non-metal mineral products, fundamental metals and fabricated metallic products and manufacturing of electrical and electronics appliances.
Underpinning Theories
There are two underpinning theories in this study, such as knowledge-based view which is extended from aid- resource-based view theory and Internationalization model which consists of Uppsala-model and Innovation-model. Knowledge-based view theory depicts the expertise primarily based competition in which business used to differentiate themselves with the competitors. This principle is used with a purpose to depict on how SMEs may want to acquire the aggressive benefit thru knowledge management and additionally how SMEs combine the knowledge asset on the way to create the knowledge management correctly. Resource-based view is used to expose on how the employer ought to gain the aggressive advantage within the marketplace (Grunert & Hildebrandt, 2004). In internationalization model, Uppsala-model defines on the involvement of modern corporations in internationalization at the same time Innovation-model defines on the importance of technology in the direction of the surroundings and internationalization process. Uppsala-model guides SMEs in deciding on the correct strategies in which assist to explain the internationalization method. In addition, Uppsala-model also facilitates SMEs to benefit their knowledge toward the internationalization (Johanson & Vahlne, 2009). Innovation-model allows SMEs to drive technology evolution in which it match all industries that capable of adapt and follow innovation of their industry. Besides that, innovation-model defines on the significance of generation towards the environment and internationalization method.
Literature Review
Export performance can attempt to improve the overall performance of the SMEs inside the control. Throughout the export overall performance, SMEs ready to see whether their commercial enterprise is in an amazing stage or worse stage. Besides that, several researches are done to discover the determinants of the export performance of the organization. Apart from this, a few researchers diagnosed numerous variables including comparative advantage, government policies, market characteristics and alternate charge fluctuations in influencing the export overall performance of the organization. Organization that involve exporting face barriers to be successful in the marketplace. Kantapipat (2009) noted that the greatest barrier in exploring is the attitudes towards adapting or assembly purchaser preferences. Aziz and Yassin (2010) said that monetary issues and absence of capital are the obstacles for exporting. This is supported by using Alam et al. (2011) that capital fund stays as one of the most difficult troubles that confronted by way of Malaysian SMEs. It happens the equal for Manufacturing SMEs that the first state of affairs for exportation is the capital shortage.
Innovation permits the organisation to reshape into new structure that could allow them to measure competitive within the marketplace compared to their competition. Innovation is represented as a result of expansion of products, services and market likewise is named as the improvement of recent gadget closer to the business (Crossan & Apaydin, 2010). Subramaniam and Youndt (2005) show that innovation allows agency to convert thoughts into original or more advantageous products or services which permits the business enterprise to stay competitive in the marketplace in addition to permit organization to differentiate the uniqueness in them compared to their competition. In short, innovation plays a crucial function towards the businesses as it can result in the overall performance enhancement of the corporate.
Knowledge is significant vital to the business as it mightwork as the source for the organization to survive within the competitive market. Liao et al. (2008) and Wang and Lin (2013) referred to that knowledge no longer solely can improve the overall performance however additionally address the challenges that organizations face. Young (2007) air out that it is critical to implement KM as an area which permit the employees to create, share and practice the knowledge that can cause the fulfilment of the business enterprise. Durst and Edvardsson (2012) and Marra et al. (2012) said that KM ought to be protected in SMEs’ daily operation if you want to drive fulfilment a few of the SMEs. There are three dimensions of knowledge management namely, knowledge acquisition, knowledge dissemination and knowledge application might be discussed on this take a glance at.
Knowledge acquisition is the system of developing or generating the knowledge. The flow of knowledge lets the employees to recognize the client well in addition to advantage competitor’s statistics via purchaser. Reisi et al. (2013) mentioned that the acquired knowledge needs to be prepared correctly as well as to be precious and useful towards the firm. Liao et al. (2010) referred to that and experience are needed in the process of obtaining the knowledge. Knowledge acquisition plays an essential position in the direction of the organisation. This is because the precise knowledge acquisition lead to the boom of the asset of understanding towards the organization and hence beautify the overall performance of the firm.
Tseng (2014) declared that knowledge dissemination or knowledge conversion allows the outside knowledge received to be remodelled into internal knowledge. Besides that, Daud and Yusoff (2010) outlined knowledge dissemination or knowledge conversion as the process in organizing the knowledge that has been created to be able to be familiar and on hand to that particular information. In addition, Makore and Eresia-Eke (2014) related knowledge dissemination as the distribution of knowledge within the business.
Daud and Yusoff (2010) defined knowledge that involves in garage and sharing software in of knowledge. Knowledge application involves in storage and sharing utility in of knowledge. Lizasoain et al. (2015) additionally stated that knowledge acquisition could assist in problem solving in which the information obtained can immediately carried out in solving the troubles confronted. Bhatt (2001) said that it is far essential for knowledge application to be carried in the organizations because it permits the companies to be additional energetic and build worth.
Innovation plays a crucial role closer to the corporation not most effective in improving the overall performance of company but also permit the organization to live on within the aggressive marketplace. Leal-Rodriguez et al. (2013) cited that it is vital to control knowledge in a company because the knowledge may result in innovation which turns the brand-new thoughts into action that could benefit to the company. For instance, have a look at that was performed by using Nawab et al. (2015) concerning the connection the knowledge management and innovation inside the banking enterprise. The outcome display that there is a wonderful dating among knowledge control and innovation. In this examine, three dimensions of knowledge control, particularly, knowledge acquisition, knowledge dissemination and knowledge application are accomplished so as to check the impact towards SMEs overall performance whereby innovation works because the mediator.
Problem Statement
SME Corp Malaysia located out that SMEs in Malaysia are dealing with numerous demanding situations in such low productiveness, low business formation, small variety number of excessive growth organization in contributing to the monetary system and the economy lifecycle. These characteristics might lead to the low usal performance of SMEs in Malaysia. According to SME Corp Malaysia (2018), SMEs in Malaysia has the low productiveness wherein the productivity whereby the productiveness in line with employee averaged RM 47000. Some SMEs are nonetheless faced lack of application knowledge and skills, limited access to relevant facts on era and dependency on terrible and obsolete technology. According to SME Corp Malaysia CEO, Datuk Dr. Hafsah, SMEs regularly lack time, manpower and investment in conducting studies and improvement. For them, research and improvement is considered as a value than as a funding.
Even though there are numerous studies which have been carried out on the business performance amongst SMEs regarding on knowledge management, the field nevertheless loss of exploration at the impact of knowledge management towards export performance. It is likewise despite that the fact that not surely understood concerning the impact of KM within the organizations. Although it is far found that there is some researcher’s awareness at the knowledge management towards the export performance amongst SMEs, the end result are blended and now no longer uniform.
Apart from it, the perception at the outcome of KM toward the export overall performance stays undergoing development in which similarly studies is needed with the intention to increase the know-how of KM towards export overall performance. In quick, there is a need to determine the relationship amongst KM and export performance among SMEs.
Research Questions
This research is carried out to examine the relationship between the dimensions of knowledge management and the export performance among SMEs in Malaysia and mediated by innovation. While the study is conducted, several questions are being asked as below:
Is there any relationship between knowledge acquisition and innovation among SMEs in Malaysia?
Is there any relationship between knowledge dissemination and innovation among SMEs in Malaysia?
Is there any relationship between knowledge application and innovation among SMEs in Malaysia?
Is there any relationship between innovation and export performance among SMEs in Malaysia?
Purpose of the Study
The primary purpose of this study is to introduce the critical of knowledge management and innovation amongst SMEs in Malaysia. This research geared toward analysing the scale of KM which could impact upon the export performance amongst SMEs which is mediated with the aid of innovation. It goals to take a look at whether or not there may be a relationship among the dimensions of KM, innovation and export performance among SMEs. The study intends to cope with the inadequate level of empirical findings regarding the impact of the expertise control toward the export performance amongst SMEs in Malaysia. Since the finding on the relationship are blended, this studies goals to offer extra results to existing researchers to ensure the connection more convincing.
Research Methods
Academic databases were explored to retrieve literature for the study. Areas related to innovation, organizational performance, and competitive advantage of the organizations were examined. Databases such as ScienceDirect, utmj.org, nih.gov, nchu.edu.tw, palgrave-journals were explored, and keywords such as SMEs, Malaysia, competitive advantage, innovation, organization performance, export performance of SMEs, resource-based view, knowledge-based view etc. were used to retrieve literature related to the study. The Google Scholar search engine, as well as institution databases such as web of science, Scopus, ProQuest etc. were searched to retrieve facts and figures and academic literature the study. Scientific research databases were explored to identify and elaborate the research variables used in the conceptual model. Databases searched for research variables were ScienceDirect, sage pub, jcu.edu.au, tamu.edu. To obtain the facts, figures and estimations about export performance of the SMEs in Malaysia, different types of sources were explored such as industry reports, government reports, market research reports, media reports, and internet sources. To retrieve literature related to variables, only scientific literature of high quality was examined.
Findings
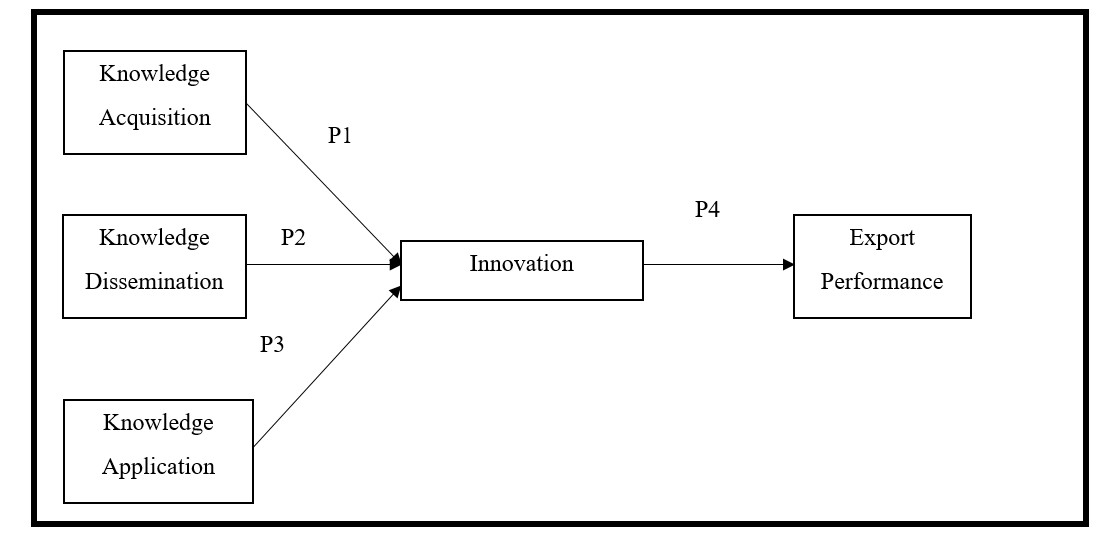
The courting between the expertise control and export performance amongst SMEs Malaysia is decided thru this study. There are numerous researches being performed by using the students in determining the connection among the innovation and business overall performance. For example, a study that was performed through Nawab et al. (2015) concerning the connection the knowledge management and innovation in the banking enterprise. The results of the observe display that there is a positive relationship between knowledge management and innovation. A observe that was conducted with the aid of Hurmelinna-Laukkanen (2011) in determining the connection among knowledge sharing and innovation performance which involve studies and improvement in Finland suggests the positive relation. Besides that, Foster et al. (2008) executed the studies and convey out the evidence that innovation is the dominant component in determining firm’s survival and productivity. Chong et al. (2011) proved that a company without innovation will result in bad organization overall performance. In this study, three dimensions of knowledge management, namely, knowledge acquisition, knowledge dissemination and knowledge application are carried out in order to test the impact towards SMEs overall performance wherein innovation works as the mediator. Besides that, conceptual framework is discussed as shown at Figure
Knowledge Acquisition
Daud and Yusoff (2010) and Mills and Smith (2011) cited that firm may improve their performance through knowledge acquisition in which the organization will convert the acquired knowledge into relevant organizational understanding and use it when it is needed. Besides that, Mills and Smith (2011) also carried out a study to look at the relationship among knowledge management and business performance in Jamaica. Throughout the study, Mills and Smith (2011), located out that there is an effective courting among knowledge acquisition and business performance. Based at the beyond research above, P1 is evolved to recognize the relationship between knowledge acquisition, innovation and export performance amongst SMEs in Malaysia. Knowledge acquisition is carried out in this study as it is believed that knowledge desires to be acquired a good way to remedy issues that come upon by using manufacturing system which include terrible system pleasant, system and cloth consumption. Organization that contain in information acquisition is assumed to have higher innovation.
Knowledge Dissemination
Reisi et al. (2013) additionally performed a research regarding the connection among the dimension of knowledge management and organisation overall performance in Iran. The outcome showed that there is an instantaneous relationship between the measurement of knowledge management which covered knowledge dissemination and firm overall performance. It is important to perform understanding dissemination particularly for SMEs. This take a look at is achieved a good way to allow SMEs to apprehend the facts communication among group members which performs as a crucial position for brand spanking new product improvement. Based on the past studies above, P2 is advanced to recognize the connection among knowledge dissemination, innovation and export performance among SMEs in Malaysia.
Knowledge Application
In the latest 12 months, a study regarding the knowledge management functionality and corporation performance is achieved by using Liu and Deng (2015). The results of the study showed that there may be an effective dating between knowledge management and enterprise performance. It is also determined that understanding knowledge was the most tremendous dimension in influencing the firm overall performance. It is vital to perform knowledge application specially for SMEs as SMEs capable of observe the obtained knowledge inside the company which could improve the export overall performance of the agency. Knowledge application not best allow to enhance the prevailing one however additionally allow the organization to have more innovation in developing new ideas. Based at the past studies above, P3 is evolved to understand the connection among knowledge dissemination, innovation and export overall performance amongst SMEs in Malaysia.
Innovation
Ndalira et al. (2013) conducted a research to determine the effect of innovation towards SMEs’ business performance in Kenya. Throughout the study, researchers found out the innovation shows a direct relationship towards business performance of SMEs in Kenya. Based on the past research above, P4 is developed to understand the relationship between knowledge dissemination, innovation and export performance among SMEs in Malaysia.
Conclusion
This research was carried out with a purpose to perceive the scale of KM that influence business export performance among SMEs in Malaysia. Therefore, the result achieve from the research could advantage and used as a guideline for SMEs which keen in paying interest on KM to improve their company’s export overall performance. It also can provide a basis for understanding the impact of innovation at the hyperlink between KM and export performance. In addition, this study can also offer a pool of knowledge on the importance of KM in affecting the export performance among SMEs. If this knowledge is well managed, the organization will bring about above performance. Others than that, this study additionally may be utilized by other academician or students as a reference for similarly studies concerning KM and export performance among SMEs. Furthermore, this study also can be used because the springing board for further studies in KM and export performance. From this study, it is hoped that it could supply the beneficial information to all SMEs and hopefully can be business consulting to them.
References
- Alam, M. M., Siwar, C., Murad, M. W., & Toriman, M. E. B. (2011). Firm Level Assessment of Climate Change, Agicultur and Food Security Issues in Malaysia. World Applied Sciences Journal, 14(3), 431-442.
- Aziz, N. A., & Yassin, N. M. (2010). How Will Market Orientation and External Environment Influence the Performance among SMEs in Agro-food Sector in Malaysia? International Business Research, 3(3), 154-164.
- Bhatt (2001). Knowledge management in organizations: Examining the interaction between technologies, techniques and people. Journal of Knowledge Management, 5(1), 68–75.
- Chong, C. W., Chong, S. C., & Gan, G. C. (2011). The KM processes in Malaysian SMEs: An empirical validation. Knowledge Management Research & Practice, 9, 185-196.
- Crossan, M. M., & Apaydin, M. (2010). A multidimensional framework of organizational innovation: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Management Studies, 47, 1154–1191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6486.2009.00880.x
- Daud, S., & Yusoff, W. (2010). Knowledge management and firm performance in SMEs: The role of social capital as a mediating variable. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 15(2), 135-155.
- Durst, S., & Edvardsson, I. R. (2012). Knowledge management in SMEs: A literature review. Journal of Knowledge Management, 16, 879–903.
- Foster, L., Haltiwanger, J., & Syverson, C. (2008). Reallocation, Firm Turnover, and Efficiency: Selection on Productivity or Profitability? NBER Working paper, 11555.
- Grunert, K. G., & Hildebrandt, L. (2004). “Success Factors, Competitive Advantage and Competence Development,” Journal of Business Research, 57, 459-461.
- Hashim, M. K., & Abdullah, M. S. (2000). Developing SMEs taxonomies in Malaysia. Malaysian Management Journal, 4(1), 43-50.
- Hurmelinna-Laukkanen, P. (2011). Enabling collaborative innovation – knowledge protection for knowledge sharing. European Journal of Innovation, 14(3), 303-321.
- Johanson, J., & Vahlne, J-E. (2009). The Uppsala Internaionalization Process Model Revisited: From Liability of Foreigennes to Liability of Outsidership. Journal of International Business Studies, 40, 1141-1431. https://doi.org/10.1057/jibs.2009.24
- Kantapipat, W. (2009). The Determinants of Successful Export Marketing Strategy in Thai Processed Agricultural Products. RU International Journal, 3(1), 91-102.
- Leal-Rodriguez, A., Leal-Millán, A., Roldán-Salgueiro, J. L., & Ortega-Gutiérrez, J. (2013). Knowledge management and the effectiveness of innovation outcomes: The role of cultural barriers. Electronic Journal of Knowledge Management, 11, 62–71.
- Liao, S. H., Wu, C. C., Hu, D. C., & Tsui K. A. (2010). Relationships between knowledge acquisition, absorptive capacity and innovation capability: An empirical study on Taiwan’s financial and manufacturing industries. Journal of Information Science, 36(1), 19-35.
- Liao, S., Fei, W., & Liu, C. (2008). Relationships between knowledge inertia, organizational learning and organization innovation. Technovation, 28, 183–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2007.11.005
- Liu, S., & Deng, Z. (2015). Understanding knowledge management capability in business process outsourcing. Management Decision, 53(1), 124-138.
- Lizasoain, A., Tort, L. F., Garcia, M., Gomez, M. M., Leite, J. P., Miagostovich, M. P., & Victoria, M. (2015). Environmental assessment reveals the presence of MLB‐1 human astrovirus in Uruguay. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 119(3), 859-867.
- Makore, S., & Eresia-Eke, C. E. (2014). The Role of Knowledge Management in Organisational Performance. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Knowledge Management (ECKM2014), 4-5 September, Santarem. Portugal. http://connection.ebscohost.com/c/articles/99225302/role-knowledgemanagement-organisational-performance
- Marra, M., Ho, W., & Edwards, J. S. (2012). Supply chain knowledge management: A literature review. Expert Systems with Applications, 39, 6103–6110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.11.035
- Mills, A. M., & Smith, T. A. (2011). Knowledge management and organizational performance: a decomposed view. Journal of Knowledge Management, 15(1), 156-171. https://doi.org/10.1108/13673271111108756
- Mustapha, M. R., Muda, M. S., & Abu Hasan, F. (2011). A survey of total quality management in the Malaysian small and medium sized manufacturing companies. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 1(2), 118-122.
- Nawab, S., Nazir, T., Zahid, M. M., & Fawad, S. M. (2015). Knowledge management, innovation and organizational performance. International Journal of Knowledge Engineering-IACSIT, 1, 43–48. htpps://doi.org/10.7763/IJKE.2015.V1.7
- Nazari, K., & Emami, M. (2012). Knowledge Management: From Theory To Practice. Australian Journal of Business and Management Research, 1(11), 22–30.
- Ndalira, D. W., Ngugi, J. K., & Chepkulei, B. (2013). Effect of the type of innovation on the growth of small and medium enterprises in Kenya: A case of garment enterprises in Jericho, Nairobi. European Journal of Management Sciences and Economics, 1, 49–57.
- Porter M. E. (1985). Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. Free Press.
- Reisi, M., Hoseini, S. E., Talebpour, M., & Nazari, V. (2013). Regression equation fitted to knowledge management and organizational effectiveness in the selected sport organizations of Iran. African Journal of Business Management, 7(39), 4159-4167.
- Sarkindaji, B. D., Hashim, N. A. Bin, & Abdullateef, A. O. (2014). Knowledge Management and Organizational Performance of Mobile Service Firms in Nigeria: A Proposed Framework. Information and Knowledge Management, 4(11), 88–95.
- SME Corp Malaysia. (2018). [Online] Available: http://smeinternational.org/sme-information/developing-malaysian-smes
- Subramaniam, M., & Youndt, M. A. (2005) the Influence of Intellectual Capital on the Types of Innovative Capabilities. Academy of Management Journal, 48, 450-463. https://dx.doi.org/10.5465/AMJ.2005.17407911
- Suraj, O. A., & Ajiferuke, I. (2013). Knowledge Management Practices in the Nigerian Telecommunications Industry. Knowledge and Process Management, 20(1), 30–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/kpm.1399
- Tseng, S.-M. (2014). The impact of knowledge management capabilities and supplier relationship management on corporate performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 154, 39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.04.009
- Wang, Y., & Lin, J. (2013). An empirical research on knowledge management orientation and organizational performance: The mediating role of organizational innovation. African Journal of Business Management, 7, 604–612.
- Yang, L.-R., Chen, J.-H., & Wang, H.-W. (2012). Assessing impacts of information technology on project success through knowledge management practice. Automation in Construction, 22, 182–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2011.06.016
- Young, R. (2007). Definition of knowledge management. http://www.knowledge-managementonline.com/Definition-of-KnowledgeManagement.html
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
06 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-087-7
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
88
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1099
Subjects
Finance, business, innovation, entrepreneurship, sustainability, environment, green business, environmental issues
Cite this article as:
Jia-Qi, K., Chelliah, S., & Khan, M. J. (2020). Knowledge Management And Export Performance Among Malaysian SMEs: A Theoretical Framework. In Z. Ahmad (Ed.), Progressing Beyond and Better: Leading Businesses for a Sustainable Future, vol 88. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 473-482). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.42

