Abstract
This article is aimed at identifying problematic aspects of the current state of regional budgeting processes. The analysis of indicators of tax and non-tax revenues of territorial budgets for the period 2012–2018 in their absolute dynamics and relative values to the gross domestic product of Russia. The fiscal state of regional budgets in terms of income and expenses, as well as the level of scarcity is considered. The role of regional budgets in ensuring the stability of the budget system of Russia at the present stage is determined. The main trends characterizing the features of the formation of territorial budgets in the dynamics of recent years are identified. The main problems of regional finance in Russia are clarified. Based on the analysis of prevailing trends, we can conclude that the recent positive processes that are emerging need stabilization and consolidation when damping the impact of negative factors. In this context, the development priorities of regional finances are determined by the achievement of adaptive stability of regional budgets and their balance in the short, medium and long term, taking into account the two-way relationship between economic activity and budget policy. Priorities are proposed for the further development of the territorial budgets of Russia, the implementation of which will stabilize the state of regional budgets and will help to balance the budget system.
Keywords: Budget systembudget revenuestax and non-tax revenuesbudget deficitbudget alignment
Introduction
The implementation of the key objective of budget policy, which is to ensure sustainable economic dynamics and expand the potential for balanced development of the country, involves strengthening the active participation of regions in these processes and the consistent development of regional finances.
These issues are particularly relevant in the context of the tasks set by Decrees of the President of the Russian Federation dated 16.01.2018 # 13 “On the Approval of the Fundamentals of State Policy of the Regional Development of the Russian Federation for the Period until 2025”, dated 07.05.2019 # 204 “On National Goals and Strategic Development Tasks of the Russian Federation for the Time Until 2024”, as well as in the new Strategy for the spatial development of the Russian Federation, which contains guidelines for the development and correction of models of socio-economic development of territories. The involvement of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in the implementation of 12 national projects defined in government documents requires the formation of an appropriate financial basis for the activities of state authorities in the regions and the strengthening of regional budgets as the core of regional finance.
In basic courses in finance and scientific economic literature, the concept of "regional finance" is interpreted, as a rule, in a broad and narrow sense. The attributive classification sign underlying this distinction is the subject-object composition of monetary relations expressing the essence of regional finance. So, in a broad sense, regional finance is considered as a set of monetary relations of economic entities localized in the region, regarding the formation and use of financial resources necessary for its socio-economic development, and in a narrow sense, as monetary relations arising in the course of formation and use financial resources of state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, primarily in the form of appropriate budgets, for the implementation of the tasks and functions of these entities. The use of one or another value is largely determined by the specifics of research programs. In this paper, the analytical outline covers the main qualitative and quantitative shifts in the development of regional finance in their narrow definition, based on the corresponding substantive understanding of this category in official government documents.
Problem Statement
The development of regional financial public relations in the context of a rapidly changing economic and financial environment requires systematic monitoring and study of current trends and processes. Timely identification of problematic aspects in the formation and expenditure of funds of territorial budgets allows you to flexibly prevent the possible negative consequences of unbalanced, subsidized, deficit regional budgets (Shah, 2004). Available scientific publications on this issue discuss various aspects of the financial situation of regions related to the formation of income and expenses of their budgets (Akindinova et al., 2016), budget balance (Tavbulatova et al., 2019) and debt regions (Tabakh & Andreeva, 2015), features of functioning in crisis conditions (Chernyavsky, 2014). At the same time, taking into account the tasks and features of the current stage of socio-economic development, it becomes necessary to identify new, recently formed trends in the field of regional finance.
Research Questions
The main issues in this study are:
To consider the structural and dynamic indicators of the budget system of the Russian Federation
To study the characteristics of individual levels of the budget system.
Identify and describe the problems and prospects of the budget mechanism.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to identify the problematic aspects of the formation of territorial budgets as an indicator of the state of the consolidated budget system of Russia to develop directions for improving the quality of intergovernmental relations.
Research Methods
Analysis results for 2011-2018 allow us to highlight the following most significant trends in the development of regional finance:
1. An increase in the share of tax and non-tax revenues in the total revenues of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, improvement since 2015 of the dynamics of own revenues of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and their correlation with expenses. The study shows that for the period 2011 -2018. tax and non-tax revenues of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in absolute terms showed positive dynamics (Figure
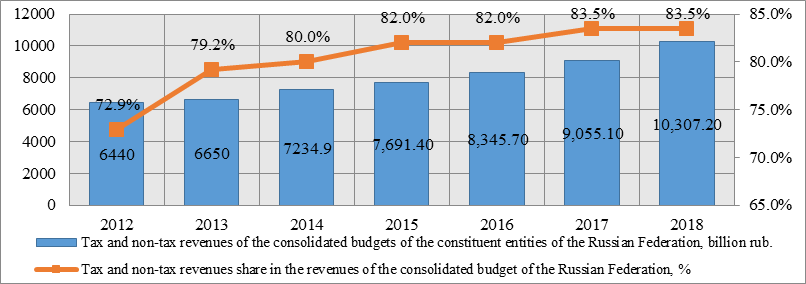
At the same time, the share of these revenues in the total revenues of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation increased from 72.9 % in 2011 to 83.5% in 2018.
However, an analysis of the dynamics of tax and non-tax revenues of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in relation to the gross domestic product (GDP) reveals its significant heterogeneity within the study period (Figure
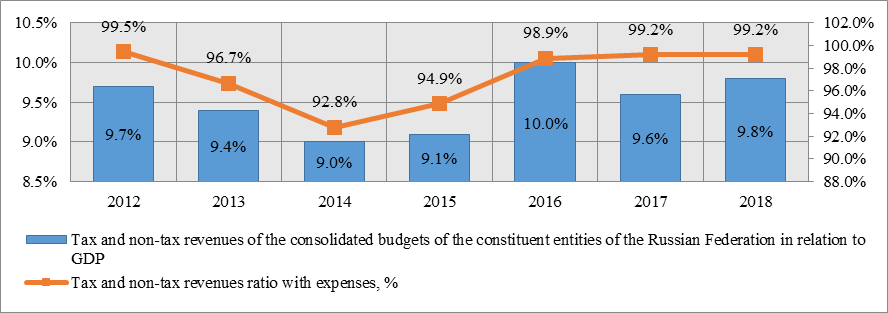
If in 2011–2014 this indicator decreased, then in 2015–2018 it was characterized by a certain increase. It should be emphasized that starting in 2015, the ratio of income (excluding gratuitous receipts) and expenses of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation began to increase, which indicates an improvement in the state of regional finances from the standpoint of providing regional budgets with their own incomes. However, with the growth of this averaged indicator, the range of its level values in different regions is very wide due to significant interregional differences, expressed, in particular, in the concentration of more than 50 % of the total tax and non-tax revenues of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, as our calculations according to the Federal State Statistics Service show in the 10 largest regions.
The trend of centralization of revenues in the federal budget, which arose in the early 2000s, changed in 2016 and 2017. to the opposite. The share of federal budget revenues in the consolidated budget revenues of the Russian Federation decreased from 61.9 % in 2015 to 57.6 % in 2017, while a corresponding increase in the share of revenues of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation was recorded – from 38.1 to 42.4 % (Figure
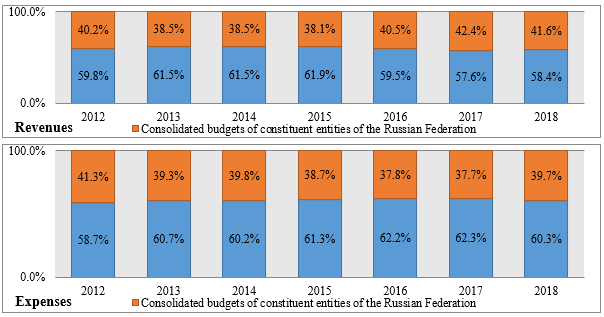
In 2018, the share of federal budget revenues in the consolidated budget revenues of the Russian Federation increased insignificantly (up to 58.4 %), while the revenues of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation decreased accordingly (up to 41.6 %). These processes were accompanied by the consolidation of budget expenditures at the federal level. For the period 2011–2017, the expenses of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, calculated at constant prices, decreased by almost 10 %, and their share in the expenses of the consolidated budget of the country decreased from 41.3 to 37.7 %. In 2018, this trend reversed: the share of expenditures of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in the expenditures of the consolidated budget of the Russian Federation increased by 2 percentage points. Despite this, in 2016–2018 it remained smaller than the corresponding indicator for income. The policy of fiscal consolidation helped to reduce the budget deficit and debt burden of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
2.Unstable dynamics of the levels of balanced budgets and debt burden of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The total deficit of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the maximum amount of which fell in 2014 (639.9 billion rubles), decreased by 2017 to 12.5 billion rubles. In 2018, the deficit of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation increased and amounted to 52.0 billion rubles, however, the number of constituent entities of the Russian Federation with a deficit budget markedly decreased, and with a surplus it increased (Figure
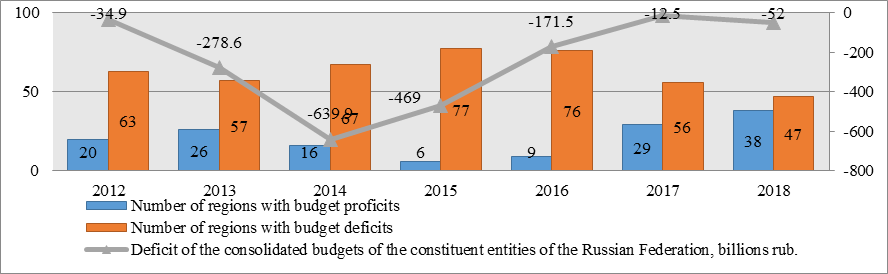
3. The transition to the implementation of the budget process on the basis of a program approach, the introduction of a mechanism for long-term budget planning in the regions.
In 2015, there were 40 regions in Russia, where the share of budget expenditures executed within the framework of targeted programs amounted to over 91 % of the total budget expenditures, and in 2018 their number increased to 73, while in eight regions more than 99 % of all budget expenditures were formed on a program basis (Chuvash Republic – 100.00 %, Kirov Region – 99.53 %, Irkutsk Region – 99.52 %, Bryansk Region – 99.36 %, Tver Region – 99.16 %, Murmansk Region and Nenets Autonomous Okrug – 99.03 %, Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug – Ugra – 99.0 2 %).
The use of program-targeted technologies of budget planning and management, focused on goals and results, is considered in world budget practice as the most effective way to increase efficiency and optimize budget expenditures (Bahl & Linn, 1994).
4. Reducing gratuitous receipts and inter-budget transfers to the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, changing the conditions for receiving inter-budget transfers, using new forms and tools for setting up the system of inter-budget relations.
Significant shifts have occurred in the transfer policy of the federal center. In 2015–2018 the share of gratuitous receipts in the revenues of the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation decreased from 19.4 to 16.5 %, and inter-budget transfers in relation to GDP – from 2.5 to 1.7 %.
5. Introduction of the basic principles of effective and responsible management of regional finances. The combination of a program approach with the use of financial management quality monitoring systems, widely tested in world practice, is designed to motivate public authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation to find the best ways to organize the budget process, taking into account modern standards of public finance management quality.
Monitoring data on compliance by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation with the requirements of budget legislation and the quality of management of regional budgets indicate that overall significant progress has been achieved in this area. So, according to the results of 2018, 70 constituent entities of the Russian Federation had a high and proper quality of managing regional finances. However, in a number of regions, from year to year, a difficult situation remained with the soundness of budget planning and debt policy, compliance with financial discipline. In four constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the parameters of the budget deficit and public debt exceeded the level established by budget legislation.
Findings
At the end of 2018, there were seven constituent entities of the Russian Federation whose public debt exceeded 100 % of the volume of tax and non-tax budget revenues (Republic of Mordovia – 225.73 %, Republic of Khakassia – 136.37 %, Kostroma Region – 135.2 %, Republic Karelia and the Kabardino-Balkarian Republic – 124.13 %, Oryol Oblast – 106.52 %, Pskov Oblast – 101.69 %).
An analysis of the implementation of regional finance recovery programs conducted in 81 regions showed that 23 of them have developed programs that are formal and low-performing (Eroshkina, 2018).
Based on the analysis of prevailing trends, we can conclude that the recent positive processes that are emerging need stabilization and consolidation when damping the impact of negative factors. In this context, the development priorities of regional finances are determined by achieving adaptive stability of regional budgets and their balance in the short, medium, and long-term periods, taking into account the two-way relationship between economic activity and budget policy (Igonina, 2014).
Conclusion
The implementation of these priorities involves solving the following tasks:
improving the system of delimitation of powers between the levels of public authority and its regulatory framework governing the requirements for the exercise of their own powers of the regions, which are financed from regional budgets and, accordingly, affect the determination of their size;
improving the balance of regional budget policy with the strategies of socio-economic development of the regions with an increase in the quality and reliability of socio-economic and budget forecasts; correlation of indicators of these strategies with the parameters of state programs; development of target-oriented planning through the introduction of design technologies to focus it on key priorities of socio-economic development; formation of realistic budgets on this basis;
building up on an ongoing basis our own revenue base, which ensures the growth of regional budgets stability, reduction of their subsidies due to the interconnection of forecasted budget revenues and expenditure obligations with the design and implementation of effective tools that compensate for the budget deficit under the influence of negative factors (peculiar budget rules based on opportunities regions and budget restrictions);
ensuring the growth of the effectiveness of regional budget expenditures, including through an assessment of the effectiveness and the abolition of ineffective tax benefits, the transition to selective support of projects that ensure the implementation of key priorities of the socio-economic development of the regions;
encouraging regions to build their own economic and budgetary potential by harmonizing the system of formation, distribution and provision of intergovernmental transfers based on inventory, objective assessment and monitoring of revenue sources and expenditure commitments of territories, long-term fixing of conditions for intergovernmental relations in order to ensure their predictability and improve the feasibility of budget planning, as well as the use of effective forms of tax redistribution, taking into account adjusting budgetary powers of public authorities in the process of elaboration of national projects;
the formation of a separate program to align the economic and tax potential of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation with the use of effective measures of financial motivation and responsibility of the regions for achieving target indicators of socio-economic development, the quality of budget planning and budget execution;
development of technologies for managing regional finances that ensure potential risk management, increasing operational efficiency and control, openness and transparency of regional finances that comply with the imperatives of the digital economy (Igonina, 2018).
References
- Akindinova, N. V., Chernyavsky, A. V., & Chepel, A. A. (2016). Regional budgets in times of crisis: can balance be achieved? Vopr. Ekon., 10, 31–48.
- Bahl, R., & Linn, J. (1994). Fiscal Decentralization and Intergovernmental Transfers in Less Developed Countries. Publius: The J. of Federalism., 24, 1–19.
- Chernyavsky, A. (2014). Problems of balancing regional budgets. Finance, 8, 15–21.
- Eroshkina, L. A. (2018). Inter-budgetary relations: new challenges and new approaches. Interview with the Director of the Department of Inter-Budget Relations of the Ministry of Finance of Russia. Finance, 7, 3–11.
- Igonina, L. L. (2014). Fiscal decentralization in the public finance management system. Digest Finance, 1(237), 2–13.
- Igonina, L. L. (2018). Current trends in the development of regional finance. Finance, 11(591), 20–27.
- Shah, A. (2004). Lessons from International Practices of Intergovernmental Fiscal Transfers. In XVI Regional Seminar on Fiscal Policy CEPAL/ECLAC (pp. 899–912). Santiago de Chile.
- Tabakh, A., & Andreeva, D. (2015). Debt strategies of the Russian regions. Econ. Issues, 10, 78–93.
- Tavbulatova, Z. K., Tashtamirov, M. R., Kulakova, N., & Nazaeva, M. I. (2019). Peculiarities of inter-budgetary equalization in Russia. European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, SCTCGM 2018, 1655–1662.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
31 October 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-091-4
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
92
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-3929
Subjects
Sociolinguistics, linguistics, semantics, discourse analysis, translation, interpretation
Cite this article as:
Arsahanova, Z. A., Tashtamirov, M. R., Fedorova, A. J., & Berkaeva, A. K. (2020). The Processes Of Formation Of Territorial Budgets Of Russia: Dynamics, Structure, Problems. In D. K. Bataev (Ed.), Social and Cultural Transformations in the Context of Modern Globalism» Dedicated to the 80th Anniversary of Turkayev Hassan Vakhitovich, vol 92. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 81-88). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.10.05.12

