Abstract
This article is devoted to systematization of scientific ideas about the financial mentality of people who make financial decisions – business owners and managers. Financial mentality is considered by authors as a factor of business management. The authors try to show how manifestations of the financial mentality affect the potential of the business profitability through the entrepreneurs’ choice of the financial policy type in their company. It is emphasized that the financial mentality is traditionally presented as a subjective factor. And this article is an attempt to characterize this phenomenon from the standpoint of behavioral economics as an objective factor. The authors use the methods of analysis and systematization of psychological and economics scientific literature to consider ‘financial mentality’, its nature, role in the modern management and relations with other phenomena. The financial mentality of entrepreneurs is considered a system of conservative, moderate or aggressive principles of asset formation and financing. It is noted that financial mentality influences the business profitability potential through entrepreneur’s choice of the financial policy type. It also determines the acceptable risk level by making important business decisions, causes differences in the structure of financial sources and directions of using financial resources of companies, their cash flows, and profitability levels.
Keywords: Financial decisionsfinancial policytypes of financial policyfinancial mentalityriskbehavioral economics
Introduction
One of the key aspects on which neoclassical economic theory is based is the provision on the behavioral rationality of economic entities. This aspect implies that economic entities that have the same economic potential should generate the same economic results through their activities. One of the possible explanations for the fact, that comparable companies under similar conditions achieve completely different results, is differences in the mentality of people who make key business decisions. Mentality, according to social psychologists, is a subconscious socio-psychological "program" of actions and behavior of people – both individuals and various social groups ( Kulikova, 2016). The formed mentality includes a system of stable views, principles, values, and corresponding goals and means to achieve them. The mentality is formed in certain sectors of the social space, one of which can be business management. Accordingly, the management mentality can be defined as a specific system of stable views, principles of management decision-making, which are inherent in entrepreneurs as a professional group as a whole and individual subjects of the entrepreneurial management activity ( Batsukh, 2011).
Problem Statement
As a component of the management mentality, the financial mentality of decision- makers (owners and/or managers) determines their attitude to the degree of acceptable risks when making essential decisions that cause the movement of financial resources and significantly affect financial results of companies. Most often, the financial mentality is considered as a factor that determines the propensity of managers to borrow ( Tolkacheva, 2014), and, more generally, to form a capital structure ( Ukolov & Supalova, 2014).
Research Questions
The main research questions are:
Financial mentality as a subjective and objective factor of business management;
The impact of financial mentality on the business profitability potential through entrepreneur’s choice of the financial policy type;
Different financial policy types and their influence on the decision-making process depending on the acceptable risk level;
Financial mentality as a factor causing differences in the structure of sources and directions of financial resources use in the business activity, cash flows, and profitability levels.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this research is to systematize scientific views on the financial mentality of entrepreneurs, people who make essential business decisions. To achieve this goal, the authors solved the following tasks in their study: analysis of the concept “financial mentality”, and its relation with the concept “financial policy”, consideration of financial mentality based on different types of the financial policy of organizations: the approach to making financial decisions depending on the acceptable level of risks used in the company.
Research Methods
To achieve the main research goal and solve the appropriate tasks, the authors used the analytical method: analyzed were psychological and economic approaches to understanding ‘mentality’. Systemizing different scientific views, the authors linked the financial mentality with the financial polity, taking into account the relation between the risk level and profitability, different principles of assets formation, the structure of sources and directions of the financial resources use. This analytical work allowed to make a conclusion about the necessity to consider financial mentality not only as an objective factor of business management.
Findings
More generally, entrepreneur’s financial mentality can be interpreted as their commitment to implementing conservative, moderate, or aggressive financial policies for individual operations or activities ( Financial Dictionary, 2020). These types of financial policy in different sources relate to different areas of the financial decision-making process. There are some examples:
The policy of working capital management: different ratios of turnover and current assets profitability levels correspond to different types of this policy ( Bocharov, 2008);
Short-term liability management policies aimed at financing current assets: different levels of short-term loans and borrowings in the financing structure correspond to different types of this policy ( Vorobyov & Leontiev, 2017);
Dividend policy: different principles for calculating dividends correspond to different types of this policy, and, accordingly, levels of dividend payments, on the one hand, and levels of profit reinvestment, on the other hand ( Guryanov, 2014);
Investment policy: different criteria for selecting investment objects correspond to different types of this policy ( Malschukova, 2011).
Summarizing the existing definitions of these types of financial policy (conservative, aggressive and moderate), we can conclude that they characterize the adopted in the company approach to making financial decisions depending on the acceptable risk level (Figure
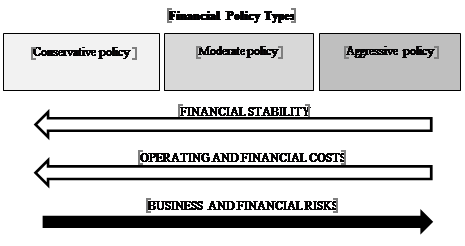
At the same time, in accordance with the concept of the relation between the risk level and profitability, there is a direct proportional relation between the risk level taken by an economic entity when performing certain business operations and the level of the expected profitability of these operations. A conservative policy (that assumes a minimum risk level) requires maximum costs for its implementation, both operational (related, for example, to maintaining high insurance reserves) and financial (related to access to stable long-term financing sources). On the contrary, an aggressive policy aimed at minimizing costs, including by using possible the shortest and, as a result, the cheapest sources, allows you to reduce costs, increasing the potential for the business profitability, and significantly increases the risk of its operation.
Conclusion
Thus, we can say that the financial mentality of those who make management decisions is a system of conservative, moderate or aggressive principles of asset formation and financing. It is the financial mentality that determines the acceptable level of risks when making business decisions, which causes differences in the structure of sources and directions of financial resources use in the business activity, cash flows, and profitability levels. At the same time, the financial mentality is traditionally considered as a subjective factor, as opposed to objective factors that influence the decision-making process. However, taking into account the development of a new scientific direction based on the criticism of one of the key provisions of the neoclassical economic theory about the rationality of the economic behavior – behavioral economics, the expediency and correctness of considering the financial mentality as a purely subjective factor is very controversial.
Behavioral economics considers human psychology as the basis for economic actions. The observed irrational behavior of economic entities is a subject of certain models and is therefore quite predictable. When making a decision, an economic entity takes into account external objective conditions through the prism of its motives, attitudes, and expectations under the influence of emotional factors. In contrast to emotional factors, which are mostly random, motives, attitudes, and expectations – what social psychologists define as a mentality – have certain social foundations, that is, they are relatively stable. Based on the above, we can draw the following conclusion. The financial mentality is a factor that links the choice of a particular financial decision with objective conditions in which this decision is made. From the standpoint of the behavioral economics, financial mentality can be considered as an objective factor of business management.
References
- Batsukh, G. (2011). Mentality of a chief as a factor of managerial activity. Bulletin of the Buryat State University, 14(a), 85-101. [in Rus.].
- Bocharov, V. V. (2008). Corporate finance. St. Petersburg: Peter. [in Rus.].
- Financial Dictionary (2020). Financial analysis: All about financial analysis. Retrieved from http://1fin.ru/?id=281&t=578&str=%D0%E8%F1%EA%EC%E5%ED%E5%E4%E6%EC%E5%ED%F2 Accessed: 29.01.19. [in Rus.].
- Guryanov, P. A. (2014). Dividend policy in Russia: Research review. Humanitarian Research, 10. Retrieved from http://human.snauka.ru/2014/10/7935 Accessed: 29.01.19. [in Rus.].
- Kulikova, E. A. (2016). Fundamentals of management. Yekaterinburg: UrGUPS. [in Rus.].
- Malschukova, O. M. (2011). Problems of investment policy development of the enterprise. Russian Journal of Innovation Economics, 4(1), 29-38. [in Rus.].
- Tolkacheva, N. A. (2014). Financial management: A course of lectures. Moscow: Direct-Media. [in Rus.].
- Ukolov, A. I., & Supalova, T. N. (2014). Enterprise risk management: Hedging instruments. Moscow: Direct-Media.
- Vorobyov, A. V., & Leontiev, V. E. (2017). Corporate finance (water transport). Kirov: MCNIP. [in Rus.].
Copyright information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
About this article
Publication Date
01 April 2020
Article Doi
eBook ISBN
978-1-80296-081-5
Publisher
European Publisher
Volume
82
Print ISBN (optional)
-
Edition Number
1st Edition
Pages
1-1004
Subjects
Business, innovation, management, management techniques, development studies
Cite this article as:
Kandrashina, E. A., & Mantulenko, V. V. (2020). Financial Mentality Of Entrepreneurs As A Factor Of Business Management. In V. V. Mantulenko (Ed.), Problems of Enterprise Development: Theory and Practice, vol 82. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences (pp. 869-873). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.04.110
