Abstract
In the current economic conditions, Russian corporations are the subject of increased attention of all participants in market relations interested in the results of the activities of these business entities. Russian corporations operate in conditions of uncertainty and dynamism of the external environment. In this regard, participants in market relations need to timely respond to the instability of the market environment. The main task for them is the formation of a financial stability strategy. High business growth rates, increased competition in the domestic and global markets contribute to improving the dependence of corporations on external sources of financing. These processes can lead to a loss of financial stability, which largely determines the need to study the factors influencing it. At the current stage of economic development, only the stable, competitive, and reliable functioning of Russian corporations can provide both their financial stability and the country as a whole. Qualitatively characterizing the financial condition of the corporation; it is necessary to determine the influence of the internal and external environment and identify the growth factors of the financial stability of the economic entity. Until now, despite a wide range of areas of research on these issues, the financial stability and growth factors in modern Russian corporations remain an undeveloped area. The need to study this issue in a dynamically developing Russian economy determines the theoretical and practical relevance of this study. This article is devoted to the development of an algorithm for diagnosing the financial stability of a corporation.
Keywords: Financial stabilitySWOT analysisstagesmethodology
Introduction
Corporations have many differences from unincorporated organizations. Therefore, the traditional analysis of financial stability using absolute and relative indicators, in our opinion, is not able to assess the level of financial security of a corporation. In this regard, it is proposed to conduct a diagnosis of the corporation's financial stability, which includes a study of all the necessary aspects. Before forming the stages of diagnosing the financial stability of a corporation, it is advisable to consider methodological approaches to the concept of "diagnostics" in a study of an organization or corporation (Table
Summarize the approaches to determining the essence of diagnostics. We can conclude that the diagnosis in the study of an organization (corporation) is a process of identifying signs of a violation of the normal state of its activity. Diagnostics is also a tool for substantiating managerial decisions taking into account the development trends of a given business entity and industry for subsequent comparison (assessment) of the current state of the parameters of the research object, which are currently recognized as optimal or dominant.
Problem Statement
In economic literature, many authors offer various relative indicators for assessing and diagnosing the financial stability of an organization, which can also be applied to corporations. Most researchers express financial stability through capital structure indicators. They believe that the analysis of financial stability consists of assessing the state of the property of an economic entity and its financing sources to identify the level of financial dependence on external sources. Almost all experts distinguish types of financial stability: absolute and reasonable security, unstable and crisis financial situation by determining reserves and costs, and causes of financing and their ratio. They emphasize an extremely detailed assessment of balance sheet liability items by identifying many factors, many of which are duplicated. Researchers who adhere to the traditional approach, propose the calculation of indicators of financial stability. In this case, indicators of economic stability reflect the impact of the structure of liabilities on long-term solvency. In this paradigm, researchers propose using only long-term borrowed funds as investments in capital investments. They orient the assessment of financial stability to the organization of the material sphere. All models used by various authors include their specific coefficients, allowing determining the level of financial stability of an economic entity. But these indicators, proposed by different authors, have no fundamental differences, and therefore these models should be attributed to the classic. In our opinion, all of the above models for assessing financial stability are based on the following elements typical to them:
1. In determining financial stability, the emphasis is on studying the acceptability for the organization's understudy of the borrowed sources share in the overall structure of liabilities. The norm is the amount of borrowed funds, not exceeding 50 % of all sources of funds.
2. The origins of information are the data of financial statements. The undoubted advantage of this approach is the availability of source data necessary for calculating financial stability indicators. Even though many authors are cautious about financial statements, as based on its data. It is possible to determine the state of financial stability only at the beginning and end of the study period. The organization's reporting serves as a source for assessing financial stability.
3. The traditional assessment model does not take into account the financial stability indicators of the amount of borrowed funds and does not evaluate their value in the formation of sources.
After analyzing the totality of the coefficients used for assessing the financial stability of the organization in the framework of the traditional approach, it should be noted that all indicators are reduced to calculating: 1) the share of equity in the overall structure of the organization's financing sources, or to determine the ratio of own and borrowed funds; 2) the percentage of long-term funds in the construction of all sources of financing.
Research Questions
The subject of the study is economic relations during the formation of the financial stability of modern Russian corporations.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is the development and theoretical justification of the algorithm for diagnosing the financial stability of a corporation. The activities of modern Russian corporations are the subject of research for a wide range of market participants interested in the effectiveness of their work. It is necessary to assess the level of its financial security to ensure the stability of the corporation. Before developing a discussion about the concept of "financial stability of a corporation," one should objectively distinguish between the categories of "organization (enterprise)" and "corporation." Based on the implementation of these tasks, it is planned to achieve the goal of this study.
Research Methods
The methodological basis of the study is the dialectical method, an integrated and systematic approach. The work used such general scientific methods and techniques as scientific abstraction, generalization, quantitative and qualitative analysis, grouping and comparison methods, economic and mathematical methods, modeling, analysis and synthesis, statistical, and graphical analysis.
Findings
Modern Russian corporations have many distinctive properties compared to other organizations. Given this fact, we have developed an algorithm for diagnosing the financial stability of a corporation. The algorithm includes some stages, the implementation of which will allow a comprehensive study of the financial stability of the corporation (Figure
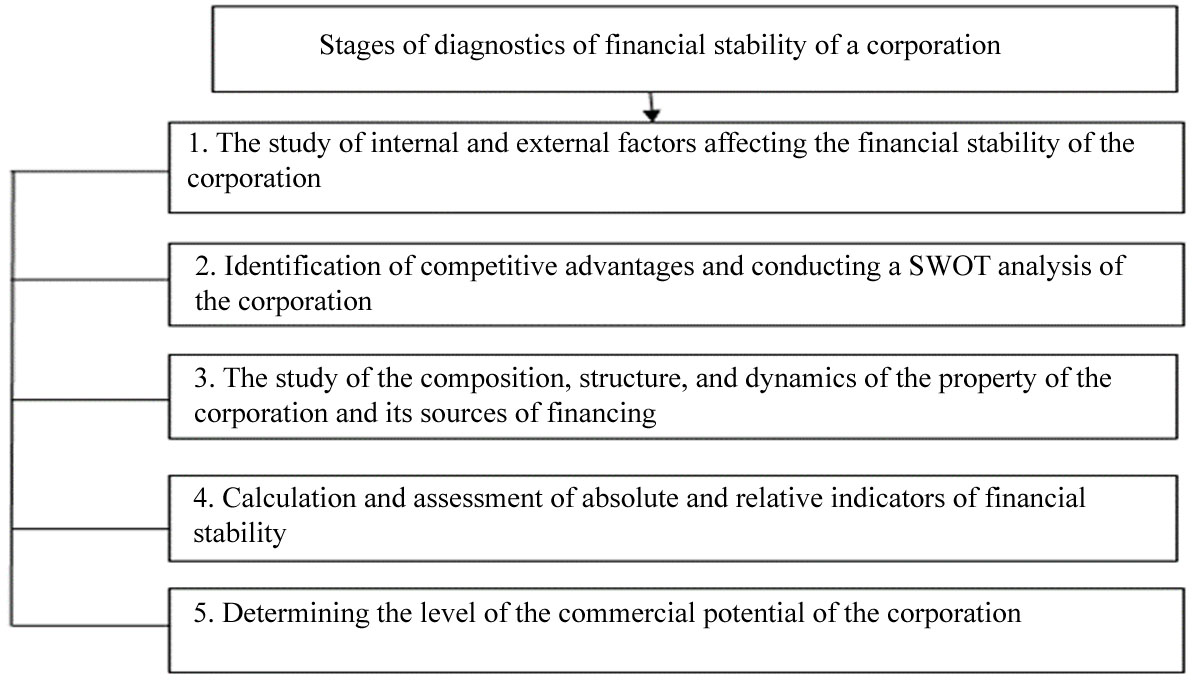
The first stage of the diagnosis of the financial stability of a corporation involves the study of internal and external factors affecting both its financial stability and the financial condition as a whole.
Further, at this stage, it is necessary to conduct a SWOT analysis. The SWOT analysis allows establishing the corporation's problematic positions in comparison with competitors, as well as the opportunities and threats of the external environment. A SWOT analysis is the detection of strengths and weaknesses of a corporation, as well as opportunities and threats for it from its close environment (external environment).
In general, the SWOT analysis is reduced to filling the matrix (Figure
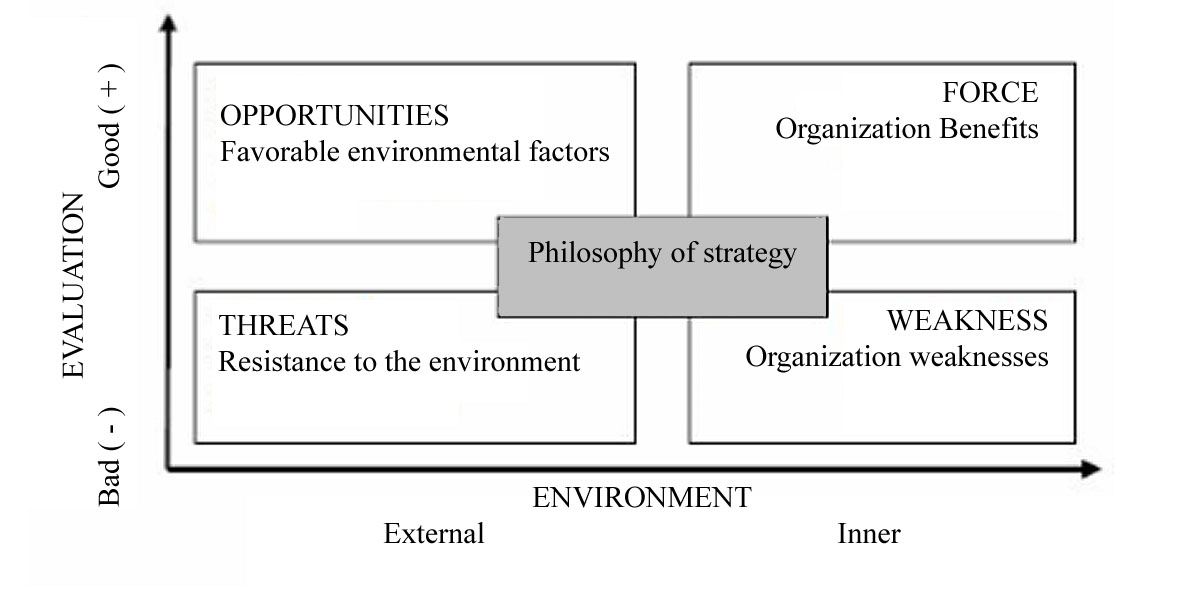
The strengths of a corporation are a combination of what it has excelled at or features that provide it with additional capabilities. For example, such features are available to experience, access to unique resources, the availability of advanced technology and modern equipment, high qualification of personnel, high quality of products, and brand recognition.
The weaknesses of the corporation are associated with the absence of an important factor necessary for its functioning. The lack of this factor puts the corporation at a disadvantage relative to other organizations, especially if it is not amenable to change. For example, such an unfavorable factor is a narrow assortment of manufactured goods, poor reputation in the market, and insufficient funding (Isaeva et al., 2018).
Market threats are events that could adversely affect the financial stability of a corporation. For example, risks are the emergence of new competitors in the market, an increase in taxes, and a change in customer preferences.
Market opportunities are situations that allow a corporation having a competitive advantage in the market. Market opportunities are embodied in increasing incomes and demand of the population, weakening competitors, the emergence of new types of equipment and production technologies.
Assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of the corporation regarding the opportunities and threats of the external environment determines its strategic prospects for its implementation.
The corporation's financial position and stability are mostly determined by the correctness and expediency of investments in financial assets. So, the third stage consists of the study and assessment of property status and sources of its formation using horizontal and vertical analysis. In the third stage, the cost of the corporation's assets on its balance sheet is determined; the structure of assets and liabilities is revealed, which has a significant impact on its financial stability.
The next, fourth stage of the diagnosis of financial stability of a corporation consists of calculating and evaluating absolute and relative indicators of financial security.
Absolute indicators of financial stability characterize the state of stocks and the level of their provision with funding sources. The defining indicator is the surplus or shortage of sources of funds for the formation of shares, defined as the difference between the value of sources of funds and stocks.
The total value of reserves = Vr.
Many indicators are used that characterize the state of various sources of reserves formation (Konina, 2009; Isaeva, 2009):
surplus/lack of own circulating assets: ± Fс = SOS – Vr;
surplus/deficiency of own and long-term borrowed sources of reserves formation: ± Fт = КF – Vr;
surplus/lack of the total value of the main sources for the formation of reserves: ± Fо = VI – Vr.
Where SOS (own current assets) = Capital and reserves – Non-current assets; KF (functioning capital) = (Capital and reserves + long-term liabilities) – Non-current assets;
VI (total value of the main sources of reserves) = (Capital and reserves + Long-term liabilities + Short-term loans and borrowings) – Non-current assets.
The above indicators allow determining what type of financial stability is typical for a corporation.
Absolute financial stability is very rare and meets the following conditions:
± Fs ≥0; ± Ft ≥0; Фо≥0, therefore, S (F) = {1; 1; 1}.
Normal financial stability guarantees the solvency of the corporation: ± Fs <0; ± Ft ≥0; Фо ≥0, therefore S (F) = {0; 1; 1}.
The unstable financial situation is accompanied by insufficient solvency. At the same time, it remains possible to restore equilibrium by accumulating own sources by reducing the amount of debt of debtors, increasing inventory turnover: ± Fs <0; ± Ft <0; Фо ≥0, that is, S (F) = {0; 0; 1}.
The crisis financial situation means that the functioning of the corporation is carried out at the expense of borrowed sources. Own capital, long- and short-term loans to finance tangible working capital are not enough, i.e., replenishment of stocks occurs at the expense of funds generated as a result of slowing down the fulfillment of obligations in the form of repayment of accounts payable: S (F) = {0; 0; 0}.
At the final stage of the financial stability diagnosis of a corporation, it is necessary to determine the level of its commercial potential. In modern economic literature, commercial potential is determined by the "availability and accessibility of financial resources; that is, sources of financing activities" of the organization. The methodology for determining financial potential consists of the following steps:
1. Assessment of the economic potential of the corporation based on financial indicators.
2. Drawing a curve of the financial potential of the corporation by economic indicators and determining the level of its commercial potential. The obtained values of financial ratios are compared with a scale that determines the level of the business potential of the corporation by financial ratios. When connecting the marked values in a single line, a curve of the economic potential of the corporation is obtained, characterizing its level.
3. Assessment of the financial potential of the corporation according to the criterion of “having an effective financial management system.”
An effective financial management system involves the technology of compiling a corporate work plan coordinated across all departments and functions (Pikhtareva, 2013).
The plan is based on a comprehensive study of forecasts of changes in external and internal factors and on obtaining, through calculations, performance indicators of the corporation – economic and financial.
A corporation refers to a particular level of financial potential according to the following principle (Baranenko, Mikhel, 2012):
a high level of the commercial potential of the corporation – the presence of a budget planning system;
the average level of the commercial potential of the corporation – the availability of a network of planned reports;
a low level of the financial potential of a corporation is the presence of a planning system using the coefficient method.
4. A comprehensive assessment of the economic potential of the corporation. This step is shown in Table
Thus, the assessment of the financial potential of the corporation is a necessary stage in the diagnosis of its financial stability, covering all basic internal processes. This analysis provides a systematic look at the corporation, allows identifying the strengths and weaknesses of its activities, and create the basis for the formation of a strategy aimed at increasing the level of financial stability.
Conclusion
The developed procedure for diagnosing the financial stability of a corporation allows investigating this indicator comprehensively and identify the causes of the negative impact of factors of the internal and external environment at any stage. Diagnostics makes it possible to make timely decisions to prevent or eliminate such an effect. The first stage of the diagnosis of the financial stability of a corporation involves the study of internal and external factors affecting its financial stability. In the second stage, one should determine competitive advantages and conduct a SWOT analysis (Filatova, 2009; Krapivin, 2010; Shkolnik, 2013). SWOT-analysis allows identifying problematic positions of the corporation in comparison with competitors, as well as opportunities and threats to the external environment. The third stage consists of the study and assessment of property status and sources of its formation. The next, fourth, stage of diagnosing the financial stability of a corporation consists of assessing its absolute and relative indicators. At the final step, the level of the economic potential of the corporation is determined. Diagnostic results of the financial stability of the corporation will help develop strategic directions for its improvement.
References
- Baranenko, S. P., & Mikhel, V.S. (2012). Methods for ensuring the financial sustainability of industrial corporations of the Russian Federation Economics. Control. Right. 2-1(26), 25.
- Filatova, V. A. (2009). Formation of a system of indicators for assessing the financial stability. Vestn. Corporat., the Volga State Univer. of Service. Ser. Econo., 7, 98.
- Isaeva E. A., Magomadova M. M., Abalakin A. A., & Abalakina, T. V. (2018). Internal and external components of the regional socio-economic development. The Europ. Proc. of Soc. & Behavioural Sci. EpSBS Conf. (SCTCGM 2018) Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism. (pp. 1906–1914).
- Isaeva, E. V. (2009). Assessment of financial stability of corporations from the position of international business management. Actual issues of econ. sci., 5-4, 181.
- Konina, N. Y. (2009). Financial stability of transnational corporations in a crisis. Corpor. finance managem., 3, 144.
- Krapivin, V. S. (2010). The financial recovery of the corporation is the basis of its stability and sustainability. Econ. sci., 64, 42.
- Pikhtareva, A. V. (2013). A methodological approach to the diagnosis of financial stability of the Vestn. Corporat., the Volga State Univer. of Service. Ser. Econ., 4(30), 116.
- Shkolnik, O. A. (2013). Financial sustainability of a corporation: a scientific discussion about the theoretical essence and practical role. Econ. and managem.: analysis of trends and develop. Prospects, 7-2, 149.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-091-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
92
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3929
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, translation, interpretation
Cite this article as:
Evgenievna, B. S., Valerievich, K. Y., Harvanovna, A. A., & Ivanovich, B. A. (2020). Algorithm For Diagnosing Financial Stability Of Corporation. In D. K. Bataev (Ed.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism» Dedicated to the 80th Anniversary of Turkayev Hassan Vakhitovich, vol 92. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 3535-3542). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.05.470

