Abstract
The article presents an analysis of the current level of financial literacy of young people in cryptocurrency. Purpose of work: revealing of the main problems connected with low growth of activity of youth in the market of cryptovoltaic currency. Identification and comparison of the main risks and opportunities on the cryptocurrency market are defined as priorities. In the article the methods of interrogation, the comparative analysis, deductive and inductive conclusions are resulted, and also construction of theoretical model of the relation of a society of the cryptocurrency by means of writing of conclusions and recommendations to this question is made. It was concluded that the low level of financial literacy of young people in the cryptocurrency is largely due to the government's passive policy in this direction, as well as the myths and illusions surrounding the cryptocurrency. There is direct connection between the level of readiness of citizens to invest their money in cryptocurrency and the level of innovation of the state economy.
Keywords: Financial literacycryptocurrencyBitcoinyouthinvestments
Introduction
Today, digitalization is one of the most important and key concepts related to the development of society. It covers all spheres of human activity. Digitalization in a narrow sense means the transformation of information into digital form, which in most cases leads to lower costs, new opportunities, etc. In a broad sense, it is the current worldwide trend of economic and social development, based on the transformation of information into digital form and resulting in a more efficient economy and better quality of life (Halin & Chernova, 2018).
It should be noted that in 2017, the Minister of Finance of the Russian Federation Anton Germanovich Siluanov (2017) proposed to include the cryptocurrency in the strategy of financial literacy until 2023 in order to explain the possible consequences of the investment, but in 2018 the media reported that the Ministry of Finance (MinFin RF, 2018) does not see the need to improve the financial literacy of the population.
Let's turn to sociological surveys. Researchers of the South Korean edition of Yonhap found out that South Koreans start to be interested in the cryptocurrency from the age of 17–18, and many 20-year-olds are already crypto investors. A sociological survey by the Korea Financial Investor Protection Foundation showed that South Korean youth are the most active investors in the world, but people in their 40s are willing to invest more in the cryptocurrency than the young and active ones. Research also shows that more than 70 % of respondents call these investments "investments for the future". And about 30 % of respondents regularly use digital currency as a means of payment (Cryptofeed, 2018).
Problem Statement
In modern conditions of development of new technologies and technical progress, the use of new innovative financial instruments, one of which is cryptocurrency, is gaining popularity.
Research Questions
The subject of the article was the knowledge and attitude of young people towards investments and savings in cryptocurrency.
Purpose of the Study
To study the level of financial literacy in Russia and compare the level of "raising" of this topic with the real problem in the framework of people's anxiety about it.
Research Methods
In the article the methods of interrogation, the comparative analysis, deductive and inductive conclusions are resulted, and also construction of theoretical model of the relation of a society of the cryptocurrency by means of writing of conclusions and recommendations to this question is made.
Findings
As part of the study of this topic through the service "Google form" was conducted a survey of young people aged 16 to 35 years. The total number of respondents is 362 people. The survey was attended by residents of all federal districts of the Russian Federation, as well as residents of the Donetsk and Lugansk People's Republics.
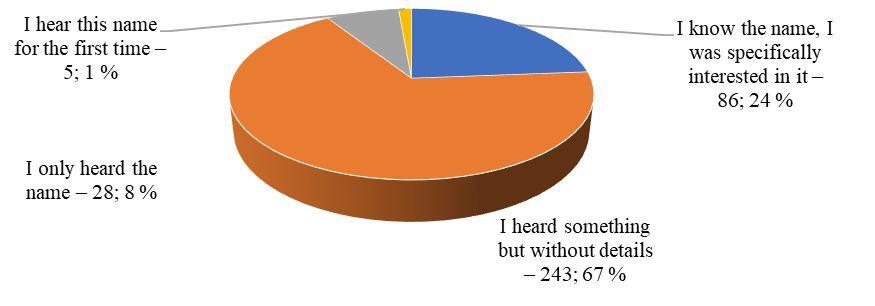
About two thirds of respondents have heard something about the cryptocurrency, but were not specifically interested in this issue (Figure
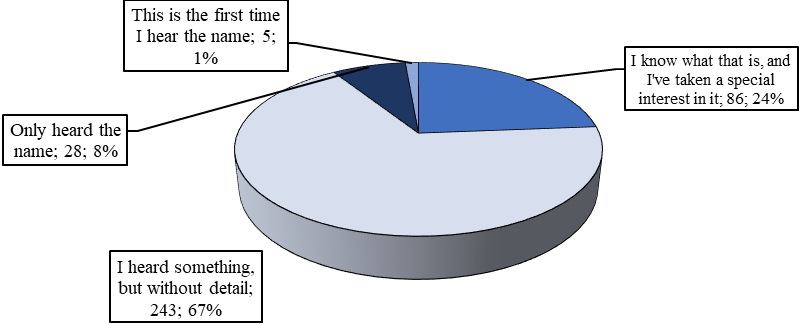
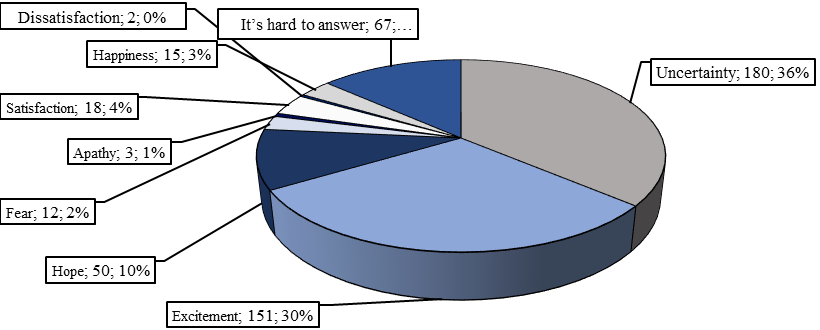
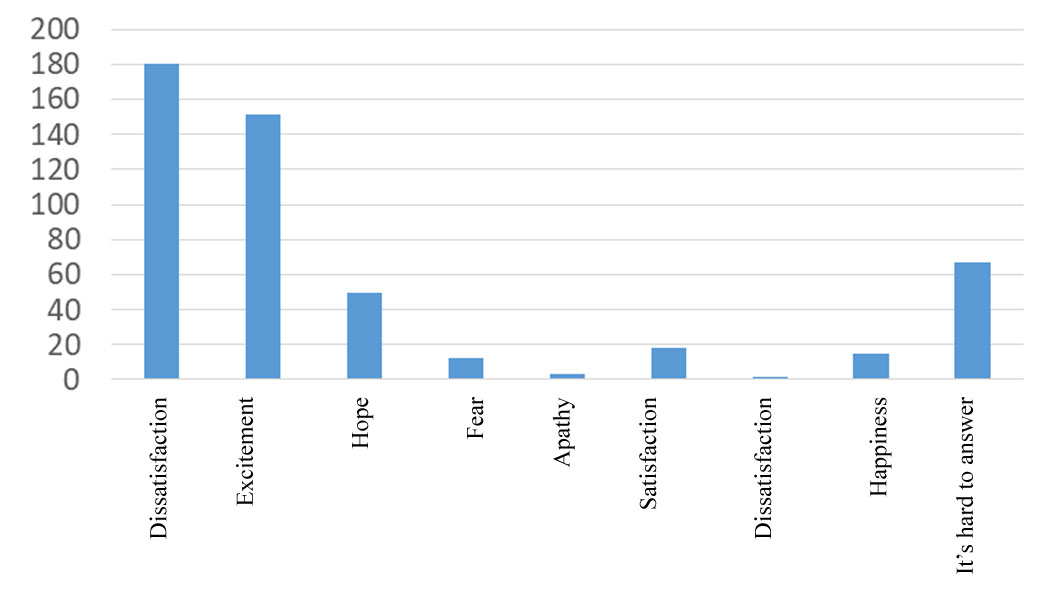
More than a third of respondents admitted that they associate the word "cryptocurrency" with "uncertainty" (Figure
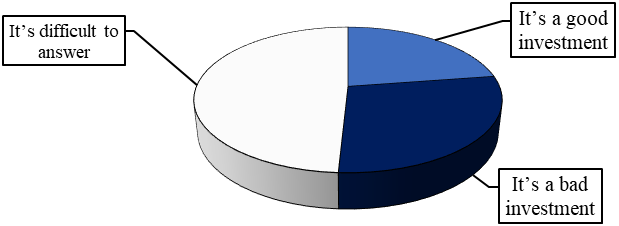
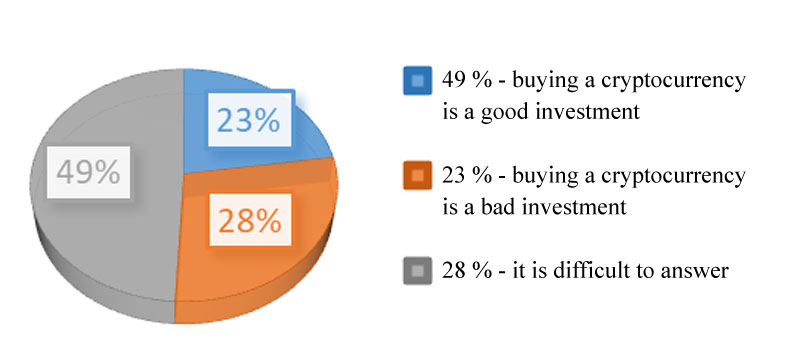
Almost half of the respondents find it difficult to answer the question whether an investment in the cryptocurrency is successful or unsuccessful, 28 percent consider the purchase of cryptocurrency an unsuccessful investment, and 23 percent consider it successful (Figure
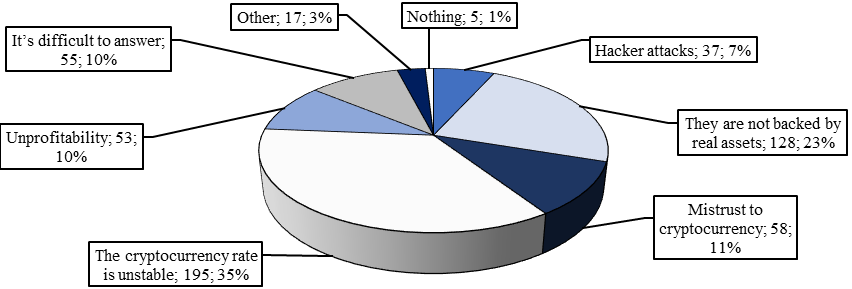
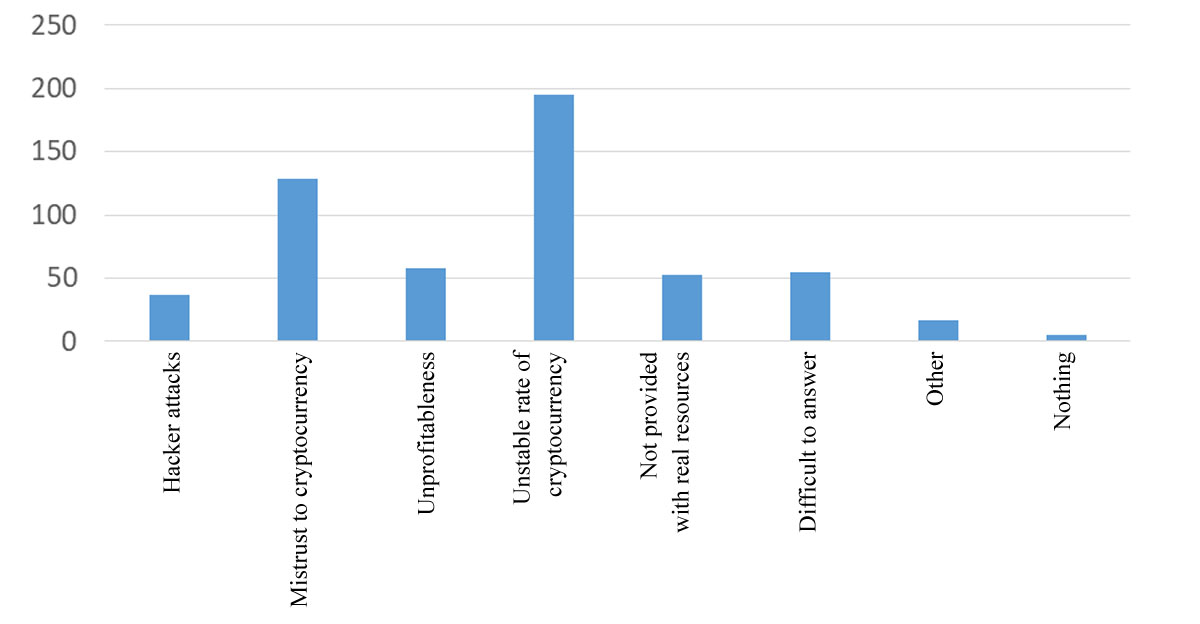
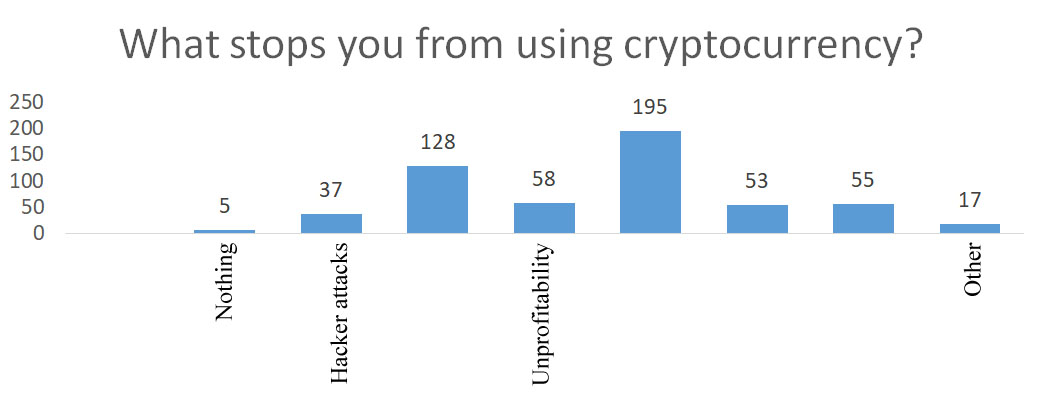
The main factors that stop people from buying the cryptocurrency are exchange rate instability, distrust and insecurity of the cryptocurrency with real assets (Figure
Respondents were also asked a series of questions testing basic knowledge of the research topic to see if they had an overall understanding of how the cryptocurrency system works:
What should not be done with the cryptocurrency?
What influences the course of any cryptocurrency?
What is meant by the terms "blockchain" and "mining"?
Who issues cryptocurrency?
Only 15.19 percent of the total number of respondents were able to answer all questions correctly (Figure
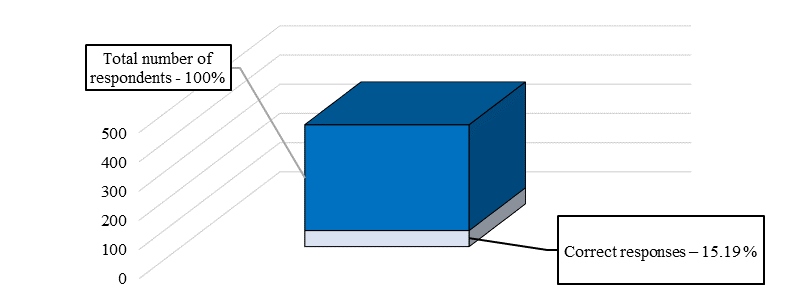
The correctness of the answers among the students of the Finance University under the Government of the Russian Federation was calculated separately (Figure
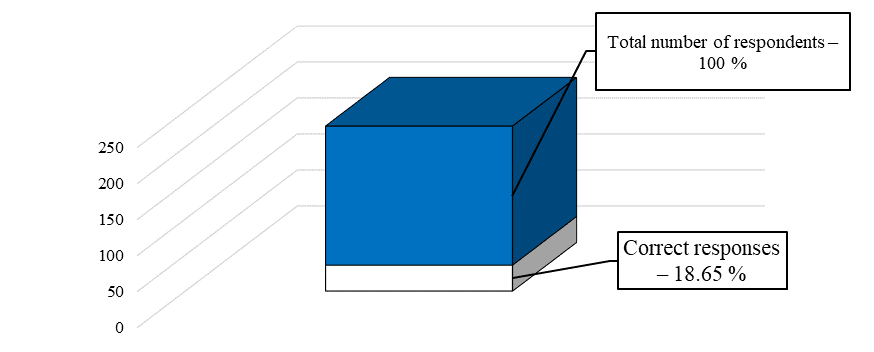
Thus, the results of the study allow us to draw the following conclusions:
The interest to cryptocurrency among respondents of own sociological poll is much lower, among respondents from USA and South Korea.
Financial literacy
The issue of financial literacy of the population in the sphere of cryptocurrency is relevant for Russia. The National Agency for Financial Research has conducted a survey among Russians regarding their level of knowledge in the field of cryptocurrency. According to the survey results, only 28 % of Russians have heard something about cryptocurrencies (Alekseev, 2017).
An author's sociological survey among young people was conducted to investigate this problem and its contradictions. The research was conducted by means of service "Google Form". The survey was attended by 362 respondents aged 18 to 35 years from 19 regions of Russia, as well as from Lugansk and Donetsk People's Republics. The survey covered 56 educational institutions in Russia.
As shown in Figure
The answers to the question: "What words do you associate with the cryptocurrency" were analyzed separately? The majority of respondents associated the cryptocurrency with uncertainty (36 %) and excitement (30 %) (Figure
Remarkable were the answers to the question: "What stops you from using cryptocurrency?" 195 respondents attribute their unwillingness to invest in cryptocurrency to an unstable rate, while 128 respondents attribute it to distrust of the cryptocurrency (Figure
Significant differences in the answer to the question: "Buying cryptocurrency is...". Almost half of the respondents (49 %) found it difficult to answer this question, 28 % said that investing in cryptocurrency software was a bad investment, and only 23 % said that buying cryptocurrency software was a good investment (Figure
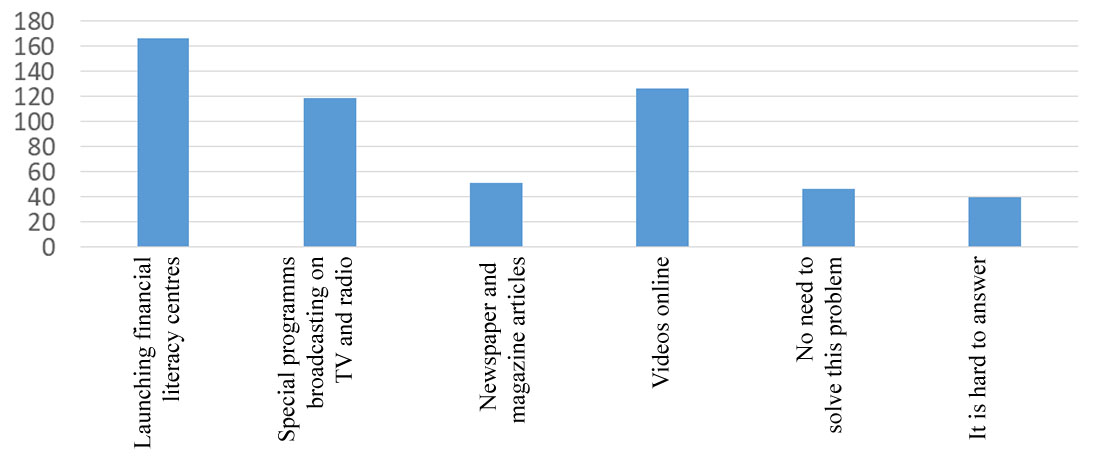
As shown in Figure
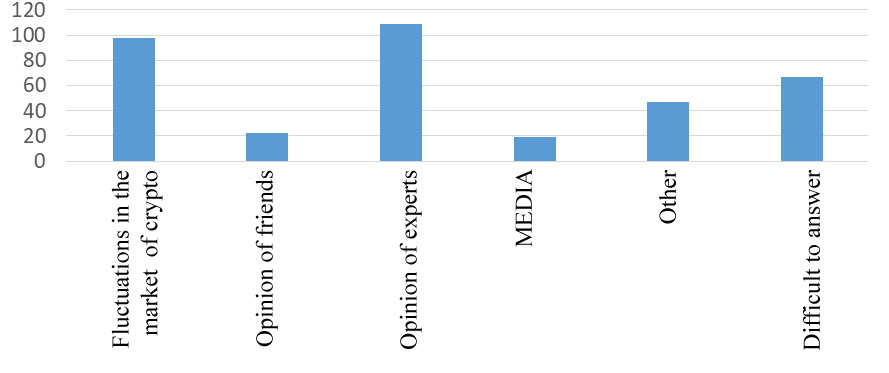
The answers to the question: "What can change your attitude towards cryptology?" were remarkable. 109 respondents answered that their opinion and attitude may be influenced by the expert's opinion. Besides, according to 98 respondents, the instability of the cryptocurrency exchange rate may have a negative impact on their opinion and attitude (Figure
There will be various opportunities and risks for the future of cryptocurrency and the improvement of financial literacy of youth in this area.
Possibilities include: 1. Adjustable cryptocurrencies may become legal and more widely distributed. Stricter rules in the cryptocurrency industry may enhance the industry's reputation, and this may lead to a reduction in fraud; 2. governments may one day allow taxes to be paid in cryptographic software. For example, in February 2018, the Arizona Senate passed a bill to allow tax payments in Bitcoins; 3. cryptocurrencies will be more positively perceived by the public. It is likely that public awareness of the cryptocurrency will continue to grow, and that the public is aware of the importance of the cryptocurrency.
The risks include: 1. Governments may prohibit or strictly regulate cryptographic currency. Some governments already regulate bitcoins and cryptocurrencies. For example, China banned Bitcoin trading in September 2017 and closed Bitcoin exchanges throughout the country. Today, cryptocurrency remains a grey area in many jurisdictions; 2) Cryptocurrencies may never be the mainstream due to negative public perception. For the average person, Bitcoin is often associated with a dark network, online fraud, online drug dealing, and anonymous transactions; 3. The destruction of the energy system. If the energy system collapses, Bitcoin is dead. It's an electronic form of cash. It only works with electricity (Vejačka, 2014).
Thus, the following conclusions can be drawn from the study: 1. The majority of young people today know about the cryptocurrency, how it is organized and works, but only a small part of them is ready to invest money in this financial instrument; 2. Most of the young generation associate the cryptocurrency with the concepts of uncertainty and excitement, which indicates high risks and profits in this market, as well as strong volatility of the cryptocurrency; 3. The main reasons for the low activity of young people in the cryptovolta market are: exchange rate instability and distrust of the cryptocurrency, which indicates a low level of financial literacy among young people; 4. The most appropriate tools to improve financial literacy among young people are: the opening of special centers, as well as the creation of TV programs, clips, and programs on the Internet; 5. The main factor influencing the attitude of young people to the cryptocurrency, is the opinion of experts.
Analysis of countries with innovative economies
We will use the Global Innovation Index (GII) to identify countries with innovative economies. It is calculated by taking a simple average score on two sub-indices: the innovation input index and the innovation output index (link to website).
Consider the attitude towards cryptocurrency based on social surveys in some of the countries represented.
USA. Only 3 % of respondents have not heard anything about the cryptocurrency, 21 % have heard something, and 76 % are familiar with the cryptocurrency. Almost 70 percent of those surveyed feel insecure about the cryptocurrency. A total of 35 percent of respondents invested in the cryptocurrency language, of which 41 percent invested in melinals, while the older generation invested no more than 25 percent (Table
South Korea. Survey data show that about 22.7 percent of respondents were in their twenties and very 'active' within cryptocurrency ecosystems. These figures were followed by South Koreans in their thirties (19.3 %) and forties (12 %).
Germany. The German company Wirtschaftswoche conducted a study among the inhabitants of Hessen and Saxony on the knowledge and level of activity on the cryptographic market. The survey was attended by 1000 Germans aged 18 to 39 years. According to the results of the survey, more than a quarter of the young Germans are ready to buy the cryptographic material.
Summarizing the survey data, we can conclude that in developed countries, more than 20 percent of respondents under 40 years of age are ready to invest in the cryptographic currency. This figure is significant if we take into account the fact that the cryptocurrency appeared only 10 years ago and gained popularity only recently. The younger generation understands the cryptocurrency most of all, so the value of cryptocurrency will only increase in the future.
You may notice that the higher the level of GII, the higher the level of readiness to use the cryptocurrency as a financial instrument (Table
Undoubtedly, the Government of the Russian Federation will take all measures to increase Russia's position among other countries in terms of the level of innovativeness, as it is a guarantee not only of the national economy's survival, but also a basis for the growth of citizens' welfare. If Russia succeeds in advancing in this direction, Russian citizens will be increasingly interested in investing in the cryptocurrency.
For a full analysis, it is important to understand how young people in Russia feel about the crypt currency. To this end, a group of students of the Financial University of the Government of the Russian Federation conducted a sociological survey to find out how Russian youth (high school students did not participate in the survey) learned about the existence of the cryptocurrency, perceives the cryptocurrency, whether willing to invest in it, how well it understands (Figure
The following conclusions were drawn from the survey:
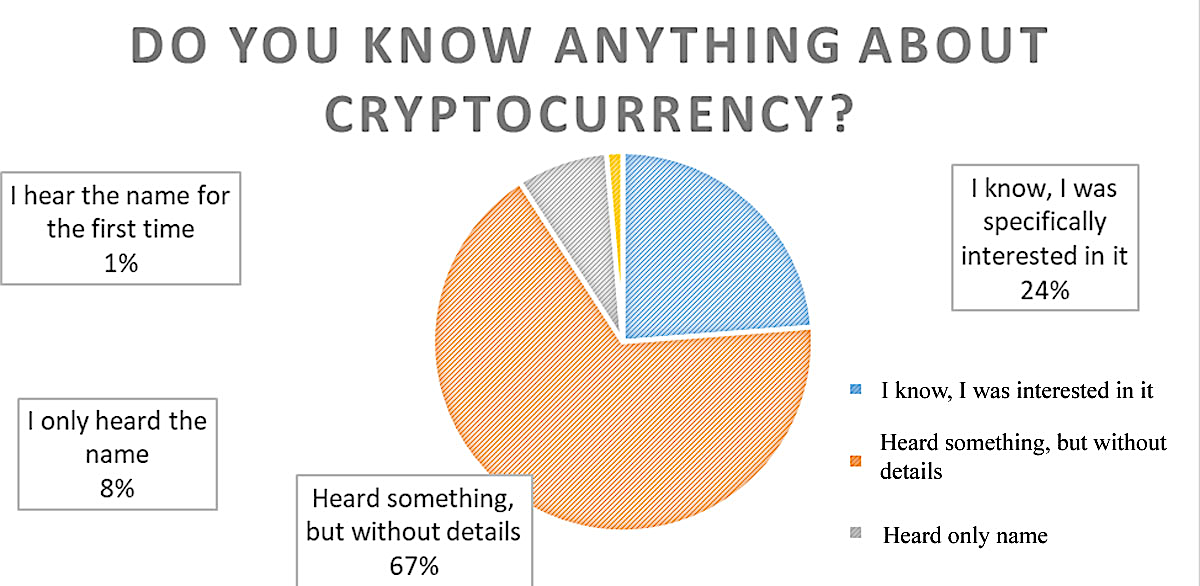
More than 90% of respondents know about cryptology, but only a quarter of them tried to figure it out.
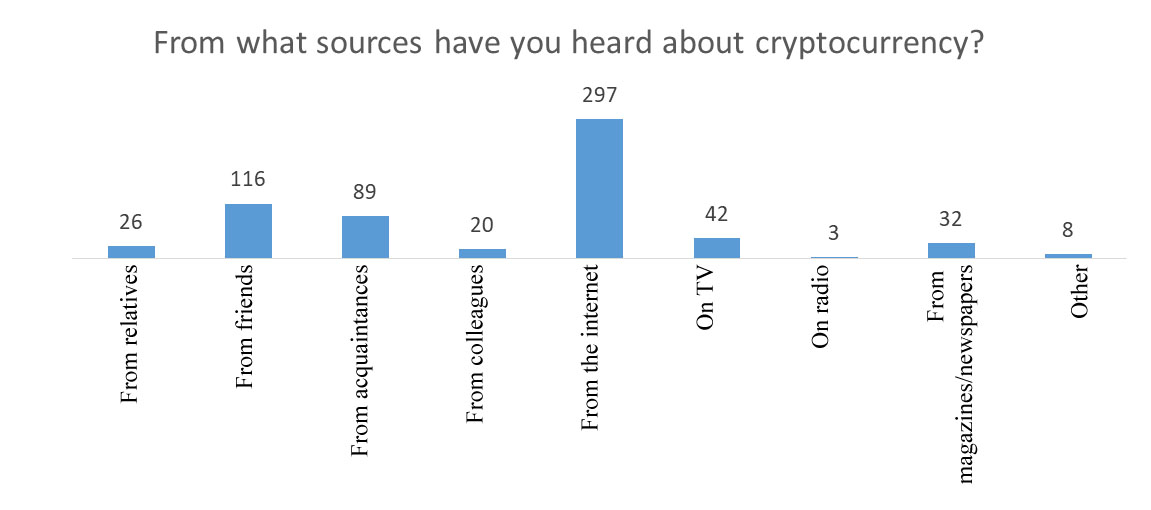
Most often respondents hear about cryptocurrency from the Internet, from friends and acquaintances. This suggests that the information comes from informal sources, and lends itself to an untargeted (Figure
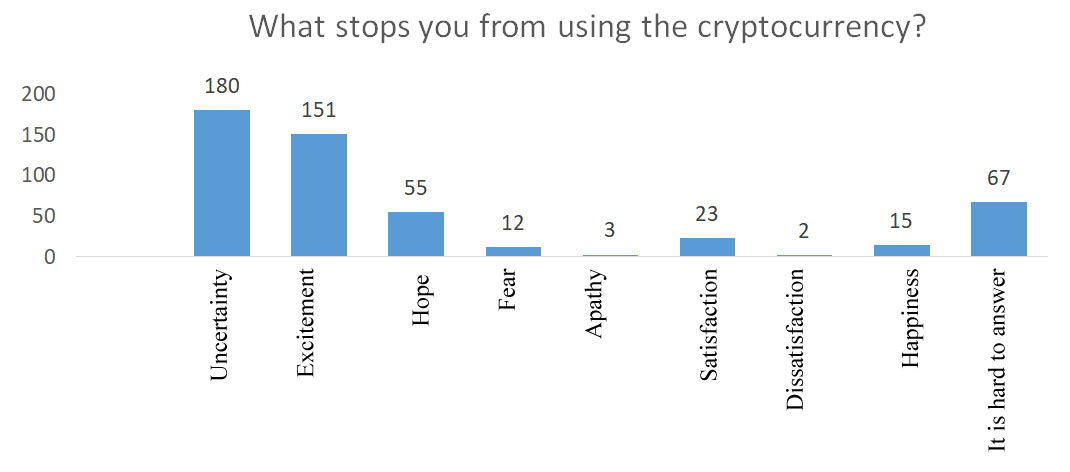
Many respondents feel the uncertainty and excitement about the cryptocurrency. This indicates that, on the one hand, the young generation is not very good at cryptocurrency software, and on the other hand, that cryptocurrency software is an opportunity to "play" in the market and earn money, similar to other financial instruments (Figure
To determine if one understands how the cryptocurrency functions, a small set of questions has been drafted. If the respondent answered all questions correctly, then it can be assumed that the respondent understands how the cryptocurrency software works. The data shows that even a fifth of those surveyed do not understand the laws of how the cryptocurrency software works. Therefore, in order to increase the number of citizens who use the cryptocurrency software, it is necessary to improve their knowledge of the cryptocurrency software.
Thus, although Russian young people are aware of the existence of the cryptocurrency, they are not yet ready to use it as a financial instrument.
Conclusion
The analysis shows a direct connection between the level of readiness of citizens to invest their money in cryptocurrency and the level of innovation of the state economy. Cryptocurrency may become a good alternative to classical financial instruments.
Recommendations:
1. The Russian leadership should take measures to increase financial literacy among the population, particularly in the field of cryptocurrency, because cryptocurrency may become one of the ways to multiply funds on the way of development of Russian innovative economy.
2. a special place in the development of a program of civic education in the field of cryptocurrency should be given to the Internet space, since it is from there that people learn most about cryptocurrency.
3. The Russian management should as soon as possible decide on the attitude to the cryptocurrency in our country, because uncertainty prevents the full use of all the advantages of cryptocurrency, does not give confidence when investing in it.
It is recommended to improve the financial literacy of young people in cryptocurrency:
1. Include cryptocurrency in the Financial Literacy Strategy 2017–2023;
2. a major financial literacy center should be opened in each region of Russia, particularly in the cryptocurrency;
3. Include a financial literacy block in the school education curriculum.
References
- Alekseev, N. V. (2017). Non-classical objects of civil law. Peculiarities of legal nature of cryptology. Pravo, history, theory, practice. Coll. of articles and conf. mater (pp. 29–37). (Bryansk, 18–19 April 2017). Bryansk.
- Cryptofeed. (2018). The most active crypto investors are students from South Korea. Retrieved from https://cryptofeed.ru/news/samye-aktivnye-kriptoinvestory-studenty-yuzhnoj-korei/.
- Halin, V. G., & Chernova, G. V. (2018). Digitalization and its influence on Russian economy and society: advantages, challenges, threats and risks. Managem. Consult., 10. Retrieved on November 2, 2019 from https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/tsifrovizatsiya-i-ee-vliyanie-na-rossiyskuyu-ekonomiku-i-obschestvo-preimuschestva-vyzovy-ugrozy-i-riski
- MinFin RF. (2018). The Ministry of Finance does not consider it necessary to improve the literacy of Russians in the field of crypt-currency. RIA Novosti, 15 February 2018. Retrieved from https://ria.ru/20180215/1514658609.html
- Siluanov, A. G. (2017). Siluanov suggested that cryptocurrencies be included in the strategy to improve financial literacy. Vedomosti, 29 September 2017. Retrieved from https://www.vedomosti.ru/finance/news/2017/09/29/735889-siluanov-kriptovalyuti
- Vejačka, M. (2014). Basic Aspects of Cryptocurrencies. J. of Econ., Busin. and Financ., 2, 75–83.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-091-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
92
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3929
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, translation, interpretation
Cite this article as:
Khasanovich, M. M., Zaurovich, A. Z., Mikhailovich, K. D., Anatolevich, G. I., & Ivanovna, V. Z. (2020). Case Study Of Youth Financial Literacy In The Field Of Cryptocurrency Use. In D. K. Bataev (Ed.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism» Dedicated to the 80th Anniversary of Turkayev Hassan Vakhitovich, vol 92. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 3153-3165). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.05.419

