Abstract
The paper is devoted to the issues of state policy while stimulating the development of small and medium-sized businesses. According to the authors, in recent years the qualitative and effective development of small and medium-sized businesses is the factor of sustainable consolidation of the Russia’s national wealth, increase of the growth rate of production and quality provision of services. However, small and medium-sized businesses in the regions and in Russia in general, bear considerable discomfort, which prevents its further development. The study emphasizes the magnitude and importance of the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the regions of the Russian Federation. The authors determine its effective impact on the overall development of the economy of the republic and the economy of Russia in general. The formation of a new organizational and economic mechanism for the development of socially oriented small and medium-sized businesses requires us to address some tasks: – to develop effective state policy in the sphere of small and medium-sized businesses using the latest technologies and development of science, as well as to develop business structures; – to develop new socially oriented and foster existing legislative and regulatory acts regulating small and medium-sized entrepreneurship; – to create a full competitive environment for small and medium-sized businesses within the country ensuring competitiveness of small businesses outside its borders, comprehensive support of socially oriented small and medium-sized businesses by the state thus ensuring its effective development.
Keywords: Public policyincentive processbusiness development
Introduction
The relevance of the study is the fact that the development of small and medium-sized businesses is determined by the state support policy, which is related to its peculiarities, and in this regard it is very important to support and stimulate the activities of this sector at all levels of government – from municipal to federal, as evidenced by world and domestic practice. According to the analysis of foreign experience of financial support to small and medium-sized enterprises, the creation of an effective mechanism of business management at the regional level allows a small and medium-sized enterprise to function thus achieving higher profitability, increasing budget effectiveness of the region. In recent years the effective development of small and medium-sized businesses has been a factor for the Russian economy towards sustainable consolidation of the national wealth, increase of production rates and provision of high-quality services. However, small and medium-sized businesses in the regions and in Russia in general, bear considerable discomfort, which prevents its further development. This is primarily caused by the crisis in the country, which negatively affected all areas of activity. It is necessary to define the role of the state in supporting small and medium-sized businesses in new conditions. There is a need to develop a new organizational and economic mechanism for socially oriented small and medium-sized businesses taking into account the state of the country’s economy and the peculiarities of the regions (Schumpeter, 2007). It is also necessary to revise the legislative framework that regulates the activities of small and medium-sized businesses and reconsider the possibility of introducing new elements into the sphere of business. The economy in the regions requires not only federal or regional support, but also the development of business structures, stimulation of investment and innovation. There is a need to create and consolidate the image of the region of potential opportunities and create better conditions for business development, which will lead to the overall growth of the economy of the entire country.
Problem Statement
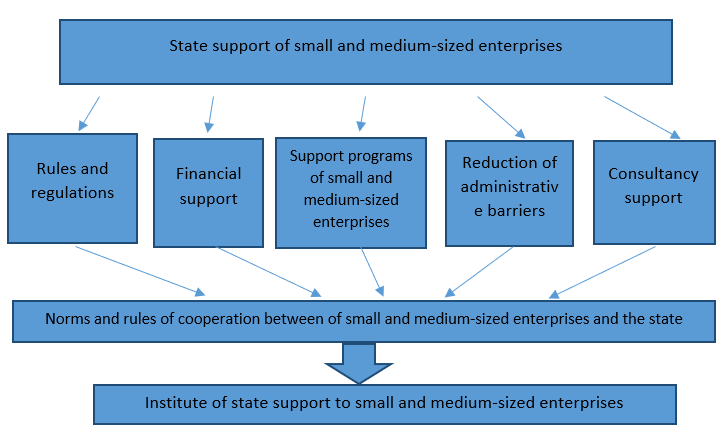
The schematic representation of the system of support for small and medium-sized enterprises shows that each direction includes certain institutions – rules of interaction between the state and small and medium-sized enterprises, and therefore, the institutional approach more accurately reflects the essence of state support to small enterprises.
In the institutional space it is possible to identify the institutions that form the principles in the economic system, the so-called basic institutions. They serve as an institutional “skeleton” and can be attributed to the first level of institutions. Further study of the institutions will result in the identification of the second, third and subsequent levels (Figure
All the above makes it possible to define the Institute of State Support for Small and Medium-sized Businesses as a set of existing relations between the state and small and medium-sized enterprises, which form the conditions for the growth of a small and medium-sized business sector itself. The regulation of entrepreneurship by the state allows achieving tactical objectives, however the study this problem has begun only in recent years, but the existing developments relate to general issues of social entrepreneurship (Sidorov, 2015). Thus, the analysis of the study of this issue suggests the following: the approach to defining the importance of small and medium-sized businesses in its possibility to influence the stimulation of regional socio-economic development is not fully formulated; and, there is little research on supporting socially oriented small and medium-sized businesses in the event of a crisis (Yalmaev & Tolstel, 2017).
Research Questions
The subject of the study includes economic relations of market participants regarding the development of socially oriented business.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to develop theoretical and methodological provisions and scientific and practical recommendations on the formation and development of an organizational and economic mechanism for socially oriented small and medium-sized businesses in the region.
Research Methods
The study is based on general scientific methods of comparative and logical analysis, functional and systemic approaches, as well as statistical and economic methods. The methods of theoretical and empirical research, methodological techniques and approaches used in the analysis of small business activities were used as methodological tools (Brizhanina, 2014).
The methodological and theoretical basis of the study included the works of current scientists on the issues of support and development of small and medium-sized businesses, social entrepreneurship (Vetrova, 2018). The recent programs of small business development and on the issues of state support of small business in general were studied. The materials of republican and municipal funds for small business support were analyzed.
Findings
The main forms of state support for small businesses areas follows:
facilitation of legislation and administrative procedures;
financial support for small and medium-sized enterprises via state subsidies;
promotion of small business development in knowledge-intensive industries focused on innovations;
assistance to small businesses in the field of training and retraining of qualified personnel;
assistance to entrepreneurship in entering foreign markets;
preferential taxation to small and medium-sized businesses;
state guarantees in the form of lend on security for small business development;
comprehensive consulting and information support for small and medium-sized businesses and much more.
Thus, state support is not provided to credit and insurance organizations, investment funds, non-state pension funds, pawn shops, professional participants of the securities market; farminees; gambling facilities (Ibadova, 2006); non-residents of the Russian Federation; production and excise goods sale enterprises; companies that produce and sell minerals (excluding common minerals). Russian development institutions currently play a significant role in supporting small enterprises that innovate in the field of science and technologies.
Financial support of small and medium business is carried out in the following main forms:
subsidies to small business;
assistance to small business lending;
tax benefits to small business through preferential taxation.
It is possible to identify the following types and sizes of subsidies to small business:
Partial compensation to small and medium-sized enterprises for expenses associated with down payment (advance payment) when concluding the equipment lease contract – 50 % of the documented costs.
Partial compensation to small and medium-sized enterprises for expenses associated with the acquisition of equipment for the purpose of creation and (or) development or modernization of production of goods (works, services) – 50 % of the documented costs.
Partial compensation to small and medium-sized enterprises providing services for the production of goods in the following areas of activity: social services to citizens, health care, physical culture and mass sports, classes for children and youth, sports classes, studios, production and (or) sale of medical equipment, prosthetic and orthopedic products, as well as technical means, including auto transport, materials for prevention of disability or rehabilitation of disabled persons, cultural and educational activities (theatres, studio schools, music institutions, creative workshops), educational services to groups of citizens with limited access to educational services, for purposes determined by the region – 85 % of the documented costs.
Partial compensation to small and medium-sized enterprises engaged in activities in the field of crafts, folk art crafts, rural and ecological tourism for the purposes determined by the government of the region.
Partial compensation to small and medium-sized enterprises for expenses associated with creation and (or) development of centers for children – pre-school daycare groups and other similar types of activities for children – 85 % of the documented costs.
Partial compensation to small and medium-sized enterprises for utility connection (electric power systems and/or gas distribution networks) – 50 % of the documented costs.
Taxation has the strongest impact on the development of small and medium-sized businesses. One of the most important problems that constrains the development of entrepreneurship in Russia as a whole is high taxes for small businesses and the complexity of the system of taxation of entrepreneurs (Volkova, 2018). At the moment, the main law and statutory instrument regulating taxation of small businesses is the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which, as of 2015, provided for 5 tax regimes for Russian private entrepreneurs and organizations: 1 general (general tax regime) and 4 special tax regimes (Simplified Tax System, Single Tax on Imputed Income, Single Agricultural Tax, Patent Taxation System). The choice of a tax system allows an organization or a private entrepreneur to take advantage of the benefits of small businesses established by tax legislation and legally reduce the tax burden.
Special regimes are the most common tax schemes chosen by small and medium-sized businesses.
The main advantage of the special regimes is the reduction of tax burdens as they allow replacing several taxes (as a rule, it is the VAT, profit/income tax, property tax) by one single tax only.
STS (Simplified Tax System) is a special tax regime that allows small and medium-sized businesses to reduce the tax burden. Simplified taxation implies not only tax deduction for small businesses, but also a significant simplification of tax reporting.
The main disadvantage of the special regimes is that the taxpayer will no longer be a VAT payer, which may cause its small attractiveness for large counterparties. It shall be noted that each special tax regime has a number of restrictions for its application by an organization or a private entrepreneur.
Another measure of state support to small and medium-sized businesses is “business holidays” – a financial tool that has proven itself in many countries of the world. This measure is aimed at increasing business activity in the country and supporting newly created small and medium-sized businesses. Of all the measures of financial support from the state, this is the most effective and cheap: subsidies, grants, material allowances for the purchase of equipment, training and rent are much more expensive.
The term “tax holidays” itself is used to temporarily limit the period during which the entrepreneur does not pay the income tax. At the same time, all other payments – insurance payments, different types of property taxes and fees transferred for employees, a businessman is obliged to regularly contribute to the treasury.
The starting point in entering the “tax holidays” was the adoption of the Federal Law No. 477-FZ of 29.12.2014 On Amendments to Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which introduced modifications to the tax legislation on patent taxation system, and most importantly, legalized the possibility of granting the so-called “tax holidays” to entrepreneurs.
However, in order to provide “tax holidays”, an entrepreneur shall meet all criteria, namely: to be registered as a private entrepreneur; if registration is completed two years before the “holidays”, it is necessary to shift to STS; if an activity patent is acquired or the work is performed within an industry related to science, production or social activities, and the total income from these activities makes at least 70 %.
The law also implies that regional authorities have the right to independently determine the types and time of activities of the period of application of this system since 2015. However, the regions have the veto power even if an entrepreneur meets all requirements. This is due to special regional requirements.
First, the possibility of working at the “zero” rate depends on the number of employees, on the limit income from the activities that give the opportunity to work. At the same time, the indicator of the upper income bar is indexed every year using the deflator factor.
Second, in addition to the tax return on a single STS tax, entrepreneurs are obliged to regularly report their compliance with the conditions of application of the zero rate.
Third, if a private entrepreneur opens several firms subject to this law and others do not, the income should be taken into account separately for each entity.
In case of violation of the terms of tax calculation, an entrepreneur loses the right for it, and is also obliged to recalculate and pay tax at a normal rate from the beginning of the tax period in which the violation was committed.
Despite the current law, the possibility to take advantage of it depends solely on the local legislation. The total tax grace period is calculated for the period from 2015 to 2020. Regional authorities have the right to impose additional restrictions on the number of employees and income limits, as well as to set the validity period independently.
Conclusion
The analysis confirms the need to combine different forms of small enterprises in the region. Small and medium-sized businesses respond quickly to market changes, contribute to infrastructure and competitiveness, increase tax contributions to the budget, create new jobs, mitigate social tensions in the society, and in some cases can become a solution to these problems.
Considering that social entrepreneurship is both a commercial activity and a charity, it is necessary to note the absence of a legally established organizational and legal form suitable for this type of different activity. Such a legal gap made it possible to formulate and propose a new organizational and legal form defining the place of social entrepreneurship in the legislation.
It can be concluded that with all the possibilities and measures of state support much depends on the level of development of the territory as a whole. The Institute of State Support for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises shall not only regulate the development of small and medium-sized enterprises, but also influence the business environment of entrepreneurship through a system of general economic measures.
References
- Brizhanina, T. V. (2014). Small business: essence, advantages, development. J. of Chelyab. State Univer. Manag, 2(9), 32–37.
- Ibadova, L. T. (2006). Financing and lending of small businesses in Russia: Legal Aspects. Volters Kluver.
- Schumpeter, J. (2007). Theory of Economic Development. Exmo.
- Sidorov, N. I. (2015). Social entrepreneurship and entrepreneurship in the social sphere (Theory and Practice). SUM Publ. House.
- Vetrova, E. A. (2018). Social entrepreneurship as a factor of social and economic development of society. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sotsialnoe-predprinimatelstvo-kak-faktor-sotsialno-ekonomicheskogo-razvitiya-obschestva
- Volkova, M. S. (2018). Concept of social entrepreneurship and its criteria. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/ponyatie-sotsialnogo-predprinimatelstva-i-ego-kriterii
- Yalmaev, R. A., & Tolstel, M. S. (2017). Financial support for small and medium-sized enterprises in conditions of asymmetry of social and economic development of Russian regions. Monograph. ChSU Publ. House.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-091-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
92
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3929
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, translation, interpretation
Cite this article as:
Idigova, L., Sulumov, S., Plieva, N., Mazhiev, K., & Mazhiev, A. (2020). Public Policy Role In Stimulating The Small And Medium-Sized Businesses Development. In D. K. Bataev (Ed.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism» Dedicated to the 80th Anniversary of Turkayev Hassan Vakhitovich, vol 92. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 455-461). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.05.60

