Abstract
In this article, the authors consider the state of the health care system of various countries that were included in the sample based on their ranks on the index of quality of life of the population. Health care financing is directly related to ensuring the necessary level of quality of life for the population. The authors analyzed works of various scientists involved in this issue. They also considered the amount of funding for the health system that came from the state budget to maintain its functioning. The share of expenditures on the health system in the total expenditure of the country was estimated. Due to the importance of the full functioning of this system, the study of these aspects is a promising research area. Based on the results obtained, it was concluded that the amount of funding for the health system has a greater impact only on the quality of medical services, large amounts of funding for the health system do not guarantee a significant increase in the quality of life of the population, the main problem of health financing is the irrationality of its use. There is no direct relation between the amount of funding for the health system and the level of quality of life of the population.
Keywords: Health carefinancingquality of life of the population
Introduction
Health financing issues are acute in all countries of the world. This situation is explained by the fact that health care is one of the key life sectors of the country's population. Health care financing is directly related to ensuring the necessary level of quality of life. Indicators of the quality of life of the population largely characterize the current state of the society, the region and the country as a whole. One of the main goals of the state is to provide a comfortable, safe and full-fledged life for its population. The country's health system has a significant responsibility in solving these tasks.
Financing various sectors of the country's functioning is particularly relevant in the context of limited available resources and the need to identify priority areas for the resource allocation. In this situation, the financing of the health system certainly meets all the indicators of significance for the country's population. However, the importance of this area in terms of funding varies from country to country. Therefore, it is important to consider approaches to financing the health system in different countries.
Problem Statement
Health system financing issues are of interest to researchers in various countries. Special attention is paid to health financing in countries with middle-income and lower income levels. It is noted that there are many unsuccessful ways to organize the financing of the health system ( Rostampour & Nosratnejad, 2020).
A number of researchers have considered the impact of the financial crisis on the health system. It was revealed that the financial crisis has led to a significant reduction in funding for all areas of health care: from outpatient appointments to hospitalization. At the same time, there were no indicators of changes in the population health ( O’Dwyer, Graever, Britto, Menezes, & Konder, 2019).
Other researchers have identified the fact that there is no single mechanism for financing the health system in different countries. It is noted that the distribution of funds to finance this area is not always fair. Often, when allocating funding, the issue of minimizing losses and improving the efficiency of the system is not raised ( Onwujekwe et al., 2019).
It is also noted that one of the problems of financing the health system is not always its insufficient volume. In some cases, it consists of inappropriate use of allocated financial resources. At the same time, this aspect has the greatest impact on the financing of personnel in the health care system ( Fahim et al., 2018).
Research Questions
As a part of this study, the authors selected several issues related to financing the health system for consideration. First of all, it is planned to make a sample of countries by indicators of the quality of life of the population. After that, it is necessary to compare the amount of funding for the health system in each specific country and show the share of funding in its total volumes. It is also important to pay attention to the possible relation between the volume of health care funding and the level of quality of life of the population.
Purpose of the Study
The main research purpose is to study the system of health care financing in different countries with different levels of quality of life. On the basis of this information, it is possible to draw conclusions about the importance of ensuring sufficient funding for health care and possible consequences of its excess or shortage. Due to the importance of the full functioning of this system, the study of these aspects is a promising research area.
Research Methods
The authors used the main theoretical research methods. The analysis of existing studies that affect the financing of certain sectors of the country's functioning, and in particular the health system, was carried out. Analyzed were studies of domestic and foreign scientists. A selection of countries with different living standards was also being carried out and the sample was formed. Then, the amount of funding for the health system in each of the selected countries was analyzed and their share in the total amount of funding was determined. These indicators were compared with each other and with the current level of quality of life of the country's population. The obtained data were summarized in the conclusions about the relation between the financing of the health system and the level of quality of life of the population.
Findings
To assess the amount of funding for the health system, several countries of the world were selected, which are in different positions in terms of the quality of life of the population. The rating was divided into 4 roughly equal parts, with two selected countries in each of them. The analyzed list also includes Russia, which is on the 67th place from total 80 in terms of the quality of life of the population. Together with the population's quality of life index, the health index was also analyzed. The distribution of ranks and values of indicators can be seen in Table
As can be seen from Table
The next stage was to consider the amount of funding for the health system in the selected countries. Table
According to the data presented in table
Noting the specifics of financing the health care system in these countries, it should be taken into account how much of the total funding belongs to the state, and what is the share of commercial organizations and patients themselves (Figure
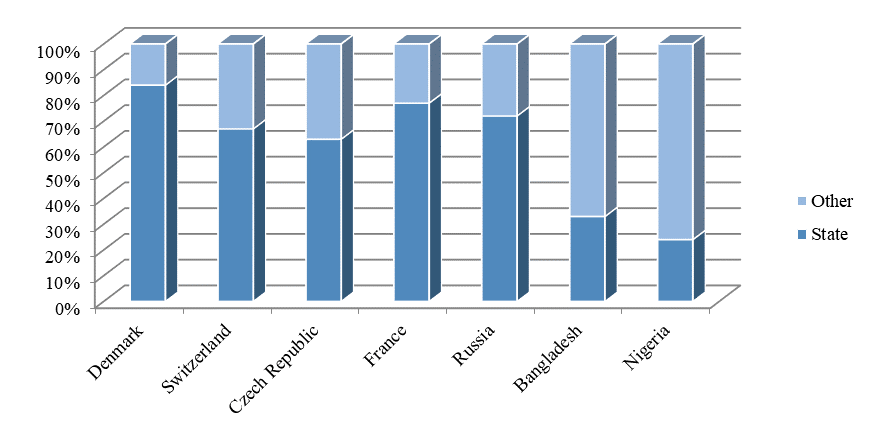
Comparing the funding sources for the health system in the considered countries, it was found that the sources can be divided into three large groups: resources of the state, resources of commercial organizations (usually insurance companies) and resources of the population. Figure
The last research task was to determine the dependence between health system financing and the level of quality of life of the population. To do this, all the considered indicators were summarized in Table
The results presented in Table
Conclusion
Based on the analysis results, several conclusions can be made:
The amount of funding for the health care system has a greater impact only on the quality of medical services, and not on the quality of life of the population directly;
Large amounts of funding for the health care system do not guarantee a significant increase in the quality of life of the population, so we can conclude that this indicator is not one of the leading indicators in assessing the quality of life of the population;
One of the main problems related to the financing of the health care system is not so much the lack of its volume as the irrationality of its use;
There is no direct correlation between the amount of funding for the health care system and the quality of life of the population. This is determined by the fact that health care is only one of the components used in assessing the quality of life of the population.
References
- Fahim, S. M., Bhuayan, T. A., Hassan, Md. Z., Zafr, A. H. A., Begum, F., Rahman, Md. M., & Alam, S. (2018). Financing health care in Bangladesh: Policy responses and challenges towards achieving universal health coverage. The International Journal of Health Planning and Management, 34(1), e11-e20.
- Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (2019). Regional health financing for 2019 will increase significantly. Retrieved from https://www.rosminzdrav.ru/regional_news/10731-finansirovanie-zdravoohraneniya-regiona-na-2019-god-suschestvenno-uvelichitsya Accessed: 11.12.2019. [in Rus.].
- Novakova, V. (2019). Healthcare resource guide: Czech Republic. Retrieved from https://2016.export.gov/industry/health/healthcareresourceguide/eg_main_116151.asp Accessed: 11.12.2019.
- Numbeo (2020). Quality of life index by country 2020. Retrieved from https://www.numbeo.com/quality-of-life/rankings_by_country.jsp?title=2020 Accessed: 11.12.2019.
- O’Dwyer, G., Graever, L., Britto, F. A., Menezes, T., & Konder, M. T. (2019). Financial crisis and healthcare: The case of the municipality of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Ciencia e Saude Coletiva, 24(12), 4555-4568.
- OECD (2019). Health spending. Retrieved from https://data.oecd.org/healthres/health-spending.htm Accessed: 11.12.2019.
- Onwujekwe, O., Ezumah, N., Mbachu, C., Obi, F., Ichoku, H., Uzochukwu, B., & Wang, H. (2019). Exploring effectiveness of different health financing mechanisms in Nigeria; What needs to change and how can it happen? BMC Health Services Research, 19, 661.
- Rostampour, M., & Nosratnejad, S. (2020). A systematic review of equity in healthcare financing in low- and middle-income countries. Value in Health Regional Issues, 21, 133-140.
- Sturny, I. (2019). The Swiss health care system. Retrieved from https://international.commonwealthfund .org/countries/switzerland/ Accessed: 11.12.2019.
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 April 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-081-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
82
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1004
Subjects
Business, innovation, management, management techniques, development studies
Cite this article as:
Lazareva, N. V., & Vaníčková, R. (2020). Financing Health Care In Various Countries. In V. V. Mantulenko (Ed.), Problems of Enterprise Development: Theory and Practice, vol 82. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 976-981). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.04.126
